BPK 241 Lecture 11
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms

Contusions
Hx = direct blow
SSx = pain, swelling, bruising, tenderness, increased warmth, reduced ROM
Tx = POLICE, padding, physio
Elbow area contusions
Laterally:
Radial nerve at risk
Extensor muscle weakness
Posterolateral numbness
Medially:
Ulnar nerve at risk
“funny bone” injury
Numbness in medial forearm and digits IV & V; flexor muscle weakness
Posteriorly:
Olecranon bursitis
Strains & Tendinopathy
Hx = resisting a force, fall, overuse
SSx = pain (worse with movement against resistance), tenderness, swelling, crepitus?
Tx = POLICE, ROM exercises, physio, taping or splints, rehab
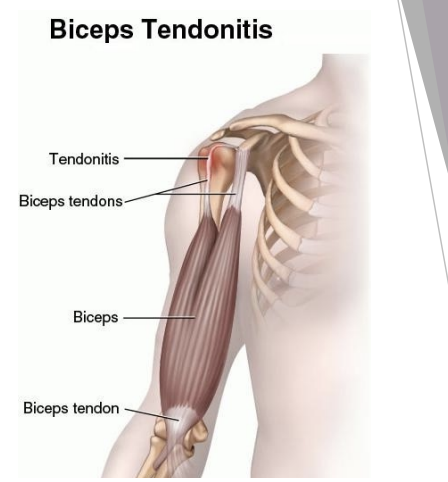
Biceps Tendinopathy
Hx: Tendinosis in biceps, on average male athletes 45 to 60 years old
SSx: pain anterior shoulder, pain with 90 to 120º shoulder flexion
Tx: Rest, ice, modified activities, ROM, strengthening
Can lead to biceps rupture
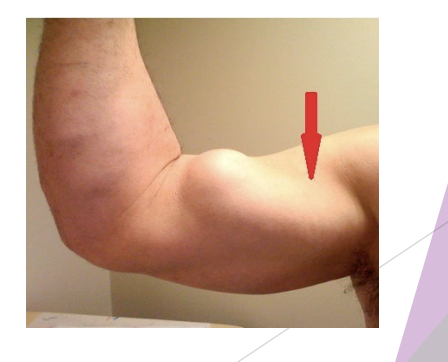
Biceps Rupture
SSx: snap, weakness, bruising, popeye’s sign
MRI or diagnostic ultrasound
Tx: surgery, rehab
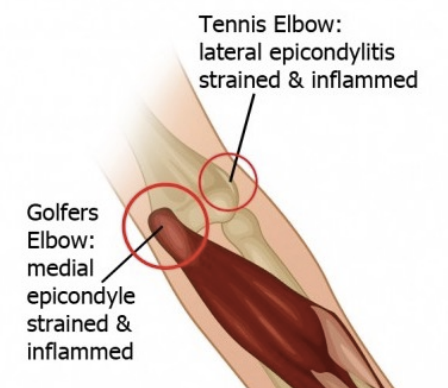
Medial/ Lateral Epicondylalgia - Golfer’s/Tennis Elbow
Also pitchers etc..
Mixed tendinopathy periostitis
SSx: aching pain, worse with movement of affected muscles vs.. resistance; tenderness, bogging
Tx: Prolonged rest, splints, ice, physio (eccentric loading), NSAIDs, rehab surgery?
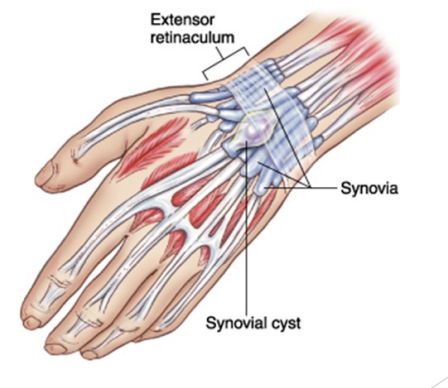
Forearm and wrist areas strains and tendinopathy
May result in ganglion
Cyst in tenosynovium or swelling within joint capsule
Mobile, swollen, tender, painful, boggy, possible crepitus with movement
May lead to carpal tunnel syndrome if on palmer side
Tx: surgical
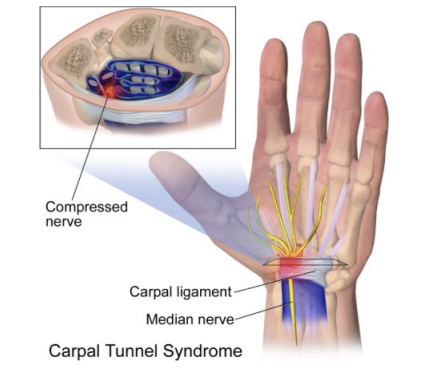
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Swelling in tunnel causes compression of median nerve
Hx = Repeated wrist flexion (tendinopathy) trauma (sprain, fracture, dislocation), ganglion, tumour, pregnancy
SSx:
Pain (worse at night, at rest)
Numbness and weakness thumb
Atrophy of thenar eminance?
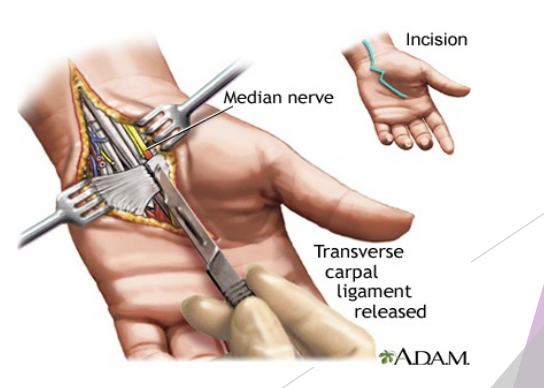
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment
POLIE; treat underlying cause
Splint
Send to MD for referral for NCS or EMG
NSAIDs (unless pregnant, allergic)
May need surgical decompression
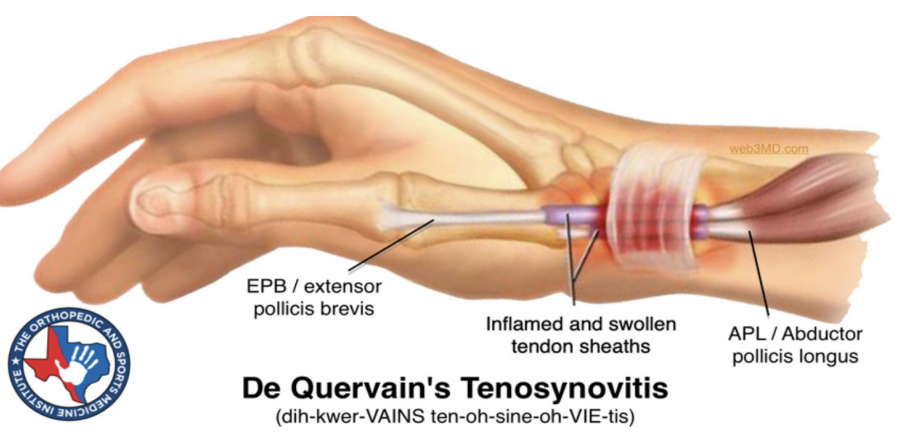
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Cause: Repetitive use of wrist/thumb, particularly with wrist in ulnar deviation
Inflammation of Abductor pollicis longus and Extensor pollicis brevis tendon sheaths
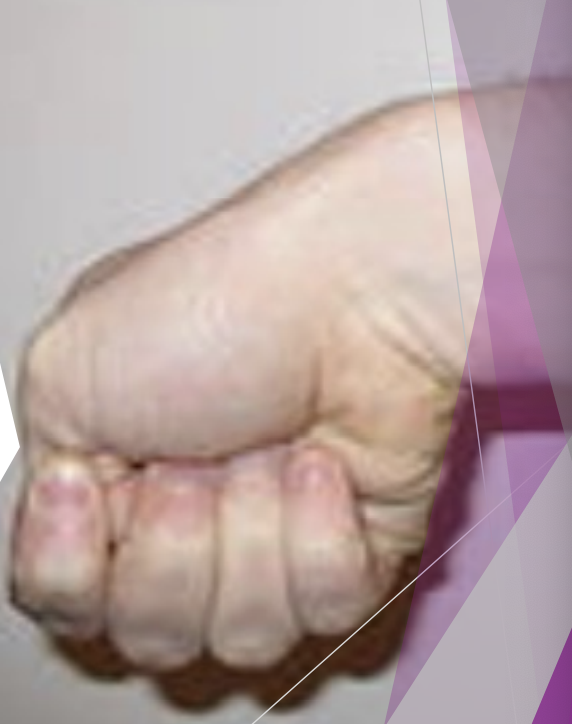

De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis SSx and Tx:
Pain/ swelling at base of thumb/radial side of wrist, pain stiffness with radial deviation of wrist and thumb flexion
Pain with resisted extension of thumb
+ve Finklestein’s test - make fist with thumb curled in fingers, ulnar deviation of wrist
POLIE, rest, brace?, physio, cortiocosteroid injection?, surgery
Hand strains & tendinopathy
Beware of possible avulsion fracture
Do not test muscle strength of finger vs FULL resistance - may convert 2nd degree to 3rd degree injury!
Upper Extremity Sprain and Dislocations
Hx:
Torsion
Resisting a force
FOOSH
SSx:
Pain, tenderness
Swelling
Deformity if dislocated
Bruising
Reduced ROM
Tx:
Check neurovascular status!
POLICE, splint, transport to hospital
X-Ray, splint or cast as necessary
Tape, physiotherpy, NSAIDs, rehab
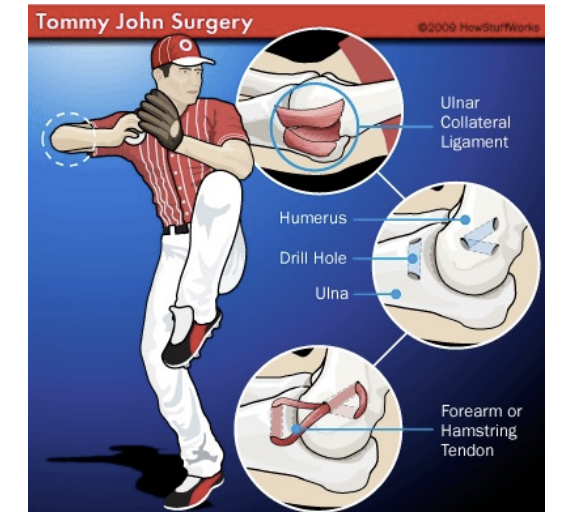
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprain
UCL is primary restraint to valgus stress to elbow
UCL sprain increases instability in elbow, higher stresses on other tissues
Pitchers, rugby/football tackles
SSx: Pain medial elbow, pain/laxity with valgus stress test, possible ulnar nerve injury
Tx: POLICE, NSAIDs, CH joint and elbow mechanics, pitching motion, surgery?
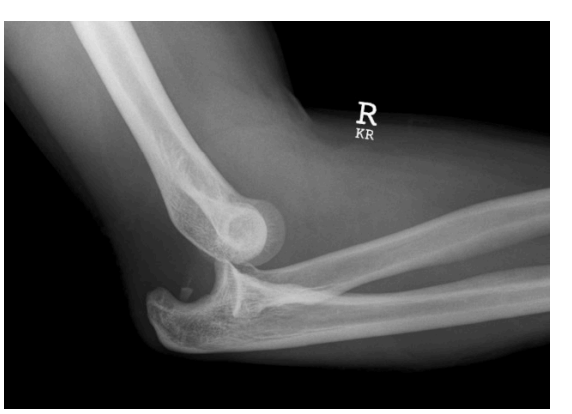
Elbow Sprain/ Dislocation
Hyperextension of annular ligament sprains (± radial head dislocation) are common (esp. wrestling)
Dislocation of elbow = emergency?
Tx:
Check neurovascular status
Splint, NPO, to hospital ASAP
X-Ray, splint or surgery as necessary, physio, NSAIDs, rehab
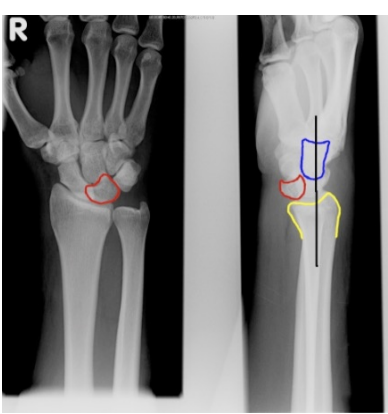
Wrist sprains and dislocations
Check neruovascular status
Complications = Lunate or other dislocations, carpal tunnel syndrome, scaphoid fracture
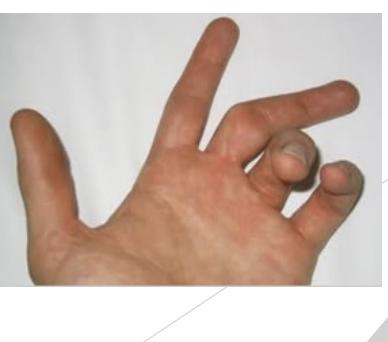
Hand Sprains and Dislocations
Check neurovascular status, avulsion?
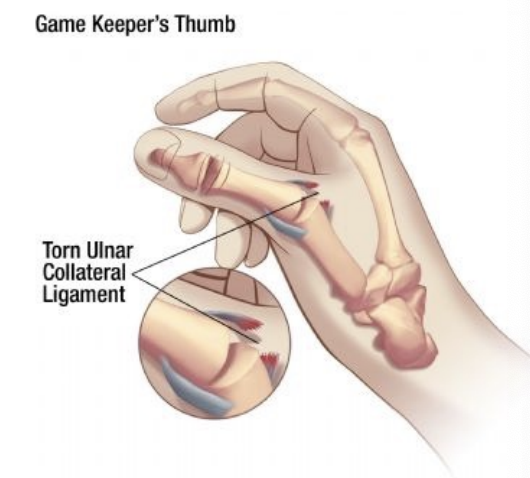
Gamekeeper’s Thumb
Hx: Forceful abduction combined with hyperextension of 1st MCP joint
Ulnar collateral ligament (UCL)
SSx: Pain over UCL, weak and painful pinch, tenderness, swelling
Tx: POLICE, splint, taping, rehab
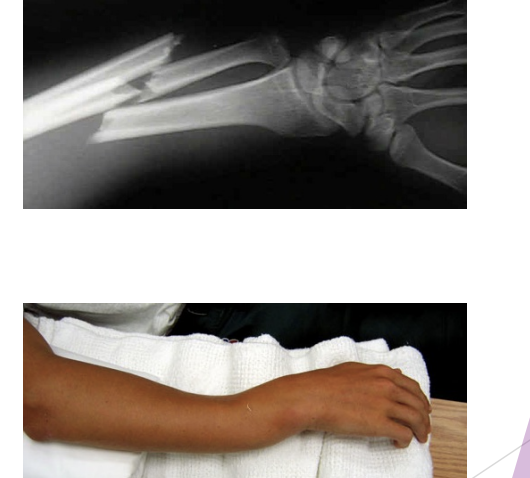
Upper Extremity Fractures
Recognize fracture likelihood
Hx
Deformity
Crepitus
Point tenderness over bone
If in doubt, send to MD for referral for X-Rays
Open fractures lead to high risk of infection (including osteomyelitis), especially of reduced “on site”
Tx = cleanse, disinfect, splint or cast, then physio, rehab, tape or splint when returns to sport
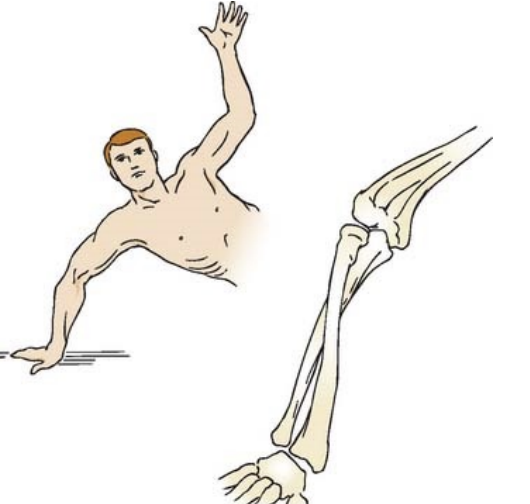
Radial Head Fracture
Hx: Radial head fracture common with FOOSH with forearm in pronated position
Among most common elbow fractures in adults
SSx: Swelling, limited pronation & supination, flexion and extension also affected
Tx: stabilize, NPO, surgery, rehab
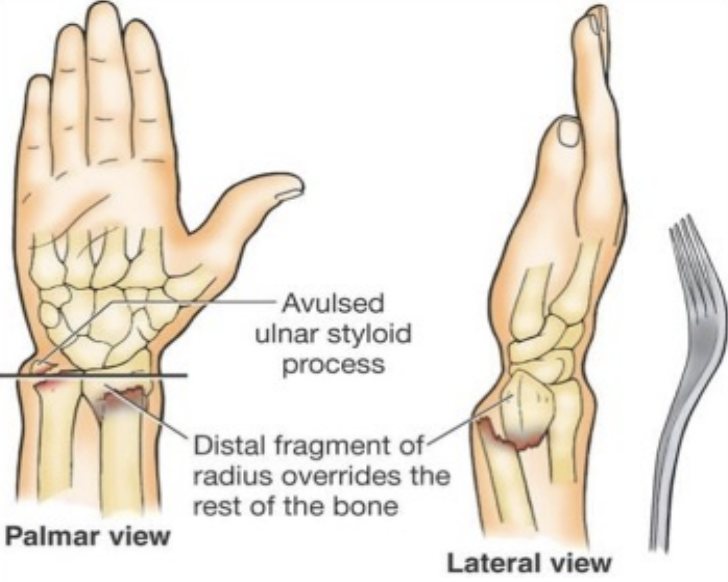
Colles Fracture
Dinner fork deformity
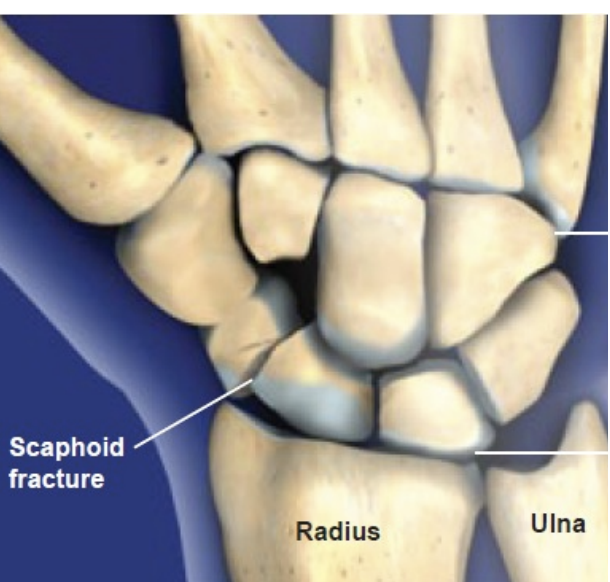
Scaphoid Fractures
Hx = fall, direct blow, sprain
SSx:
Tenderness in floor of anatomical snuffbox
X-Ray may be positive, but negative X-Ray does not rule out fracture!
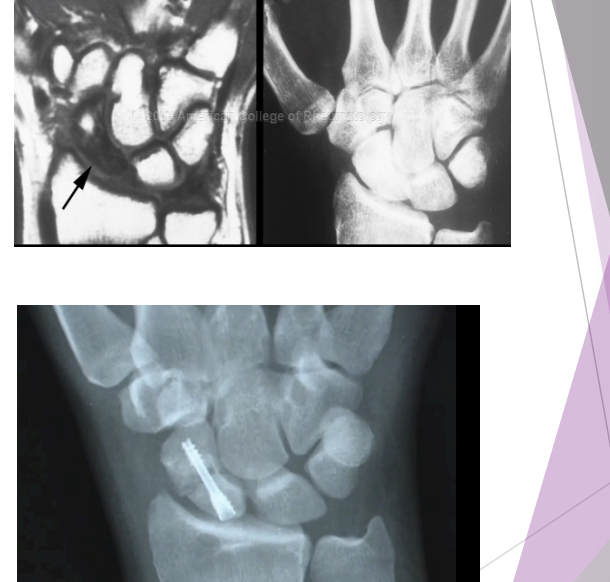
Scaphoid Fracture Tx
Tenderness? Then X-Ray
X-Ray positive?
Cast for 8 weeks, then physio and rehab
X-Ray negative?
Cast for 10 days, then re X-Ray, if positive for fracture, cast for 6 more weeks; if second X-Ray is negative, then physio, rehab
Avulsion
Tx = keep clean, send to MD, may need antibiotics, padding
Subungual hematoma
Hx = contusion, crush
If bleeding openly, have MD assess (X-Ray); beware of open fracture → osteomyelitis
Otherwise, Tx = Decompression under sterile conditions, then POLICE
Hand abrasions, lacerations
Cleanse wound throughly
Apply topical antibiotic
Beware of possible tendon injury
Monitor carefully for signs of infection, send to MD ASAP for antibiotics if needed!