Biology Unit 2B Notes
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mr. Poynton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
mouth
food is broken into smaller pieces, saliva moistens food to form bolus; amylase enzyme promotes breakdown of starch to sigars.
pharynx
area behind uvula, bolus moves through __ to esophagus
Esophagus
tube connecting pharynx to stomach, strong muscles propel bolus using peristalsis
stomach
bolus mixed/ground by strong muscle contraction SL enzymes (pepsin) and HCI acid react to break down protein molecules
liver
produces bile, bile emulsifies fats to promote digestion
emulsifies
syn for “separates into droplets”
gallbladder
storage area for bile produced in liver
Pancreas
produces digestive enzymes, enter small intestine through duct.
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
3 parts of small intestine (first, middle, final, d,j, i )
large intestine
water reabsorption occurs, feces formed.
both
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, MOUTH
none
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, PHARYNX
none
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, ESOPHAGUS
both
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, STOMACH
Mechanical
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, LIVER
Mechanical
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none,GALLBLADDER
Chemical
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, PANCREAS
Chemical
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, SMALL INTESTINE
none
Mechanical or Chemical Digestion, Both, Or none, LARGE INTESTINE
Heart
Muscle used to pump blood throughout the body
amylase, lipase, nuclease, protease
What enzymes does pancreas create, (a,l,n,p)
Left
Pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to the body. , left or right side of heart?
Right
Pumps deoxygenated blood from the body to the lungs. Left or right side of heart?
Right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle
4 chambers of heart
superior vena cava
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body (head, neck, arms, and chest) to the right atrium of the heart.
inferior vena cava
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body (legs, abdomen, pelvis) to the right atrium of the heart.
aorta
the main artery of the body,
aorta
artery supplying oxygenated blood to the circulatory system. (main one)
pulmonary semilunar valve
valve prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle of the heart after it has been pumped into the pulmonary artery. It ensures that blood is directed to the lungs for oxygenation, one of three semilunar valves in the heart, located at the base of the pulmonary artery
Large intestine
Where does water absorption occur?
Large Intestine
where are feces formed?
veins
veins or arteries: bring blood back to the heart
arteries
veins or arteries: bring blood away from the heart
blood
transports nutrients and wastes to and from all body tissues
buffy coat
thin, light-colored layer of a blood sample that contains most of the white blood cells and platelets after the blood has been separated through centrifugation
buffy coat
used in medical research for studying immune responses, DNA extraction, and diagnosing diseases like malaria.
buffy coat
The size (thickness) of the _____ ___ in a centrifuged blood sample is primarily a visual indicator of the concentration of white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets
arteries
veins or arteries; much more muscular
veins
veins or arteries; contain one way valves
pulmonary artery
all arteries except for this one carry oxygenated blood
pulmonary vein
all veins carry deoxygenated blood except for this one?
platelets
tiny, colorless blood cells that help your blood clot to stop bleeding when you get a cut or injury
platelets, red blood cells, white blood cells
three blood cells names
red blood cells
this type of blood cells carry oxygen to body tissues
hemoglobin
name of protein that carries oxygen
red blood cells and white blood cells
this type of blood cells is made in the bone marrow
white blood cells
this type of blood cell is made in the lymph nodes, bone marrow, and also lymph nodes
F
T or F, there are more red blood cells than white blood cells
T
T or F, there are less white blood cells than red
F
T or F, red blood cells are larger than white blood cells
T
T or F, white blood cells are larger than white blood cells
white blood cells
This type of blood cell helps w defending the body against infection from microorganisms
white blood cells
this blood cell has several types
white blood cells
this type of blood cell engulfs microorganisms, other types produce antibodies
platelets
this type of blood cell helps to form blood clots
blood plasma, buffy coat, blood cells
blood is separated into these 3 things. Start from top to bottom
red blood cells
when you are anemic you are low in this type of blood cell
F
T or F, oxygenated blood is actually blue.
Arteries, veins, capillaries
3 types of blood vessels from thickest to thinnest
capillaries
smallest blood cell
capillaries
one cell layer thick blood vessel
white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets
blood cells from biggest to smallest
water
What is blood plasma mostly composed of ?
sodium chloride, potassium chloride.
blood plasma contains salts, which two types are there
water, salts, proteins, nutrients
list what is in blood plasma (w,s,p,n)
regulation
the process of controlling body systems to maintain ideal function and homeostasis
Endocrine, Nervous
what two systems does regulation depend on
stimulus
a detectable change in the environment
control center
Brain/gland that senses stimulus message and decides on a response, sends a message to an effector
effector
organ/gland/muscle that performs an action
response
any behavior of a living organisms that results from external or internal stimulus
F
T or F, a stimulus can only be physical
receptor
what is this an example of: brain senses temperature
receptor
syn for control center
neuron
what is this a diagram of
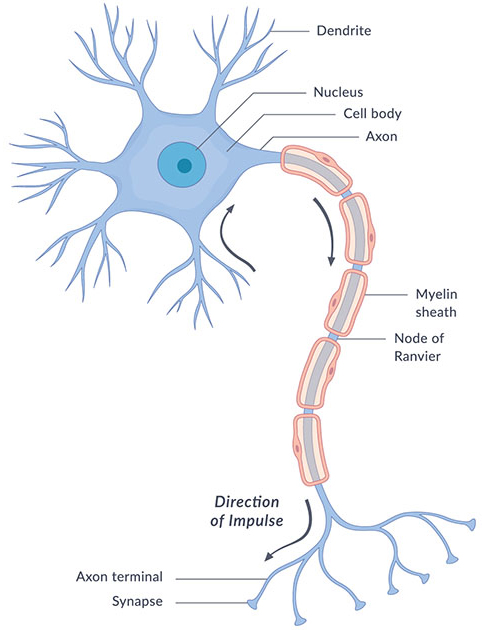
cell body
What is the circle in the middle of the sun shaped thing.
dendrites
what are the fork like things surrounding the cell body
axon
what the cord like thing going from the star shaped thing.
myelin sheath
what is the layer of fat surrounding the axon called
neuron
a highly specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell.
axon terminal
end of the cord in diagram
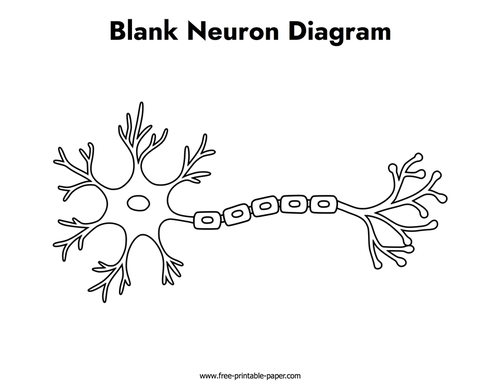
muscle fiber, another neuron, gland cell
these are the three possible “effectors”, (what the axon terminal can latch onto.
synaptic gap
space inbetween the end of the cord like thing to another “effector cell”; (another neuron, muscle, or gland)
synaptic gap
tiny, fluid-filled space is where neurotransmitters diffuse from the axon terminal to the effector cell to transmit a signal
schwann cell
this cell produces myelin sheath
sodium and potassium
these are the two ions that are used to send messages
nervous system
nervous system or endocrine system: electrochemical signal
endocrine system
endocrine system or nervous system: sends a hormone/chemical message
negative feedback loop
nerve or endocrine response that corrects or negates stimuli to help maintain homeostasis in the body.
alveoli
what is this a diargram of
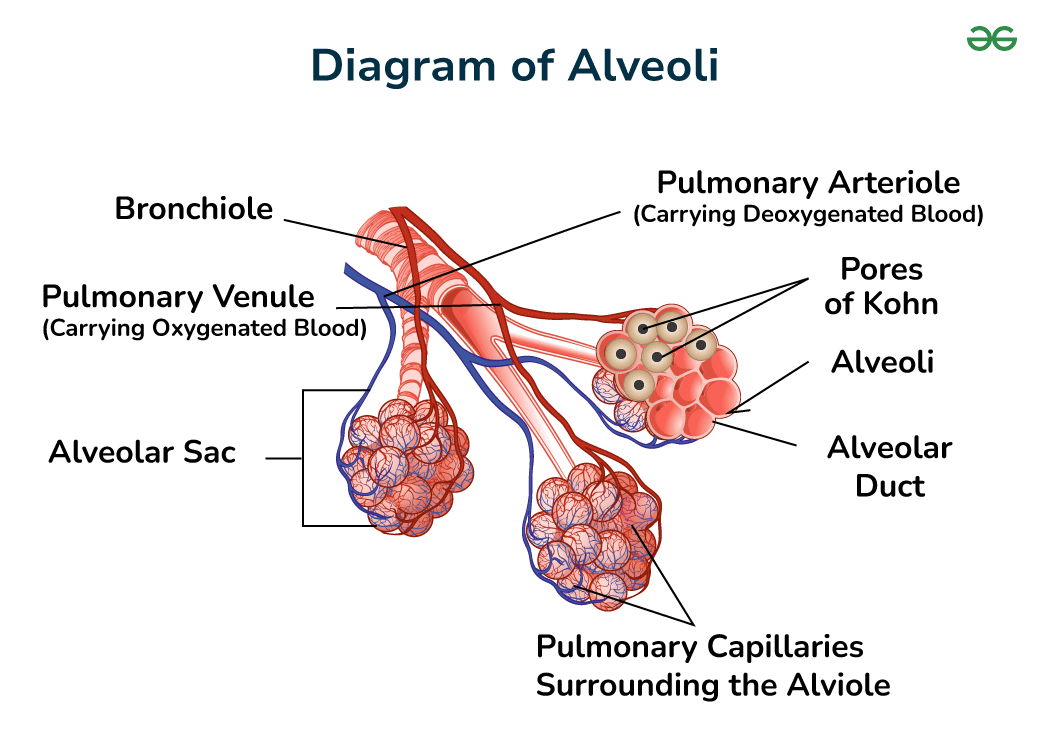
pulmonary artery
deoxygenated blood goes into the alveoli from the ___
F
T or F, deoxygenated blood goes from the alveoli into the pulmonary artery.
T
T or F, oxygenated blood goes out of the alveoli and into the pulmonary vein
capillaries
the diffusion of 02, CO2, nutrients, wastes, ect. happen here
hormone
chemical substances that act like messenger molecules in the body
reflex arc
synonym for involuntary movement
nervous system
Which one (endocrine system or nervous system) has a short duration
endocrine system
which one (nervous system, endocrine system) has a longer duration
endocrine system
which one (endocrine system or nervous system) has a slower response time