NURS 333 Chapter 23 Conditions Occurring After Delivery
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Maternal Early Warning Criteria
-maternal aggitation, confusion, or unresponsiveness
-report of headache, or SOB by patient with preeclampsia
-systolic BP <90 or >160
-diastolic BP >100
-HR <50 or >120
-RR <10 or >30
-O2 sat on room air at sea level <95%
-oliguria for 2 or more hours (<35 ml/hr)
Postpartum Hemorrhage
is bleeding of more than 1,000 mL despite uterine massage and first-line uterotonics (such as oxytocin).
After birth the uterus normally maintains hemostasis and prevents PPH by clotting and contraction of the myometrium of the uterus.
PPH is often caused by uterine atony, blood coagulopathies, or trauma.
Postpartum Hemorrhage Risk Factors
- prolonged labor
- augmented labor
- rapid labor
- operative delivery
- overdistended uterur
- hx of PPH
- chorioamnionitis
early PPH
occurs within 24 hours of birth
delayed or secondary PPH
24 hours to 12 weeks after delivery
uterine atony
Clinical manifestations:
Boggy uterus
Heavy bleeding
Confirmed by bimanual exam
Prevention:
Recognizing risk factors
Initiating early intervention and treatment
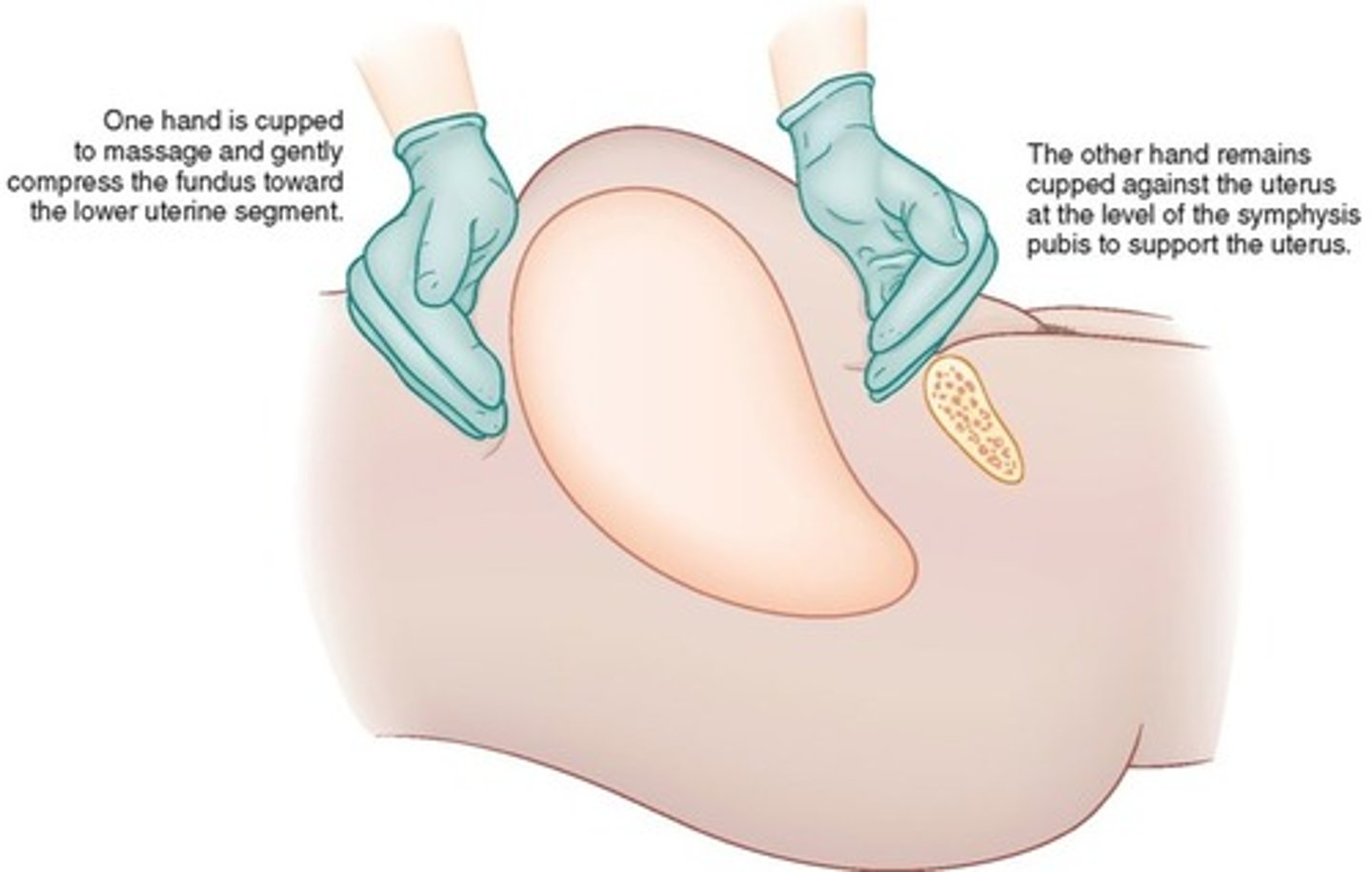
Nursing Actions and Interventions for Uterine Atony
Review prenatal and/or intrapartum records
Monitor vital signs
Establish intravenous access and draw labs
Perform fundal checks, assess bleeding, fundal massage
Assess and monitor patient more frequently
Administer and/or have uterotonics per orders and protocol
Reassure patient and provide explanation for nursing action/ interventions
Provide comfort measures
Lacerations
Clinical manifestations
Steady stream of bleeding despite firm fundus
Absence of clots
Origin is often masked
Pain and hemodynamic instability are often presenting symptoms
Tachycardia and hypotension
Diagnosis
Inspection of the lower genital tract
Prevention
Minimal use of instrumentation
Limited use of an episiotomy
Offer operative delivery
Nursing Actions and Interventions for Lacerations
Review prenatal and intrapartum records
Monitor vital signs
Perform fundal checks and assess for bleeding
Monitor blood loss
Prepare patient for pending pelvic exam
Administer pain medication as prescribed
Provide comfort measures and emotional support
hematoma
Risk Factors
Episiotomy
Instrumented vaginal delivery
Prolonged Second Stage
Clinical Manifestations
Severe pain in the vaginal or perineal areas
Pain often uncontrolled by standard analgesia
Swelling, discoloration, and tenderness
Vaginal bleeding may or may not be present
Diagnosis
Examine affected areas
Prevention
Avoid episiotomy and operative deliveries
Minimize second stage of labor
Nursing Actions and Interventions for Hematoma
Review prenatal and intrapartum records
Monitor vital signs
Apply ice to perineal area for first 24 hours postpartum
Assess pain
Administer pain meds as prescribed
Review lab results
Inform physician or APN as indicated
Postpartum hemorrhage treatment
Call for help.
Fundal massage of a boggy uterus.
Assess for lacerations or hematoma if the fundus is firm.
Bladder catheterization for inability to void.
Establishing intravenous access.
Oxytocin administered as a first-line uterotonic medication.
Oxytocin
Pitocin
20 to 40 units IV in Lactated Ringers; 10 units IM
IVF bolus
Immediate
Duration: 1 hour
Contracts the upper segment of the myometrium which constricts arteries and decreasing blood flow to the uterus
Don't administer an undiluted rapid IV infusion because it will cause hypotension
Methylergonovine (Methergine)
0.2 mg IM; PO*
Every 2 to 4 hours
Ergot alkaloid that causes generalized smooth muscle contraction in the upper and lower uterine segments
used with caution with those with preeclampsia, hypertension
Carboprost
Hemabate
250 mcg IM
Every 15 min up to 2 mg
Prostaglandin causes uterine contraction and vasoconstriction
Absolute contraindication is hypersensitivity; used with caution with those with asthma
Misoprostol
Cytotec
100 to 200 mcg rectally
Prostaglandin that promotes uterine contractility and tone
B. Evaluate the patient's uterus and lochia.
A family member of a postpartum patient comes out of the patient's room to tell the nurse that the patient is pale, sweaty, and "isn't acting right." What should the nurse do first?
A. Notify the patient's primary health care provider.
B. Evaluate the patient's uterus and lochia.
C. Obtain a set of vital signs.
D. Reassure the family member that the patient is doing well.
Hypovolemic Shock
Triggered when the volume of circulating blood decreases to a degree that the body's organs do not have enough oxygen to function properly
Symptoms of hypovolemic shock
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Oliguria
Mental status changes
Cool, pale, and clammy skin
Slowed capillary refill
Thromboembolic Disease
is a blood clot or multiple clots that form within a vein.
account for 9.2% of maternal deaths in the United States.
symptoms include swelling, pain, localized redness, warmth, and tenderness.
are often diagnosed with ultrasound imaging.
Treatment may include anticoagulation therapy or surgery.
risk factors for thromboembolic disease
include dilated veins leading to slower blood flow and pooling, endothelial injury related to surgical intervention or placental detachment, and the increase of coagulation factors in pregnancy to decrease the risk of hemorrhage.
superficial vein thrombosis
is more common than a DVT. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and redness along the length of the vein. The vein may feel cord-like. A superficial vein thrombosis is often self-limiting
Postpartum Infections
can be related to perineal wounds, cesarean wounds, endometritis, mastitis, and urinary tract infections.
Symptoms can be nonspecific.
General symptoms include:
A fever that persists beyond the initial 24 hours after birth.
A fever that begins 2 to 10 days after birth.
Elevated white blood cell count that continues to rise rather than fall.
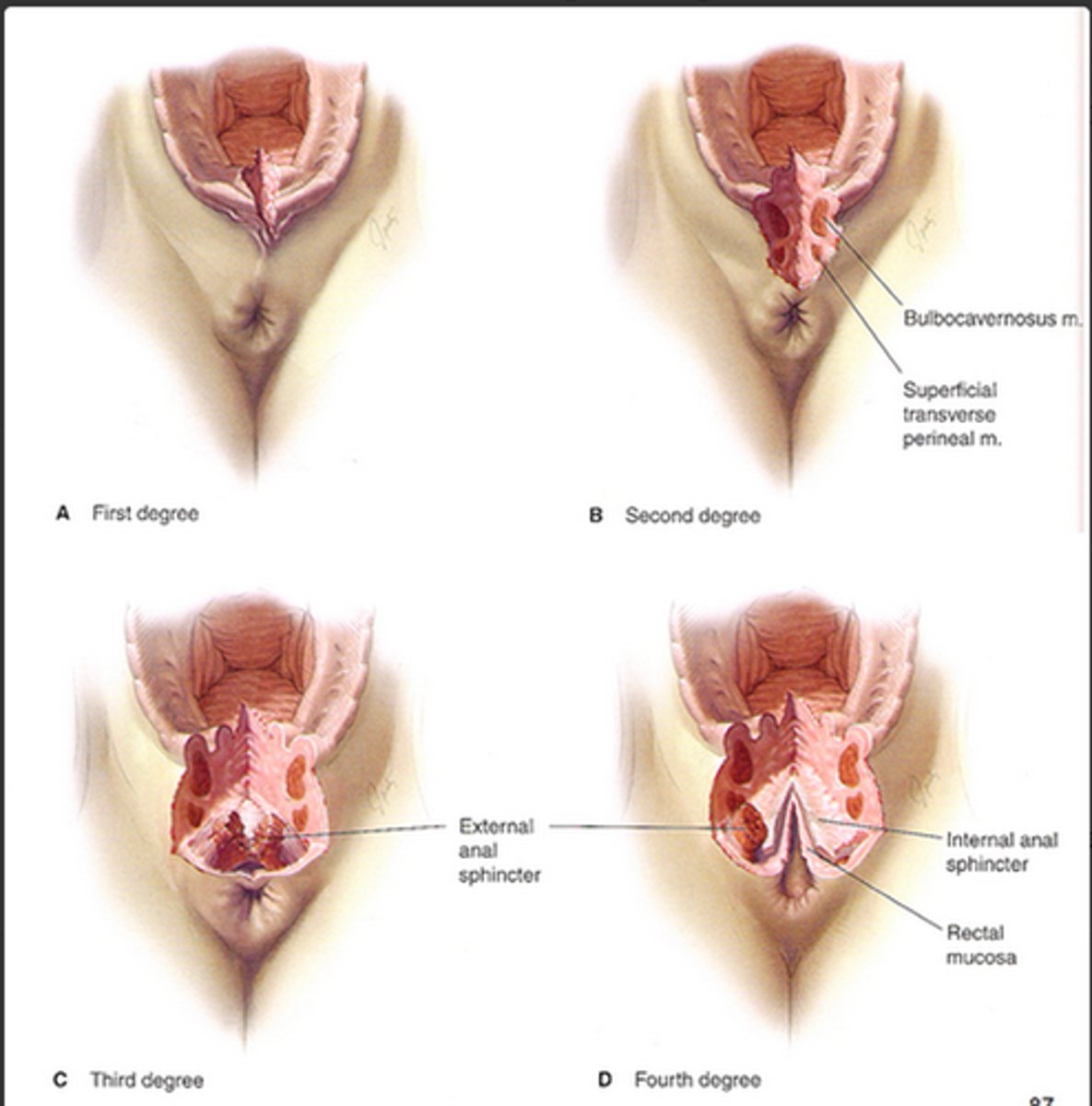
Perineal Wounds
Associated with third- and fourth-degree lacerations.
Risk factors include:
Operative vaginal delivery
Prolonged second stage of labor
Third- or fourth-degree laceration
Meconium-stained fluid
Assessment findings include tenderness, redness, and swelling, as well as purulent discharge.
Treatment requires removal of sutures and opening of the wound.
Antibiotics are not necessary unless there is evidence of cellulitis.
Endometritis
infection of the lining of the uterus.
Occurs in up to 27% of cesarean births and 1% to 3% of vaginal deliveries.
Risk factors include chorioamnionitis, prolonged labor, and prolonged rupture of membranes.
Infection may cause the uterus to become soft and subinvoluted, which predisposes the woman to hemorrhage.
Signs and symptoms include:
Fever
Uterine tenderness
Flu-like symptoms
Tachycardia
Typically treated with intravenous infusion of a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Lactational Mastitis
Inflammation of the breast tissue often associated with infection.
Factors contributing to mastitis include delayed breast emptying, poor drainage of one or more ducts, inconsistent pressure on breasts (like poorly fitting bra), oversupply of milk, or nipple trauma.
Most common in the first 3 months of breastfeeding.
Symptoms include tender, red area of breast, malaise, or a high fever.
Treatment may include:
Cold compresses
NSAIDs
Regular and complete emptying of the breast
Antibiotics
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Postpartum women are prone to UTIs because of the frequency of bladder catheterization and genital procedures.
Symptoms include urinary urgency and pain with urination.
Pyelonephritis is a UTI of the upper urinary tract.
Symptoms include flank pain, nausea and vomiting, and fever.
Treatment is generally antibiotics.
False
Is the following statement true or false?
A patient who had a spontaneous vaginal delivery 12 hours ago and is found to have a low-grade fever and slightly elevated white blood cell count probably has an infection that should be treated.
postpartum blues
is a transient, self-limiting mood disorder that starts 2 or 3 days after delivery and resolves within 2 weeks
postpartum depression
is major depression with an onset during pregnancy or in the first 4 weeks after birth.
Estimated 10% to 16% of women experience
postpartum psychosis
is a rare disorder that affects a woman's sense of reality.
Disturbance of a woman's perception of reality as evidenced by hallucinations, thought disorganization, disorganized behavior, and delusions.
Most common in women who suffer from depression with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, or psychosis.
Condition may occur within 48 hours of delivery.
The priority of care is the safety of the patient and the safety of the infant.
Treatment often requires inpatient psychiatric care.
Warning signs for postpartum depression
Low mood for at least 2 weeks
Negative attitude toward the infant
Anxiety about the health of the infant
Concern about the ability to care for the infant
Use of alcohol, street drugs, drugs prescribed to others, or tobacco
B. Interview the patient using open-ended questions.
A home health nurse notices the patient, who delivered 6 weeks ago, appears disheveled, the house is dirty, and the infant appears to be well-fed but is wearing a dirty onesie. What should the nurse do first?
A. Notify the patients primary health care provider.
B. Interview the patient using open-ended questions.
C. Call child protective services due to the risk of postpartum psychosis.
D. Realize the patient has a new baby and is likely sleep deprived.