Cell Compounds - Organic
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Organic molecules always contain …
Carbon
Carbon has … electrons in its outermost energy level.
four
A carbon atom shares electrons with hydrogen forming … bonds
Covalent
Carbon share electrons with other carbons to form …
Rings
Basic unit of organic compounds is called … and repeat over and over to form larger molecules called …
Monomer; polymers
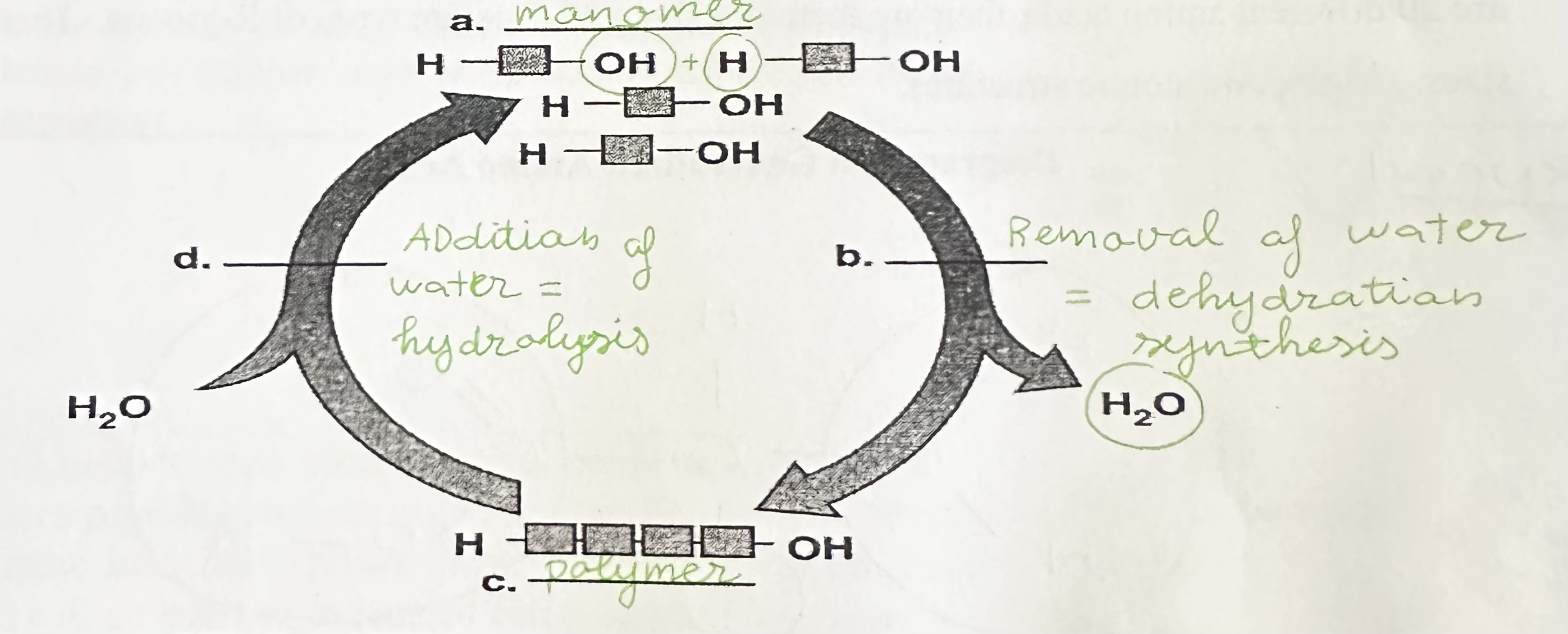
Define dehydration synthesis
The creation of larger molecules through the removal of water.
Define hydrolysis
The breaking apart of polymers, by splitting bonds through the addition of water.
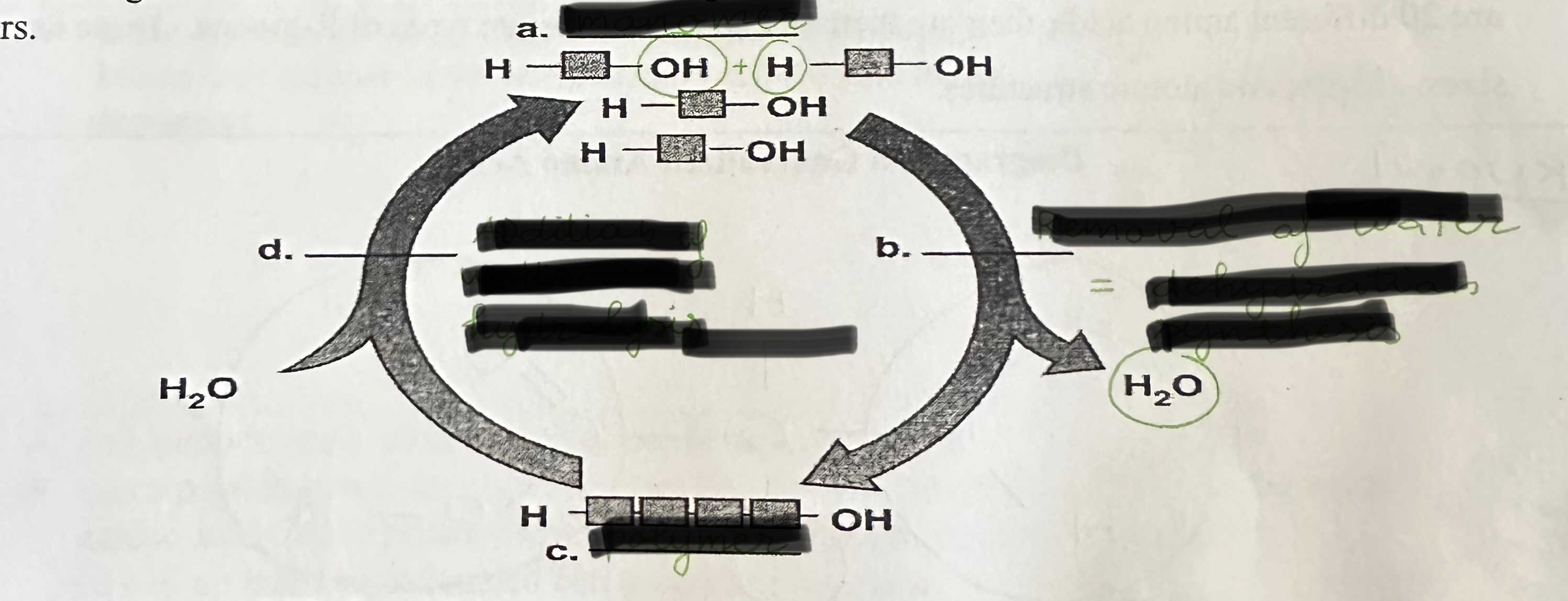
Label a, b, c, and d
a = monomer
b = dehydration synthesis
c = polymer
d = hydrolysis
The four main groups of organic molecules
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic acid
Three main functions of proteins (no need for detail)
Structural support
Movement
Metabolic Functions
Examples of structural support (protein name and function or found in)
Keratin - hair, nails
Collagen - ligaments, cartilage
Example of protein that functions in movement
Actin - enables muscles to contract
4 Elaborations of protein function in metabolic function and name the protein if possible.
Enzymes - speed up chemical reactions
Antibodies - immobilize pathogens
Hemoglobin - carries oxygen in blood
Insulin - lowers blood sugar conc.
Protein monomers are called …
Amino acids
There are … amino acids in the human body. … are … amino acids meaning our body … and must be obtained through … . The remaining … amino acids our body …
20; 8; essential; cannot make them; food; 12; can make
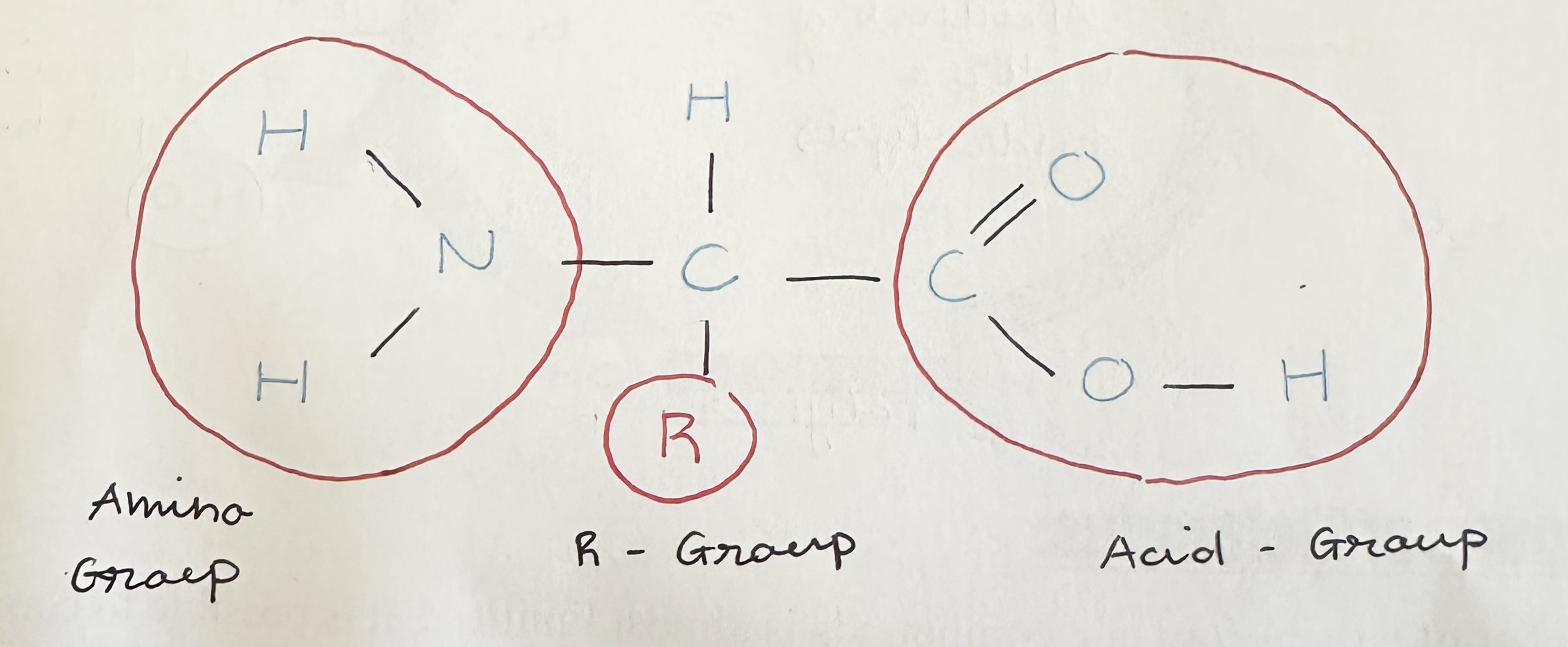
Two functional groups inside the amino acid, that is same for every A.A.
Amino group
Acid group
A.A.’s differ from one another in their … , and there are … different kinds
R-group; 20
Draw and label a generalized model of an amino acid
Amino acids can be linked by … through …
peptide bonds, dehydration synthesis
A peptide bond is … and …
covalent; polar
Draw a dipeptide and label the peptide bond
A long chain of amino acids is a …
polypeptide
When one or more polypeptides assume a unique 3-dimensional shape, it is a …
protein
Four level of protein organization
Primary structure
Secondary (…)
Tertiary (…)
Quaternary (…)
Primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Secondary structure is when the polypeptide chain takes …
a particular orientation in space.
Secondary structure occurs since … are …, … occurs between … causing the chain … into a … or into … called …
peptide bonds; polar; hydrogen bonding; amino acids; coil up; alpha helix; layers; beta-pleated sheets
Tertiary structure has … between … makes … forming … . Its shape is … by these bonds.
Tertiary structure has different types of bonding (ionic, covalent, hydrogen) between R groups makes the secondary structure forming a 3 dimensional shape. Its shape is stabilized by these bonds.
Quaternary structure is the … of …
Quaternary structure is the binding of two or more polypeptide chains.
The final shape of the protein is …
very important for its function
When a protein loses its shape, it has … and it …
denatured; no longer functions.
A protein can become denatured by
High heat, wrong pH, and exposure to heavy metals.
Sources of lead
Toys (crayons), old pipes, old paint, and cosmetics.
Sources of mercury
Light bulbs, batteries, fish, cavity fillings, vaccines.
three functions of carbohydrates
Short term energy source, e.g. glucose used in cellular respiration.
Storage of energy, e.g. starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
Structure, cellulose in plant cell walls.
Carbohydrates is … composed of …
organic molecule; carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Carbohydrates have contain hydrogen and oxygen in the same proportion as … with … and … linked to … giving carbohydrates a … property.
water; hydrogen ion; hydroxide ion; carbon; polar.
The empirical formula for a carbohydrate is … where … can be … . For example glucose empirical formula is …
(CH2O)n; n; almost any number; C6H12O6
Monomers of carbohydrates are …
monosaccharides
Polymers of carbohydrates are …
polysaccharides
Three classes of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides are … consisting of … and are indicated by …
simple sugars; one molecule; “ose”
Monosaccharides are either … or … arranged in a …
5-carbon sugar “pentose”; 6-carbon “hexose”; ring
Glucose, fructose, and galactose have the same molecular formula but differ in shape and arrangement meaning it is an …
isomer
The forming of a disaccharides from two monosaccharide is an example of …, and the reverse is an example of …
dehydration synthesis; hydrolysis
Polysaccharides contain … number of …
large; monosaccharides
Three common polysaccharides are:
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Starch is the stored form of glucose in … and is a … chain of glucose with … branches
plants; relatively straight; few
Glycogen is the stored form of glucose in … and is a … chain of glucose molecules
animals; highly branched
Cellulose is the … component in … , is a … chain of glucose with … branches
structural; plant cell walls; straight; no
Humans are unable to … cellulose. Cellulose adds … to fecal matter and help prevent …
digest; roughage/mass; colon cancer
The proportion of hydrogen and carbon to oxygen is … in lipids
much greater
Lipids is an … and contain …
organic molecule; carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
lipids are … meaning it is … in water
non-polar; insoluble
Three classes of lipids
Neutral fats (triglyceride)
Phospholipids
Steroids
Neutrals fats or also called a … are formed by linking a … and … and again is an example of …
triglyceride; glycerol; three fatty acids; dehydration synthesis
A neutral fat is called neutral because it is …
non-polar
fatty acids have a … and ends in a ..., and contain … carbon atom per molecule
hydrocarbon; carboxyl group(-COOH), 16-18
Saturated fatty acids have … between carbon atoms, it is “saturated” with … atoms. Are … at room temp. Causes … .
no double bonds; hydrogen; solid; atherosclerosis
Unsaturated fatty acids have … between carbon atoms, and have … hydrogen atoms than saturated fatty acids. It is … at room temp. An example is …
double bonds; fewer; liquid; vegetable oil
Functions of neutral fats
Use for long term energy storage
Insulates from heat loss
Acts as a protective cushion for organs
Phospholipids are an important component of …
cell membranes
Structure of a phospholipid
A glycerol with two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
The phospholipid has a … and … head region and a … and … tail region
polar; hydrophilic; non-polar; hydrophobic
The cell membrane is a … composed of …, with the … facing outwards and the … facing inwards.
bilayer; phospholipids; hydrophilic heads; hydrophobic tails
Steroid “basic skeleton”
4 interconnected rings of carbons
The most common steroid is …
cholesterol
Functions of steroid hormones and examples
sex hormones - estrogen and testosterone
aldosterone - regulate blood sodium
What are the two “types” of cholesterol and which is good and bad?
high density lipoprotein (HDL) is good and low … (LDL) is bad
Function of nucleic acid
Growth and reproduction
Two kinds of nucleic acid POLYMERS and their function
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) makes up all living things genomes
ribonucleic acid (RNA) used in protein synthesis
The monomer of nucleic acids, and form nucleic acids through …
nucleotides; dehydration synthesis
Nucleotide composition
phosphate group
pentose
nitrogenous base
Four kinds of DNA nucleotides
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
Genes are
sections of DNA
RNA is formed inside …
the nucleus
ATP stands for …
adenosine triphosphate
ATP functions as …
primary energy carrier in cells
ATP consists of …
a ribose, adenine base, and three phosphate group
ATP is formed during …
cellular respiration
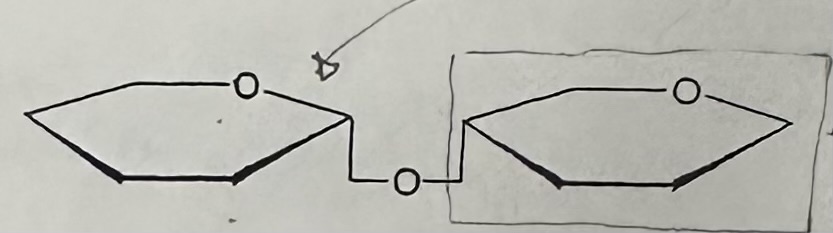
Dissaccharide
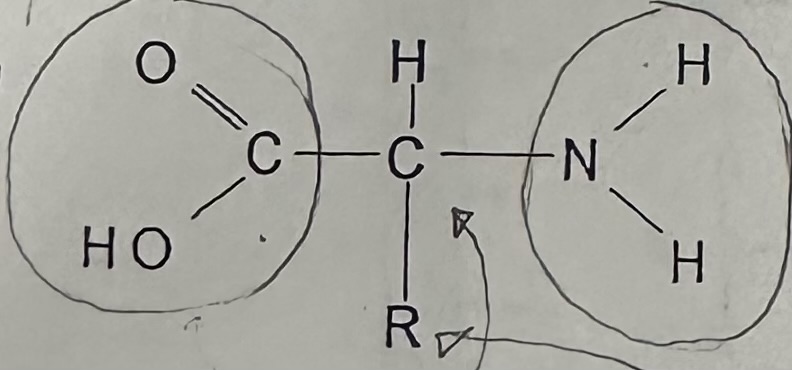
Amino acid, acid group, amine group, and remainder group
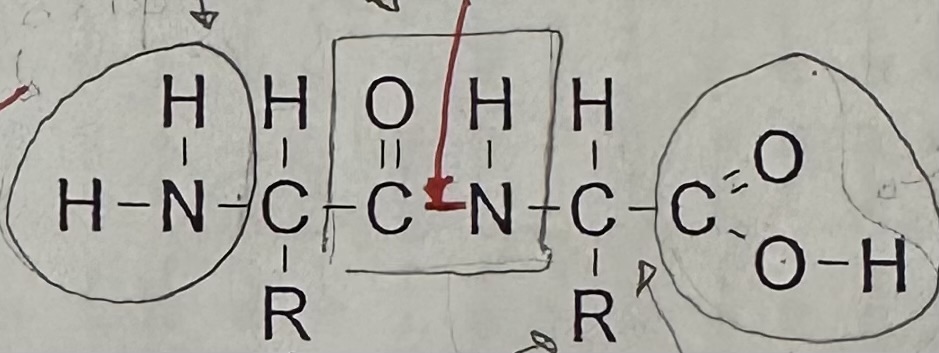
Dipeptide
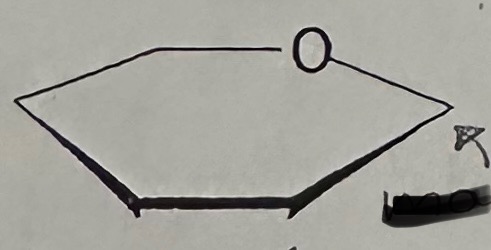
Hexose → Glucose
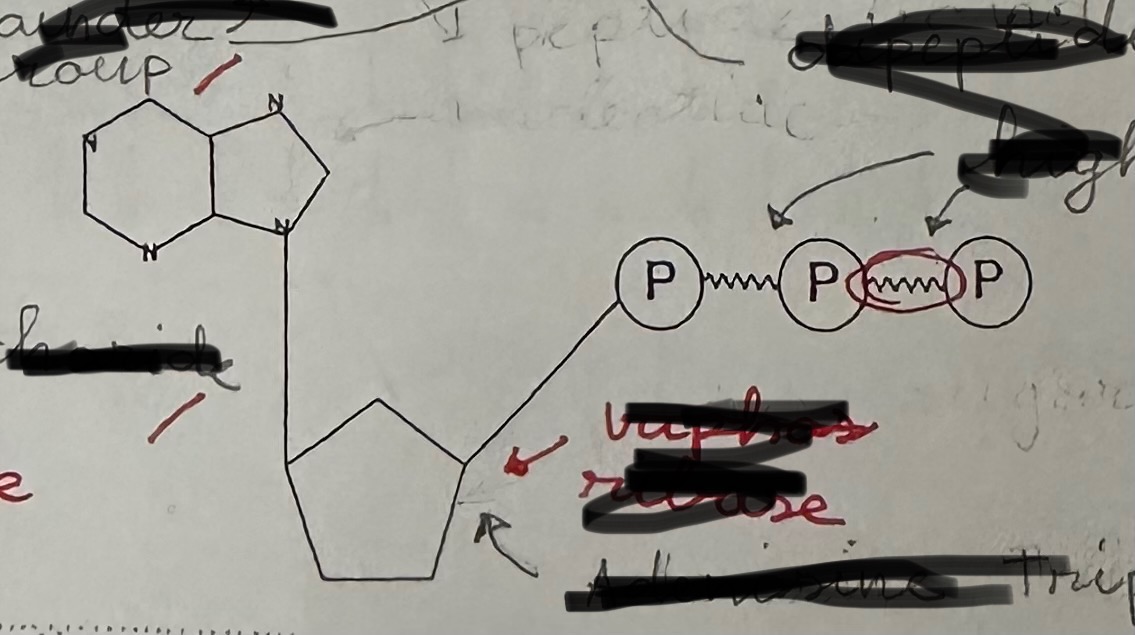
ATP, high energy bonds
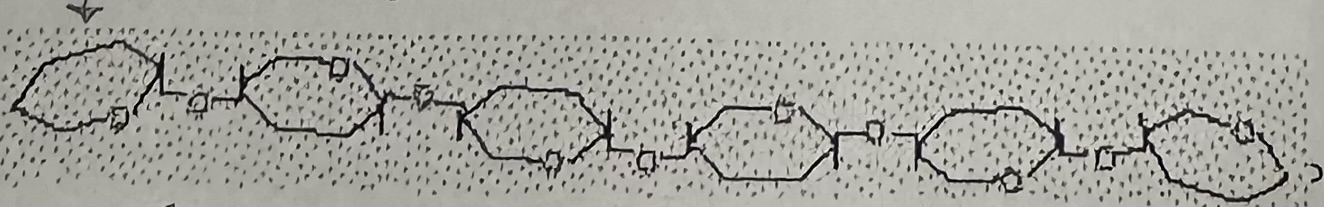
Cellulose
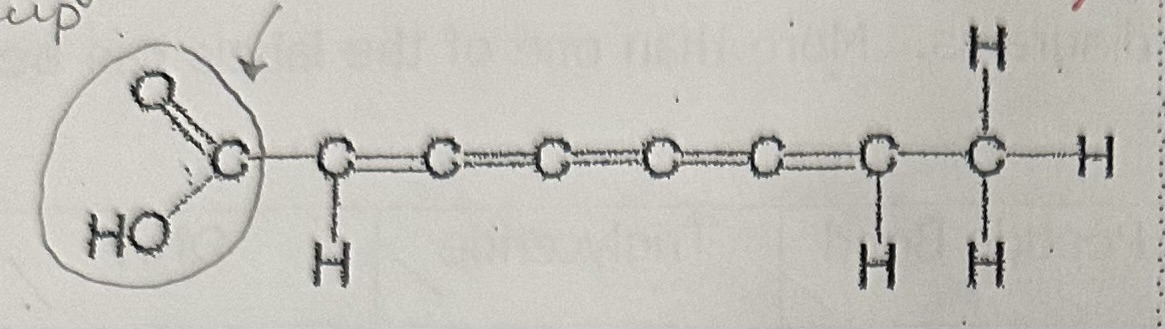
Poly-unsaturated fatty acid
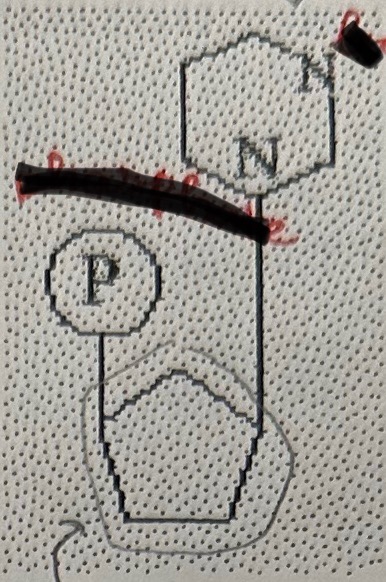
Nucleotide
Primary structure
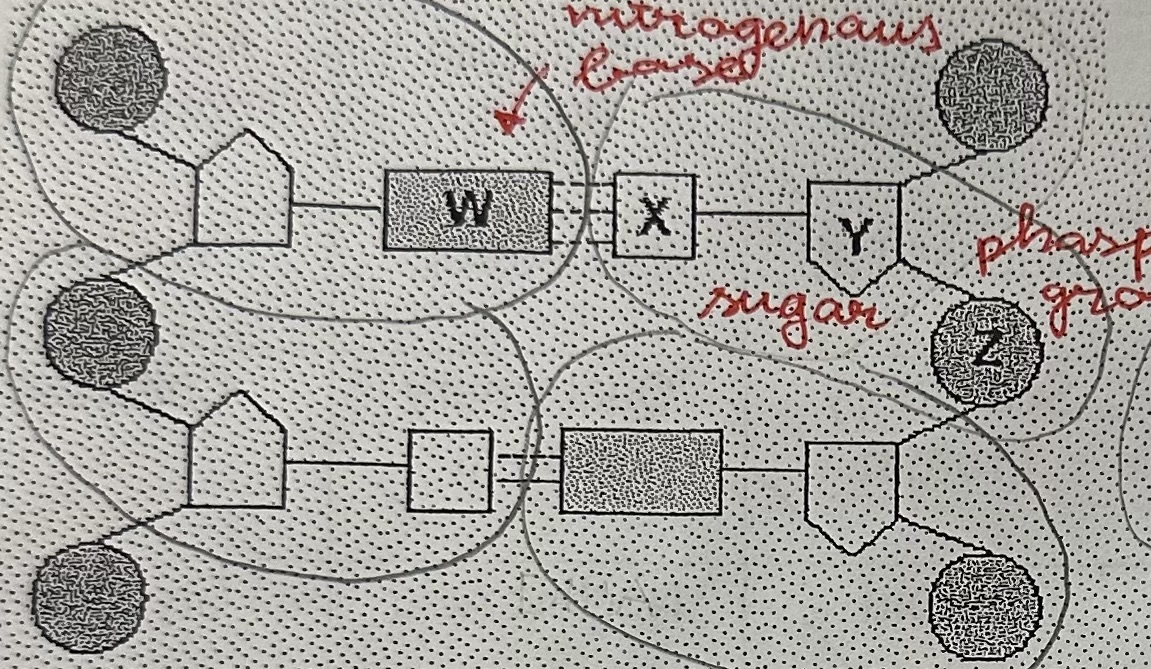
DNA
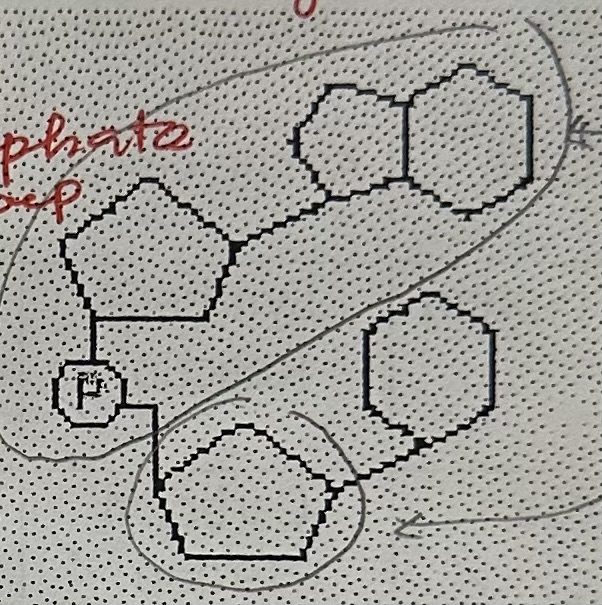
RNA
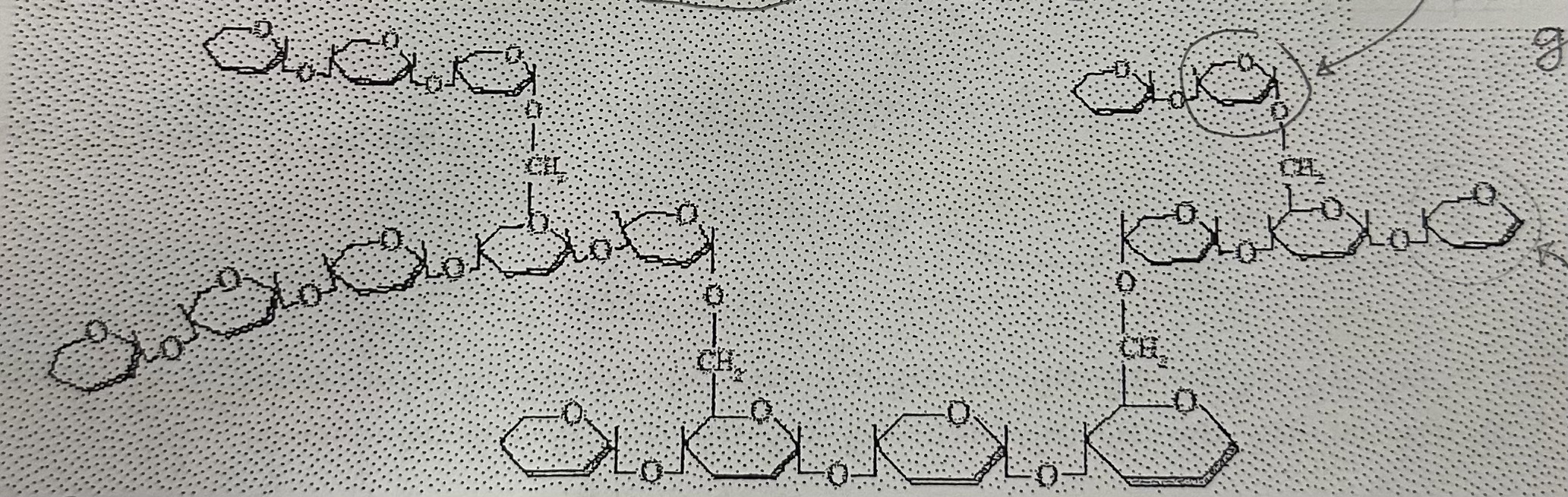
Glycogen
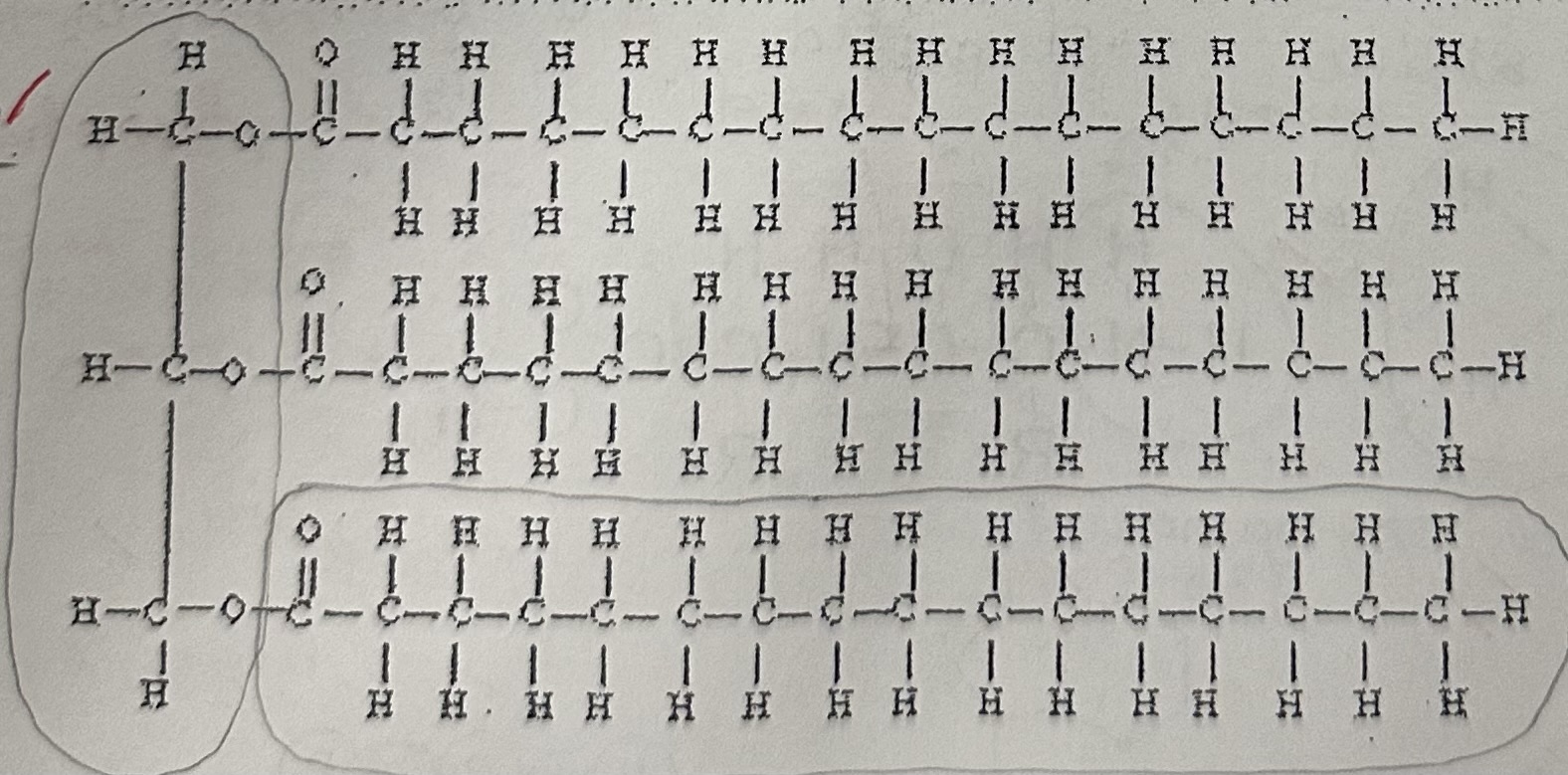
Triglyceride/ neutral fat
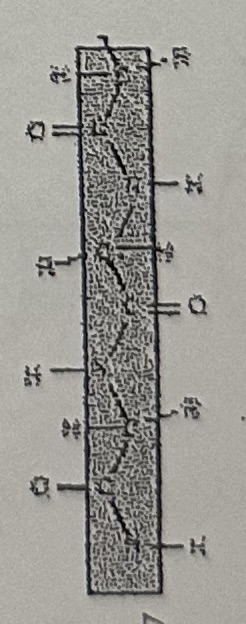
Primary structure
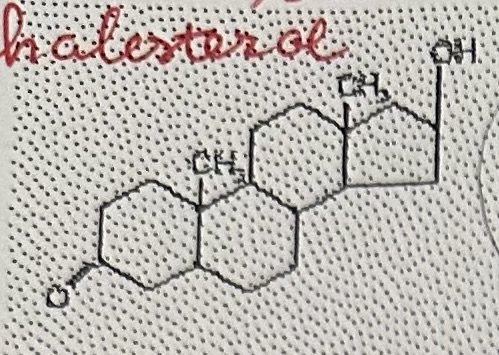
Steroid → cholesterol
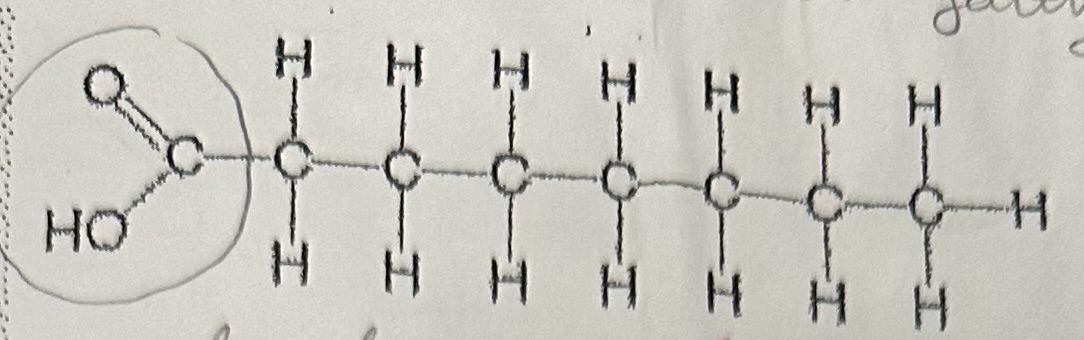
Saturated fatty acid
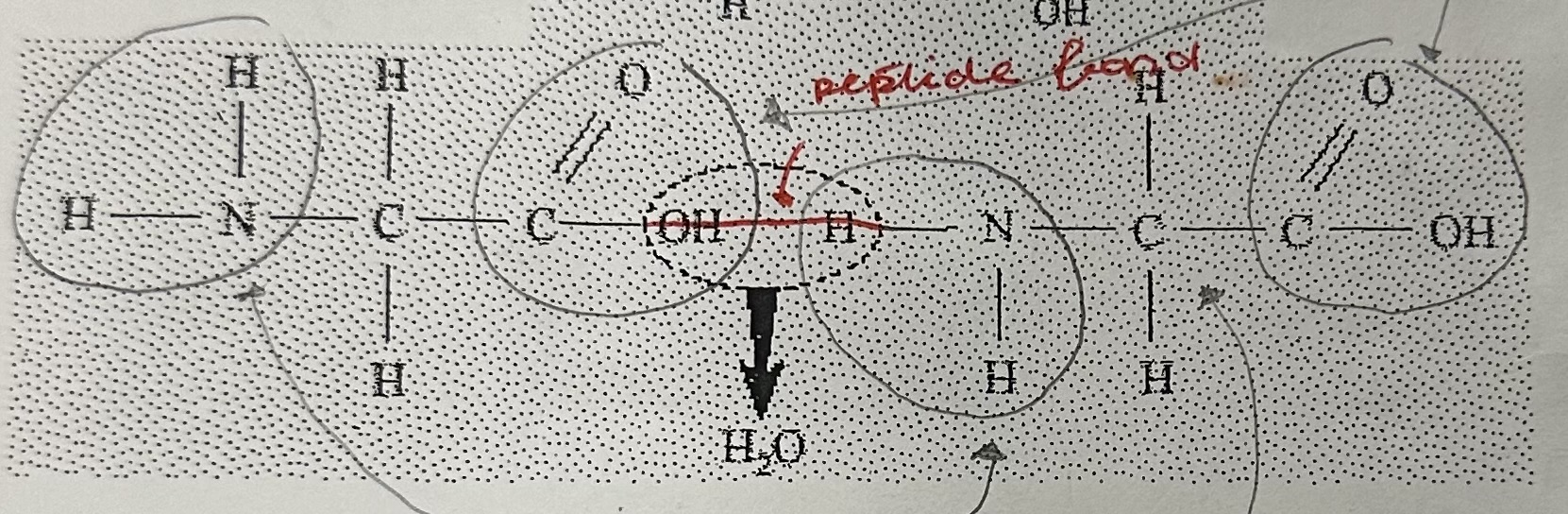
Dehydration synthesis
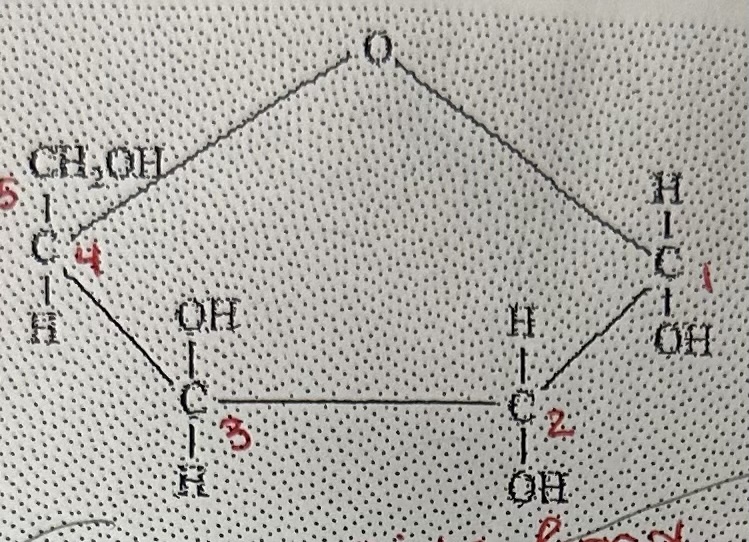
Pentose

Quaternary structure
Tertiary structure