5 - Carbonates
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
2 types of biogenic sediments
Biogenic and Chemical
Biogenic carbonates
Metabolised by organisms
Skeletal material/ ‘Hard parts’→ carbonates, silicates and phosphates
‘Soft parts’ → organic matter
Chemical sediments
Evaporites precipitated directly from the atmosphere or water
What % of seawater is salt
3.5%
Where do sea salts come from
Metal species weathered from continental and mid ocean ridge processes
What makes up 86% of sea salts
Cl- and Na+ combining to form salt through supersaturation
Carbonate ion
CO3 2-
Aragonite
CaCo3
High pressure polymorph of calcium carbonate
Less heavier than calcite
Metabolised from organisms → more structurally sound shells (due to lack of cleavage)
Breaks down into calcite after death
Dolomite
CaMg(CO3)2
Most stable form of carbonate
Abiogenic equation for calcite production
Dependent on Ca2+ availability
Partial dissociation of CO2 in the water
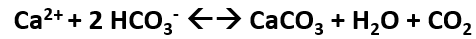
Conditions to remove CO2 from seawater
Increase temperature
Decrease pressure
Agitating water
Autotrophs
Build organic molecules from inorganic molecules
Using chemicals or light
Base of food chain
Plants, algae, some bacteria
Heterotrophs
Consume organic molecules
Animals
Within the upper 1m of water
all red light is absorbed by green photoautotrophs
Factors affecting carbonate precipitation
Light levels
Temperature
Pressure
Best conditions for carbonate production
High temperatures
Shallow waters
Evaporation > freshwater input so salinity increases
Low rainfall poorly connected to the open ocean
Balancing salinity
Higher reduces CO2 solubility
Lower is better for majority of heterotrophs, and all but highly specialized autotrophs
Chlorozoan association
T>15°C
32-40% salinity
Tropical
Coral reef
Chloroalgal association
T>15°C
>40% salinity
Tropical Mediterranean
Green algae
Foramol association
T<15°C
Temperate
High diversity of heterotrophs
Molluscs, Formanifera, echinoderms, bryazoans, ostracods
Composition of carbonates
Grains
Matrix (micrite = carbonate mud matrix)
Cement
Pore space
Bioclasts
Grains/fossil fragments from living organisms
Encrusters
Usually reef builders
Adult phase anchored to sea floor
Buried in place after death
Encrusted by younger organisms
Frameworks form as organisms grow on top of each other
Non skeletal grains
Coated grains
Peloids
Clasts
Coated grains
Ooids
Oncoids
Ooids
<1mm
Micrite precipitates chemically in an ocilating flow with many layers of cement
Oncoids
Micrite precipitates by algal and microbial coatings on the outside grains → less regular structure
Peloids
Fish poo
100-500mm diameter
No spherical layers
Grain aggregates
Form by algal binding and cementation
Grapestones - spherical grains
Lumps - smooth outline and hollow interior
Botryoidal lumps - thin oolitic coating
Intraclasts
Reworked partially lithified material from locally within the basin
Extraclasts
Lithified material from outside the immediate depositional area