Chatpter 1 Anatomy
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Anatomy
the identification and description of the structures of living things.
Physiology
the study of how many different parts of the body work
Homeostasis
The body’s attempt to balance itself and reach equilibrium
wants a relatively constant internal environment.
Gross Anatomy
Examination of relatively large structures and features usually visible with the unaided eye.
Microscopic Anatomy
Structures that cannot be seen without magnification.
Cytology
The study of cells
Histology
The study of tissues
Pathology
The study of diseases
Organ System
mulitple organs working with one another
Organ
Two or more tissues working together.
Cell
the smallest living unit
Chemicals/Molucules
made of of atoms
Autoregulation
Automatic response in a cell, tissue, or organ to an environmental change.
Extrinsic Regulation
Responses controlled by nervous and endocrine systems.
Proximal
Toward the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk.
Lateral
Away from the midline.
Medial
Towards the midline
Distal
Away from the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk
Anterior/Ventral
The front surface
The belly side. (equivalent to anterior when referring to the human bod.)
Posterior/Dorsal
the back surface
The back. (equivalent to posterior when referring to the human body)
Cranial/Cephalic
The cranial nerves are in the head.
Towards the head
Caudal
Toward the tail; (coccyx in humans)
Fused caudal vertebrae form the skeleton of the tail
Superficial
At, near, or relatively close to the body surface.
Deep
Toward the interior of the body; farther from the surface
Frontal/Coronal Plane
a vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior (front) and posterior(back) portions.
Sagittal Plane
a vertical plane that divides the body into left and right portions.
midsagittal plane
A cut in the sagittal plane that is in the middle.
parasagittal plane
A cut in the sagittal plane that is not towards the middle.
Transverse Plane
divides the body into superior and inferior portions.
thoracic cavity
everything deep to the chest wall of the _______ region
holds
the left and right pleural cavities
the lungs and the heart
associated organs of the respiratory, cardiovascular, and lymphatic systems; the inferior portions of the esophagus; and the thymus
abdominopelvic cavity
and all of the structures deep to the abdominal and pelvic walls
holds
the peritoneal cavity
body cavities
They protect delicate organs from shocks and impacts,
they permit significant changes in the size and shape of internal organs
mediastinum
what separates the right and left pleural cavities
also holds the pericardial cavity
peritoneal cavity
allows the organs of the digestive system to slide across one another without damage to themselves or the walls of the cavity
receptor
a sensor that is sensitive to a particular stimulus or environmental change;
control center
which receives and processes the information supplied by the receptor and sends out commands;
effector
a cell or organ that responds to the commands of the control center and whose activity either opposes or enhances the stimulus.
negative feedback
The response of the effector negates the stimulus.
positive feedback
initial stimulus produces a response that amplifies or enhances the original change in conditions, rather than opposing it.
frontal
forhead
nasal
nose
ocular/orbital
eye
otic
ear
buccal
cheek
cervical
neck
thoracic
chest/thorax
breast
mammary
abdominal
abdomen
umbilical
naval
pelvis
pelvic
manual
hand
inguinal
groin
pubic
pubis
fermoral
thigh
pedal
foot
hallux
great toe/big toe
digits
toes/fingers
tarsal
ankle
crural
leg
pollex
thumb
palmar
palm
carpal
wrist
antebrachial
forarm
antecubital
front of elbow
brachial
arm
axillary
armpit
mental
chin
mouth
oral
cephallic
head
facial
face
cranial
skull
acromial
shoulder
dorsal
back
olecranial
back of elbow
lumbar
loin
gluteal
buttock
popiteal
back of knee
sural
calf
calcaneal
heel of foot
plantar
sole of foot
Anatomical Relationships
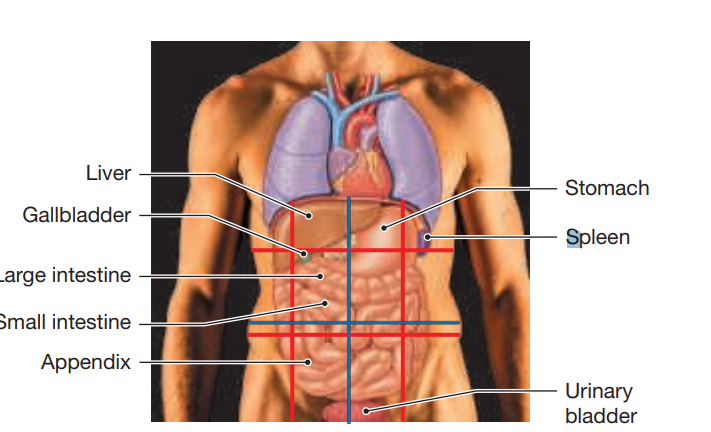
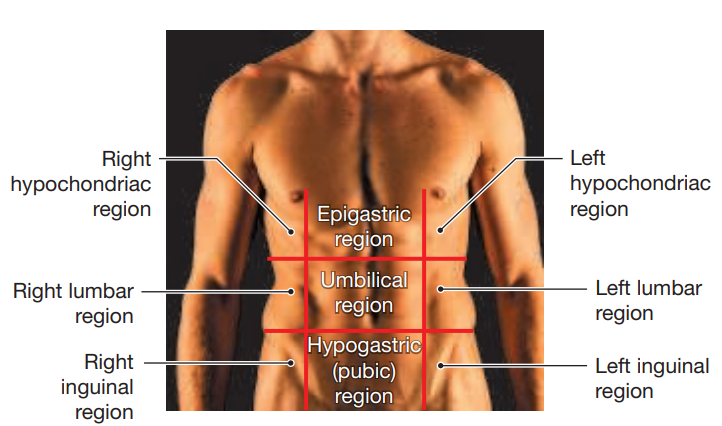
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Supine
facing up
prone
facing down