epistaxis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is epistaxis?
nosebleeds
what are the primary causes of epistaxis?
unknown
what are the secondary causes of epistaxis?
- alcohol
- antiplatelet
- aspirin
- NSAIDs
- anticoagulants
- coagulopathy
- trauma
- tumours
- surgery
- septal perforation
- HTN
what are examples of coagulopathies causing epistaxis?
haemophilia + Von Willebrand's disease
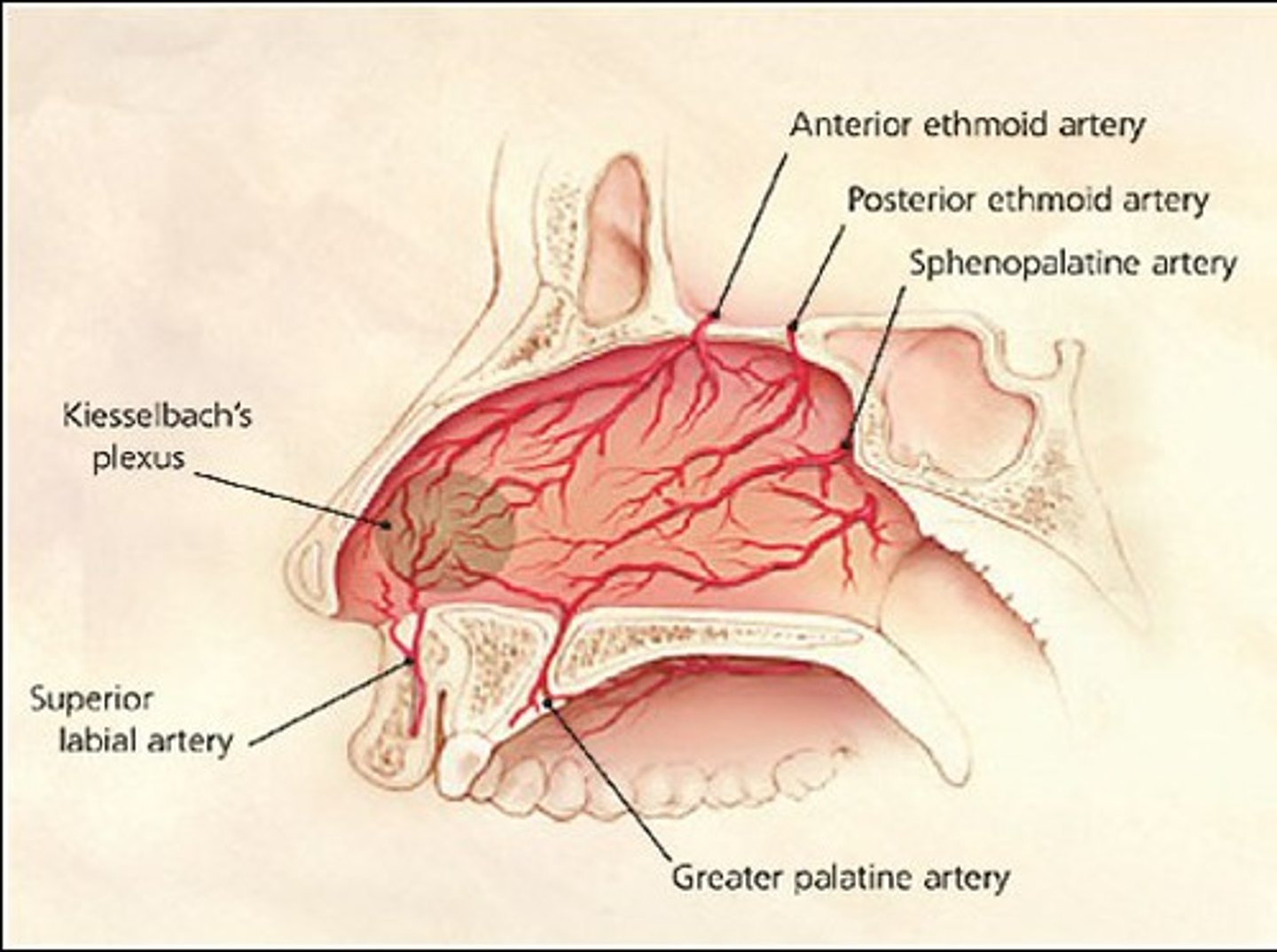
where do anterior epistaxes originate from?
Kiesselbach's plexus in Little's area
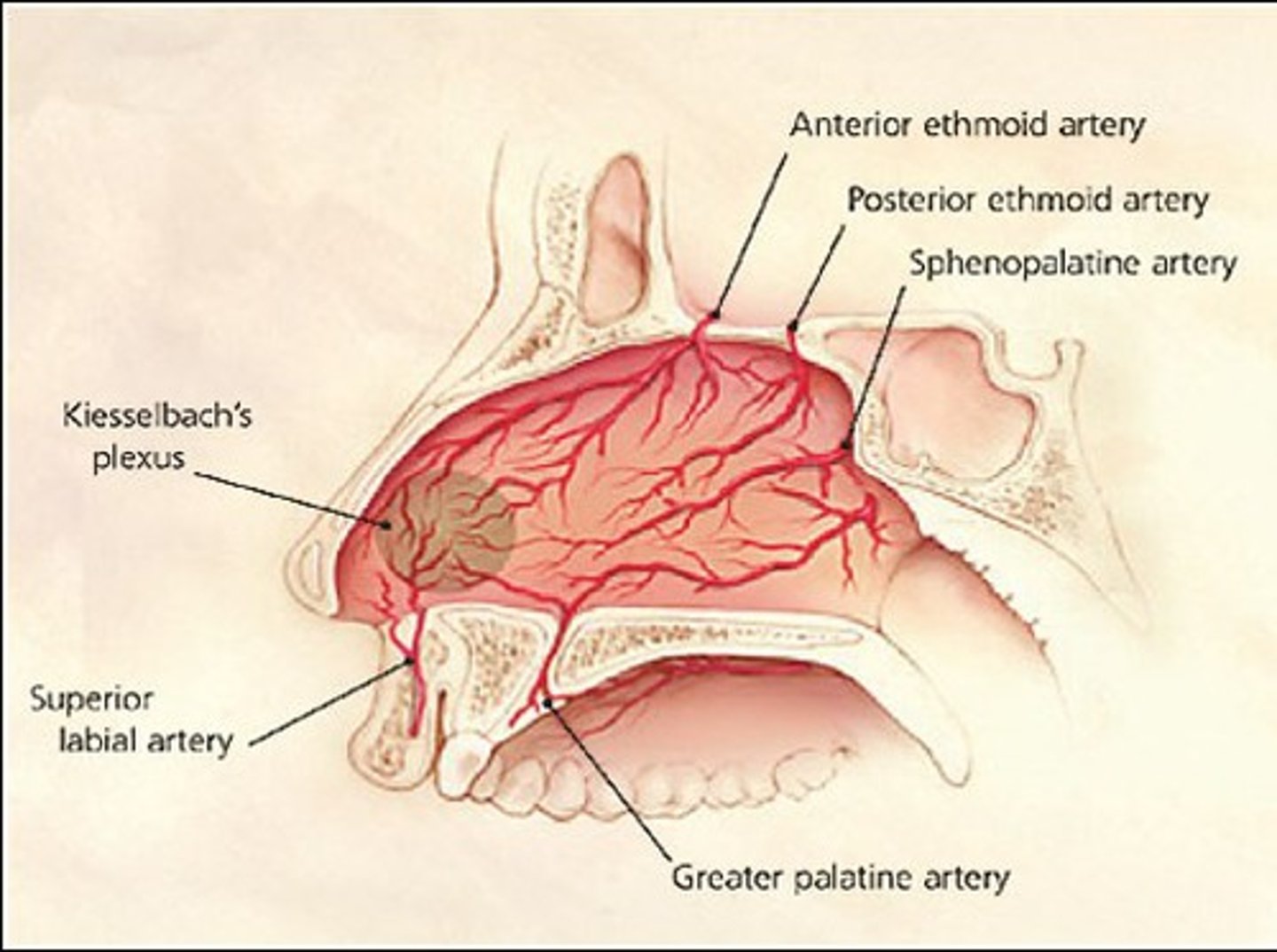
which arteries terminate at Kiesselbach's plexus?
- anterior ethmoid artery
- sphenopalatine artery
- greater palatine artery
- superior labial artery (septal branch)
gass
which artery is most likely to bleed?
sphenopalatine artery
what is Little's area?
mesh of blood vessels - Kiesselbach's plexus
why is little's area clinically relevant?
common site of epistaxis
where do posterior epistaxes originate from?
sphenopalatine artery
what is the first investigation?
examine both nostrils with a nasal speculum
what would indicate a posterior bleed?
bleeding is profuse from both nostrils or site of bleeding cannot be identified on speculum
what ages are nosebleed uncommon in?
<2 years old
what may nosebleeds in <2 year olds indicate?
haemophilia or leukaemia
what is the first line management for epistaxis?
1) control bleeding with direct compression
what are the steps for direct compression?
- pinch nasal alae FIRMLY for 10-15 minutes
- pt should be sitting upright and leaning forwards to avoid blood entering oral cavity and pharynx
- do not swallow blood!
what should be considered if bleeding stops after 10-15 minutes?
naseptin - to reduce crusting and vestibulitis
what is naseptin?
antibiotic cream
what should be done if bleeding does not stop after 15 minutes?
if posterior bleed - admit to hospital
if anterior bleed - nasal cautery
when else should admission be considered?
co-morbidities or suspected underlying cause
when would cautery not be appropriate?
cannot identify bleeding site
what are the different types of cautery?
chemical or electrical (thermal)
what is chemical cautery?
- apply 75% silver nitrate sticks to bleeding site for 3-10 seconds
- then dabbed with cotton bud and topical antiseptic applied - e.g. naseptin
- the naseptin is applied 4 times a day for 10 days to reduce crusting and vestibulitis
what should be done after nasal cautery if bleeding is still present?
nasal packing
what is used for nasal packing?
nasal tampons
what are the types of nasal packing?
- anterior
- posterior
what should be done after nasal packing if bleeding site is unknown?
admission
what are the more aggressive therapies that can be used?
- nasal balloon catheter
- transnasal endoscopy with direct cautery/arterial ligation
what is the last line if all other interventions have not worked?
surgical ligation of sphenopalatine artery