Key Concepts in Business Studies and Marketing
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
254 Terms
Business
Organizations that produce goods/services to satisfy needs.
Value Addition
Enhancing raw materials to meet consumer demands.
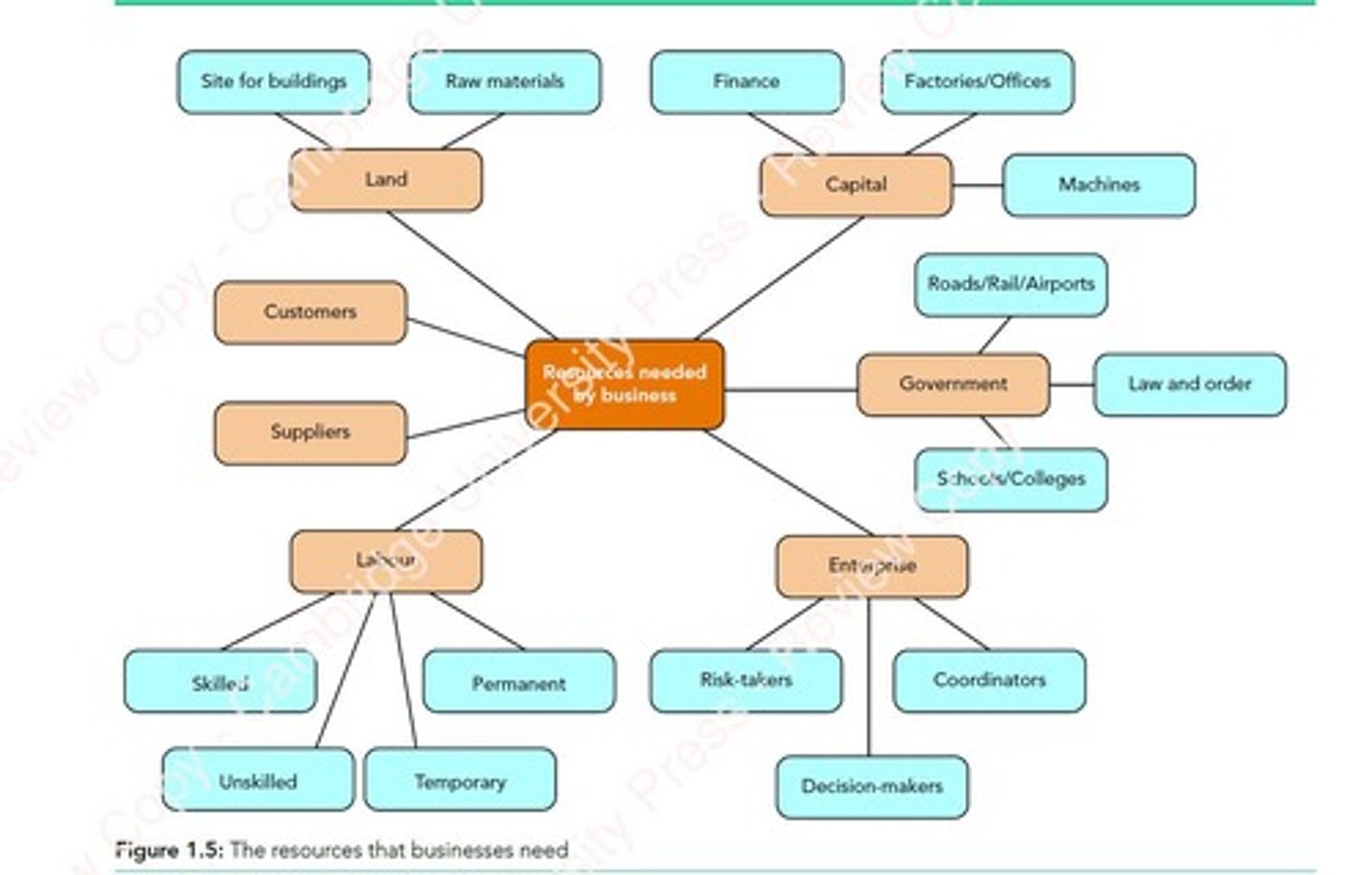
Factors of Production
Resources needed: land, labour, capital, enterprise.
Added Value
Selling price minus cost of materials.
Opportunity Cost
Next best alternative forgone when making a choice.
Local Business
Serves goods/services to local population.

National Business
Operates within the domestic market.
Multinational Business
Operates in multiple countries.

Successful Business Traits
Understanding customer needs, efficient management.
Business Failure Reasons
Poor record keeping, lack of cash, management skills.
Entrepreneur
Individual who starts and runs a business.
Intrapreneur
Employee who innovates within a company.
Innovation
Creating new ideas or products.
Commitment
Dedication to achieving business goals.
Risk-taking
Willingness to invest in uncertain outcomes.
Economic Growth
Increase in a country's production of goods/services.
Employment Creation
Jobs generated through business activities.
Technological Change
Advancements that improve production processes.
Cash Shortages
Insufficient funds to meet business obligations.
Lean Production
Minimizing waste while maximizing productivity.
Market Changes
Shifts in competition, regulations, or consumer spending.
Business Expansion
Growth of a business into new markets.
Intrapreneurship
Creativity and innovation within existing businesses.
Business Plan
Document outlining business strategy and operations.
Executive Summary
Brief overview of the business plan.
Marketing Strategy
Plan for promoting and selling products.
Financial Forecast
Projected financial performance of the business.
Industrialisation Benefits
Increased GDP and job creation from manufacturing.
Deindustrialisation Consequences
Job losses and retraining needs in service sectors.
Limited Liability
Owners' financial responsibility limited to investment.
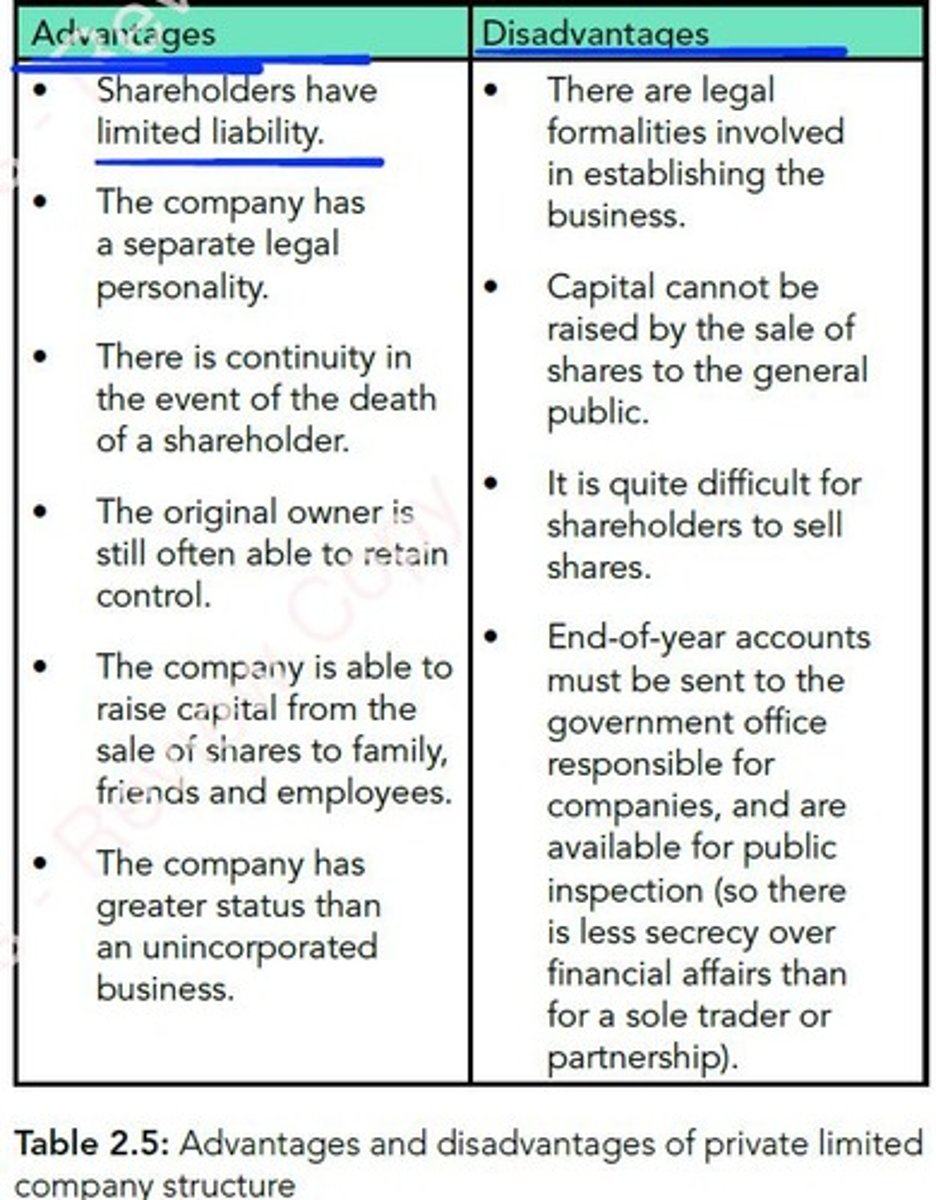
Private Limited Company
Company type protecting owners from personal liability.
Memorandum of Association
Document stating company's objectives and structure.
Articles of Association
Rules governing company's operations and management.
Cooperative Features
Member involvement in decision-making and profit sharing.
Joint Venture
Partnership to share costs and risks of projects.
Economic Sectors
Classification of business activities by industry type.
Tertiary Sector
Service industry, including healthcare and education.
Quaternary Sector
Knowledge-based services, such as IT and research.
Competitive Advantage
Unique edge over competitors in the market.
Original Thinkers
Innovators encouraged to remain within the business.
Social Cohesion
Strengthening community bonds and relationships.
Multinational Companies
Firms operating in multiple countries, impacting economies.
Job Opportunities
Employment openings in growing service industries.
Capital Shortages
Insufficient funds for business operations or expansion.
Decision-Making in Cooperatives
Consensus required among members for important choices.
Major Markets
Countries where businesses can effectively expand.
Social Enterprises
Organizations with social aims using ethical practices.
Limited Liability
Protection of owners' capital from business debts.
Changing Ownership
Transitioning from one business structure to another.
Sole Trader
Individual ownership with full control and responsibility.

Private Limited Company
Business structure limiting owner liability and sharing profits.
Measuring Business Size
Assessing business scale through various metrics.
Number of Employees
Count of workers to gauge business size.
Revenue
Total sales value used for industry comparisons.
Capital Employed
Total long-term finance available in a business.
Market Capitalisation
Current share price multiplied by total shares issued.
Market Share
Percentage of total industry sales attributed to a business.
Absolute Size
Business size assessed using multiple criteria.
Comparative Size
Business size compared against other entities.
Dynamic Entrepreneurs
Innovative individuals driving small business success.
Small Businesses
Firms with limited scale, often job creators.
Micro-Businesses
Very small firms, typically with few employees.
Business Risks
Potential issues arising from partnerships and management styles.
Legal Costs
Expenses incurred during ownership structure changes.
Profit Sharing
Distribution of earnings among multiple owners.
Competition Creation
Small businesses fostering rivalry with larger firms.
Insubstantial Measurement Problems
Limitations of using employee count for size assessment.
Monopoly
Market structure with a single seller.
Specialist goods
Products tailored for specific consumer needs.
Economies of scale
Cost advantages due to increased production.
Government assistance
Support provided to small businesses.
Loan guarantee scheme
Government backing for small business loans.
Small business advantages
Flexibility and personal customer relations.
Large business advantages
Ability to employ specialists and lower prices.
Small business disadvantages
Limited access to finance and high risks.
Large business disadvantages
Diseconomies of scale and management conflicts.
Family business
Owned and managed by family members.
Knowledge continuity
Passing business knowledge to the next generation.
Nepotism
Favoritism based on family relationships.
Business growth reasons
Increased profits and market share.
Internal growth
Expansion through existing operations.
Business objectives
Goals guiding business strategies and performance.
Profit maximisation
Aim to achieve the highest possible profit.
Profit satisficing
Achieving sufficient profit to satisfy stakeholders.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Business commitment to ethical practices.
Triple bottom line
Focus on profit, social, and environmental goals.
Social enterprises
Businesses aiming for social and environmental impact.
Market share
A company's sales as a percentage of total sales.
Survival
The primary goal of many small businesses.
Shareholder value
Maximizing returns for company shareholders.
Public-sector businesses
Government-owned entities serving public interests.
Efficient service
Reliable public services like water and postal.
Economic development
Enhancing growth in underprivileged areas.
Employment creation
Generating jobs or preventing layoffs.
Financial targets
Goals set by government, not profit-driven.
Environmental standards
High benchmarks for ecological responsibility.
SMART objectives
Framework for setting effective goals.
Specific (S)
Clear and well-defined objectives.
Measurable (M)
Quantifiable criteria to track progress.
Achievable (A)
Realistic goals that can be accomplished.