DPT 745 (Lesson 7)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What are the orbits of the eyeball?
2 bone cavities that house the eyeball
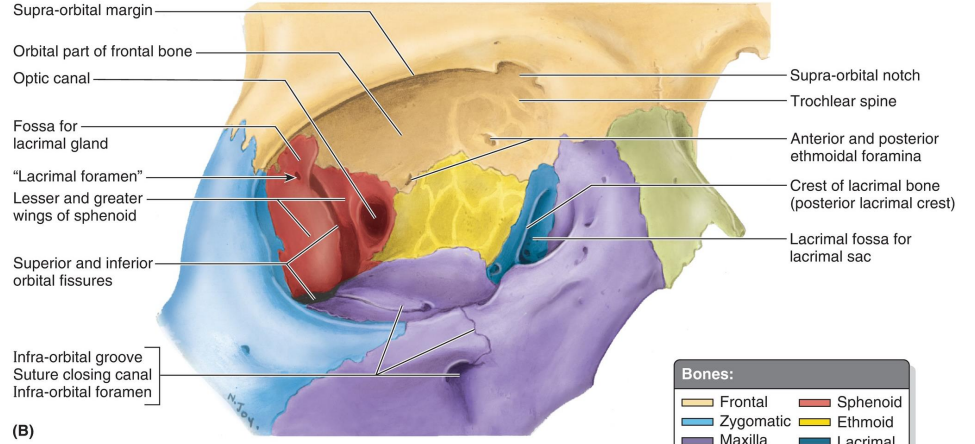
What bone forms the superior wall of the orbit?
Orbital plate of the frontal bone
What bone forms the lateral wall of the orbit?
Zygomatic bone
What bone forms the floor of the orbit?
The maxilla
What bone forms the medial wall of the orbit?
Orbital plate of the ethmoid bone
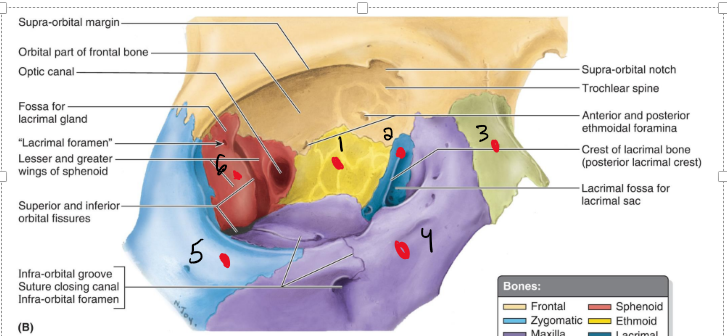
Name the structures
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Nasal
Maxilla
Zygomatic
Sphenoid
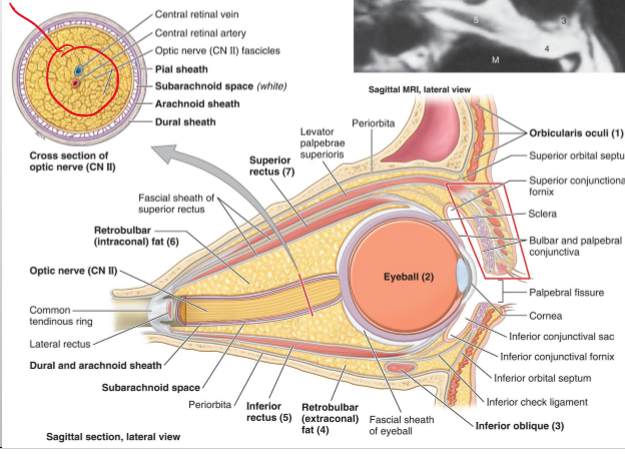
Is there a lot of fat that covers the eye?
YESSs
What 2 muscles are on in charge of the eyelids?
Orbicularis Oculi and Levator palpebrae superioris
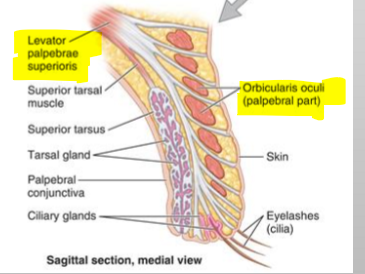
Name the structures
Levator palpebrae superioris
Orbicularis oculi (palpebral part)
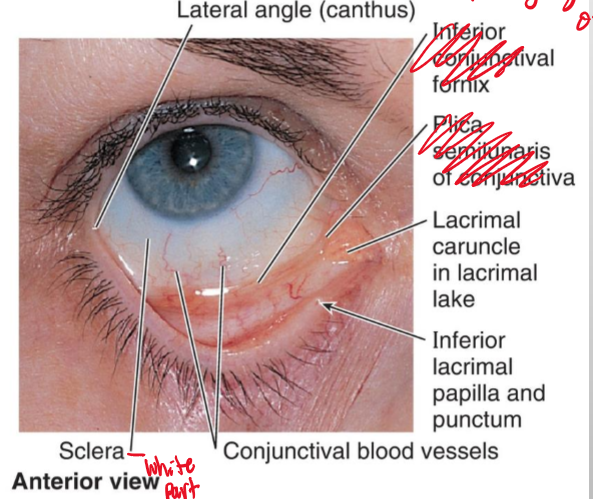
The conjunctiva is distinct color is what and what is it purpose?
It is the white part of the high or also known as “Sclera” and it helps forigen objects from going into the back of the high and causing an infection
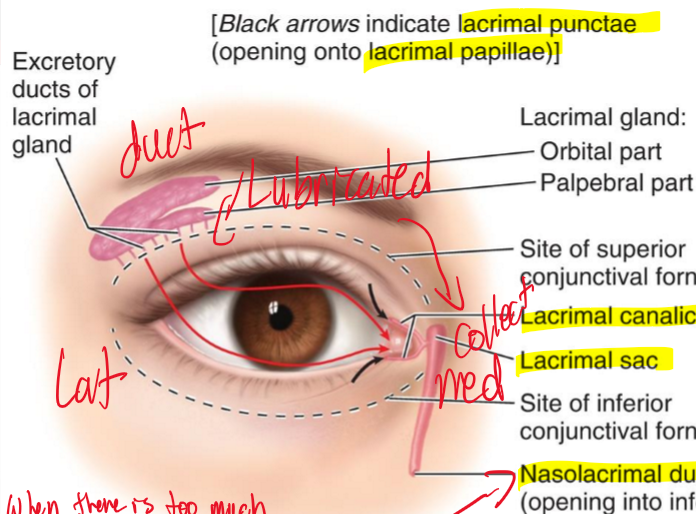
What is the main purpose of the lacrimal apparatus?
The main purpose is to collect our fluid of eye and collect it
What gland is in charge of producing fluid in the eye?
The lacrimal gland is located in superolateral side of eye and produces fluid to lubricate the eye?
In the lacrimal apparatus what structure is in charge of collecting fluid?
The lacrimal punctae collect the fluid and then brings the tears into a canal called the lacrimal canaliculi.
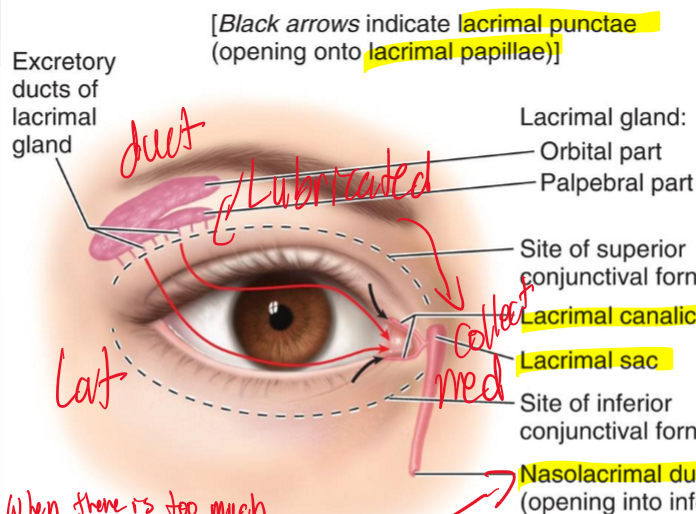
What is the sac that holds the fluid and where does it drain into?
The sac that holds the fluid is the lacrimal sac which then gets drained into the nasolacrimal duct which drains it into the nasal area.
What does the eyeball enclose?
The lens, vitreous body, and aqueous humor
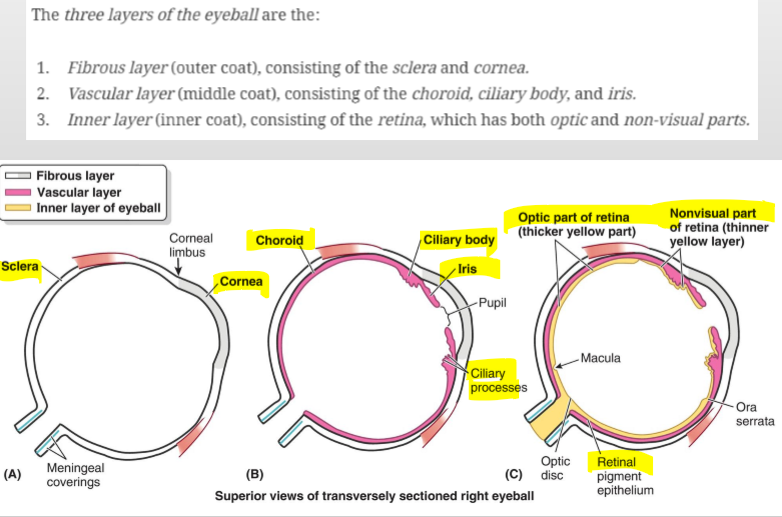
What are the three concentric layers of the eyeball?
External fibrous tunic
Middle vascular tunic (uvea)
Internal nervous tunic (retina)
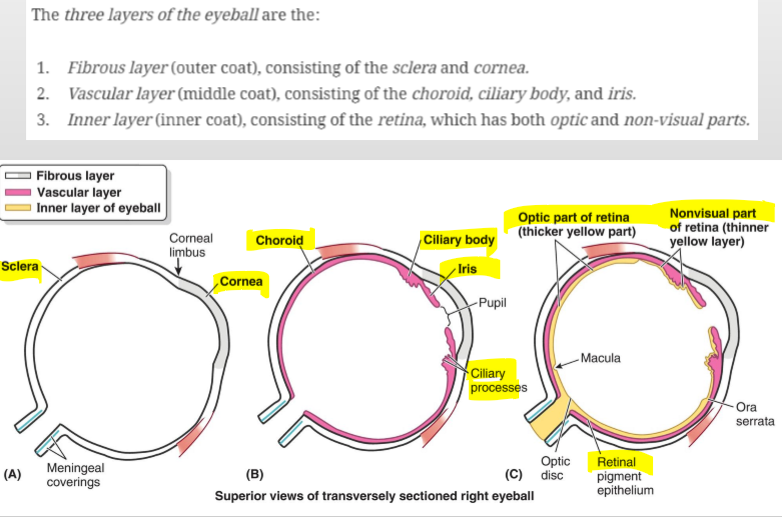
What structures make up the external fibrous tunic of the eye?
The cornea and sclera
What is the primary function of the cornea?
Responsible for most of the light refraction in the eye
What is the sclera?
The posterior opaque (white) part of the fibrous tunic
What attaches to the sclera?
The tendons of the muscles of the eyeball
What are the components of the middle vascular tunic (uvea)?
Choroid, ciliary body, and iris
What structures arise from the ciliary body?
Ciliary processes
What do the ciliary processes do?
Produce aqueous humor and provide attachment for the suspensory ligaments of the lens
What is the iris?
The part of the uvea that divides the space between the cornea and lens into anterior and posterior aqueous chambers
What is the internal nervous tunic of the eye?
The retina – the innermost layer of the eye.
What type of cells are found in the retina?
Rods and cones.
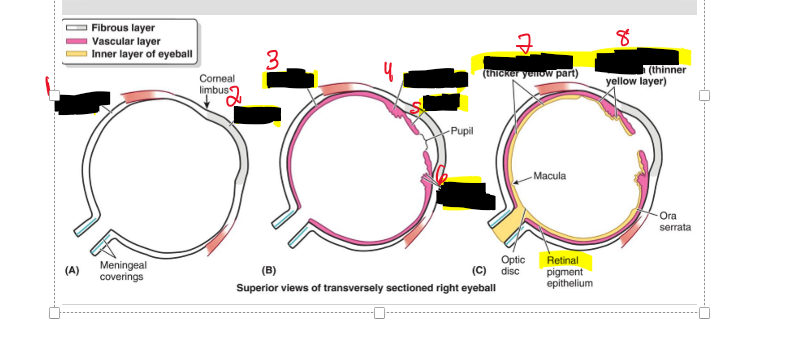
Name the structure
Sclera
Cornea
Choroid
Ciliary body
Iris
Ciliary processes
Optic part of retina
Nonvisual part of retina
What is the lens?
A transparent structure enclosed in a capsule, suspended between the posterior chamber and vitreous body by ciliary zonules.
Through what pathway does aqueous humor flow (the clear fluid)
From the posterior chamber → through the pupil → into the anterior chamber.
What is the function of aqueous humor?
Provides nourishment to the cornea and lens.
Where is vitreous humor located?
In the vitreous body, posterior to the lens.
For the lens to change what needs to happen?
Images needs to focus on retina, so the lens can change shape to see clearly.
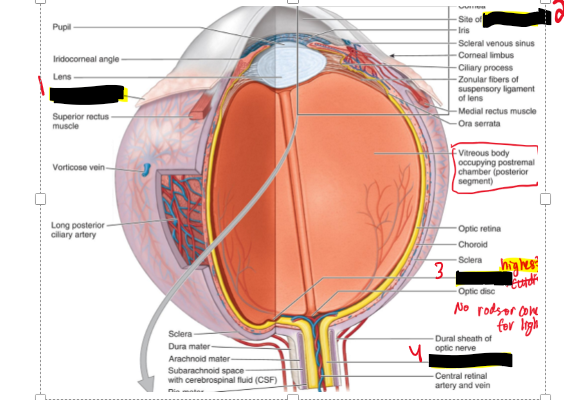
Name the structure.
Bulbar conjunctiva
Aqueous humor
Macula lutea
Optic nerve
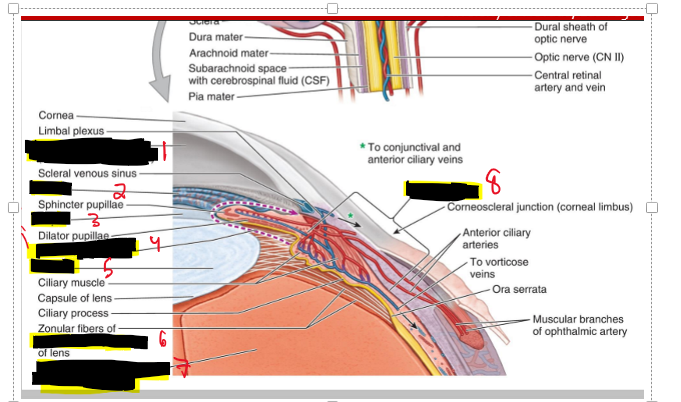
Name the structure.
Anterior chamber (site of aqueous humor)
Iris
Pupil
Posterior chamber
Lens
Suspensory ligament
Vitreous body (containing viteous humor)
Ciliary body
What structure of the eye has the highest visual acuity
Macula lutea and is responsible for sharp, central vision,
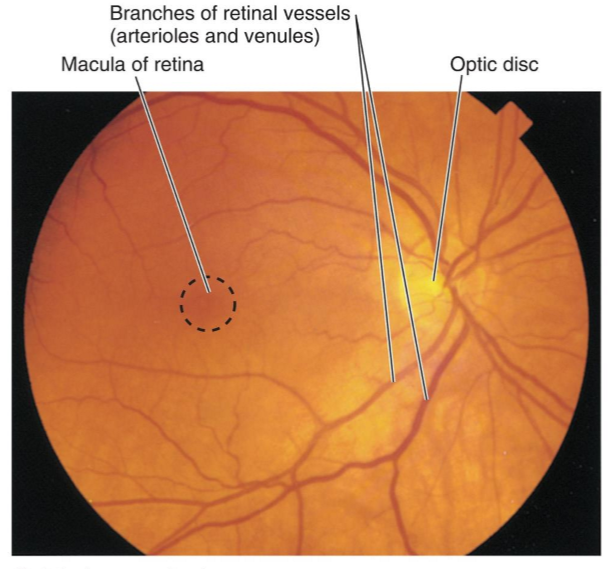
When light doesn’t hit the optic disc it is called what?
A blind spot
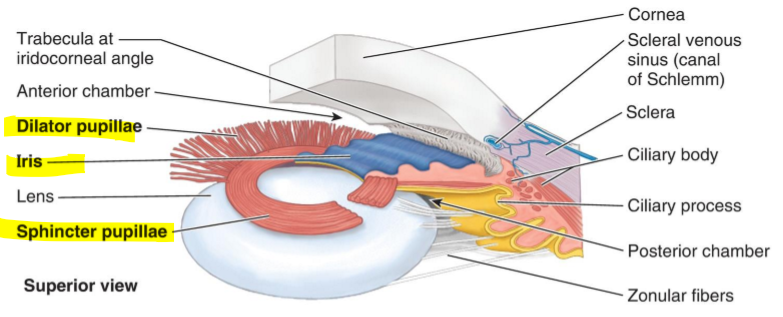
Name the structure
Dilator pupillae
Iris
Sphincter pupillae
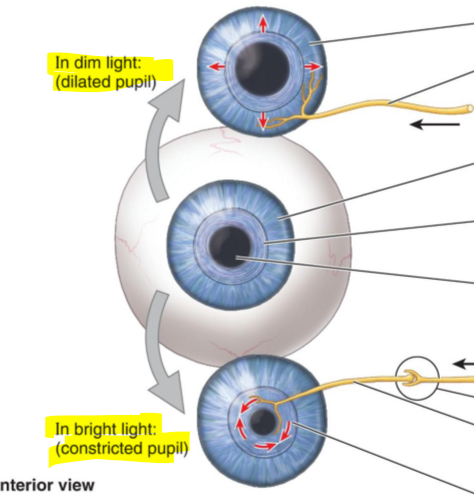
In the dim light the pupil do what?
They dilate
In the bright light the pupil do what?
They constrict the pupil.
Muscle fibers of the dilator pupillae are what?
They are radially arranged smooth muscle fibers
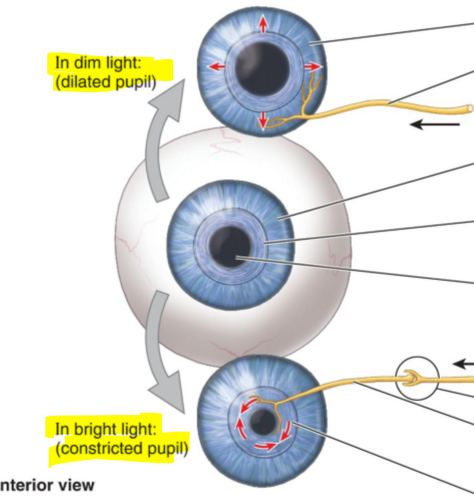
Muscle fibers of the sphincter pupillae are what?
What is the primary artery supplying the eye?
The ophthalmic artery.
Where does the ophthalmic artery arise from?
The internal carotid artery.
What are the two main routes of venous drainage from the eye?
To the facial vein and the cavernous sinus.
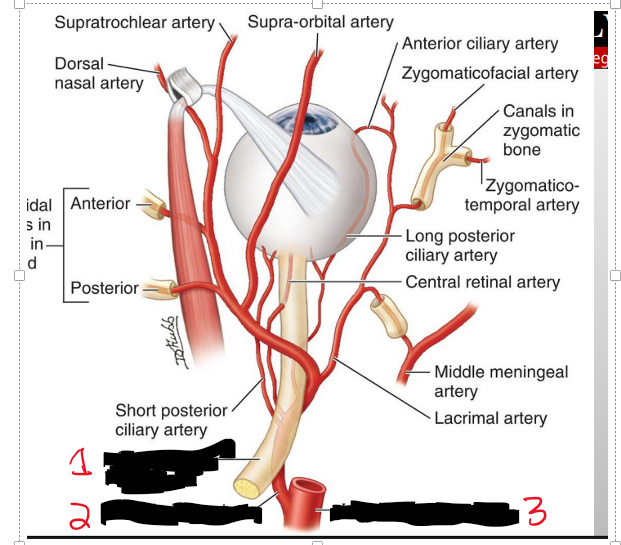
Name the strucure.
Optic nerve
Opthalmic a.
Internal carotid a.
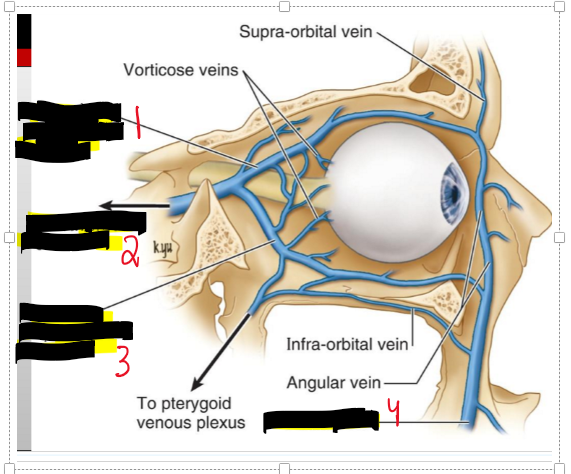
Name the structure
Superior ophthalmic
To cavernous sinus
Inferior opthalmic v
Facial v.
What are all the muscles that are consider “Extra-ocular Muscles”
Rectus muscles (Anterior portion of the sclera)
Superior
Inferior
Medial
Lateral
Superior oblique (Orgin: Sphenoid bone Insert: Posteriolateral aspect of the sclera)
Inferior Oblique (Orgin: anteriomedial aspect of the floor of the orbit Insert: posterolateral aspect of the sclera)
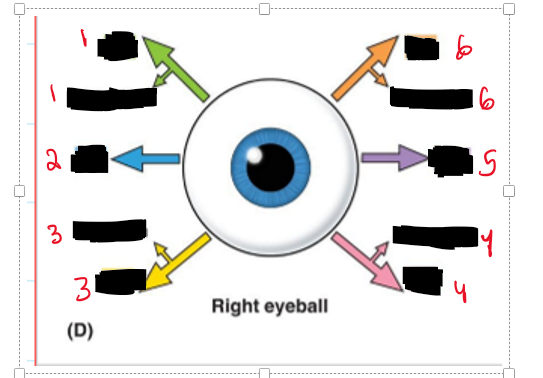
Name the structure and movement
Inferior oblique (extorsion)
Lateral rectus (Lateral)
Superior oblique (Intorsion)
Inferior rectus (Extorsion)
Medial rectus (Medially)
Superior rectus (intorsion)
How is the eye able to so many different movments?
B/c the eye is set at an angle which allows for all types of movment.
What is known as spinning of the eye and why does it do it?
extorsion and intorsion. It keeps the image stable if we didnt have this movement image would be a blur.
What are the sensory nerves of the orbit?
Optic (CN II) and Ophthalmic n (CN V1)
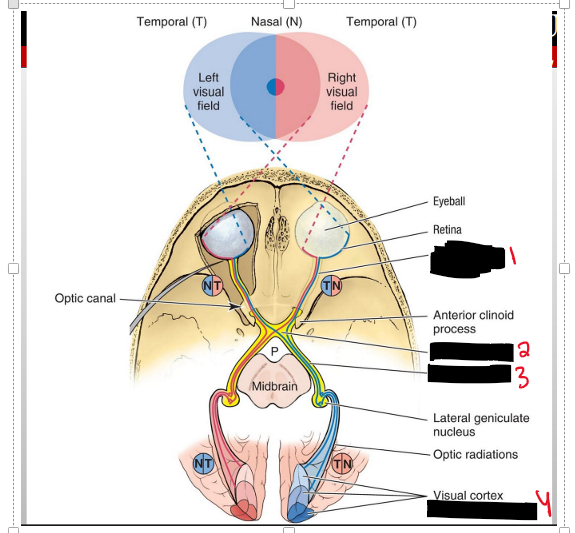
Name the structure
Optic Nerve
Optic Chiasm
Optic tract
(Occiptal lobe)
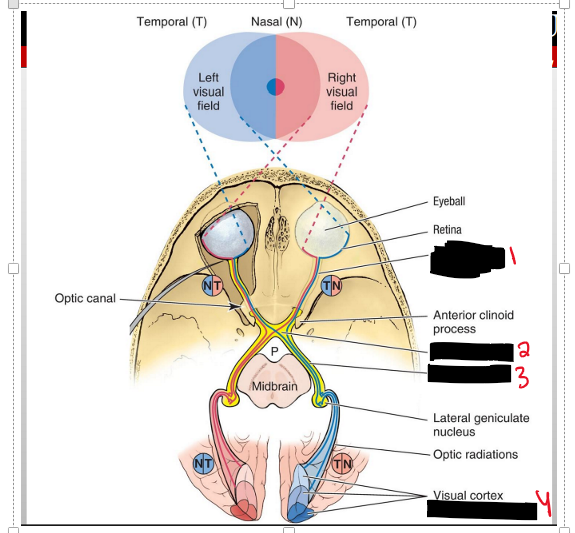
The Left or right visual field of the temporal side does what?
You will receive the vision of the same side but It is going to cross to the opposite side into the optic chiasm- into the optic tract- into the occipital lobe
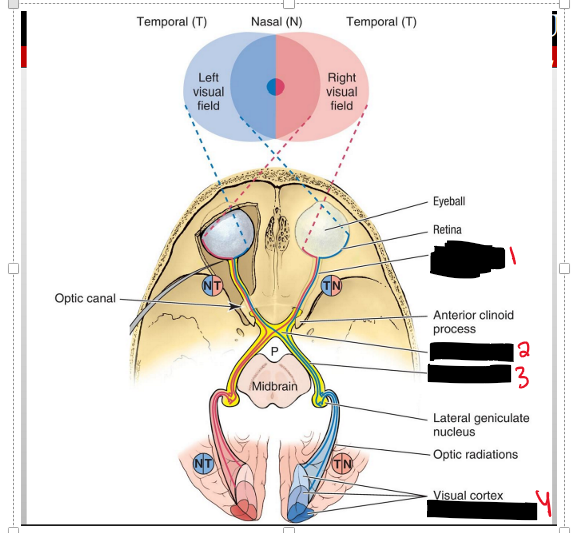
The left or right visual field of the nasal side does what?
So the opposide eye of the visual field will recieve the image, meaning if the image is coming from the RIGHT visual field the left eye will recieve the image on the left of the retina.
This time when it enters the opic chiasm it WILL NOT cross over the other side but stay on the same side.
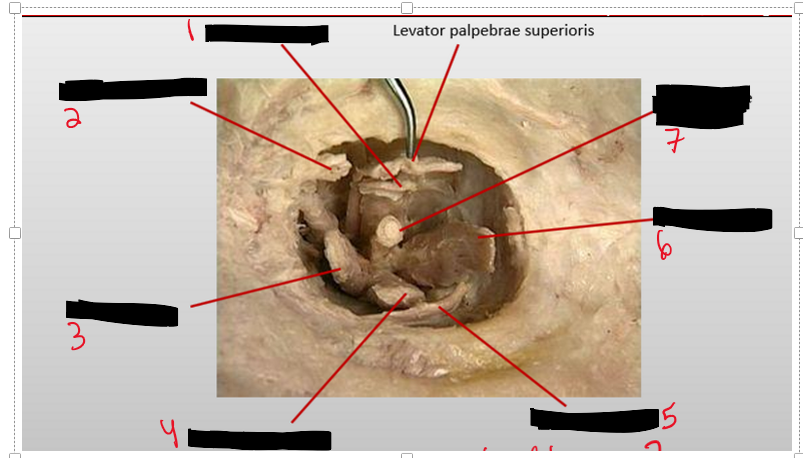
Name the structure.
Superior Rectus
Superior oblique
Medial rectus
Inferior rectus
Inferior oblique
Lateral rectus
Optic n.
Levator palpebrae superioris
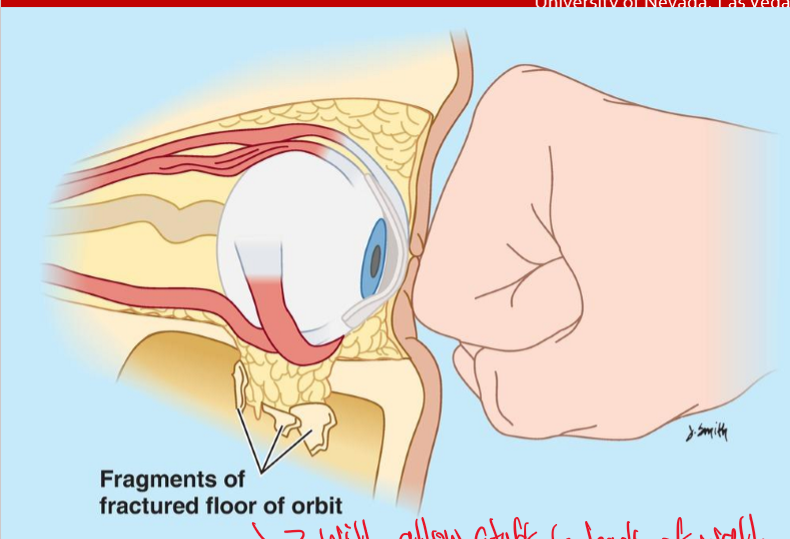
If you fracture the floor of the orbit why is that bad?
Because it will allow foreign objects to back of the wall.
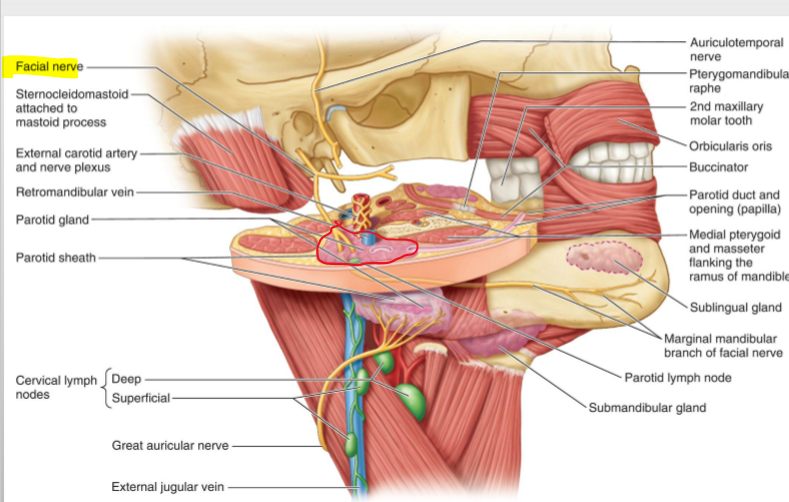
What is the largest of the paired salivary glands?
The parotid gland.
Where is the parotid gland located?
Anterior and inferior to the ear.
What is the path of the parotid duct?
It extends from the gland, penetrates the buccinator muscle, and enters the oral cavity.
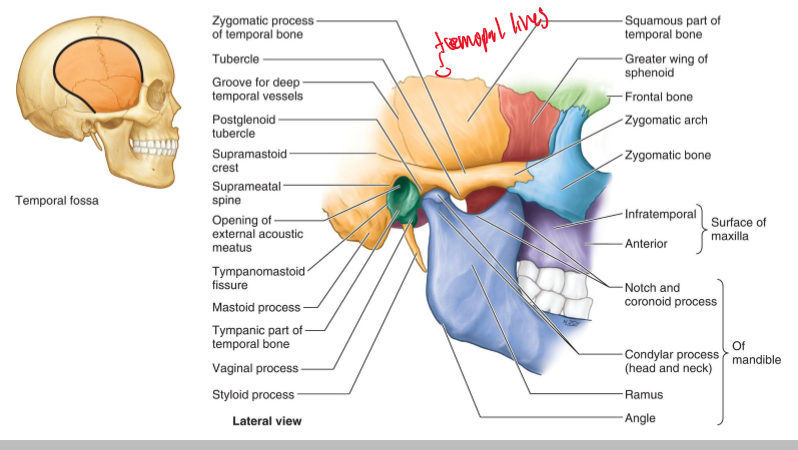
What are the boundaries of the temporal fossa?
Superiorly by the temporal lines, and inferiorly by the zygomatic arch.
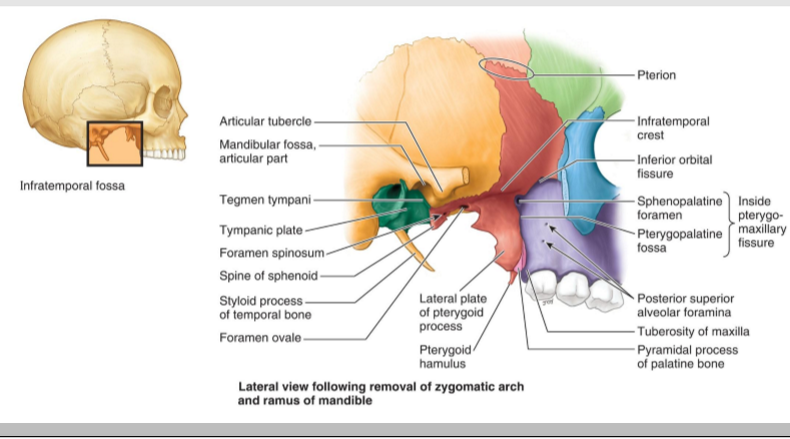
Where is the infratemporal fossa located?
Inferior to the temporal fossa and partially covered by the masseter muscle.H
How far down does the temporal fossa go?
It goes down to the masseter muscles
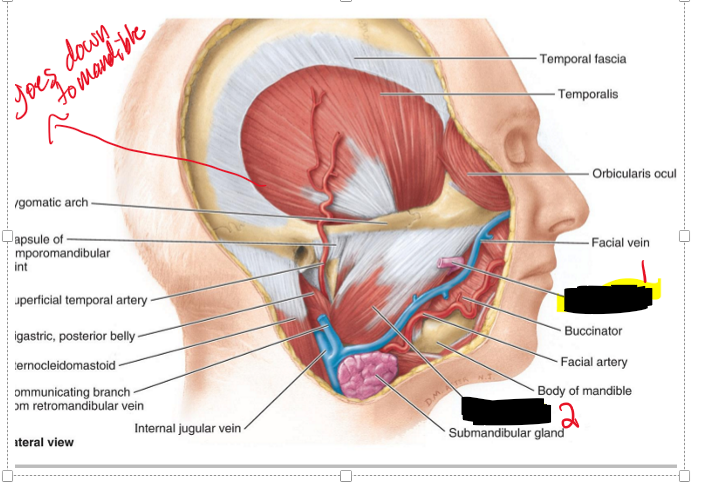
Name the structure
Parotid duct
Masseter
Where is the articular disc of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint) located?
Between the head of the mandible and the mandibular fossa.
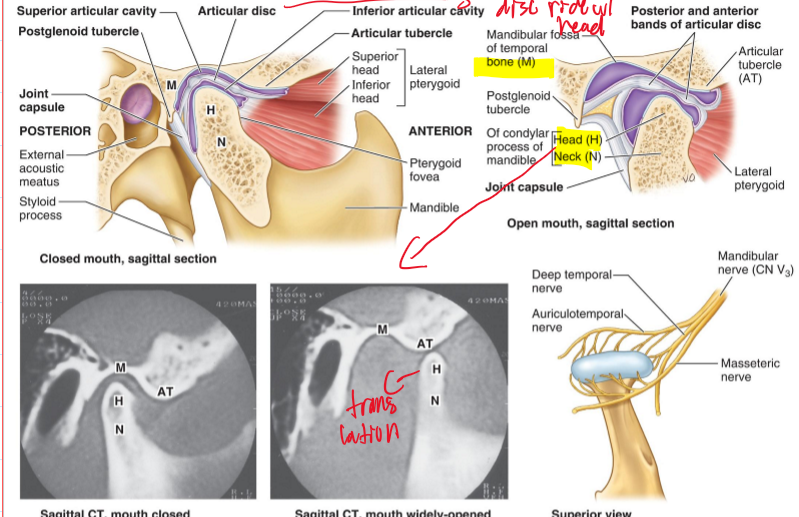
What movement does the articular disc perform with the mandible?
It moves with the head of the mandible as it slides anteriorly during mouth opening and closing.
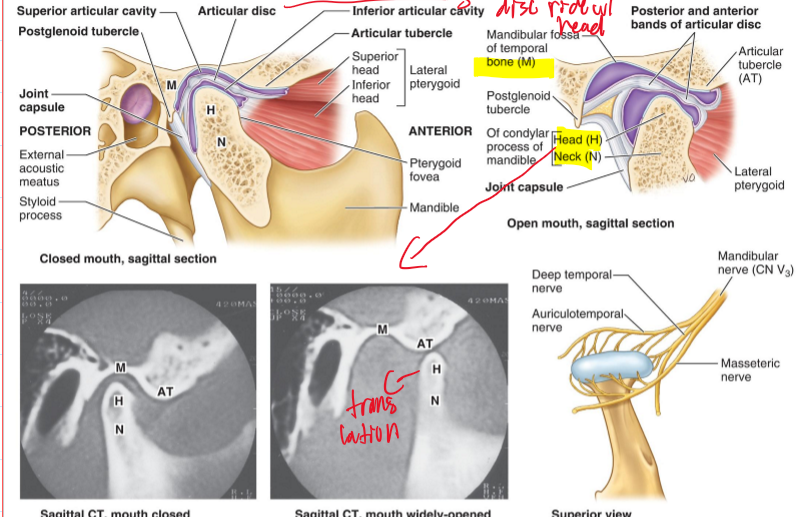
What kind of movements does the TMJ joint do?
Hinge movement and Sliding movement (occurs when opening mouth)
What kind of joint is the TMJ and what kind of capsule does it have?
Synovial joint and has a loose fibrous capsule.
What ligament is associated with the TMJ joint?
Temporomandibular joint
What must the disc do when their is movement of the TMJ joint and why?
the disc MUST ride w/ the mandible. because it can lead to disc displacement, joint clicking, or TMJ dysfunction (lock jaw)
With which structure is the articular disc of the TMJ more closely associated and what does this lead to?
The head of the mandible and therefore moves with the head of the mandible as it slides anteriorly during opening and closing of the mouth.
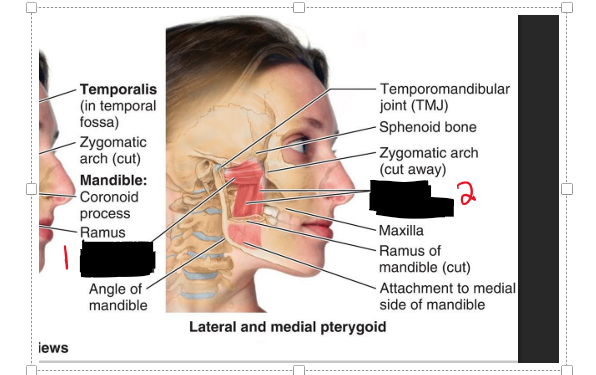
Name the muscles.
Lateral pterygoid
Medial pterygoid
What vessels are associated with the TMJ area?
MAIN: External carotid a.
Superficial temporal a.
Maxillary s.
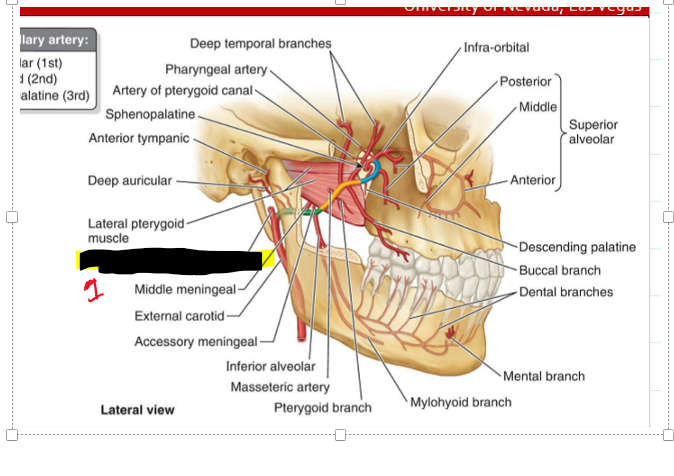
Name the structure
Superficial temporal a.
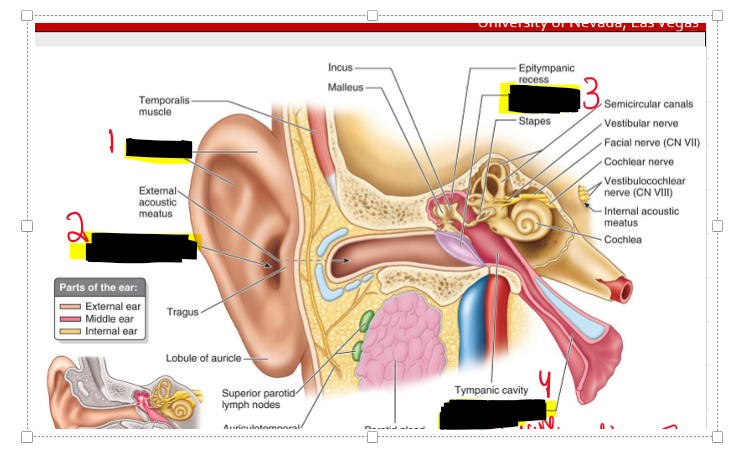
Name the structure.
Incus (bone)
Stapes (bone)
Malleus (bone)
THESE are all apart of the Tympanic Membrane
What is the tympanic membrane known as?
It create soundwaves!!
What are the auditory ossicles of the ear?
They are the bones which are
Stapes
Incus
Malleus
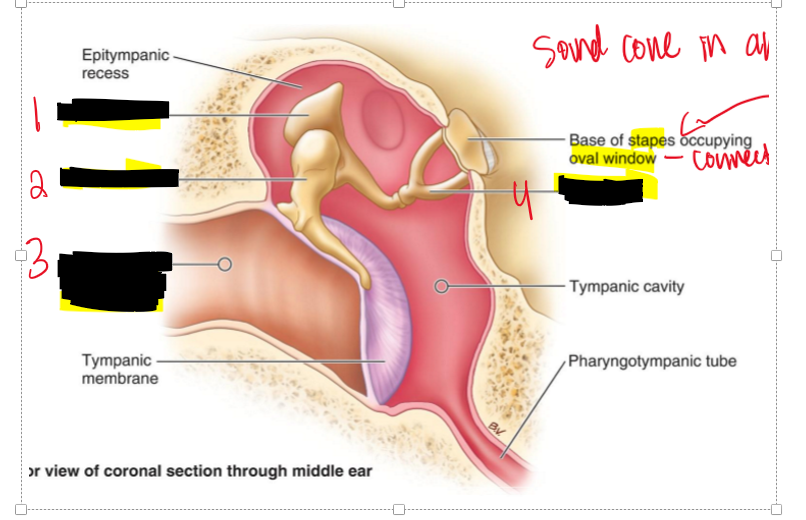
Name the structure.
Incus
Malleus
External acoustic meatus
Stapes
Describe the process of the Tympanic membrane.
basically sound comes into the ear which causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate and then that vibration is sent to the bones Malleus- Incus - Stapes. The stapes then vibrates onto inner ear and the sound continues to the brain.
What are the three parts of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear?
Semicircular canals, vestibule, and cochlea.
What structure of the Bony labyrinth responds to angular acceleration?
Semicircular canals
What structure of the Bony labyrinth responds to linear acceleration?
Vestibule
What are the components of the membranous labyrinth?
Semicircular ducts, utricle, saccule, and cochlear duct.
The Cochlear is filled with what?
It is filled with fluid and crystals that stimulate the hairs
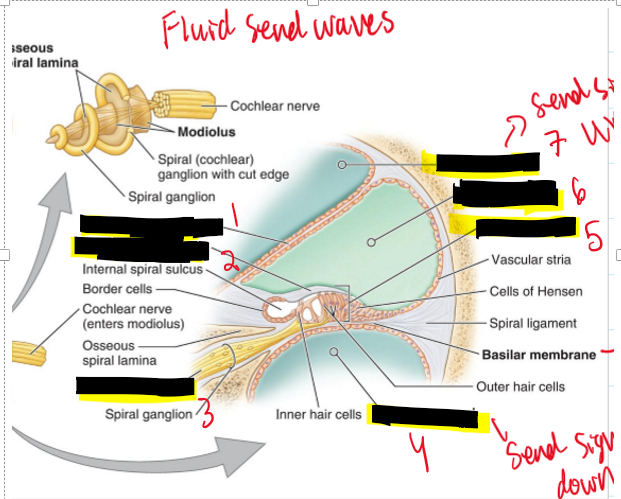
Name the structures.
Vestibular membrane
Tectorial membrane
Cochlear nerve
Scale tympani
Spiral organ
Cochlear duct
Scale Vestibuli
Explain to the process of sound transmission through the ear.
Sound is first received by the tectorial membrane
It is received by the bones and they vibrate to the last bone which is the stapes and sends that vibration to the inner ear
That is received by the Scala vestibuli and sent UP to the Cochlear nerve
Then the Scala Lympani is sending signals DOWN
Until it gets to the Round window
The rest of the pressure is then sent out the pharyngotympanic tube
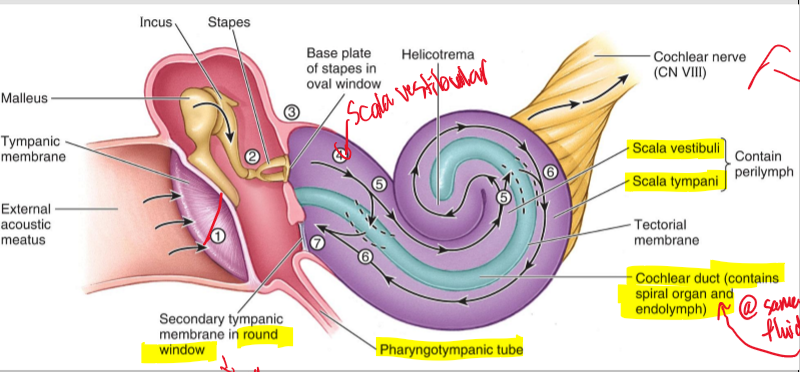
The Scala vestibuli send signals UP or DOWN?
UP!
The Scala tympani send signals UP or DOWN?
DOWN
The pharyngotympanic tube function is what?
It helps equalize the pressure in the ear and that is why sometimes your ears pop!