Microbiology Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Last updated 9:33 PM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
Microbiology
The study of microorganisms
2
New cards
Bacteriology
The study of bacteria
3
New cards
Pathogen
Disease causing bacteria
4
New cards
Group: Protists
An informal group that aren’t plants, animals, or fungi.
5
New cards
Describe the ubiquity of microbes.
Microbes are found everywhere.
* 3:1 in humans
* most abundant cellular organism in the ocean (500mil/1L)
* 10bill per 1L of water in the ocean
* 3:1 in humans
* most abundant cellular organism in the ocean (500mil/1L)
* 10bill per 1L of water in the ocean
6
New cards
Advantages of Microbes
* 70% of photosynthesis
* Decomposition
* Nutrient recycling
* Decomposition
* Nutrient recycling
7
New cards
Disadvantages of Microbes
Disease
8
New cards
Characteristics of Viruses
* Acellular (non-living)
* Require host for metabolic activities
* Have hereditary material (dsDNA,ssDNA,ssRNA,dsRNA)
* Protein coat (capsid)
* may have an envelope
*
* Require host for metabolic activities
* Have hereditary material (dsDNA,ssDNA,ssRNA,dsRNA)
* Protein coat (capsid)
* may have an envelope
*
9
New cards
Characteristics of Prions
* Acellular (non-living)
* Misfolded proteins
* infectious (CJD, fatal familial insomnia)
*
* Misfolded proteins
* infectious (CJD, fatal familial insomnia)
*
10
New cards
3 Domains of Microbes
* Bacteria
* Archaea
* Eukaryotes
* Archaea
* Eukaryotes
11
New cards
Characteristics of Bacteria and Archaea
* Single-celled
* w/o nucleus or other organelles
* 0.5-10μm
* w/o nucleus or other organelles
* 0.5-10μm
12
New cards
Characteristics of Eukaryotes
* Single-cellular or multi-cellular
* Contains a nucleus
* >10μm
* less abundant
* Contains a nucleus
* >10μm
* less abundant
13
New cards
Nomenclature
__Genus Species__
14
New cards
Taxonomy
the science of classifying living things into taxa.
15
New cards
Classification
a hierarchical arrangement of organisms.
16
New cards
Taxa in hierarchical Order
* domain
* kingdom
* phylum
* class
* order
* family
* genus
* species
* kingdom
* phylum
* class
* order
* family
* genus
* species
17
New cards
Epidemology
the study of incidence distribution and control of disease.
18
New cards
Prevalance
the total number of individuals with a disease at a point in time.
19
New cards
incidence
the proportion of __new__ cases of a disease in a single specified time.
20
New cards
Noncommunicable disease
Doesn’t spread from person-2-person.
21
New cards
Communicable
able to spread from person to person.
22
New cards
Contagious
a communicable disease that spread easily.
23
New cards
Sporadic
Occur infrequently and irregularly.
24
New cards
Endemic
Constant in the region.
25
New cards
Epidemic
A large increase of cases in a specific region.
26
New cards
Pandemic
Worldwide epidemic.
27
New cards
Pure Culture
Single known species in a culture.
28
New cards
Mixed Culture
2+ known species in a culture.
29
New cards
Contaminated Culture
1 known culture & unknown contaminants in a culture.
30
New cards
Inoculation
Introduce a sample of microbes to a growth medium.
\-Goal: add microbes to a sterile growth medium.
\-Goal: add microbes to a sterile growth medium.
31
New cards
Incubation
To grow microbial culture under suitable conditions.
\-Goal: to grow microbes under controlled conditions.
\-Goal: to grow microbes under controlled conditions.
32
New cards
Isolation
To separate a specific species or strain from all others.
\-Goal: to obtain a colony of bacteria that grew from a single bacterium.
\-Goal: to obtain a colony of bacteria that grew from a single bacterium.
33
New cards
Inspection
Examine by macroscopic or microscopic appearance.
\-Goal: to identify colony size, shape, color, and texture on a __**macroscopic scale**__; and to identify cell size, shape, arrangement, and staining on a __**microscopic scale**__.
\-Goal: to identify colony size, shape, color, and texture on a __**macroscopic scale**__; and to identify cell size, shape, arrangement, and staining on a __**microscopic scale**__.
34
New cards
Identification
determine identity using biochemical, genetic, or immunological tests.
\-Goal: identify species or strain.
\-Goal: identify species or strain.
35
New cards
Liquid Broth Media
This media allows uniform growth.
36
New cards
Semi-solid Media
This media allows motility assays.
37
New cards
Solid/Liquid Broth
The media allows surface growth.
* 1%-5% agar
* 12% gelatin
* 1%-5% agar
* 12% gelatin
38
New cards
General Purpose Media
This media allows broad spectrum growth.
39
New cards
Enriched Media
This media has complex substances added to it that’s required by certain fastidious species to grow.
40
New cards
Selective Media
This media inhibits growth of unwanted species.
41
New cards
Differential Media
This media causes a visual change when specific microbes grow on it.
42
New cards
Resolution
The power to distinguish 2 points from each other.
43
New cards
Contrast
Difference in light between image and background.
44
New cards
Working Distance
The distance between the tip of the objective lens and the specimen on the stage.
\-This distance decreases as magnification increases.
\-This distance decreases as magnification increases.
45
New cards
Field of View
The area that you can see through the lens.
\-This decreases as magnification increases.
\-This decreases as magnification increases.
46
New cards
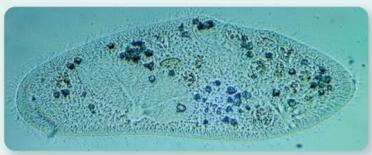
\
Bright Field Microscopy
47
New cards
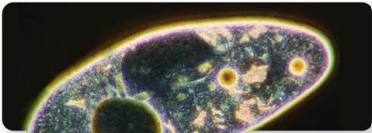
Dark Field Microscopy
48
New cards
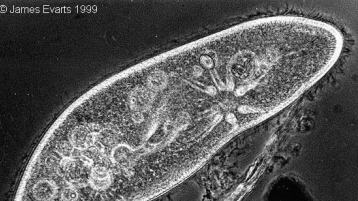
Phase Contrast Microscopy
49
New cards
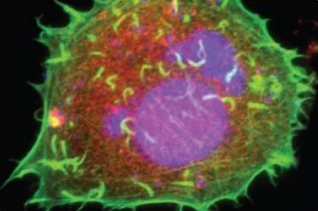
Fluorescence Microscopy
50
New cards
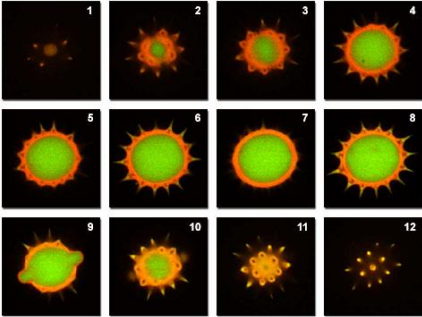
Confocal Microscopy
51
New cards
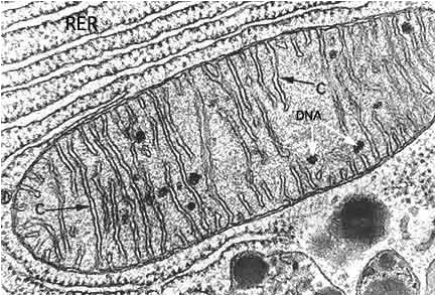
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
52
New cards
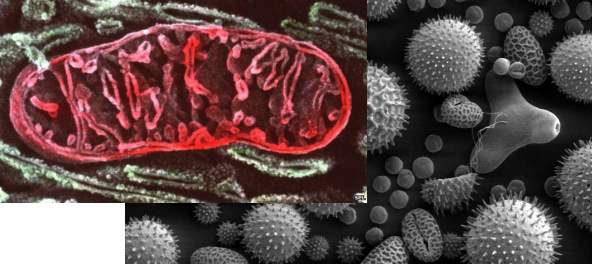
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
53
New cards
Light Microscopy
Use light to visualize images.
54
New cards
Brightfield Microscope
A compound microscope with 2+ lenses that produce a dark image on a bright background.
55
New cards
Darkfield Microscope
A compound microscope with 2+ lenses and a disk between the illuminator and condenser lens that produces a bright image on a dark background.
56
New cards
Phase Contrast Microscope
This microscope uses refraction and interference caused by structures in specimen to create a high contrast, high resolution image w/o staining.
57
New cards
Fluorescence Microscope
This microscope uses fluorescent chromophores (fluorochromes) that absorb energy from light sources and uses the energy to emit visible light.
58
New cards
Confocal Microscope
This microscope uses a laser to scan multiple Z-planes successfully that produces multiple 2-D, high resolution at various depths which can be constructed into a 3-D image.
59
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
This microscope requires the specimen to be sectioned & stained with metal, then electrons are transmitted through specimen to visualize internal structures with high magnification and resolution.
60
New cards
Scanning lens
10x \* 4x = 40x
61
New cards
Low Power lense
10x \* 10x = 100x
62
New cards
High Dry Lens
10x \* 50x = 500x
63
New cards
Oil Immersion lens
10x \* 100x = 1,000x
64
New cards
Simple Staining
This type of staining uses a single dye that emphasizes particular structures in a sample.
65
New cards
Differential Staining
This type of staining distinguishes organisms based on their interactions with multiple stains.
66
New cards
Gram Stain
This staining method is used to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls.
67
New cards
Endospore Stain
This staining method uses 2 stains to differentiate endospores from the rest of the cell.
68
New cards
Acid-Fast Stain
This method of staining is used to differentiate 2 types of gram (+) cell: those that have mycolic acids or not.
69
New cards
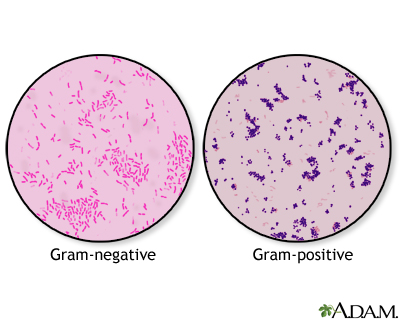
Gram Stain
70
New cards
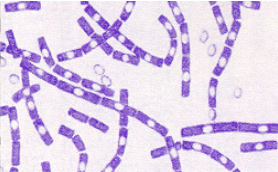
Endospore Stain
71
New cards
Acid-Fast Stain
72
New cards
Coccus
Spheres
73
New cards
Bacillus
Rod-Shaped
\
\
74
New cards
Vibro
Curved rods (Mac&Cheese noodles)
75
New cards
Spirillum
Curled (loose coils)
76
New cards
Spirochete
Springy spiral
77
New cards
Branching filaments
Tree branches.
78
New cards
Cytoplasmic Membrane
* phospholipid bilayer
* selectively permeable
* regulates nutrients and waste products
* the site for metabolic reactions
* Found in only Gram (+)
* selectively permeable
* regulates nutrients and waste products
* the site for metabolic reactions
* Found in only Gram (+)
79
New cards
Cell Wall
* provides structural support
* Made of peptidoglycan (thick, rigid/sturdy)
* found in both Gram (+) & Gram (-)
* Made of peptidoglycan (thick, rigid/sturdy)
* found in both Gram (+) & Gram (-)
80
New cards
Cell Envelope
Surrounds the cytoplasm and protects the bacteria cell.
81
New cards
Outer Membrane
* has phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides(LPS)
* found only in Gram (-)
* found only in Gram (-)
82
New cards
S Layer
* protein layer inside the glycocalyx
* in all archaea
* in bacteria found in hostile environments
* in all archaea
* in bacteria found in hostile environments
83
New cards
Glycocalyx
* coat of polysaccharides
* Slime layer
* capsule
* Slime layer
* capsule
84
New cards
Cytoplasm
This internal structure is composed of mostly water and is considered a pool of nutrients and building materials.
85
New cards
Cytoskeleton
This internal structure contributes to cell shape and division.
86
New cards
Chromosomes
This internal structure contains the DNA for the cell
* bacteria have 1 circular
* eukaryotes have many and are rod shaped
* bacteria have 1 circular
* eukaryotes have many and are rod shaped
87
New cards
Bacteria Ribosomes
30s = small subunit
50s = large subunit
70s = 30s+50s
50s = large subunit
70s = 30s+50s
88
New cards
Inclusion Bodies
This internal structure in prokaryotes are storage compartments.
89
New cards
Bacterial Endospores
This internal structure is produced by both Gram (+) and Gram (-) bacteria. It helps to resist extremes including:
* temperature
* radiation
* drying
* chemicals
* temperature
* radiation
* drying
* chemicals
90
New cards
Fimbriae
This external structure is found mostly in Gram (-) bacteria. Its hair-like and aid in attachment and colonization.
91
New cards
Pili
This external structure is a hollow tube used to connect with other bacterium to share plasmid DNA. It also assists in conjugation in Gram (-) bacteria, aids in attachment, and movement.
92
New cards
Nanotubes
This external structure is a tiny membrane extension that is capable of nutrient transfer between cells.
93
New cards
Flagella
This external structure aids in movement. This structure can have multiple arrangements and various modes of movement including:
* Run = rotating counterclockwise
* tumble=rotating clockwise
* Random walk = alternating between running and tumbling.
* Run = rotating counterclockwise
* tumble=rotating clockwise
* Random walk = alternating between running and tumbling.
94
New cards
Chemotaxis
Cells moving in response to chemical signals. (more running than tumbling)
95
New cards
(+) chemotaxis
Cell moving towards a chemical signal (stimuli)
96
New cards
(-) Chemotaxis
cell moving away from chemical signal (repellant)
97
New cards
Nucleus
This internal organelle is surrounded by a complex membrane and houses the DNA genome. This organelle also, controls all cell activity.
98
New cards
Mitosis
This process is clonal reproduction for eukaryotes (IPPMAT)
99
New cards
Karyokinesis
Division of the nucleus. (PPMAT)
100
New cards
Cytokinesis
Separation of the cytoplasm.