Unit 1: Intro to Geography & It's Perspectives (Entire Unit)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Geography
the study of where things are on Earth's surface, why they are located there, and why we care (Greek: geo = "Earth", graphy = "to write")

Place
a specific point on Earth with its own particular characteristics
Region (Regionalization)
a larger area of Earth defined by one or more distinctive characteristics
Scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole - ranging from local to global
Space
the physical gap or interval between objects and the relationship/connection/spatial association between them
Spatial Perspective
a way of looking at the human and physical patterns on Earth and their relationships to one another - an essential part of geography
Cartography
the science of making maps

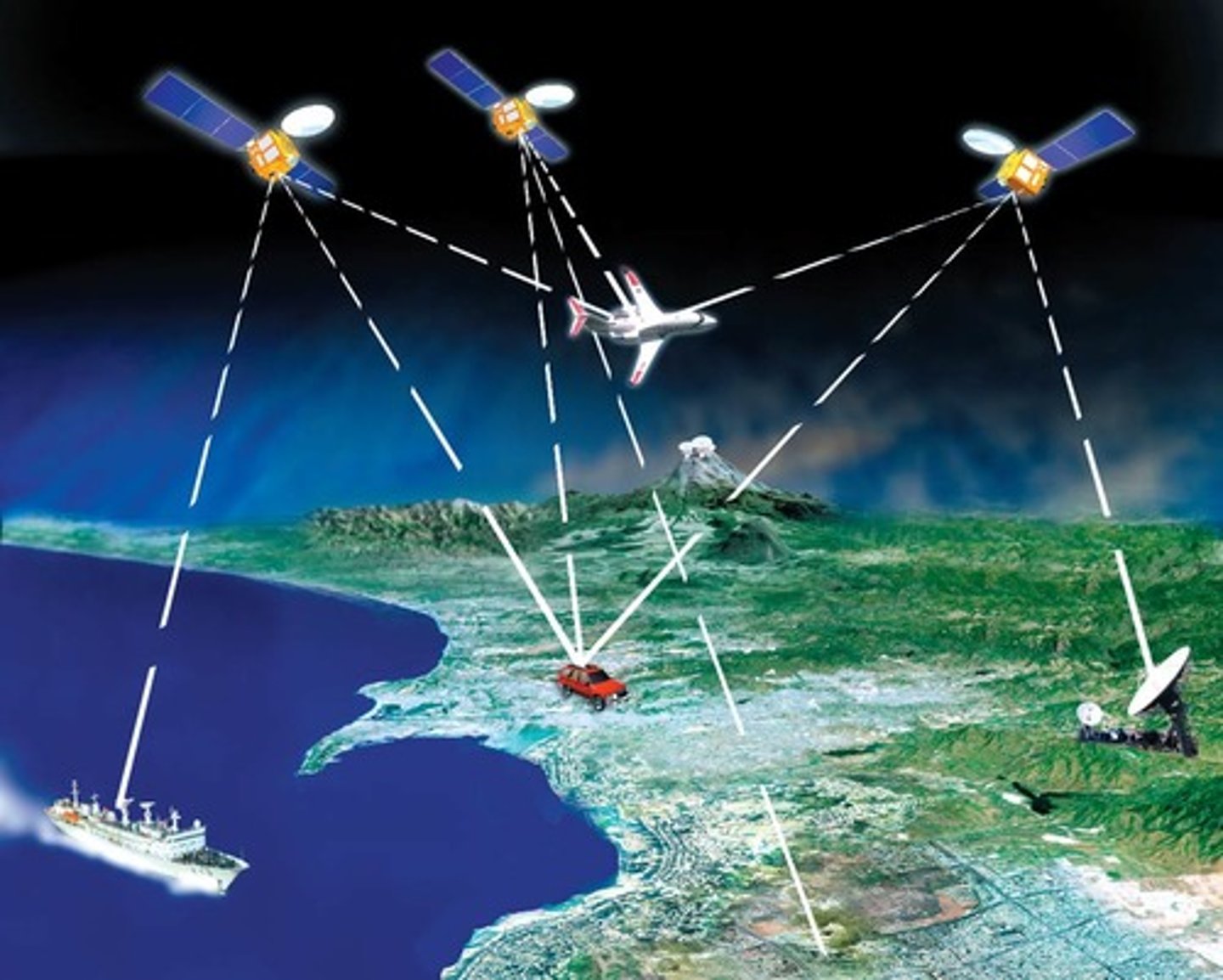
Global Position System (GPS)
a system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers
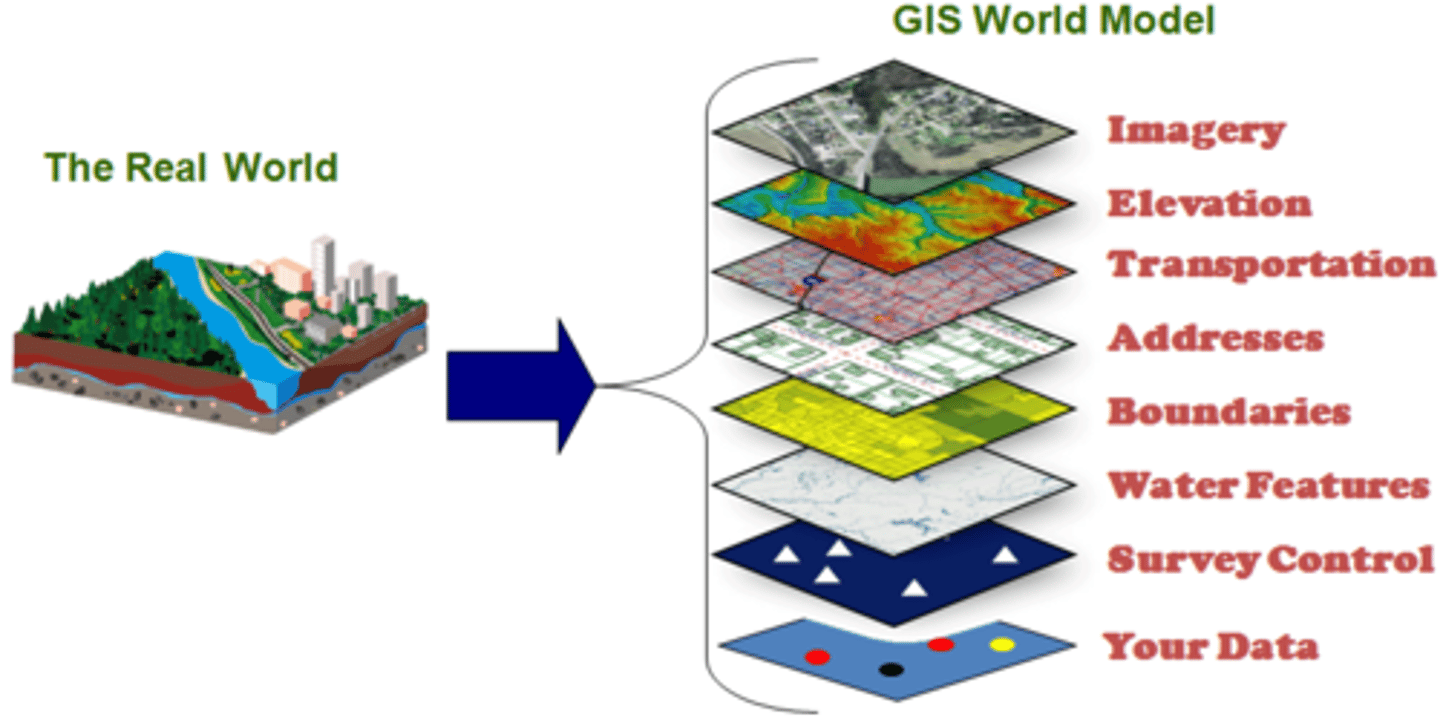
Geographic Information System (GIS)
a computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data (often in layers)
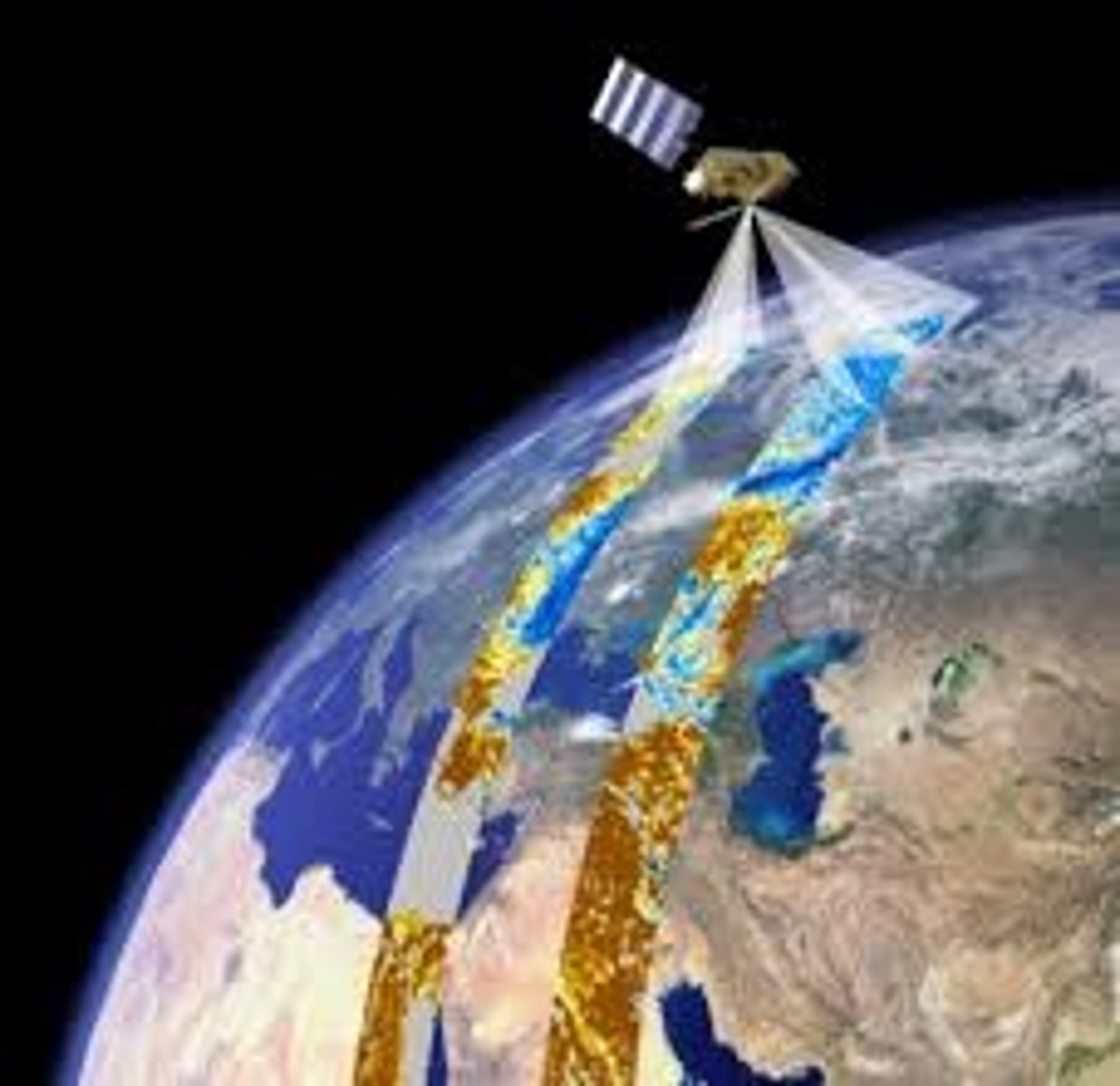
Remote Sensing
the scanning of the earth by satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it (ex: temperature, atmosphere or soil compositions, images, etc.)

Map Scale
the relationship between size and distance on a map and the size and distance of the actual feature on Earth's surface
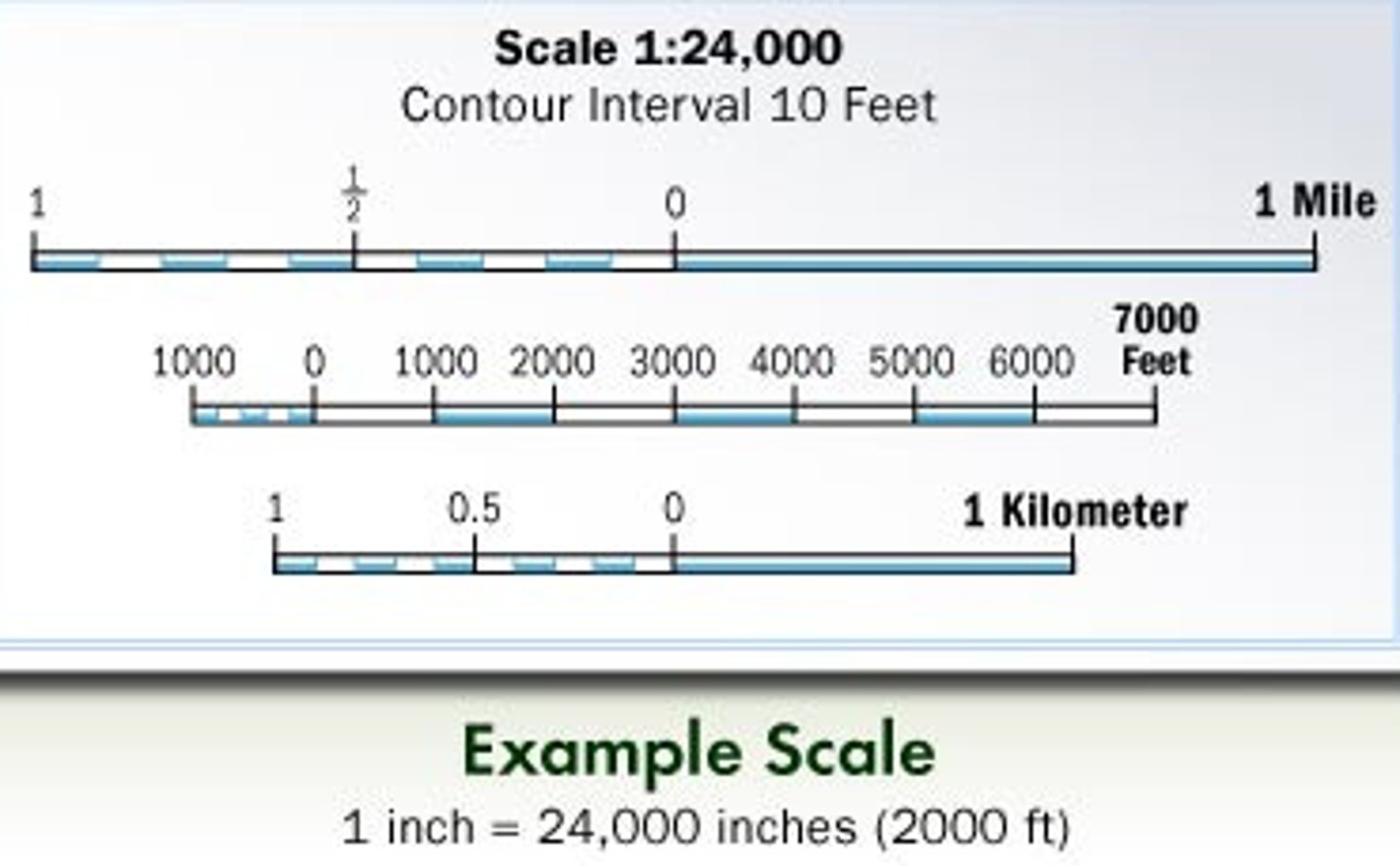
Map Projection
the scientific method of transferring locations on the Earth's spherical surface to a flat map - will always create distortion in shape, size/area, distance and/or direction
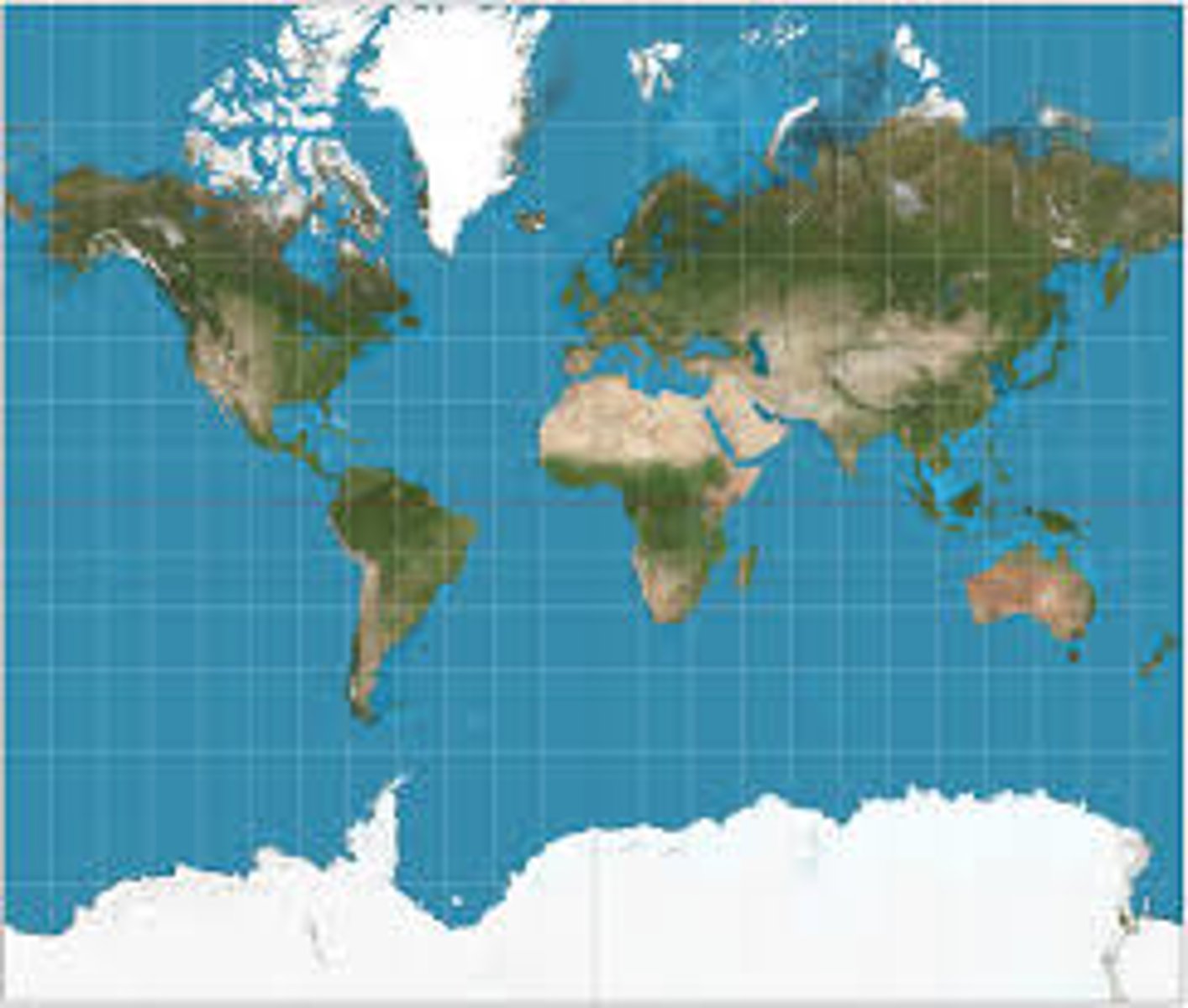
Mercator Projection
a cylindrical projection of the world where the cylinder touches at the equator resulting in increased size and distance distortion at the poles
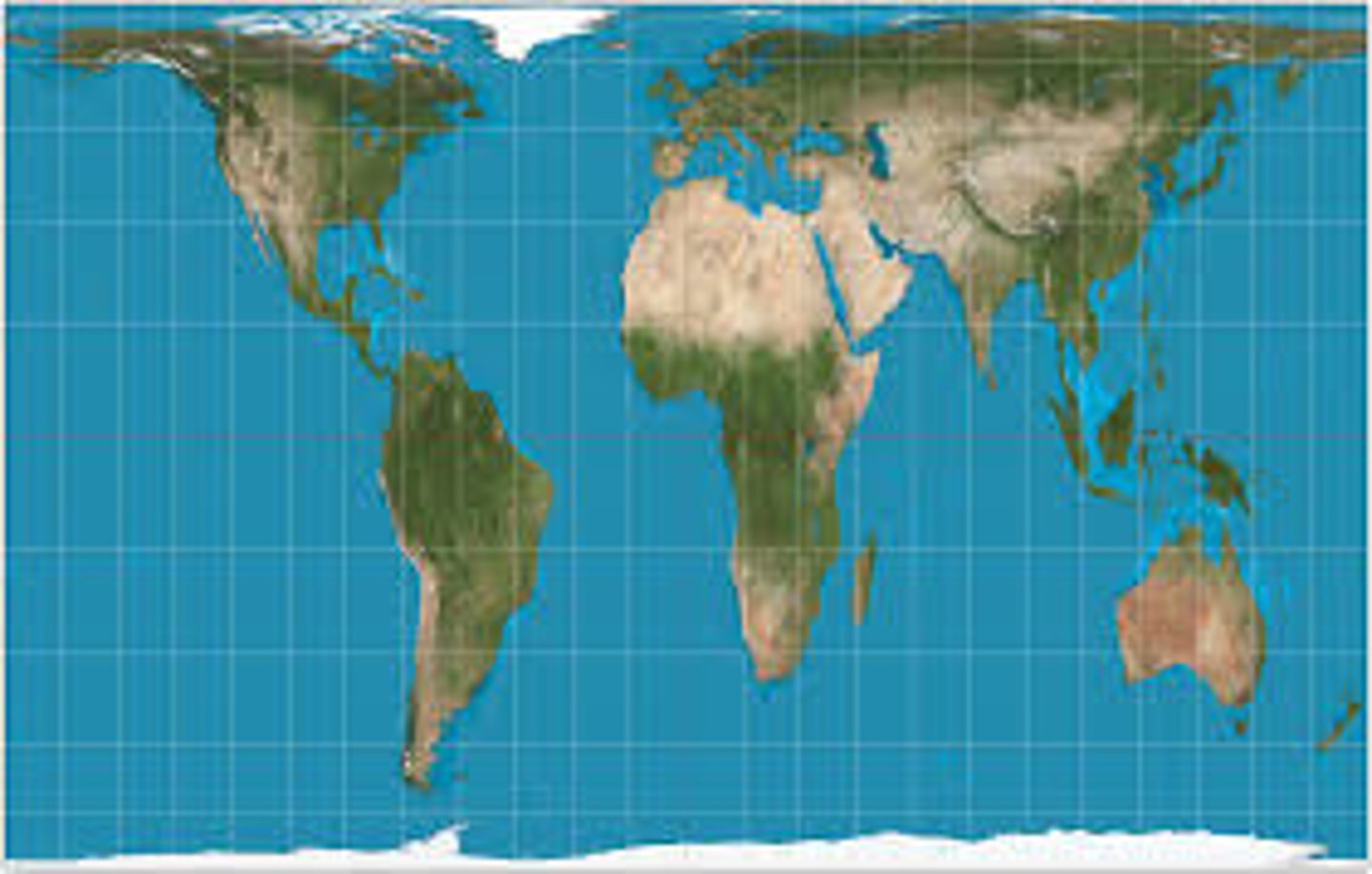
Peters Projection
a cylindrical, equal-area projection of the world purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth equally (major distortions: shape and distance at poles)
Robinson Projection
a map projection that attempts to balance distortions by distorting everything: size/area, shape, distance, and direction (latitude is straight, longitude is curved)
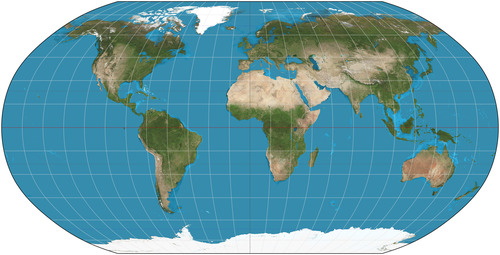
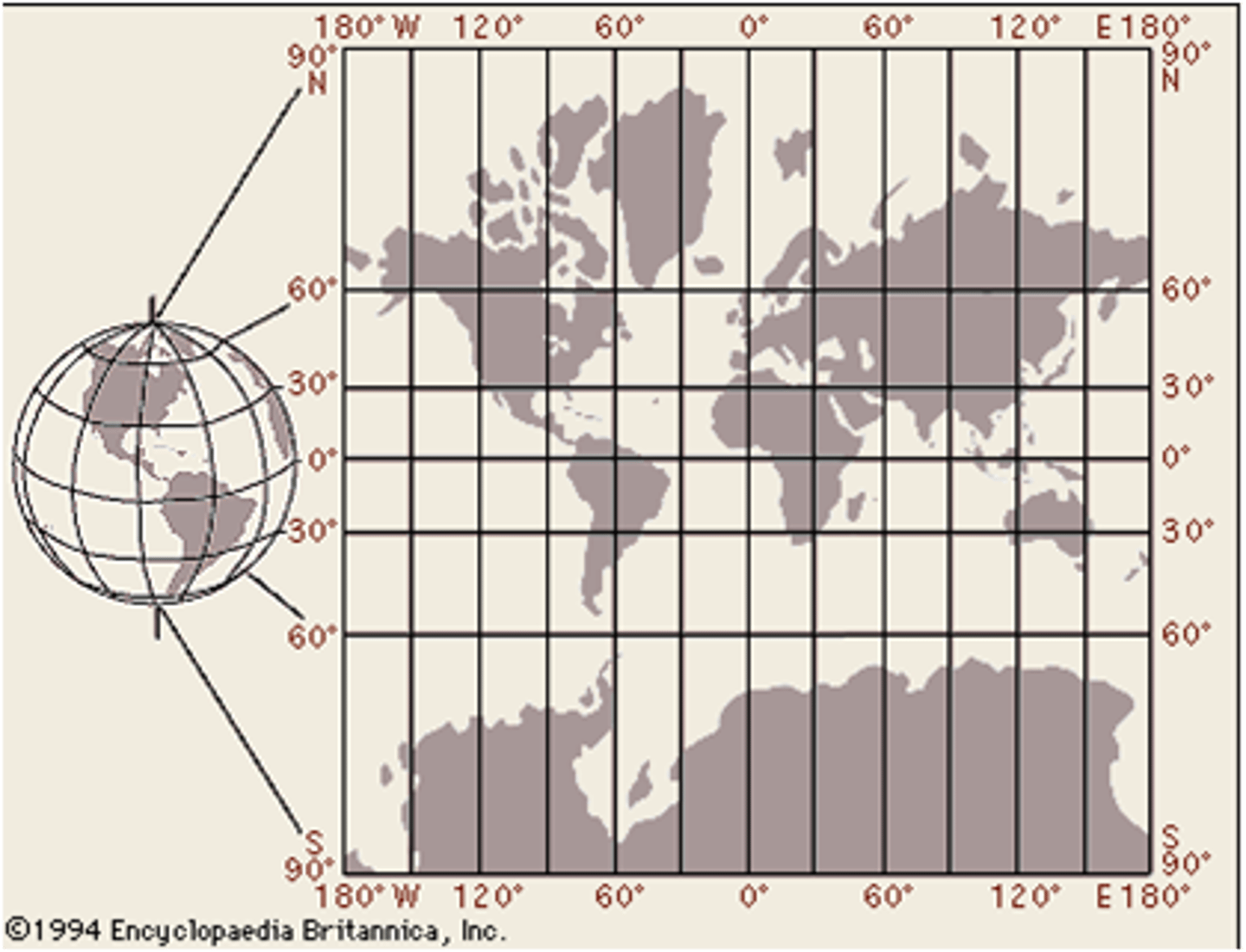
Longitude
the distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees
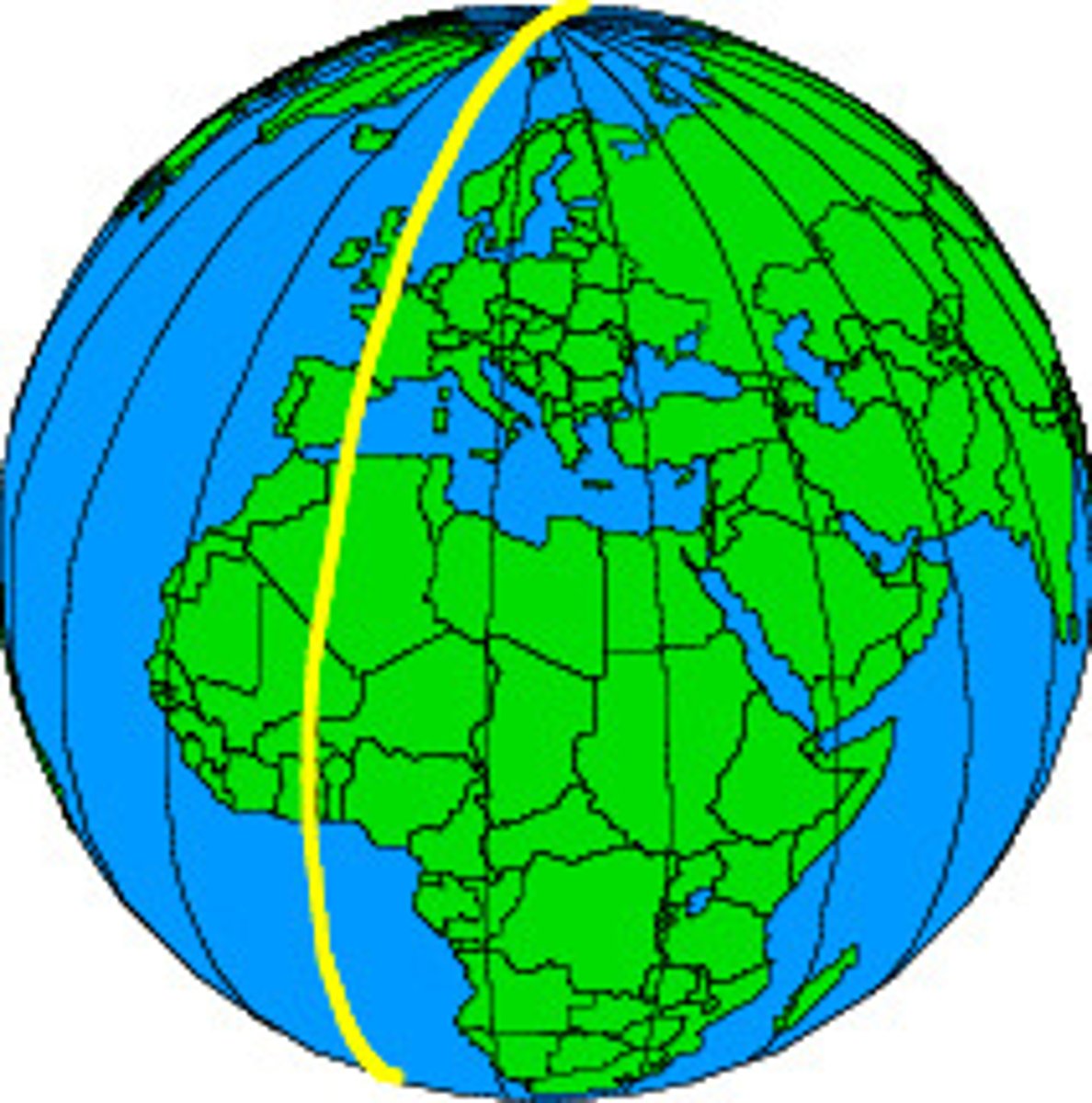
Latitude
the distance north or south of the equator; lines run east/west (AKA parallel)
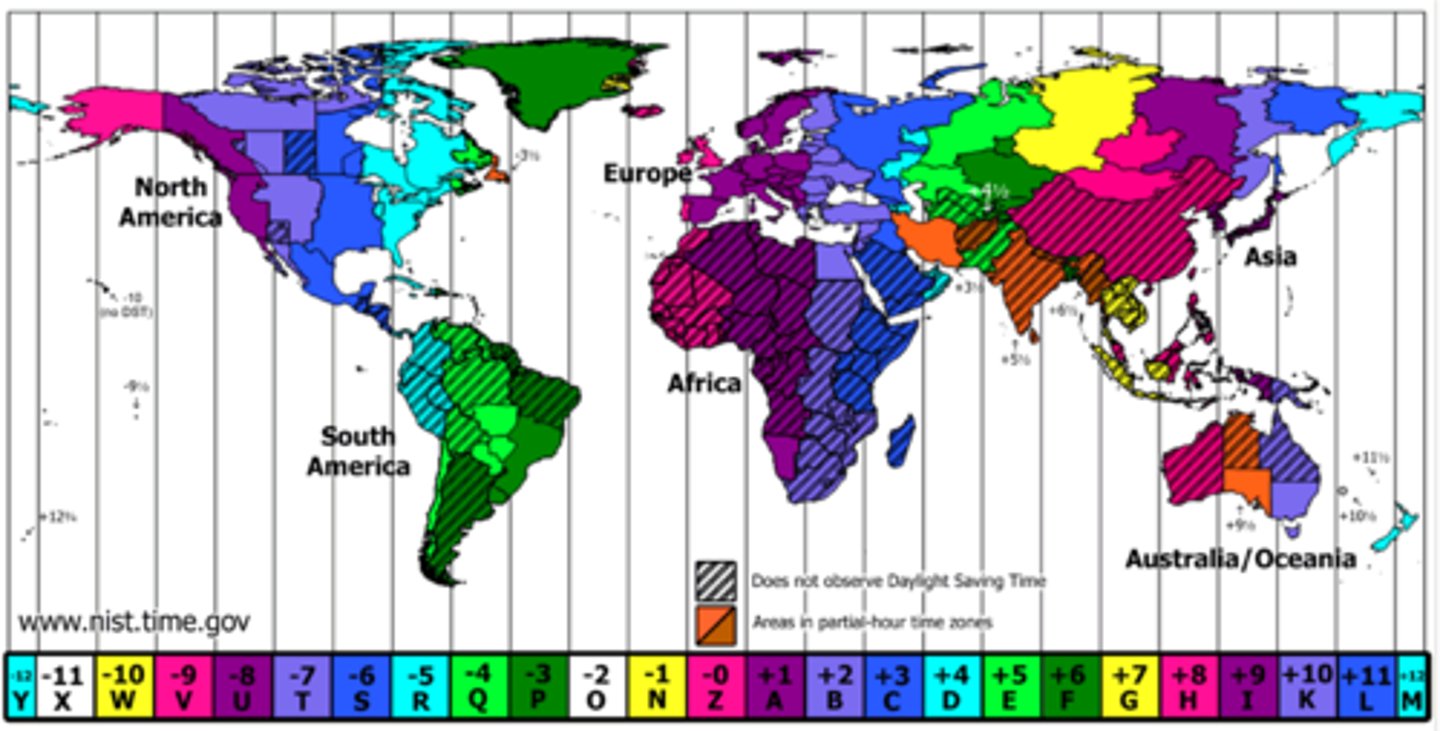
Time Zones
24 regions or divisions of the globe approximately coinciding with meridians at successive hours from the observatory at Greenwich, England
Reference Map
a map type that shows reference information for a particular place, making it useful for finding landmarks and for navigation
Thematic Map
a map that emphasizes a single idea or a particular kind of information about an area
Physical map
A map that shows a physical environment: mountains, hills, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans, etc.
Political map
A map that shows man-made political boundaries such as those surrounding countries, counties, and cities.
Categorical Map
A thematic map that depicts areas that are different in kind & uses several distinct colors to show different categories
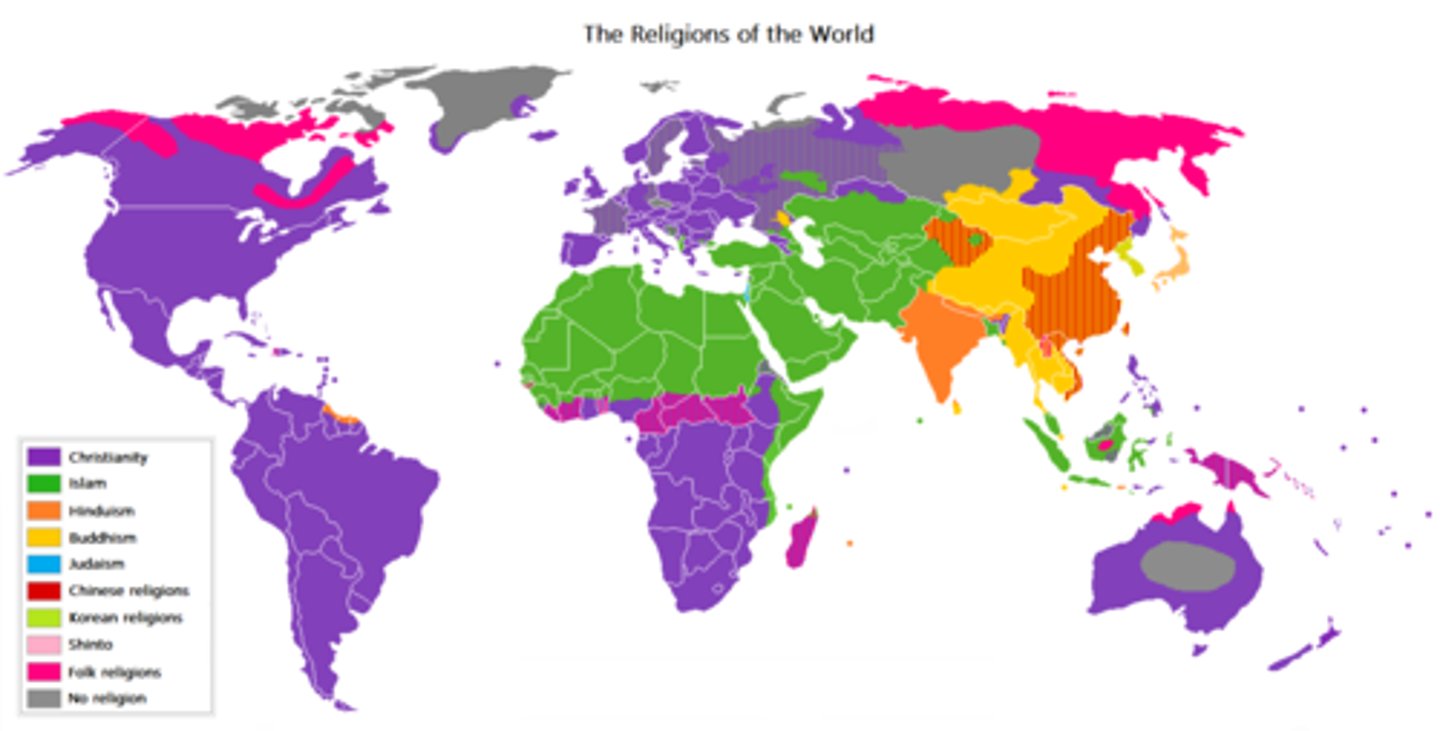
Choropleth Map
a thematic map that depicts areas that are different in amount & use shades of similar colors to show different values
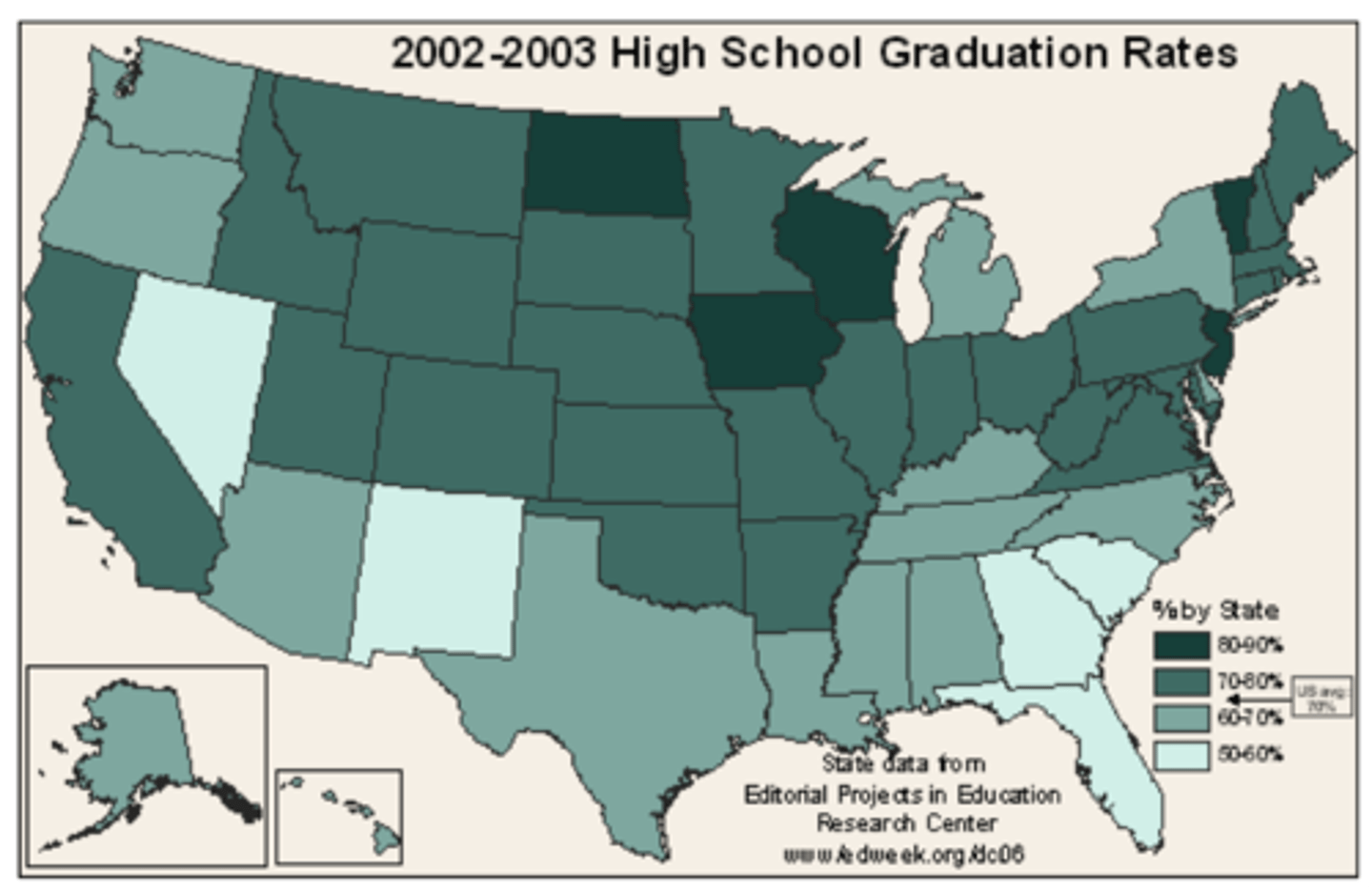
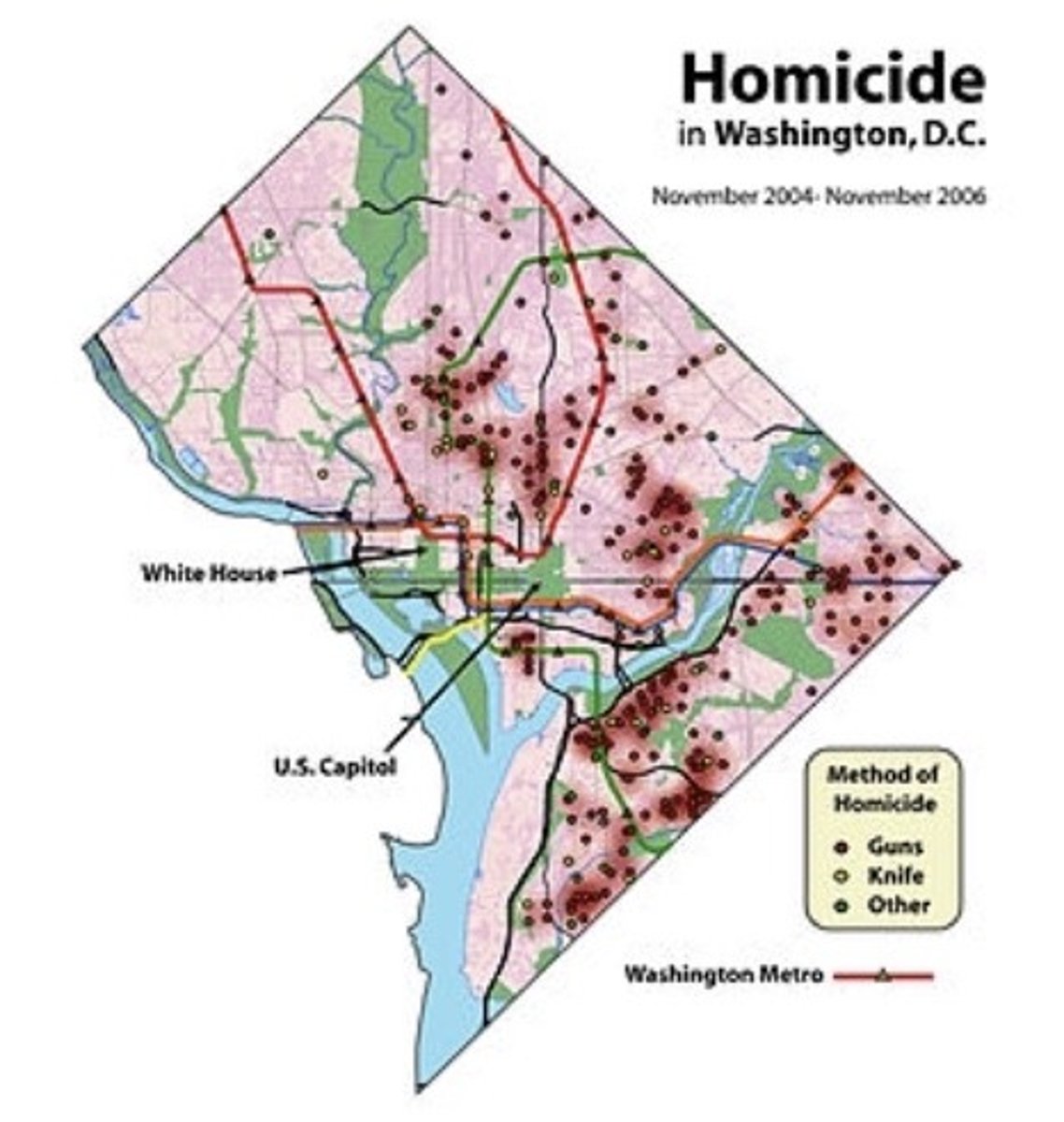
Dot Map
a thematic map that uses dots to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents,or births
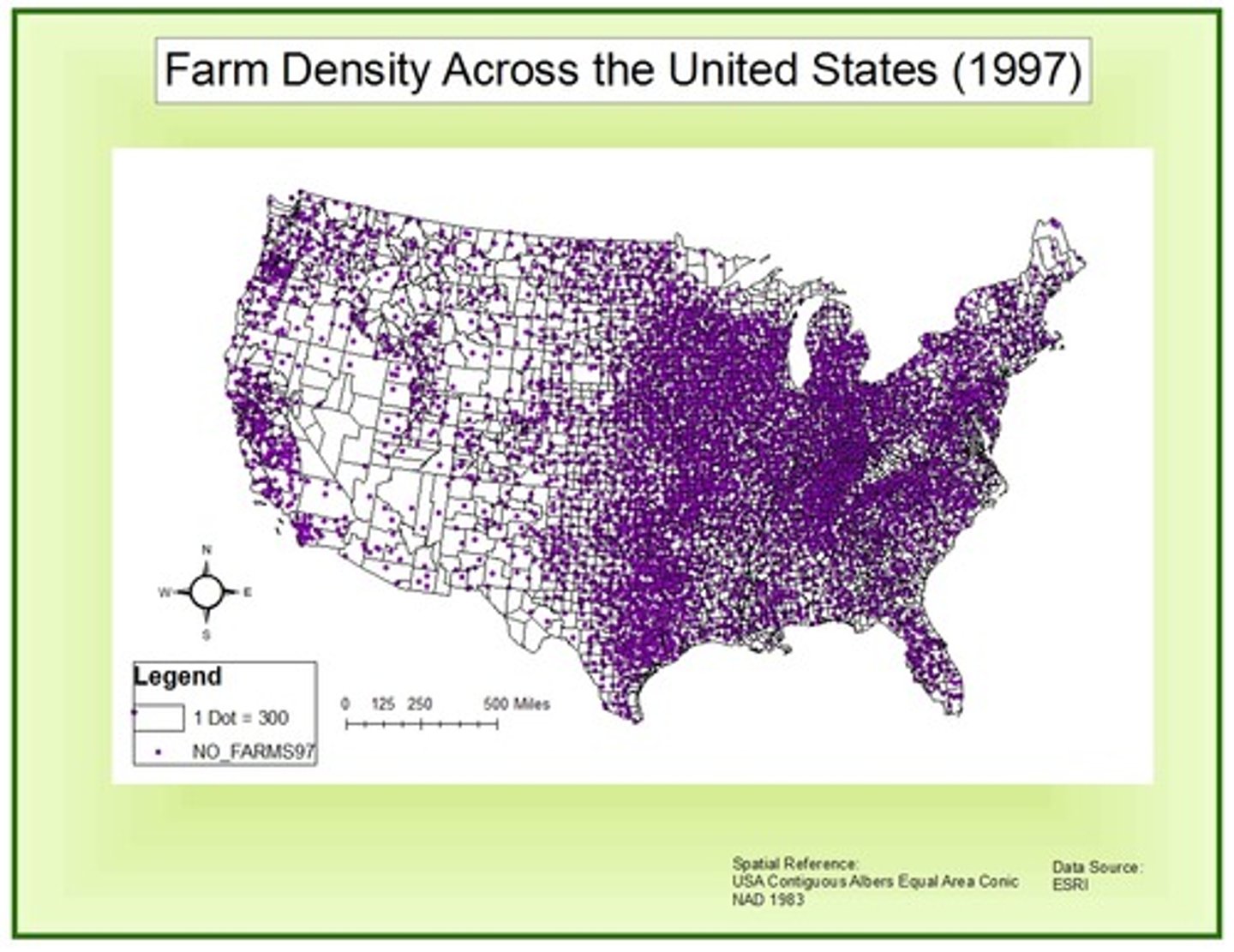
Graduated Symbol Map
a thematic map with symbols of different sizes according to the value of the attribute they represent
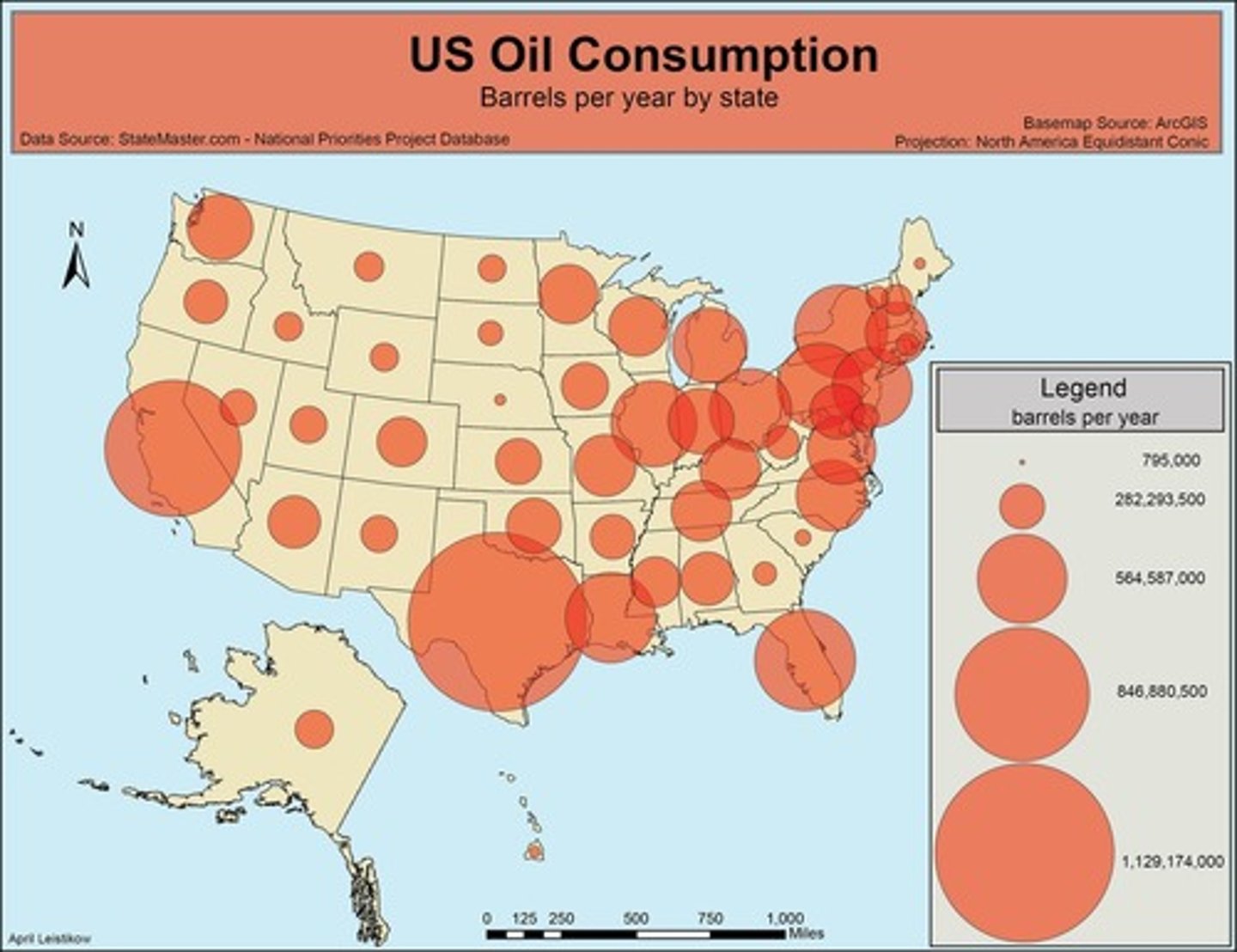
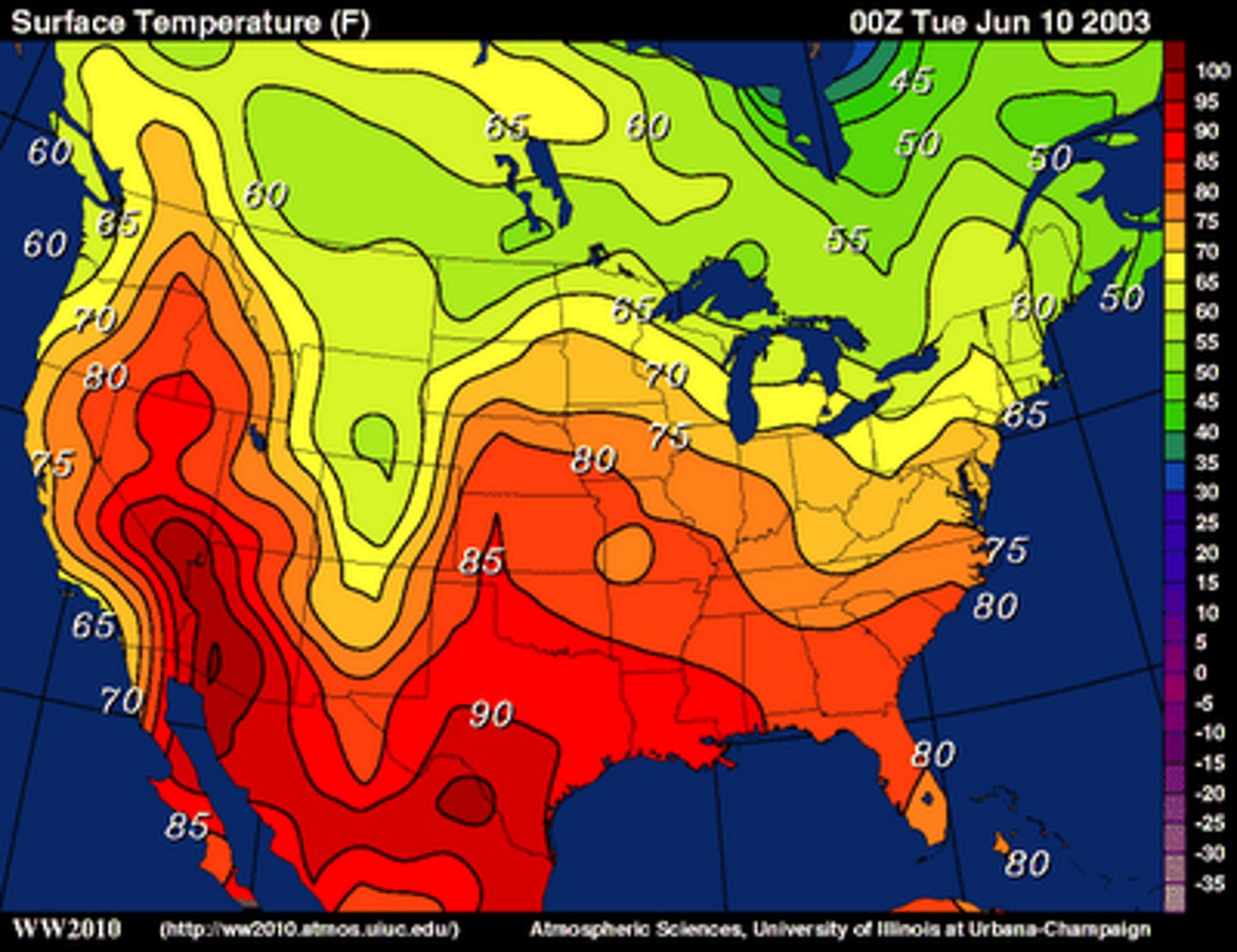
Isoline Map
a thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value (ex: elevation, temperature, etc.)
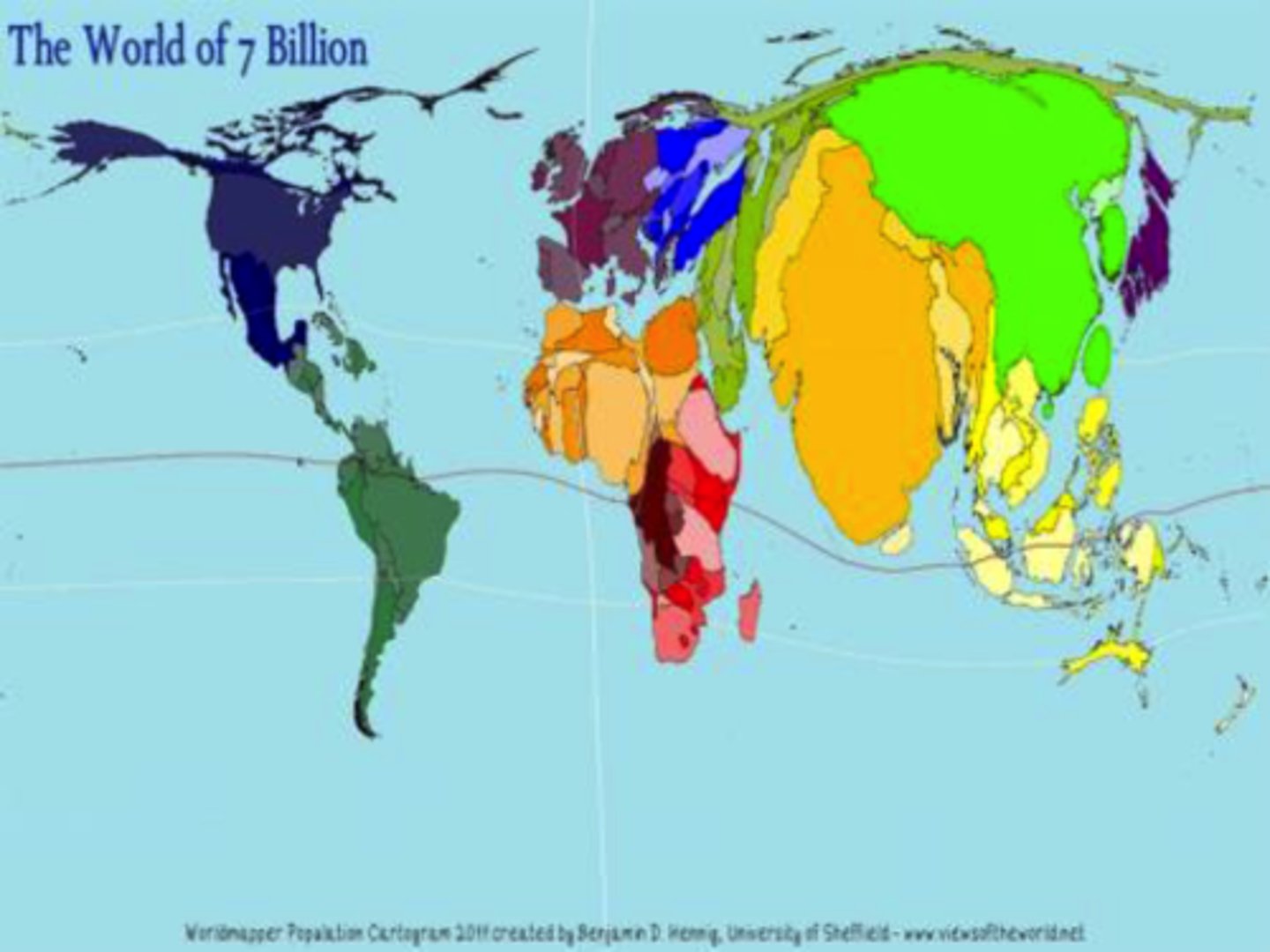
Cartogram Map
a thematic map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as population, voting results, economic production, etc.
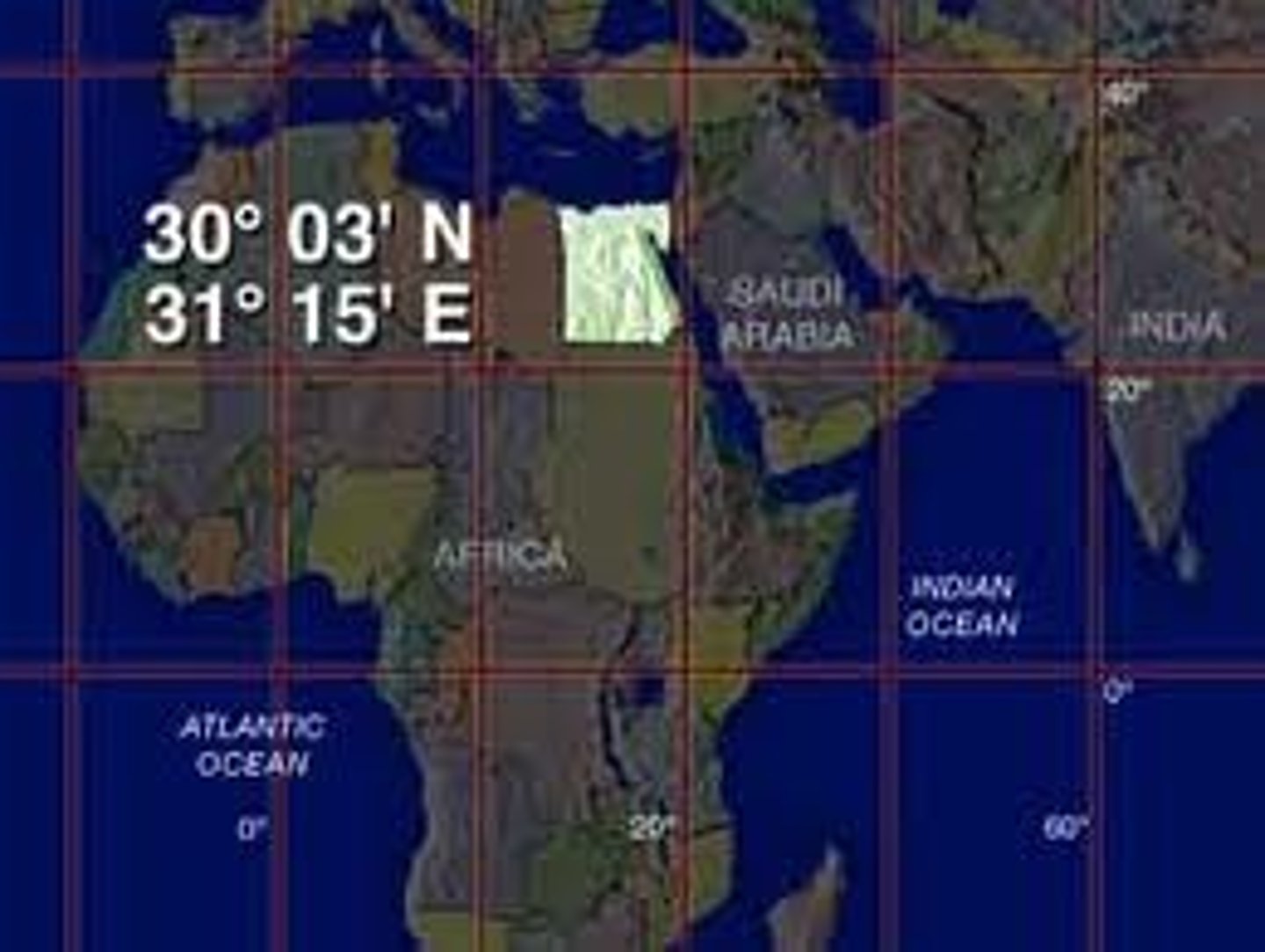
Absolute Location
the exact position of a place on the Earth's surface described by global coordinates
Relative location
indicates a place's location within a larger context; where a place is located in relation to another place
Toponym
the name given to a place on Earth

Site
the physical characteristics of a place, such as its topography, vegetation, and water resources

Situation
the location of a place relative to other places (AKA relative location)

Cultural Landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape

Formal Region (AKA Uniform Region)
-an area where everyone shares at least one characteristic
-there is a measurable, cultural linkage
-can be physical/political boundary but doesn't have to be
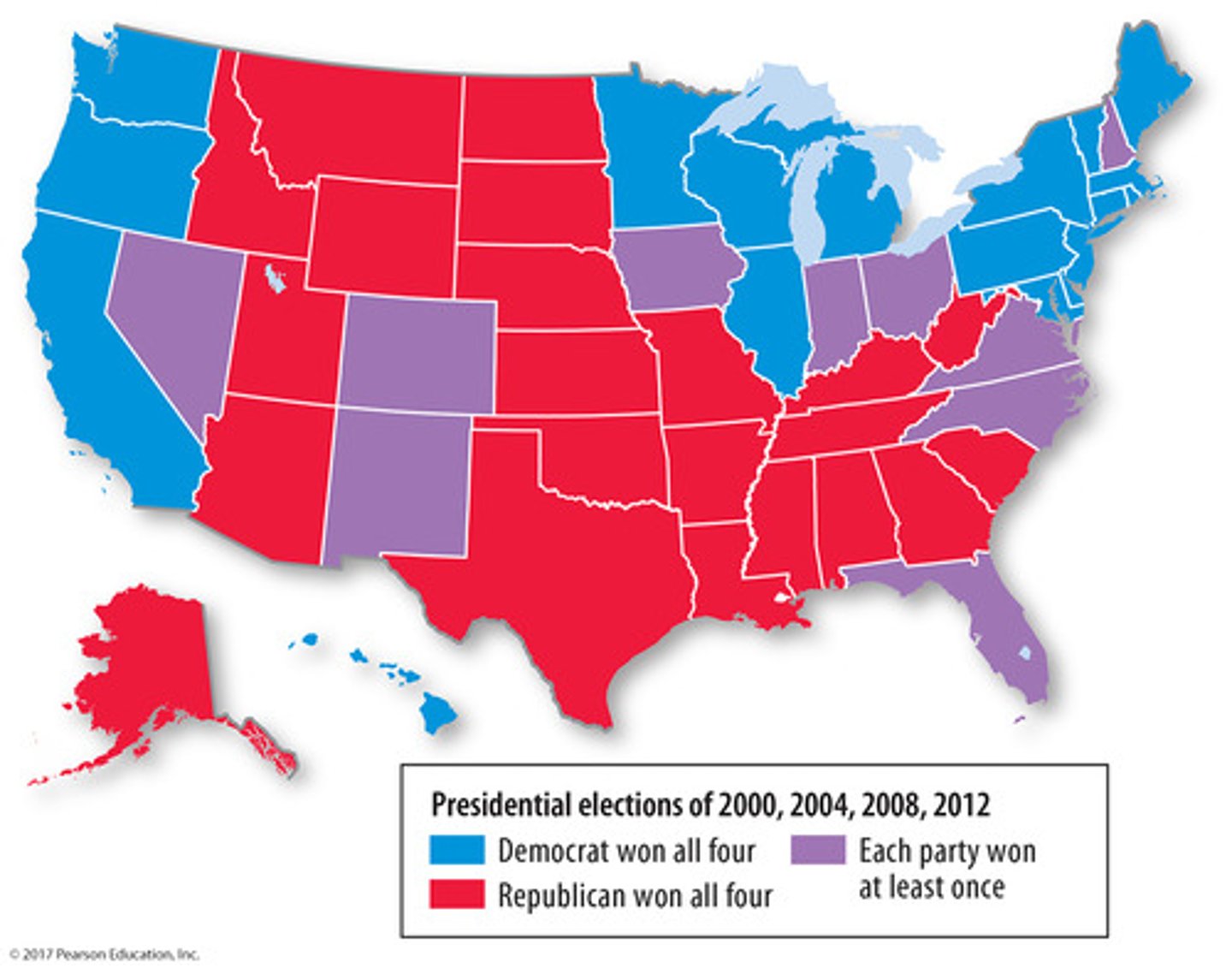
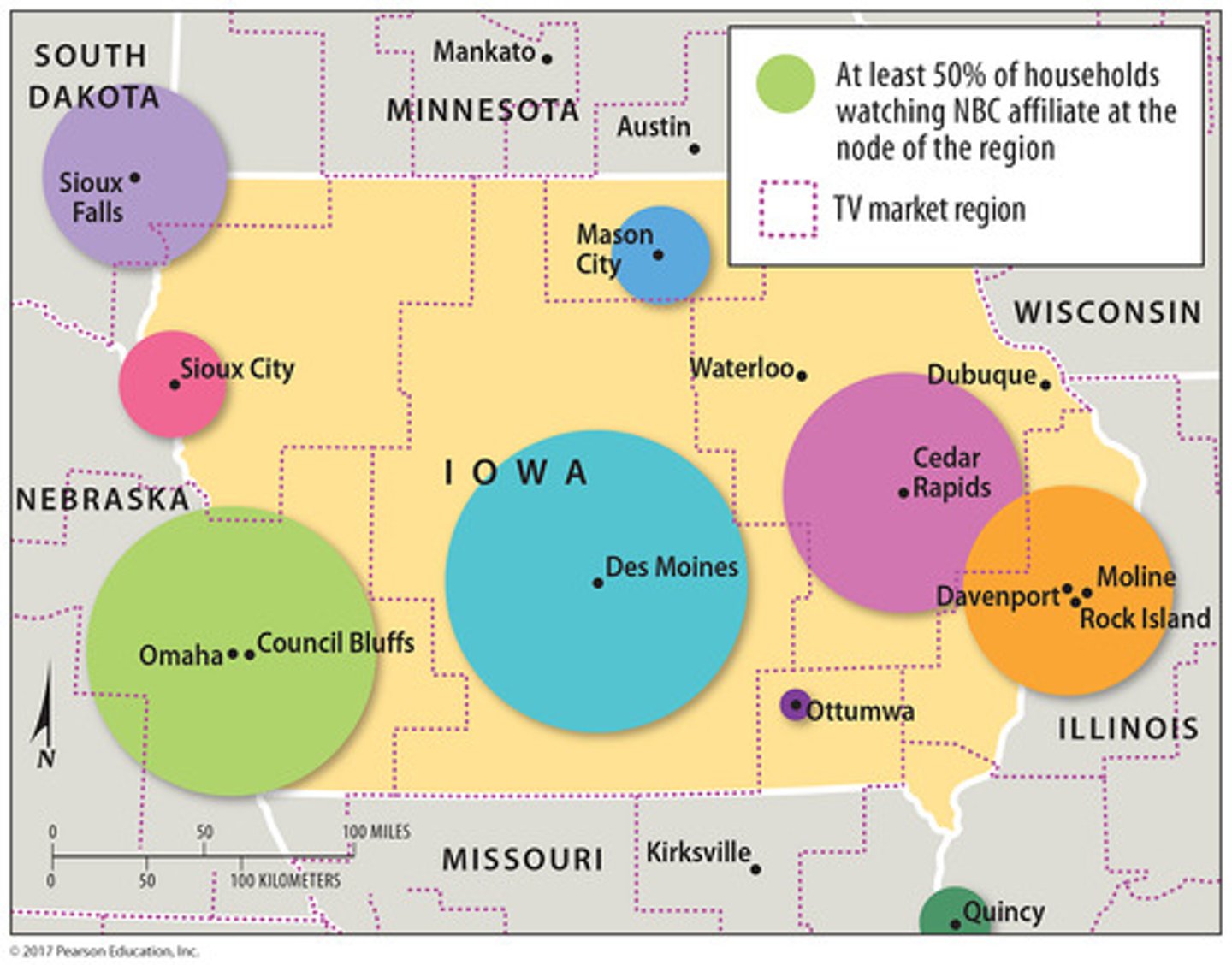
Functional Region (AKA Nodal Region)
-an area organized around one focal point
central activity in the focal point
-other points surround and branch off from focal point
-interactions between focal point and surrounding points
connectivity
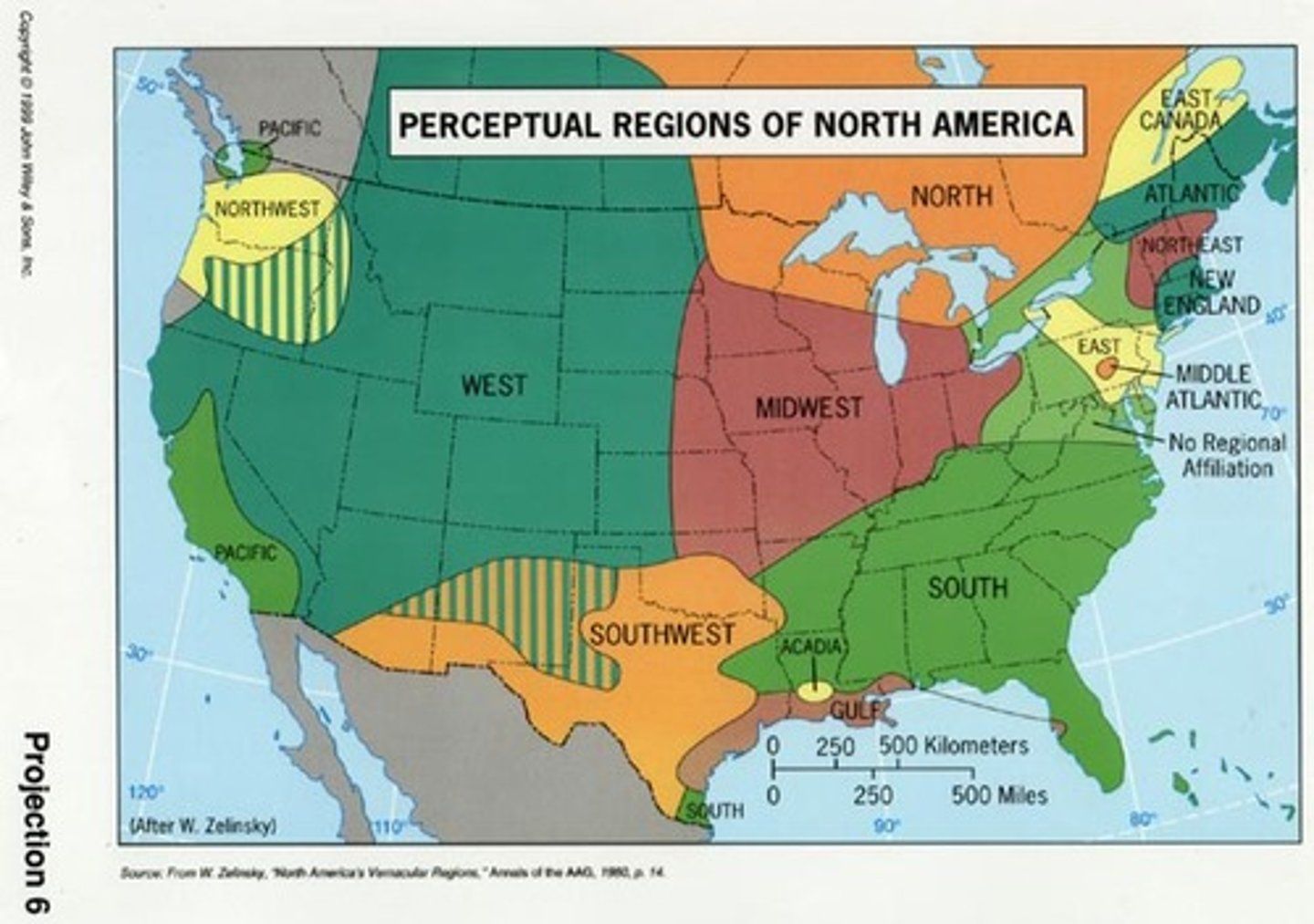
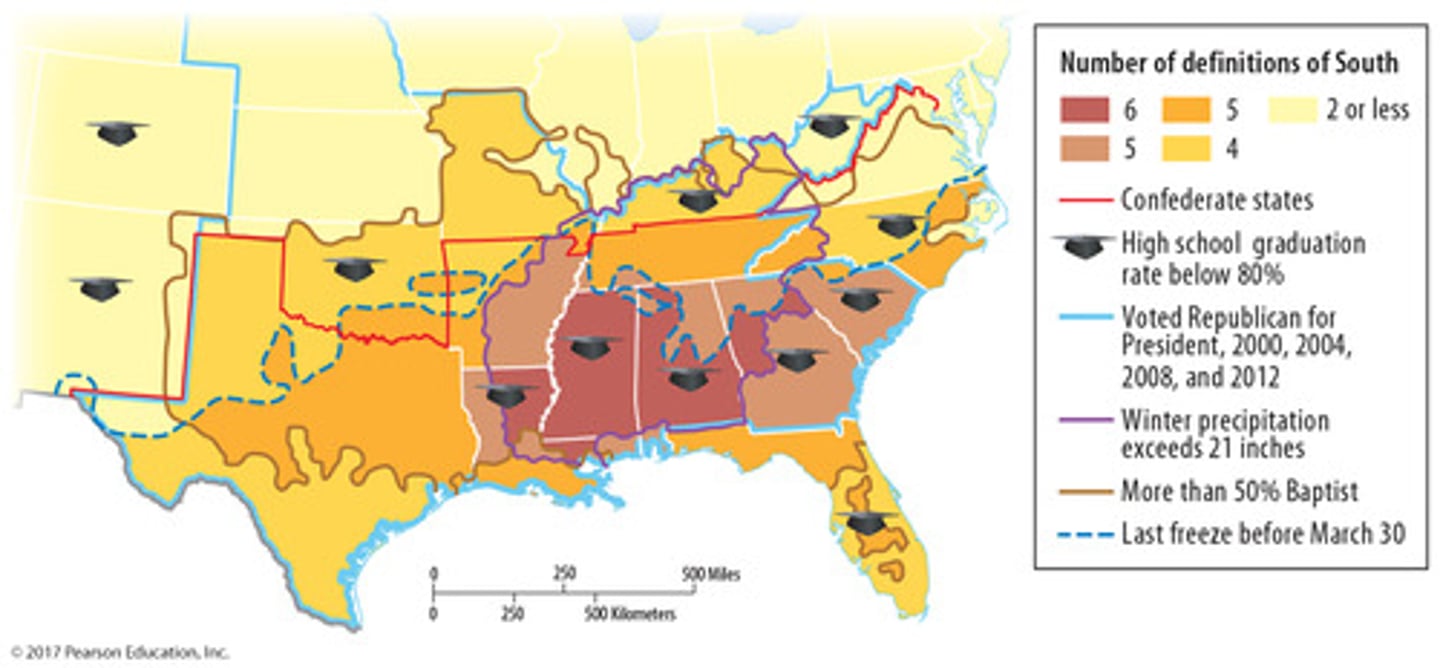
Vernacular Region (AKA Perceptual Region)
-an area that exists in people's minds
-part of their cultural identity
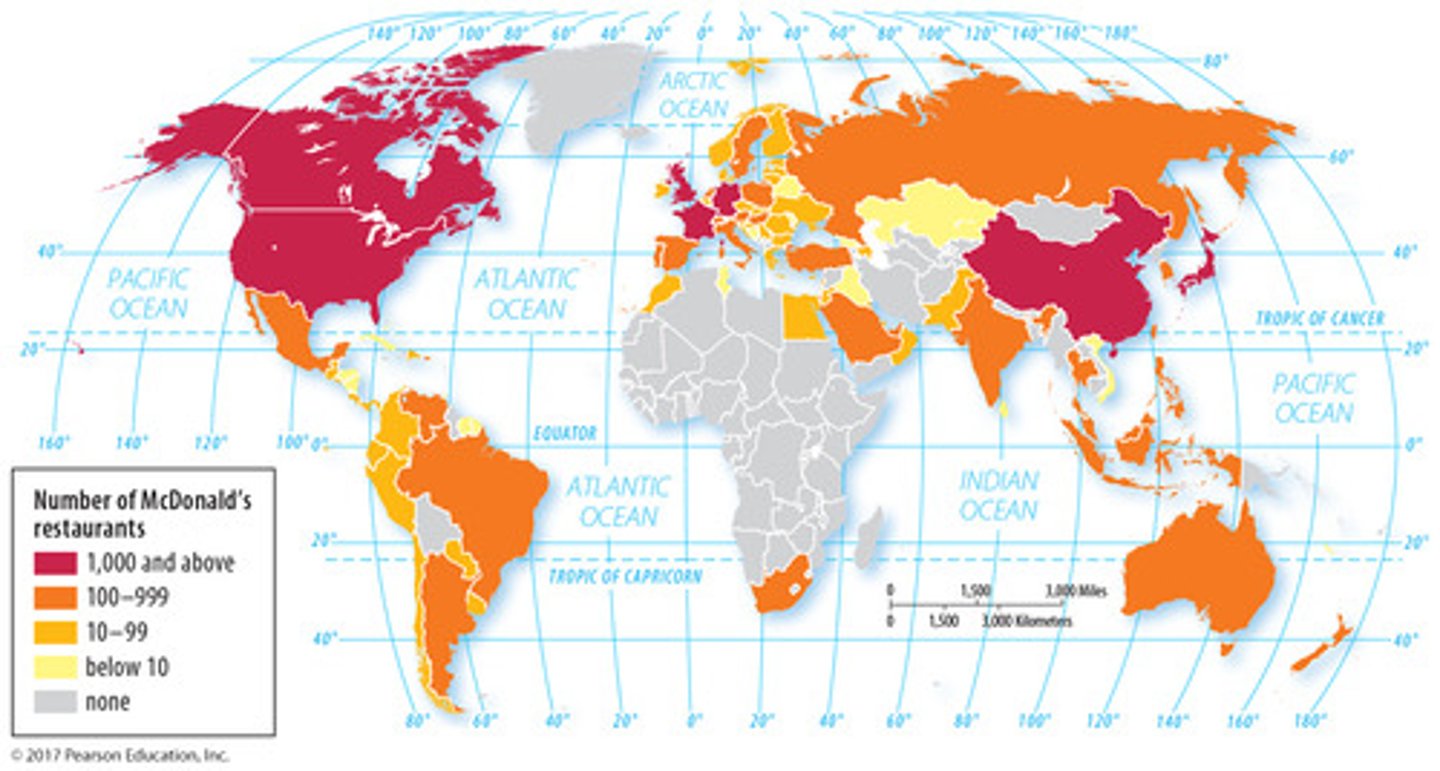
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.

Transnational Corporation
a company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located
Distribution
the arrangement of a feature in space - consists of density, concentration, and pattern
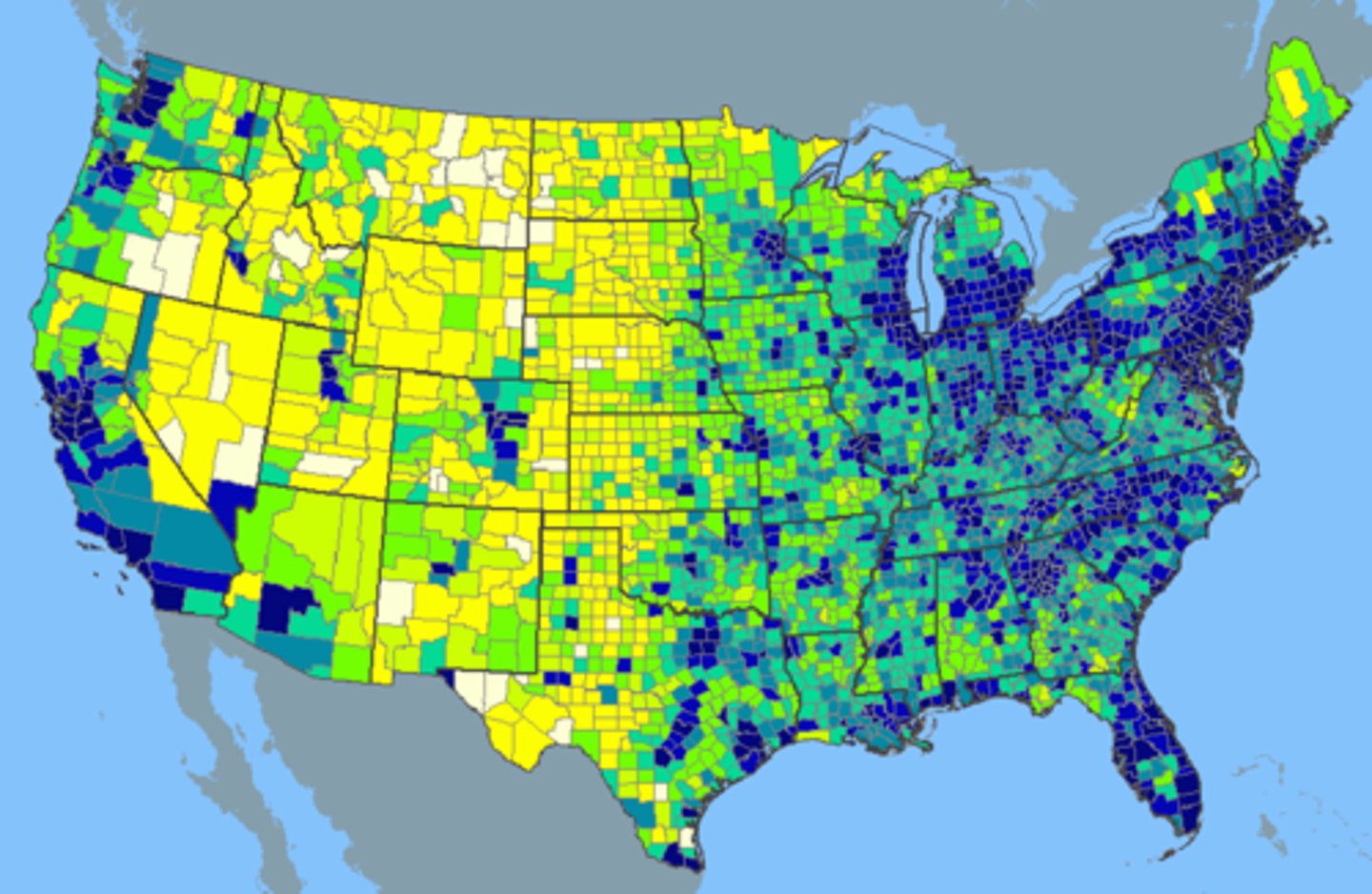
Density
the frequency with which something exists within a given unit of area (ex: people per square mile)
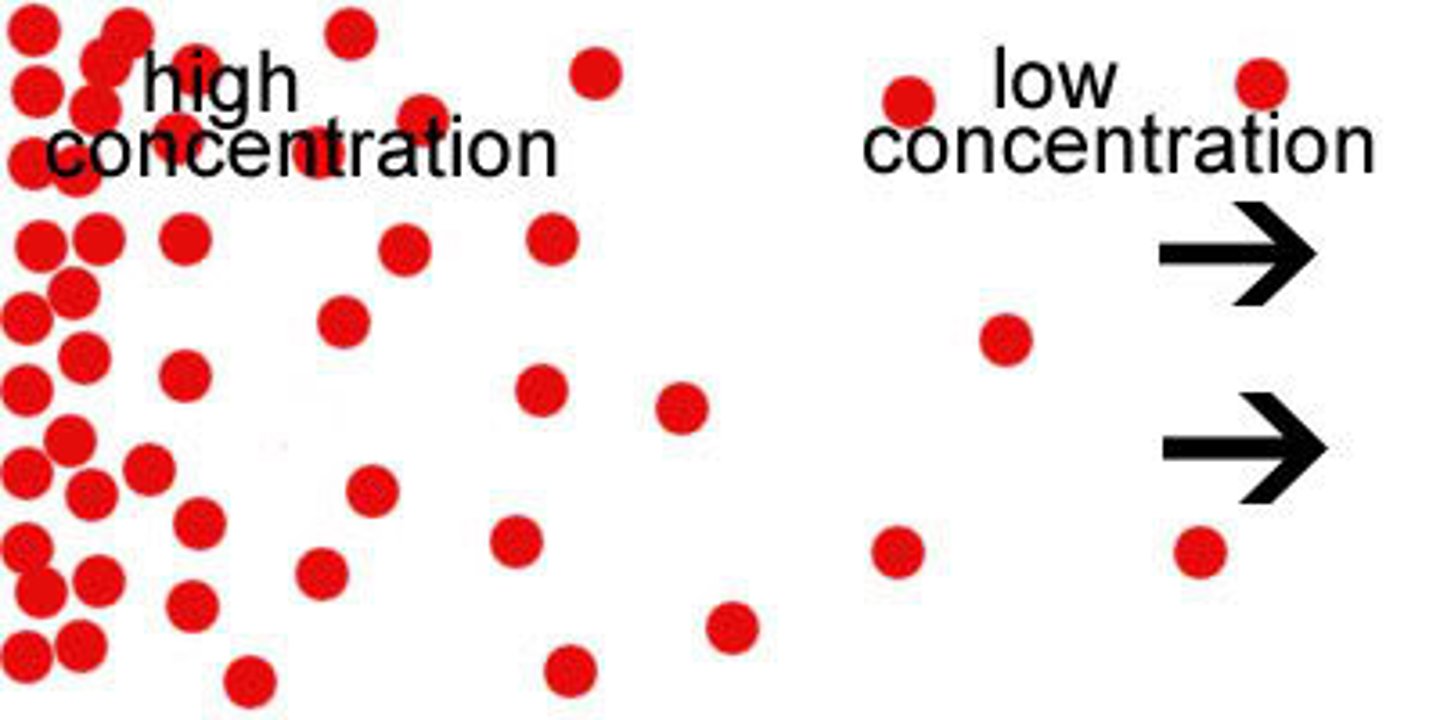
Concentration
the spread of something over a given area (ex: clustered or dispersed)
Assimilation
the social process of adopting most or all of the cultural traits of another cultural group (possible at the group or individual level)

Acculturation
the social process of adopting some of the cultural traits resulting from the meeting of two groups - both groups may change but both retain two distinct cultures

Syncretism
the blending of cultural traits from two or more different groups into a new culture

Diffusion
the process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
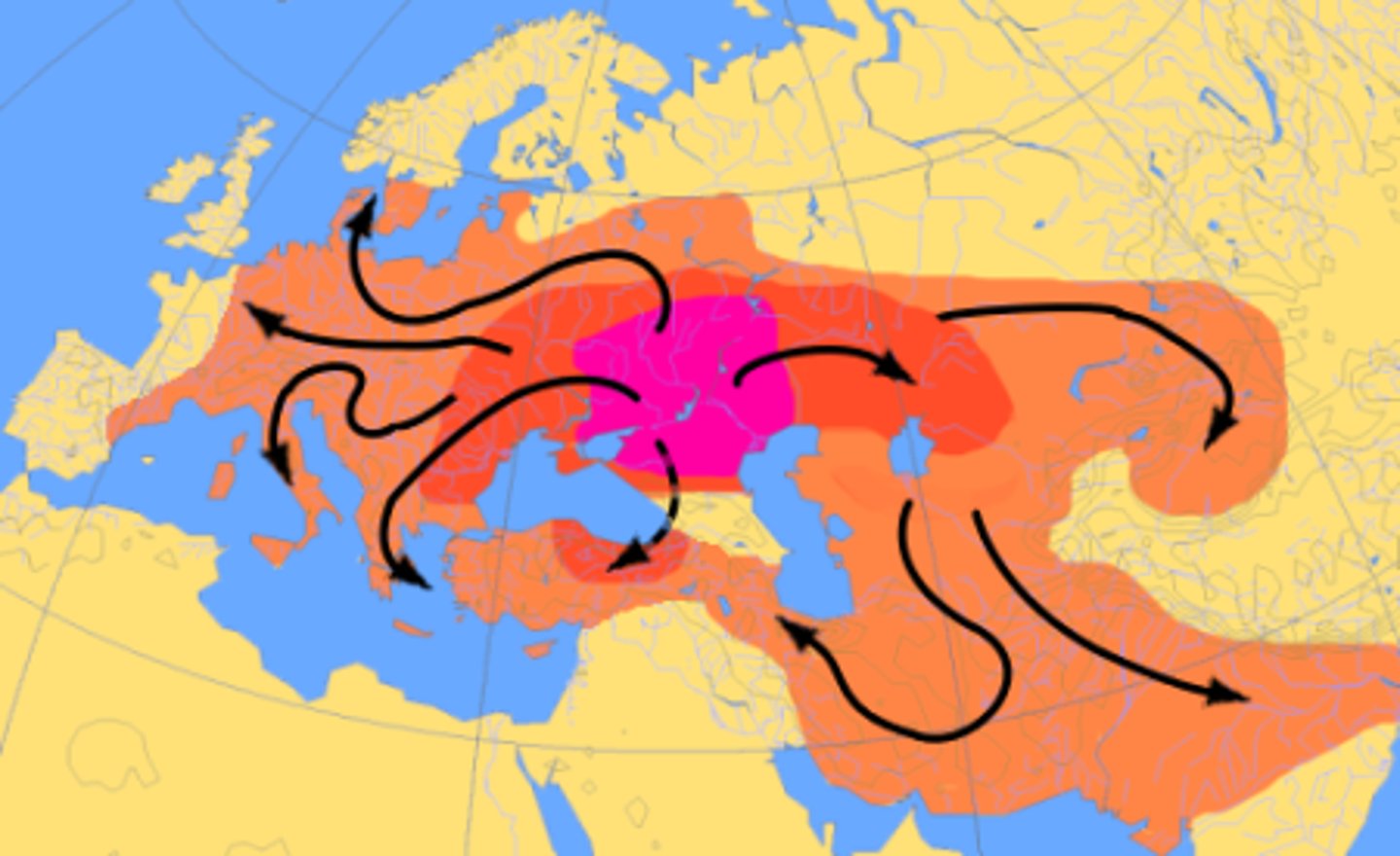
Hearth
a place from which an innovation originates
Relocation Diffusion
the spread of an idea or cultural trait through physical movement of the people with the idea or trait from one place to another

Expansion Diffusion
the spread of an idea or cultural trait from one place to another by other people adopting the idea or trait - there are three kinds

Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of an idea or innovation by passing first among the most connected places or peoples (i.e. only certain people get it)
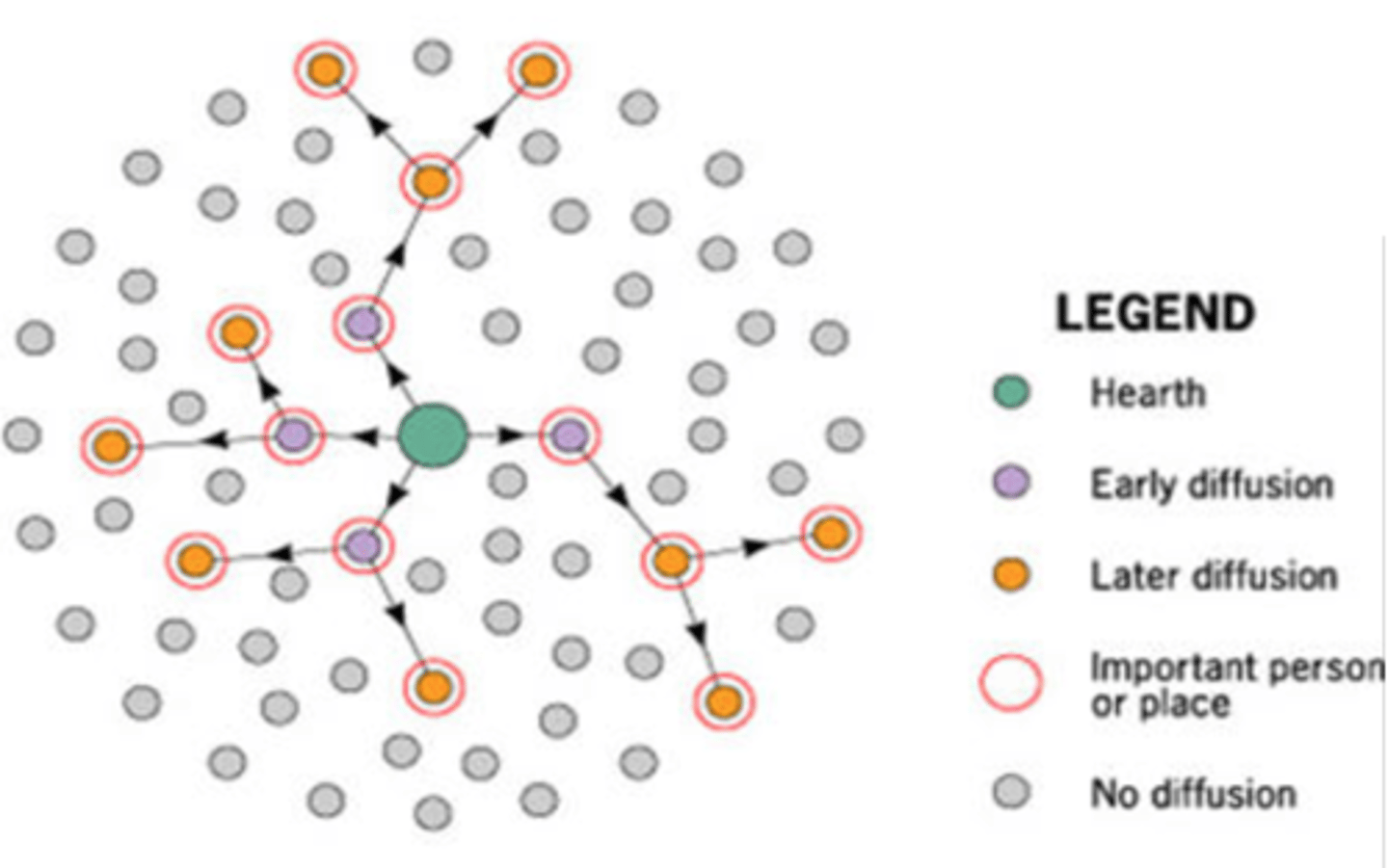
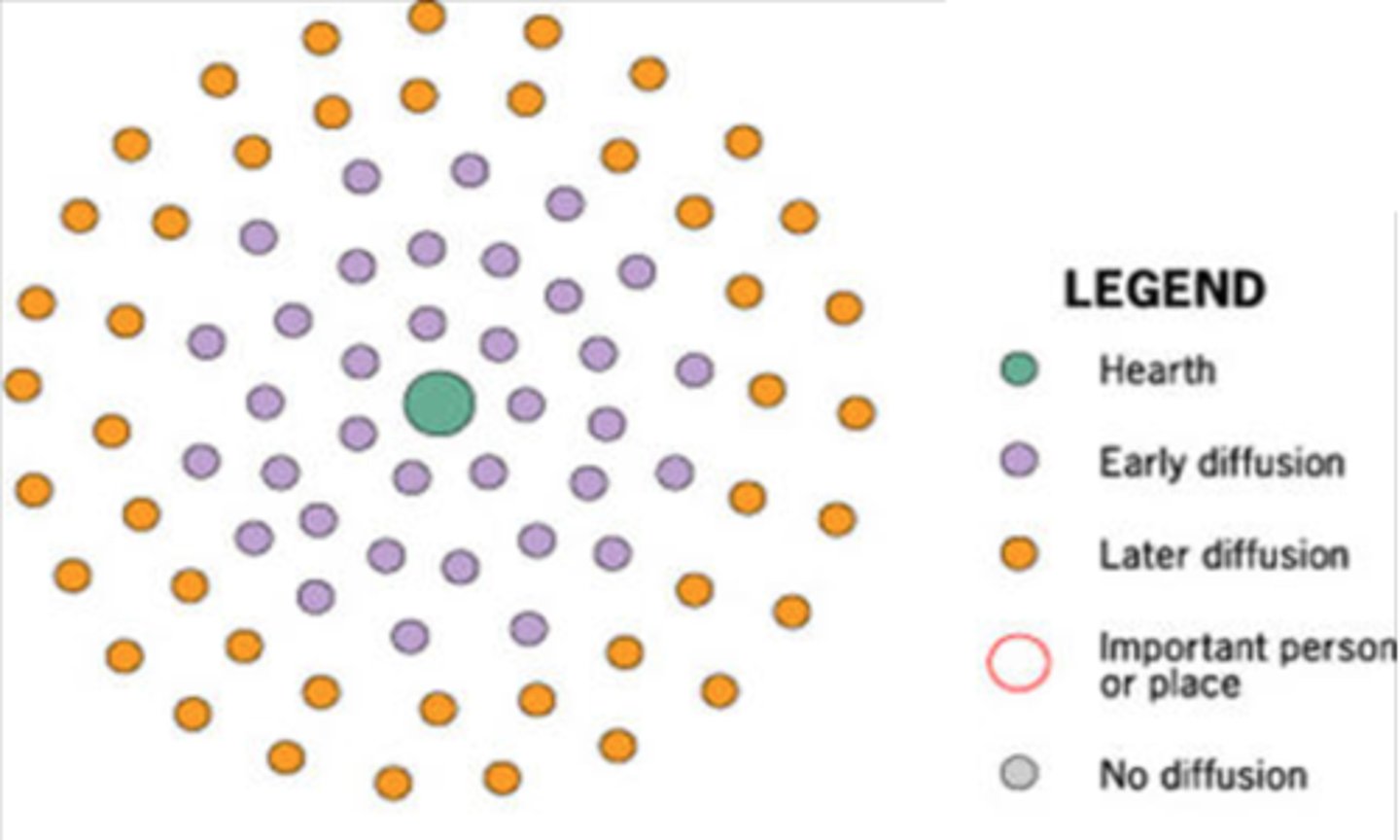
Contagious Diffusion
the rapid, widespread diffusion of an idea or innovation throughout the population
Stimulus Diffusion
the spread of an underlying principle of an idea or innovation, even though the specific idea or innovation itself fails to diffuse

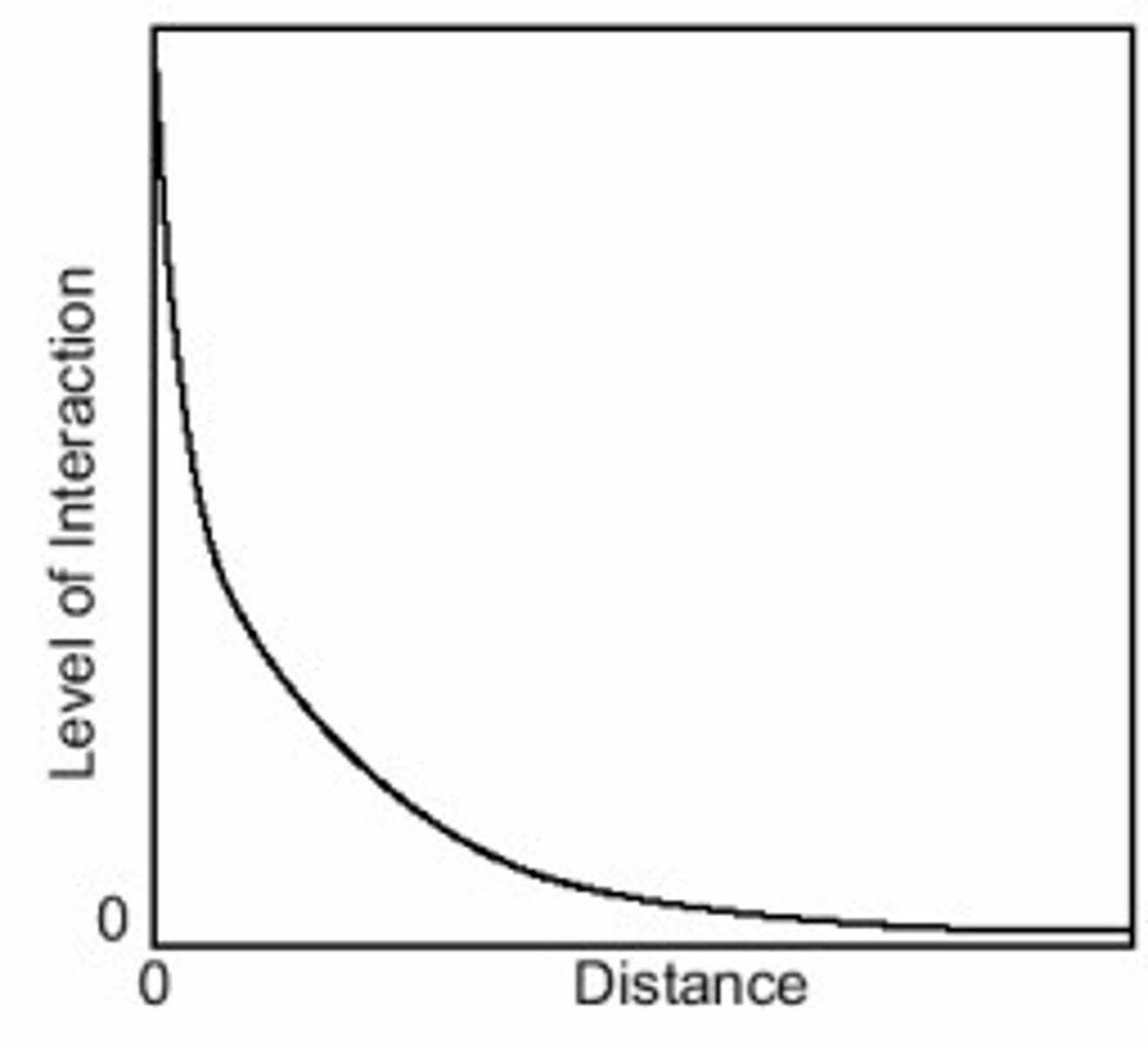
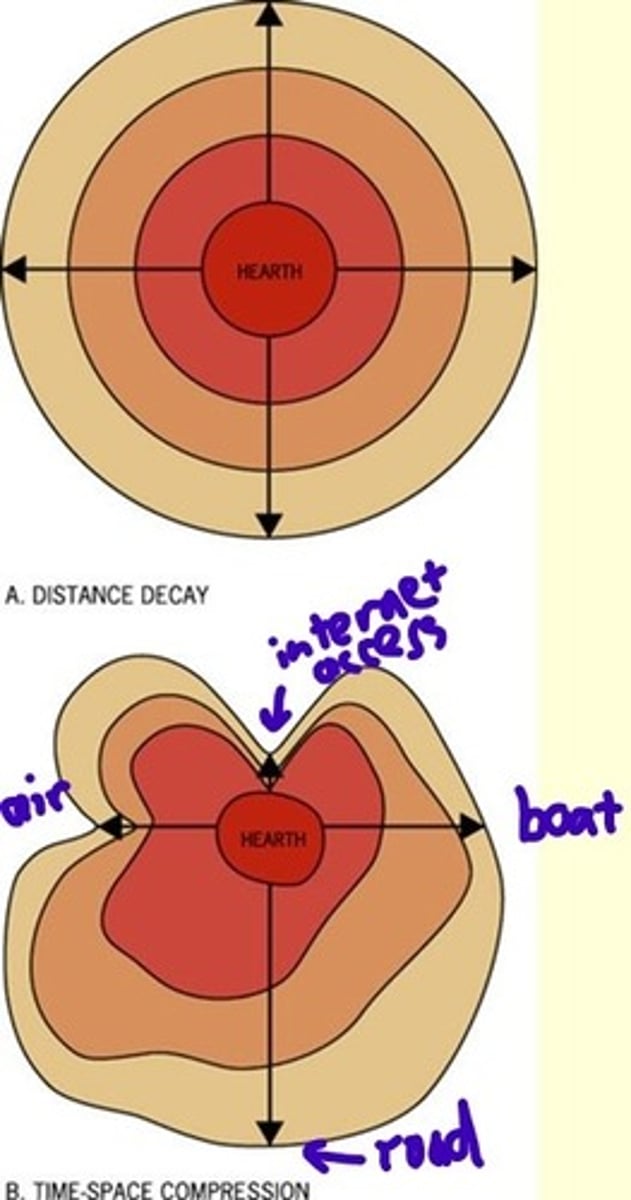
Distance Decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction
Time Space Compression
the uses of communication and transportation technology innovations that decrease the impact of distance and increases the connectivity between people and places
Sustainability
the use of Earth's natural resources in ways that ensure their availability in the future (do not deplete nonrenewable resources, do not destroy renewable resources through pollution or overuse)

Conservation
the concept that humans should consume renewable and nonrenewable resources at a less rapid rate (consume less = more for future generations)

Preservation
The maintenance of resources in their present condition, with as little human impact as possible

Cultural Ecology
the geographic study of human-environment relationships

Environmental Determinism
the theory that the physical environment of a place causes the social development and actions of the people living in that place

Possibilism
the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives

climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time

Culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next

Distance Decay
the effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions;
the interaction between 2 locations declines as the distance between them increases
Geospatial
relating to or indicating data that is associated with a particular location on Earth's surface

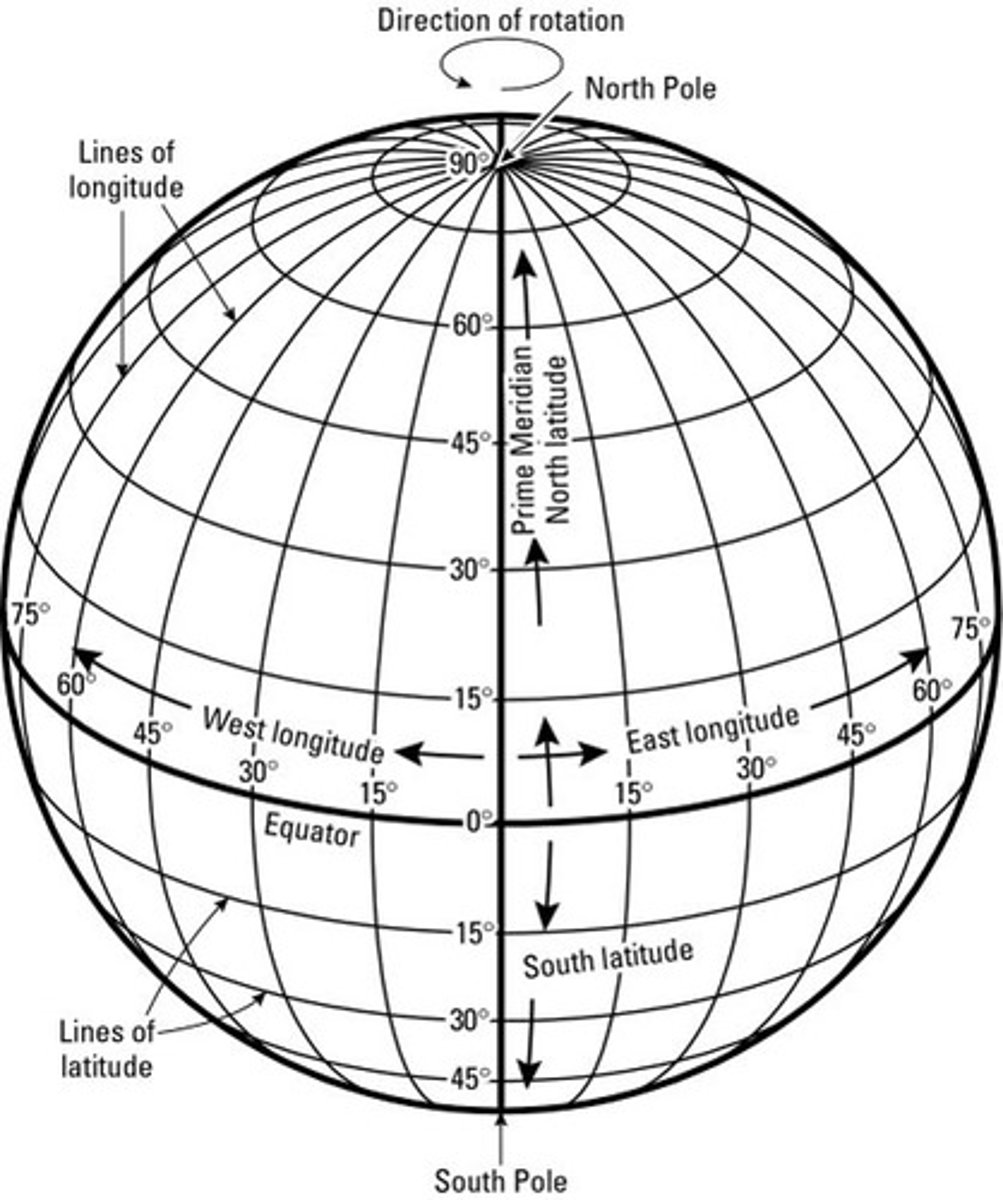
global grid
the system of imaginary lines (called parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude) used to divide the surface of Earth on maps and globes
field experience
research that occurs outside a classroom or institution, "in the field" or place that the research pertains to

mashup (map)
map that overlays different data sets on top of one another
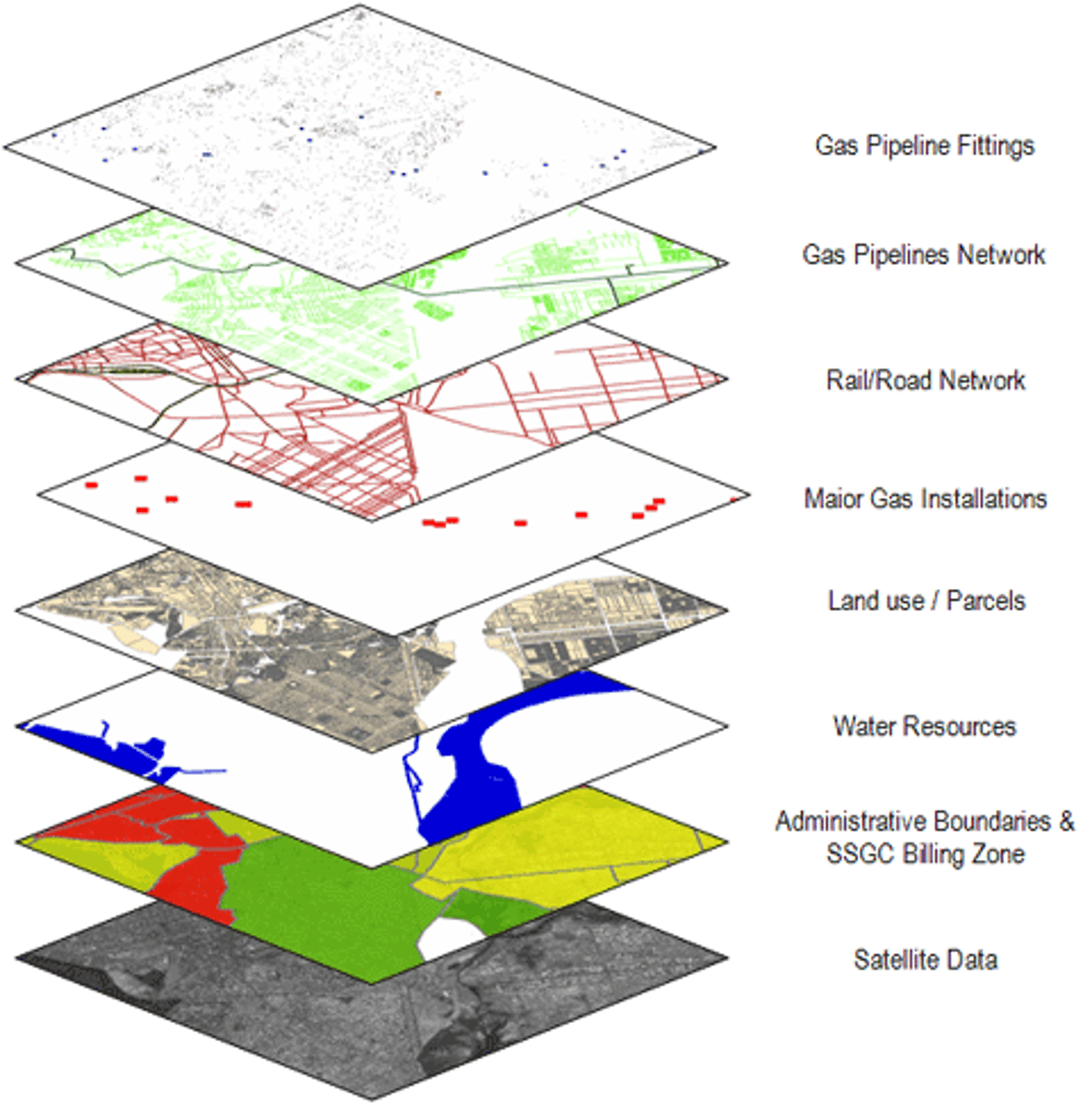
Network
a connection of multiple things across space (EX: roads connecting cities)
sense of place
State of mind derived through the infusion of a place with meaning and emotion by remembering important events that occurred in that place or by labeling a place with a certain character.

Spatial Association
the degree to which things are similarly arranged in space. If the distributions are similar, then the spatial association is strong, and vice versa.
spatial interaction
the movement of peoples, ideas, and commodities between different places
Visualization
Use of sophisticated software to create dynamic computer maps, some of which are three dimensional or interactive.