BIO- The Tissue Level and Histology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Working Distance
Space between lens and table
Fine adjustment
only used on high power
Course adjustment
used on scanning and low power
Parfocal lens
a lens that stays in focus when magnification or focal length is changed
DOF (depth of field)
the amount of depth (layers of specimen) seen with a specific objective lens
FOV (field of view)
The amount of area seen with a specific objective lens. (Decreases with increasing magnification)
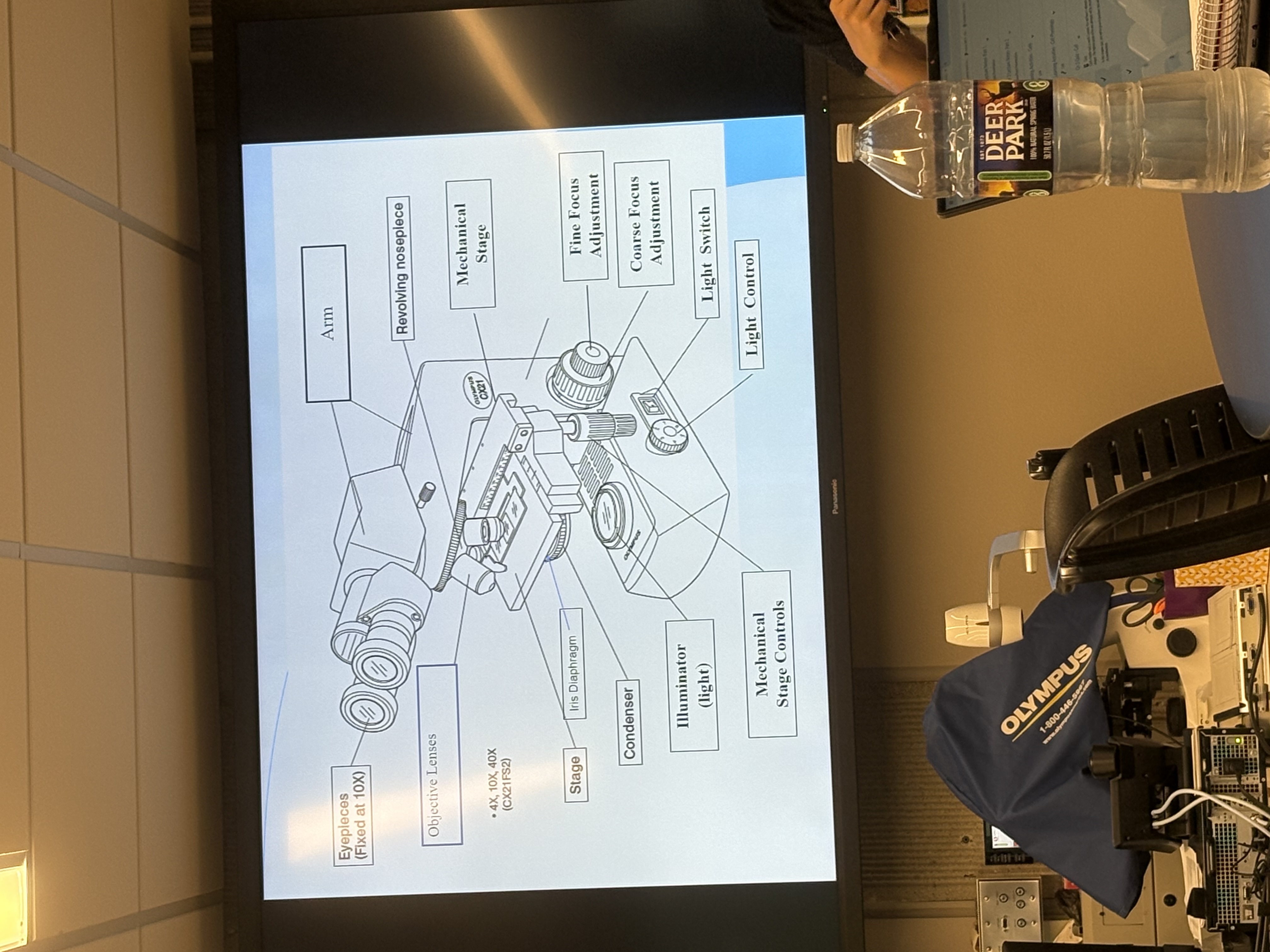
Identify parts of microscope
Epithelial Tissue
Lines body cavities, cover organs.
Connective Tissue
Connects tissues to each other, connects skin to muscle.
Muscular Tissue (Cardiac)
Pumps blood
Smooth muscle tissue
lines digestive system, helps things move.
Skeletal muscle
Connects to skelton, muscle pulls on bones and helps movement, contracts and relaxes.
Nervous tissue
Consists of neurons and sends signals. Found in nervous system organs such as the brain and spinal cord as well as nerves.
Apical surface
top
Basement membrane
bottom
Regeneration
easily undergoes mitosis for replacement and repair
High mitotic rate
cell division
Endocrine glands
produce hormones
Exocrine glands
non-hormonal
Tight junctions
prevent substances from passing between cells
Desmosomes
(Strong) Hold cells together with the assistance of intermediate filaments
Gap junctions
Allow substances to move through cells
Simple
One layer. (Easy for substances to move through)
Stratified
Many cell layers. (Difficult for substances to move through, designed for protection.)
Squamous
flat cells
Cuboidal
cube shaped cells
Columnar
tall, thin cells
Simple Squamous
Lines blood vessels, found in kidneys and lungs. Cover organs, lines cavities (serous membranes). Allows diffusion. Produces serous fluid. Promotes gas exchange.
Simple Cuboidal
Found in glands, ducts and kidney tubules. Involved in secretion and absorption of nutrients and ions. Allows movement of chemicals across wall.
Simple Columnar
Lines GI tract (stomach to large intestine). Involved in secretion of digestive enzymes and absorption of nutrients.
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Lines respiratory tract (lungs, nasal cavity, trachea). Allows production of mucus and movement of mucus by cilia.
Stratisfied Squamous
Skin, lining of oral cavity, throat, and esophagus (rectum, anus, and vagina). Provides protection and withstands abrasion.
Transitional
Urinary bladder, ureters. Allows organ distention. When stretched appears small and compressed, when empty appears expanded.
Connective Tissue
cells spread out, much extracellular space, different types of cells.
Collagen
sturdy, won’t tear
Reticular
smaller & branching
Elastic
stretch & recoil
Dense regular connective tissue
Skin. Collagen fibers arrange in one direction with fibroblasts. Found in tendons and ligaments.
Dense irregular connective tissue
Tendons. Dermis of skin, collagen fibers, shaped irregular.
Areolar loose connective tissue
Fills space in body, wraps organs. Holds and conveys fluid for damaged areas. Protects and cushions.
Adipose loose connective tissue
Under layers of skin, around organs. Cushions, insulates, stores lipids.
Hyaline Cartilage
Between articulating bones. Provides flexible support and reduces friction.
Elastic cartilage
External ear, epiglottis. Supports with tremendous flexibility.
Mucous membrane
produce mucous. underneath is areolar connective tissue.
Serous membrane
lines body cavities that are not open to the exterior of the body. produces serous fluid. lubricates organs.
pleural
lungs
pericardial
heart
peritoneum
abdomen
visceral
directly to organ
parietal
along wall
cutaneous
dry membrane. synovial membrane articulating joints of the limbs.
Stratum corneum
outer layer of skin. (dead skin)
stratum granulosum
layer of skin. keratin and kertohyalin, cells dehydrate.
stratum spinosum
spiny layer of skin, some cell division
stratum basale
germinative layer of skin, mitosis occurs, new cells created
stratum lucidum
only in thick skin. translucent layer.
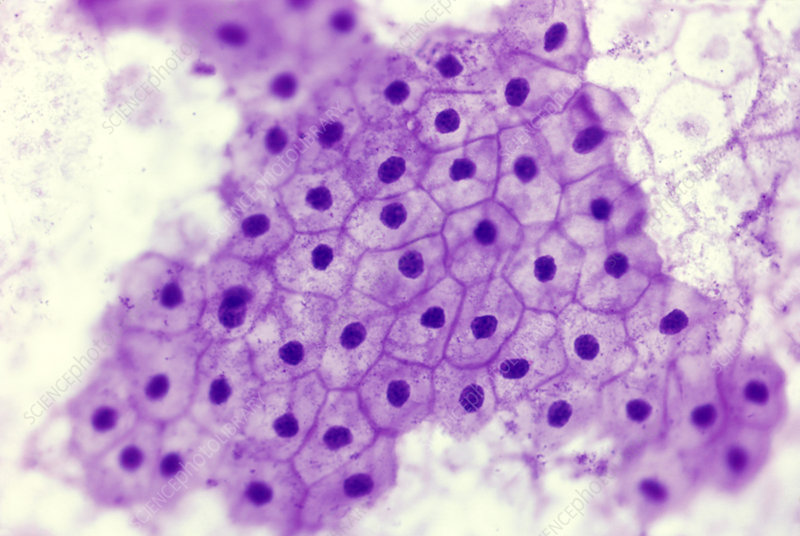
Simple Squamous Epithelium
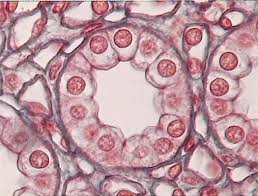
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
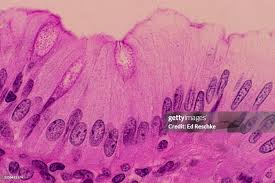
Simple Columnar Epithelium
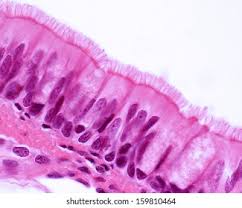
Pseudostratisfied Ciliated Epithelium
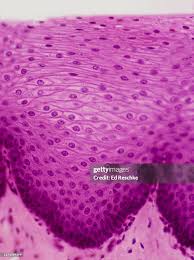
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
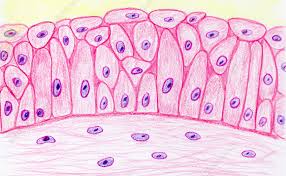
Transitional Epithelium
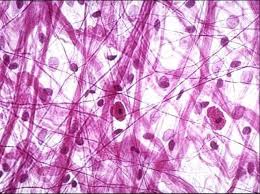
Areolar Connective Tissue
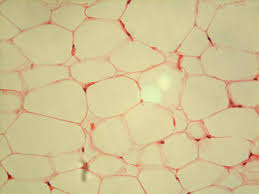
Adipose Connective Tissue

Dense Regular Connective Tissue
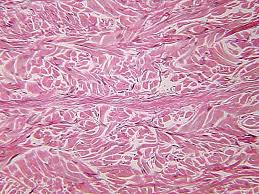
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
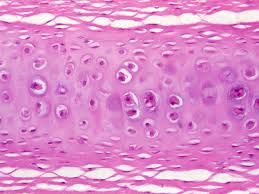
Hyaline Cartilage
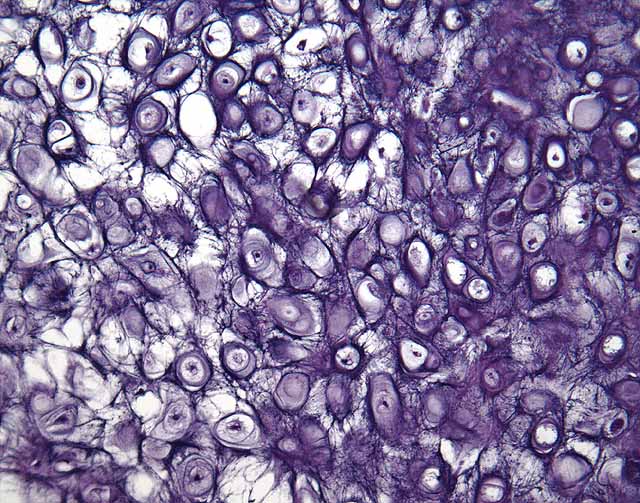
Elastic Cartilage
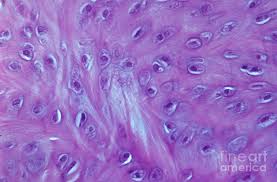
Fibrocartilage

Bone