AP World History: Chapter 7
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1200 Update Ways of the World with Sources for the AP® Modern Course Book by Eric Nelson and Robert W. Straye
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Which of the following is an example of how Mughal India handled religious differences in the early modern era?
d. Akbar formulated a state cult that combined elements of Islam, Hinduism, and
Zoroastrianism.
What facilitated the spread of the Protestant Reformation in Europe?
b. The printing press
What did the New England Puritans in North America emphasize?
c. Education and a sense of civic responsibility
Which group had the greatest success in converting people outside Europe to Christianity?
b. Spanish missionaries in the Philippines
Which of the following were the most intent on converting native peoples to their religion?
b. Catholics
Which of the following was a goal of the Wahhabi movement?
a. To return to what was considered the pure faith of early Islam
Which of the following is a principle or practice upheld in Sikhism?
c. Equality of men and women
Scholars have identified which of the following as a key factor that contributed to the Scientific Revolution in Europe?
a. The relative independence of European universities
Which of the following describes a feature of the syncretic religions of African slave
communities in the New World?
d. The identification of West African deities with Catholic saints
Wang Yangming in his view of Confucianism
c. argued that individuals could find their own path to virtue and salvation.
Which of the following represents a form of Hinduism that shared features with mystical Sufi forms of Islam?
b. The bhakti movement
In what way did nineteenth-century developments in the sciences depart from Enlightenment principles?
a. They emphasized conflict and struggle as the motors of progress.
Why did Sikhism evolve from a peaceful religion into a militant community?
d. Sikhs had to defend themselves against both Mughal and Hindu hostility.
How was the Enlightenment related to the Scientific Revolution?
The Enlightenment applied the idea of natural laws to human affairs rather than the
physical universe.
Which of the following describes the reception of modern European science in China, Japan, and the Ottoman Empire during the early modern era?
c. Selective adoption of European scientific learning
What made Martin Luther's Ninety-Five Theses revolutionary?
b. The idea that an individual could find salvation by faith alone
How did the Peace of Westphalia seek to settle religious differences?
It granted the ruler of each European state the authority to control religious affairs within his own domain.
What factor made some parts of the world more receptive to Christianity than others?
a. The absence of a literate world religion
Why did the Chinese imperial court initially welcome the Jesuit missionaries?
c. The Jesuits' knowledge in mathematics, astronomy, technology, geography, and mapmaking was useful to the Chinese.
Which of the following marked a major turning point in the relationship between China and Christian missionaries?
b. The pope's claim of authority over Chinese Christians
What similar feature did Andean Christianity and Mexican Christianity share?
d. Both reinterpreted Christian practices within the framework of local customs.
During the centuries between 1450 and 1750, the spread of Islam was usually the
a. work of Muslim holy men, scholars, and traders.
What did the kaozheng movement in China emphasize?
Verification, precision, accuracy, and rigorous analysis in all fields of inquiry
Europeans who participated in the Scientific Revolution placed value on knowledge that was acquired through
b. rational inquiry based on evidence.
The early scientists in the Scientific Revolution
viewed science and religion as compatible
Which of the following did all Enlightenment thinkers share?
c. The belief in progress and reason
Which of the following was a reaction against too much reliance on human reason during the eighteenth century in Europe?
a. Romanticism
Which of the following reflects the Enlightenment view of the innate qualities of the individual?
d. Thoughtful, rational, and independent
Which of the following figures is associated with the Scientific Revolution?
b. Newton
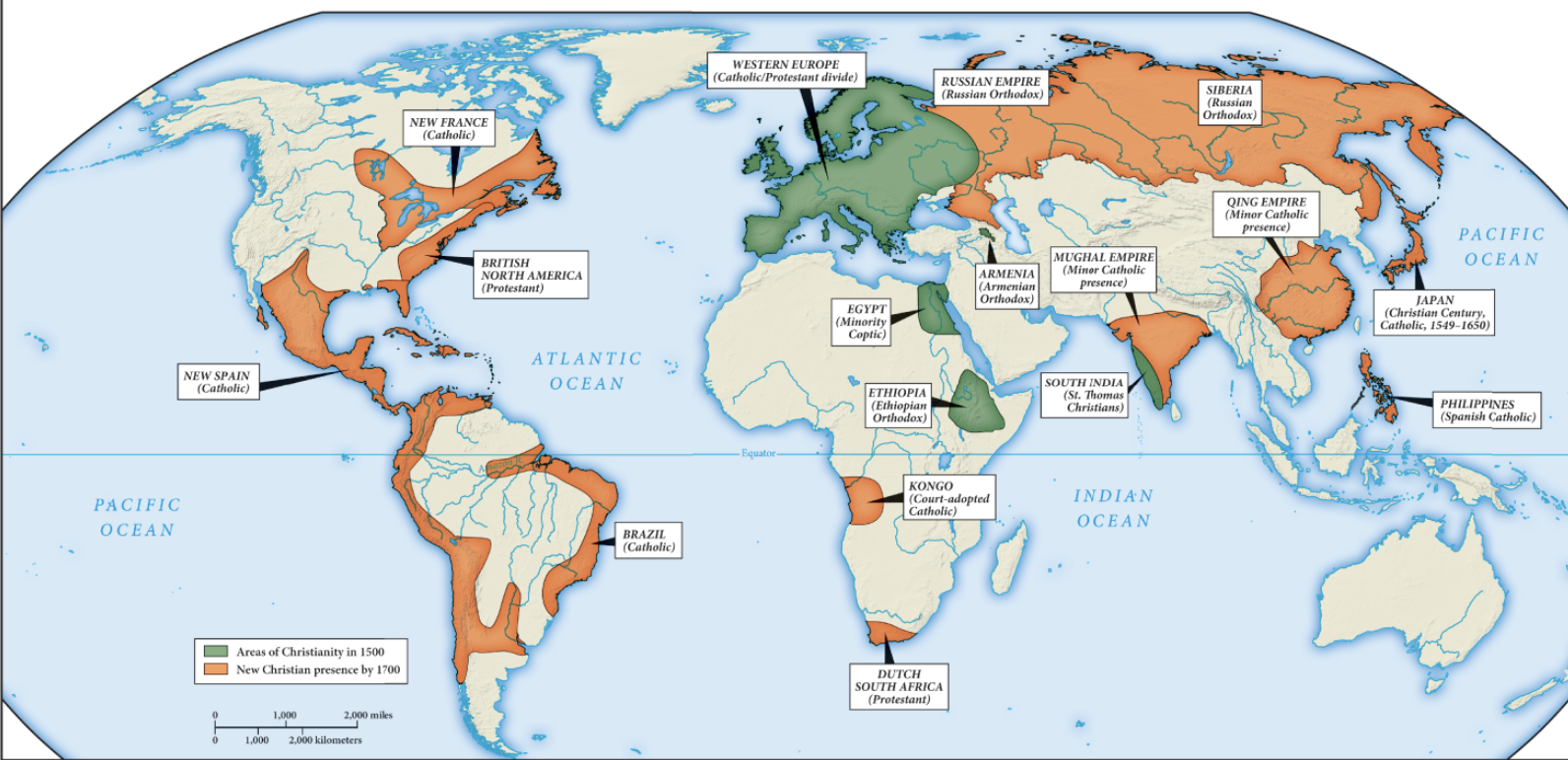
Refer to Map 7.2 in the textbook. In which country was the spread of Christianity in the early modern era not accompanied by European conquest?
a. Japan
According to Map 7.1, "Reformation Europe in the Sixteenth Century," which of the
following was the dominant faith in north-central Europe?
d. Protestant
Based on Map 7.1, "Reformation Europe in the Sixteenth Century," after its founding, in
which direction did the Protestant faith predominantly spread?
North
Which of the following is true regarding the symbolic importance of the map of China being held by the two Jesuits in this illustration?
a. It was due to their mapmaking skills that Jesuits were first welcomed by Chinese elite.
According to Map 7.2, "The Globalization of Christianity," in which of the following
regions was Christianity most prevalent prior to the year 1700?
c. Europe
According to Map 7.1, "Reformation Europe in the Sixteenth Century," in which of the
following regions did the Protestant Reformation begin?
a. Saxony
how did Catholic Spanish and Portuguese view their movement overseas ?
as a continuation of a long crusading tradition that only recently had completed the liberation of their countries from Muslim control

According to map 7.2 Where did Protestants establish overseas colonies?
Egypt, Ethiopia, anf south India
Romanticism
an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement in Europe from the late 18th to the mid-19th century that reacted against the Age of Enlightenment's emphasis on reason and order
How did Protestants react to indigenous people
They did not show much interest in converting native peoples but sought rather to push them out of their ancestral territories
How did Catholics react to indigenous people
They actively spread the Christian message beyond European communities.
Where did Portuguese missionaries take lead
.Africa and Asia
Where did Spanish and French missionaries take lead
.Americas
Europeans saw their political and military success as a
demonstration of the power of the Christian God.
Why was there a high cost for Latin women to cover to Catholisism
Many women who had long served as priests, shamans, or ritual specialists had no corresponding role in a Catholic church, led by an all-male clergy.
Taki Onqoy (dancing sickness)
traveling dancers and teachers predicted that an alliance of Andean deities would soon overcome the Christian God, inflict the intruding Europeans with the same diseases that they had brought to the Americas, and restore the world of the Andes to an imagined earlier harmony
Cofradias
church-based associations of laypeople,
who is the fiscal
leader of the church staff, was a native Christian of great local prestige who carried on the traditions and role of earlier religious specialists.
How did Jesuits present Christianity to Chinese
pointing out parallels between Confucianism and Christianity rather than portraying Christianity as something new and foreign.