Grade 12 Biology
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Macromolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Polymer
Long chains of repeating subunits
Monomer
small molecule that may react chemically to link with other, similar molecules.
Anabolic reaction
produces large molecules by joining smaller subunits
Catabolic Reaction
Large molecules are broken into smaller subunits
Condensation Reaction
The formation of an H2O molecule when 2 subunits are chemically joined (also called dehydration)
Hydrolysis Reaction
Involve the incorporation of an H2O molecule when a large molecule is broken into 2 subunits
Isomer
Molecules with the same formula but different structures
Maltose
Formed by the condensation of 2 a-glucose molecules, resulting in an a 1-4 linkage
Sucrose
Composed of a-glucose and a-fructose with an a 1-2 linkage
Amylose
An unbranched a-glucose polymer held together by a 1-4 glycosidic linkages
amylopectin
a branched a-glucose polymer composed of a main chain with glucose molecules attached by a 1-4 glycosidic bonds and branch points formed by a 1-6 glycosidic linkages
glycogen
Structurally similar to amylopectin. a 1-4 linkages between a-glucose monomers in the main chain and a 1-6 linkages at the branch points. It's more highly branched than amylopectin.
glycerides (fats)
Contain 1, 2 or 3 fatty acids connected to a glycerol with an ester linkage
phospholipid
Polar phosphate group in the head (hydrophilic)
Non-polar fatty acid tails (Hydrophobic)
Joining amino acids to form polypeptides
Amino acids are joined together by ribosomes in condensation reactions and form a peptide (amide) bond
Primary protein structure
Sequence of a chain of amino acids
secondary protein structure
Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes the amino acids to fold into a repeating pattern
Tertiary protein structure
3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
Quaternary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain.
Only some proteins have a quaternary structure - if they're composed of more than one protein structure
Homeostasis
cells maintain a constant internal environment even with external changes
Passive transport
transport without energy expenditure
Diffusion
Substances move from high to low concentration
Facilitated Diffusion
Proteins help in the diffusion process
Carrier protein
Change shape to allow large, uncharged molecules to enter
channel proteins
tunnel shape allows charged particles to enter
Osmosis
DIffusion of water across a membrane
Hypotonic Solution
Higher water concentration outside, enters the cell and causes it to lyse
Hypertonic solution
Lower water concentration outside, water leaves cell and causes it to be flaccid
isotonic solution
Same concentration in and out of the cell
Thylakoid
tiny compartments found inside of chloroplasts
Lumen
The inside of the thylakoid. Light energy is converted into chemical energy
Stroma
connects the thylakoid
Chloroplast
The organelle that contains pigment molecules and enables plants to capture some solar energy and convert it into chemical potential energy
Granum
Stacks of thylakoid
Mitochondria
The organelle in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur. Has a double membrane
Matrix
The innermost part of the mitochondria, surrounded by the membrane. Where metabolic processes
Christae
Inner folds of the mitochondrial membrane that increase its surface area
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate. Made of adenine, a ribose, and 3 phosphates
NAD+
Nicotinamide adenide dinucleotide
FAD
Flavin adenide dinucleotide
Acetyl Co-A
Acetyl coenzyme A
Transforming principle
The factor that changes the phenotype - some unknown heritable substance from dead S cells changed the genetic makeup of the R- strain (GRIFFITH)
Double Helix
The structure of DNA. 2 intertwined strands of nucleotides form the basic structure of the genetic material
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
A polymer composed of 2 polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix
Ribonucleic Acid
Single-stranded nucleic acid. Like DNA but has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymene
Nucleotide
Composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose base (ribose/deoxyribose) and a phosphate group
Pyrimidine
Nucleotides with a single ring structure (thymene and cytosine)
Purine
Nucleotides with a double ring structure (adenine and guanine)
Adenine
A nucleotide base that is complementary to thymine (uracil in DNA)
Thymene
a nucleotide base that is complementary to adenine
Uracil
A nucleotide base in RNA that is complementary to Adenine
Cytosine
a nucleotide base that is complementary to guanine
Guanine
A nucleotide base that is complemetary to Cytosine
phosphodiester bond
The type of bond that links the nucleotides in DNA or RNA. joins the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide
glycosyl bond
a type of ether bond that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group
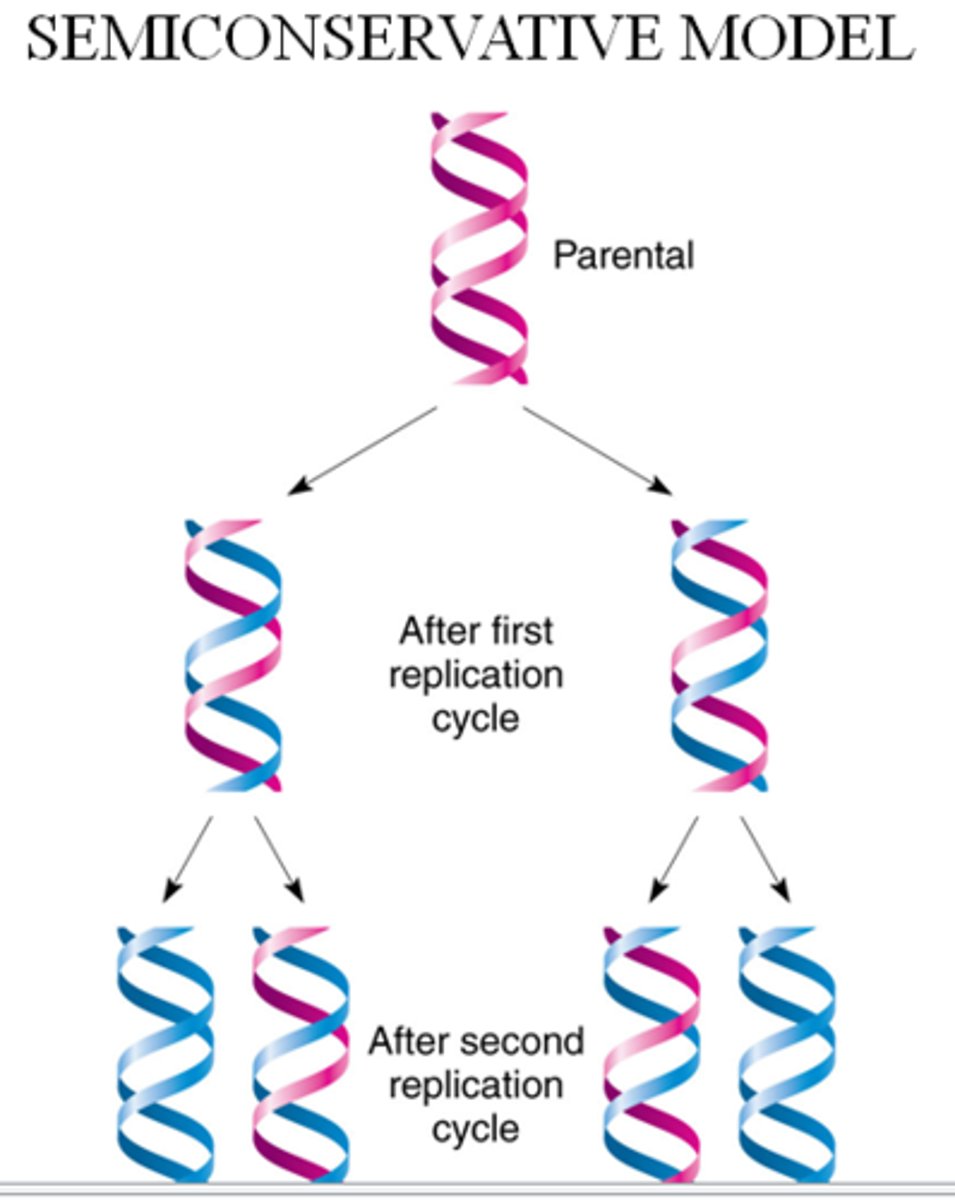
semi-conservative replication
The process where a new DNA double helix is created using 1 original strand and 1 newly synthesized strand
transcription
The conversion of information from 1 'language' (DNA), to another (protein made of amino acids)
Translation
Decodes mRNA into amino acids, which form proteins
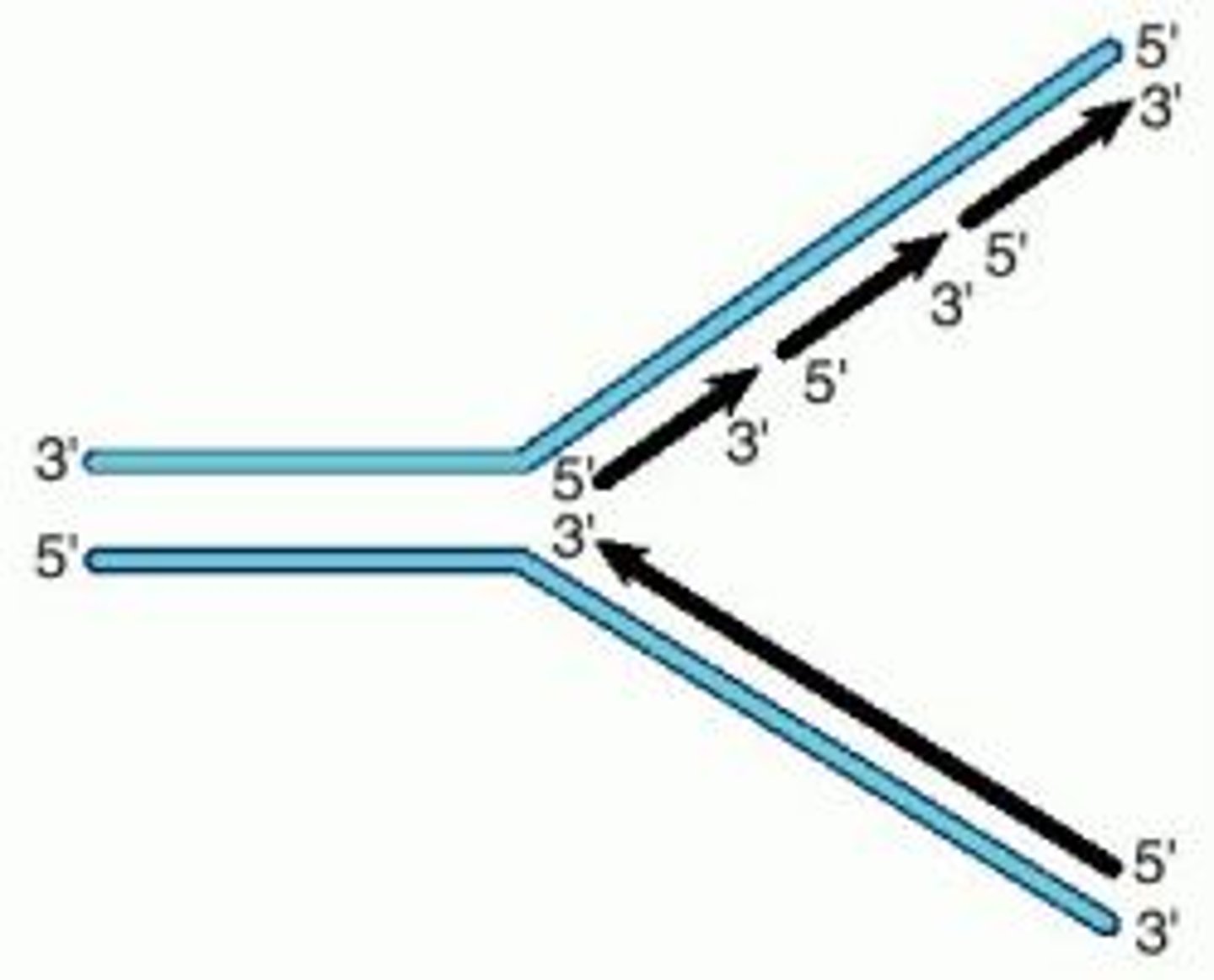
Replication fork
Y-shaped structure that forms during DNA replication. The DNA molecule is unwound, and the 2 parental strands are separated
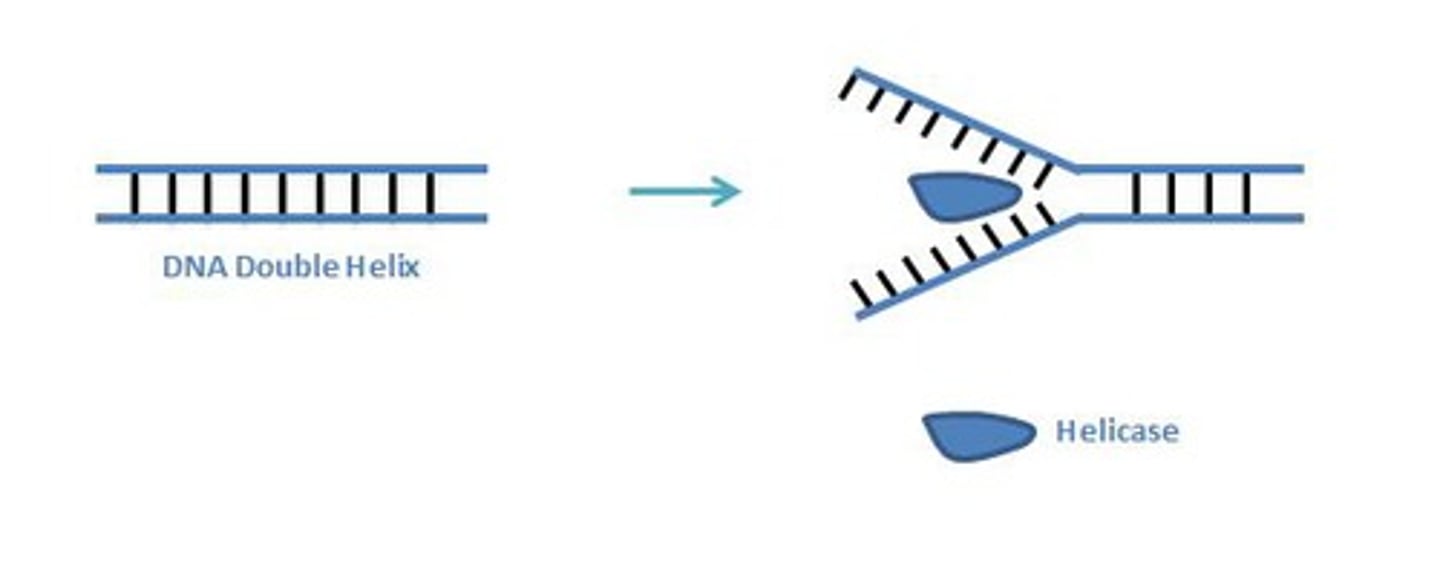
Helicase
Unwinds DNA by disrupting hydrogen bonds
Gyrase
Keeps the DNA steady when it's being unwound and replicated
Single-strand binding proteins
SSB's keep separated strands of DNA apart
DNA Polymerase III
Adds complementary nucleotides in the 5' - 3' direction. Use RNA primers as starting points
DNA polymerase 1
Fills gaps in DNA that occue during replication
Ligase
Joins fragments by creating phosphodiester bonds
Primase
The enzyme that builds RNA primers
Primer
Starting point for DNA synthesis
Okazaki Fragments
short fragments of DNA that are the result fo the synthesis of the lagging strand during DNA replication
Spliceosome
The enzyme that cuts introns and reconnects exons to produce an mRNA transcript, which is now ready to leave the nucleus and be translated into protein
5' cap
protects the mRNA from digestion by nucleases and phosphates as it exits the nucleus and helps initiate translation
poly A tail
a strand of ~200 adenine bases are added to the 3' end for the same reason as the 5' cap
Promoter
Indicates to RNA polymerase where the beginning of the gene is and on which strand it's located
Transcription bubble
Temporary local unwinding of DNA during transcription
RNA polymerase
an enzyme that synthesyzes RNA from the DNA template during transcription
Template strand
Strand that is transcribed
Coding strand
Strand that is not transcribed
Glycolysation
Sugars are added to amino acid residues
Phosphorylation
phosphates are added to amino acid residues
epigenitics
Study of how an organism's behaviours and environments can affect the way it's genes work
Housekeeping Genes
Genes that are always turned on because they are needed for vital life functions in organisms
Operon
A cluster of genes (a segment of DNA) under the control of 1 promoter and 1 operator in prokaryotic cells. Turn genes on/off
Repressor
A protein that inhibits the expression of 1 or more genes, turning them off to reduce their activity
Co-repressor
a protein that interacts with a repressor protein to enhance its ability to inhibit gene transcription
Mutation
Sudden, random change in a gene, or unit of hereditary material (DNA), that can alter an inheritable characteristic. Can have positive or negative, or no effect on an organism.
point mutation
Mutations at a specific base pair in the genome (affect only 1 base). Caused by substitutions, where 1 base is replaced by another base.
silent mutation
mutation that doesn't change amino acids due to redundancy in the code.
Missense mutation
results in a change in the amino acid sequence
Nonsense mutation
a mutation that causes a stop codon to form
frameshift mutation
A mutation that changes the reading frame of the codons
Translocation Mutations
Transfer of a fragment of DNA from one site in the genome to another location. Can disrupt the normal function and structure of the genes
Anticodon
The three-base sequence at the bottom of the tRNA, which is complementary to a codon
Cytoplasm
Where glycolysis takes place