IB Biology - Carbohydrates and Lipids B1.1
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Covalent bond
sharing of a pair of electrons between 2 adjacent atoms
The amount of bonds carbon atoms can form
4
Macromolecules
Molecules composed of large number of atoms
Main classes of macromolecules in living organisms
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
How are macromolecules made
By linking subunits (monomers) into a chain (polymer)
Condensation reaction
Chemical process that links a monomer onto the end of a polymer by removing a hydroxyl group (OH) and a hydrogen (H)
What is created during a condensation reaction
a construction of a macromolecule, removal of a simpler molecule (H2O)
Glycosidic bond
the bond resulting from condensation reaction in carbohydrates
Is energy required for the production of macromolecules? What energy?
Yes. ATP.
Disaccharide + Examples
2 monosaccharides linked together through a glycosidic bond. Lactose, sucrose, maltose
Polysaccharide + Examples
Chain of monosaccharides. Glycogen, starch, cellulose
Glucose
Monosaccharide used to make the polysaccharides glycogen, starch, and cellulose
Structure of glucose
1 hydroxyl group (OH) and 1 hydrogen (H) attached to the first Carbon. 6 carbons total. Approximate formula: (CH2O)n
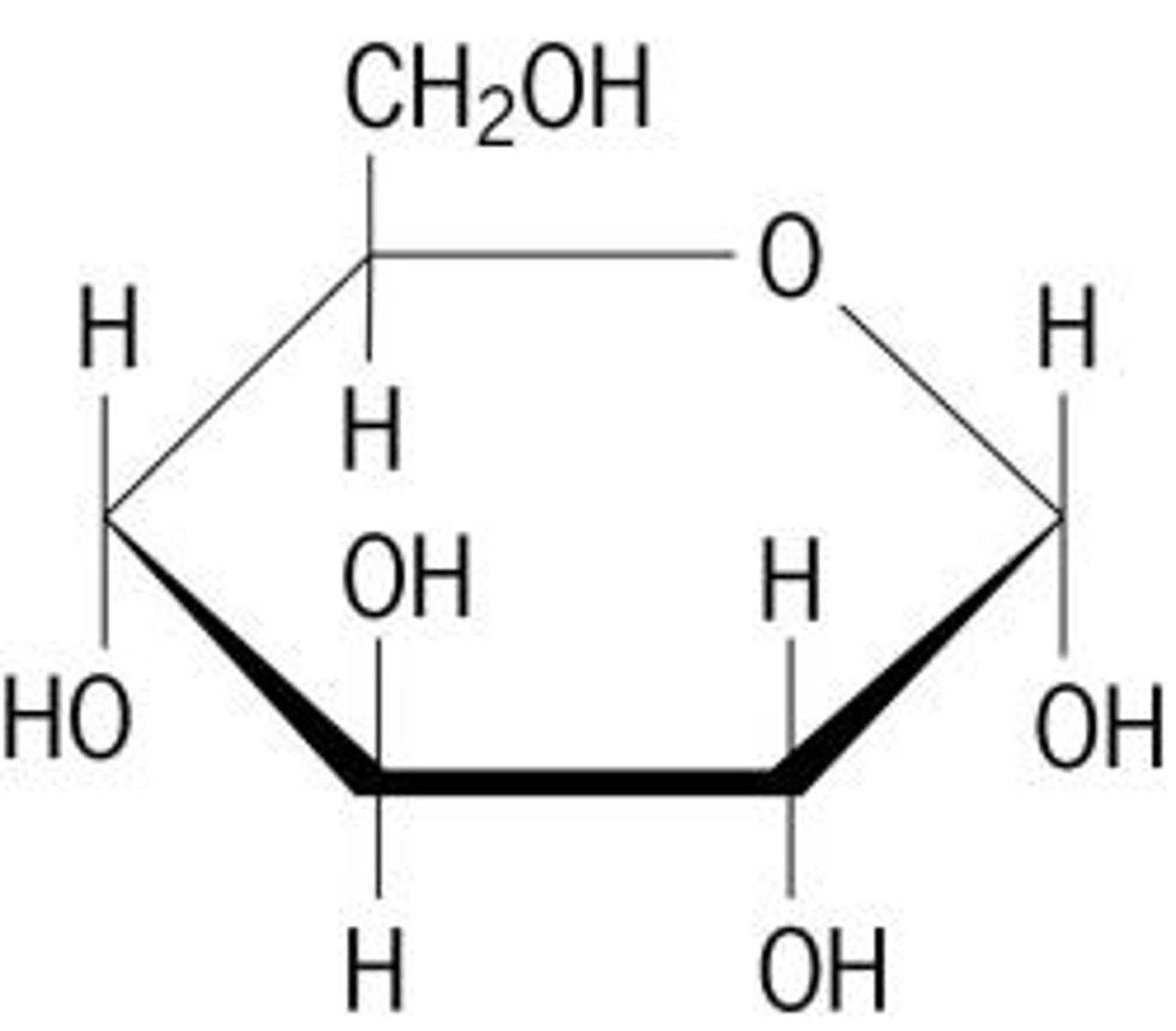
Glucose features?
Soluble in aqueous soulutuons: polar + hydrophillic (easy transport)
Chemical stability: strong covalent bonds- useful with storage
ATP released when oxidised
Hydrolysis Reaction
Reaction that deconstructs polymers into monomers by adding split water molecules
Monomer of Carbohydrate
Monosaccharide
Monomer of Lipid
Glycerol and fatty acids
Monomer of Protein
amino acid
Monomer of nucleic acid
Nucleotide
How many carbon atoms can a monosaccharide have?
3-7 carbon atoms
Pentose
Monosaccharide with 5 carbon atoms
Hexose
Monosaccharide with 6 carbon atoms
Starch and glycogen
Polysaccharides made of glucose that store energy
Starch stores energy in
plants
Glycogen:
Polysaccharide
animal
A Glucose
1-4 and 1-6 bonds
branches every 10 subunits- high free ends where glucose can be broken off and hydrolysed
can be broken down quicly supplying metabollic needs
liver +muscles contain glycogen granules
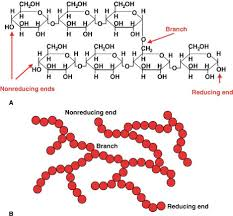
alpha-glucose
1 hydrogen (H) on top
beta-glucose
1 hydroxyl group (OH) on top
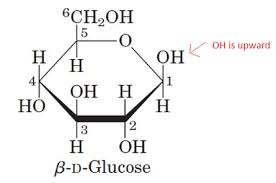
2 types of starch
1. Amylose (unbranched)
2. Amylopectin (branched)
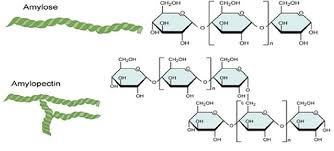
Amylose:
Polysaccharide - Starch
plant
A Glucose
1-4 bonds
compact structure so decreased digestion
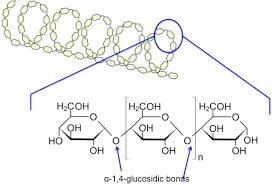
Amylopectin:
Polysaccharide - Starch
plant
A Glucose
1-4 and 1-6 bonds
Insoluble
Branches per 20 subunits- increased terminal glucose molecules - increased hydrolysis
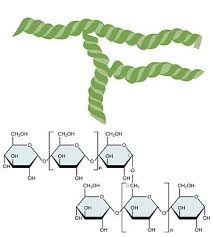
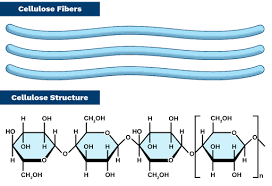
Cellulose
Polysaccharide
plants cell wall
B glucose
1-4 Bonds
flips itself to form glycosidic bonds- allows hydrogen bonds for form between strands
forms microfibrils with tensile strength
Why is cellulose an effective structural protein?
chemically inert
strong
insoluble
elastic
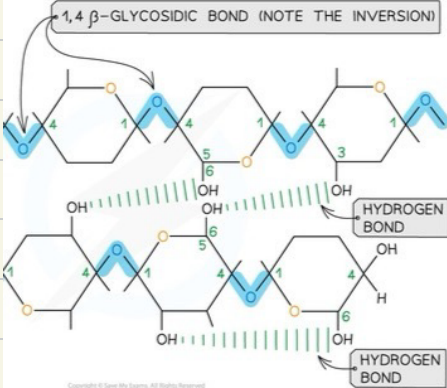
Microfibrils
Bundles of cellulose molecules arranged in parallel that form the base of the cell wall
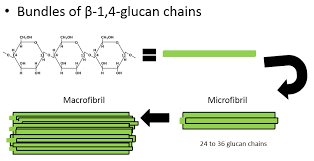
Microfibrils as the base of the cell wall is good because
It has high tensile strength. It is made of strong covalent bonds.
Compare and contrast condensation and hydrolysis
Same:
both involve water
both require enzymes
both are metabollic
Diff.:
condenstaion releases water, hydrolysis adds
Cond.= anabolic, Hydro. = catabolic
Cond. uses ATP, Hydro. releases ATP
Cond. endothermic, Hydro. Exothermic
Lipids + Examples
Diverse group of macromolecules in organisms that dissolve in non-polar solvents. Fats, oils, waxes, steroids
Are all lipids hydrophopic?
No. Sparingly soluble in aqueous (water-based) solvents
Amphipathic
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
Triglyceride
Combination of 3 fatty acids with 1 glycerol
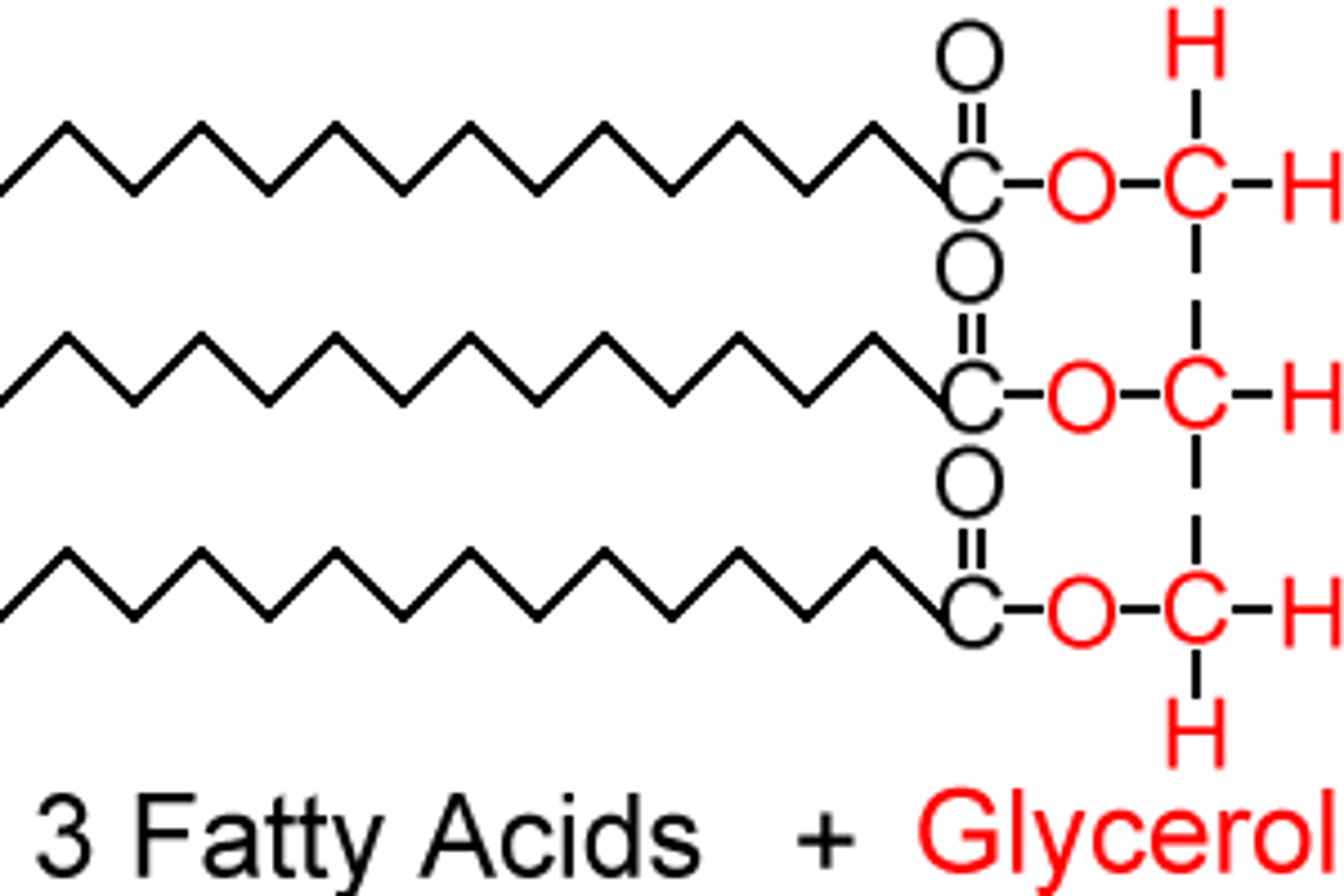
How many water molecules are produced through the production of a triglyceride?
3
Ester bond
linkage formed between fatty acid and glycerol
How many ester bonds in a triglyceride?
3
How many ester bonds in a phospholipid?
2
Are triglycerides hydrophilic, hydrophobic, or amphipathic?
Hydrophobic
Phospholipid
Combination of 2 fatty acids with 1 glycerol and a phosphate group
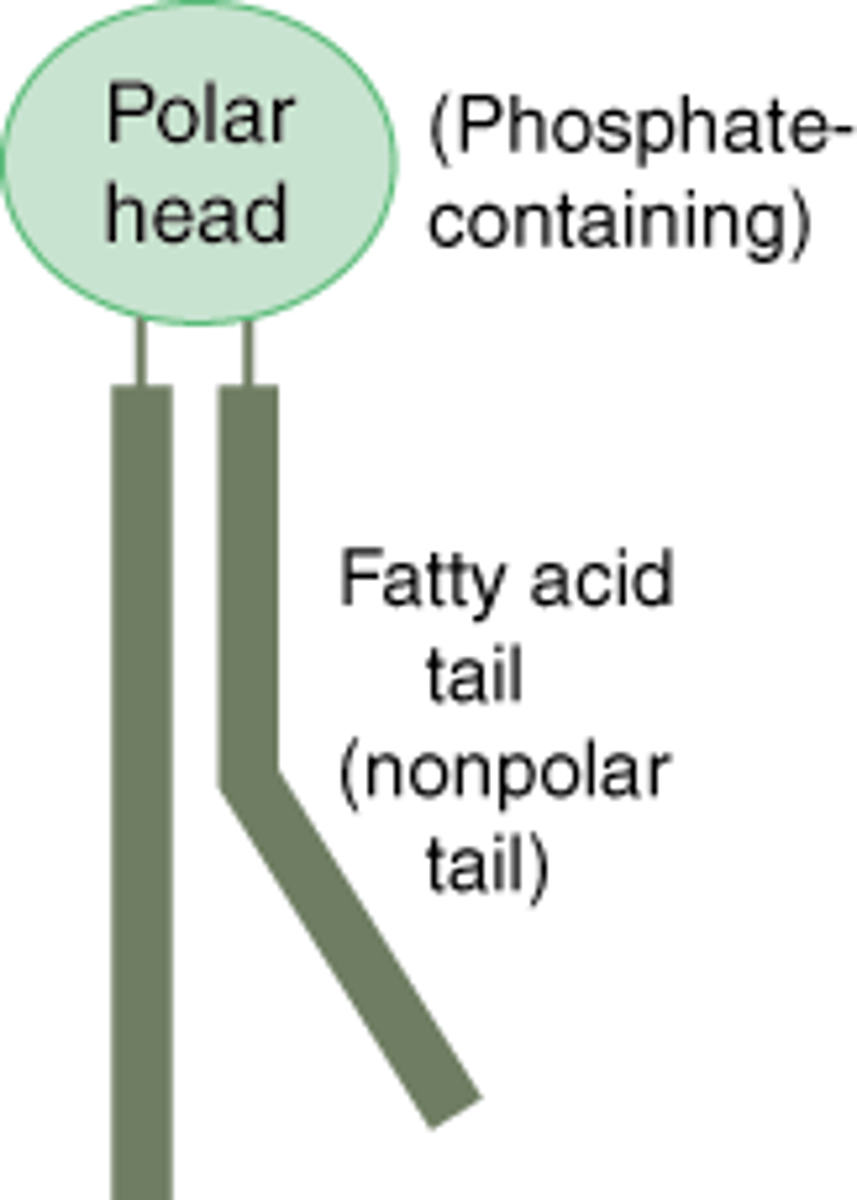
Are phospholipids hydrophilic, hydrophobic, or amphipathic?
Amphipathic (hydrophilic phosphate group)
What nicknames are used to refer to the parts of a phospholipid?
"Phosphate head", "Hydrocarbon tails"
Fatty acids
an unbranched chain of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms covalently bonded
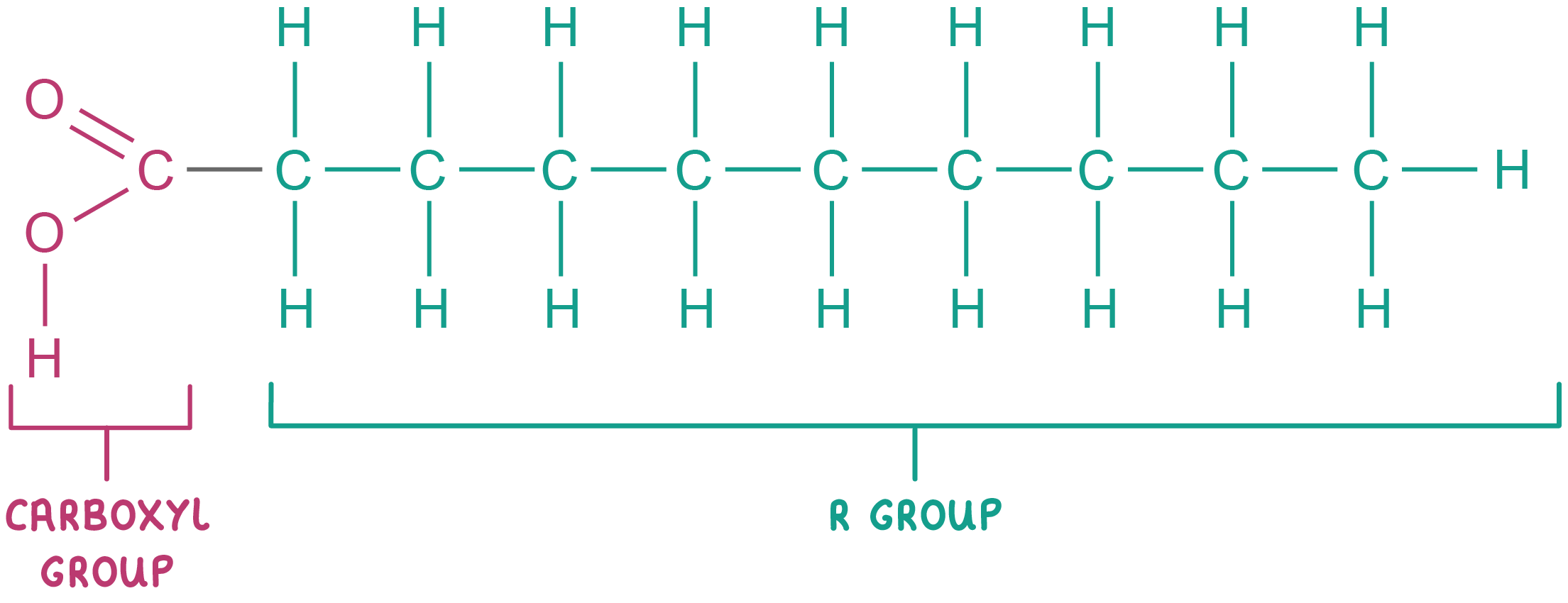
Name for the chain of a fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain
Around how many carbon atoms in a fatty acid?
14-20
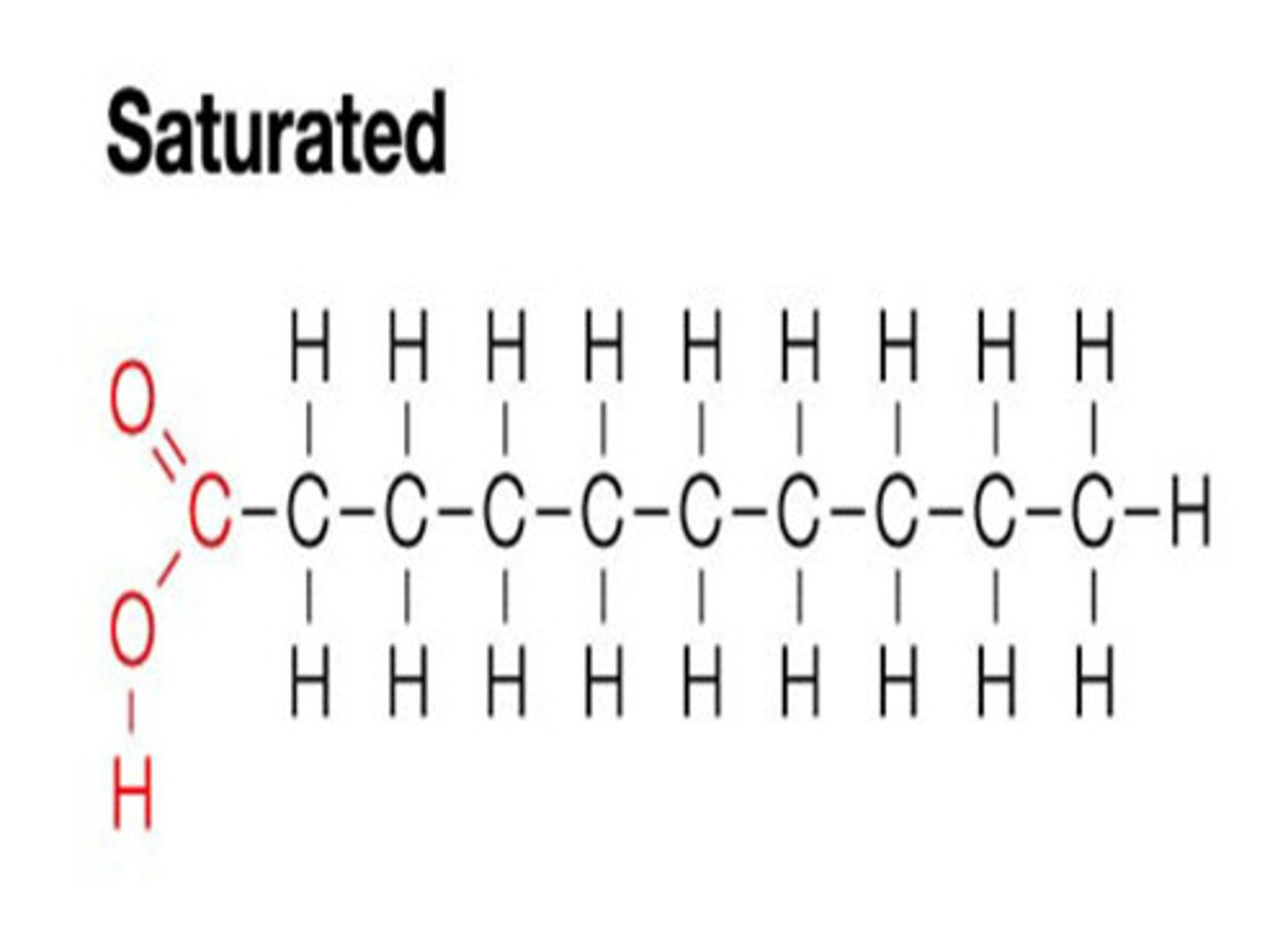
Saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid with single bonds between all of its carbon atoms. It contains as much hydrogen as it possibly could.
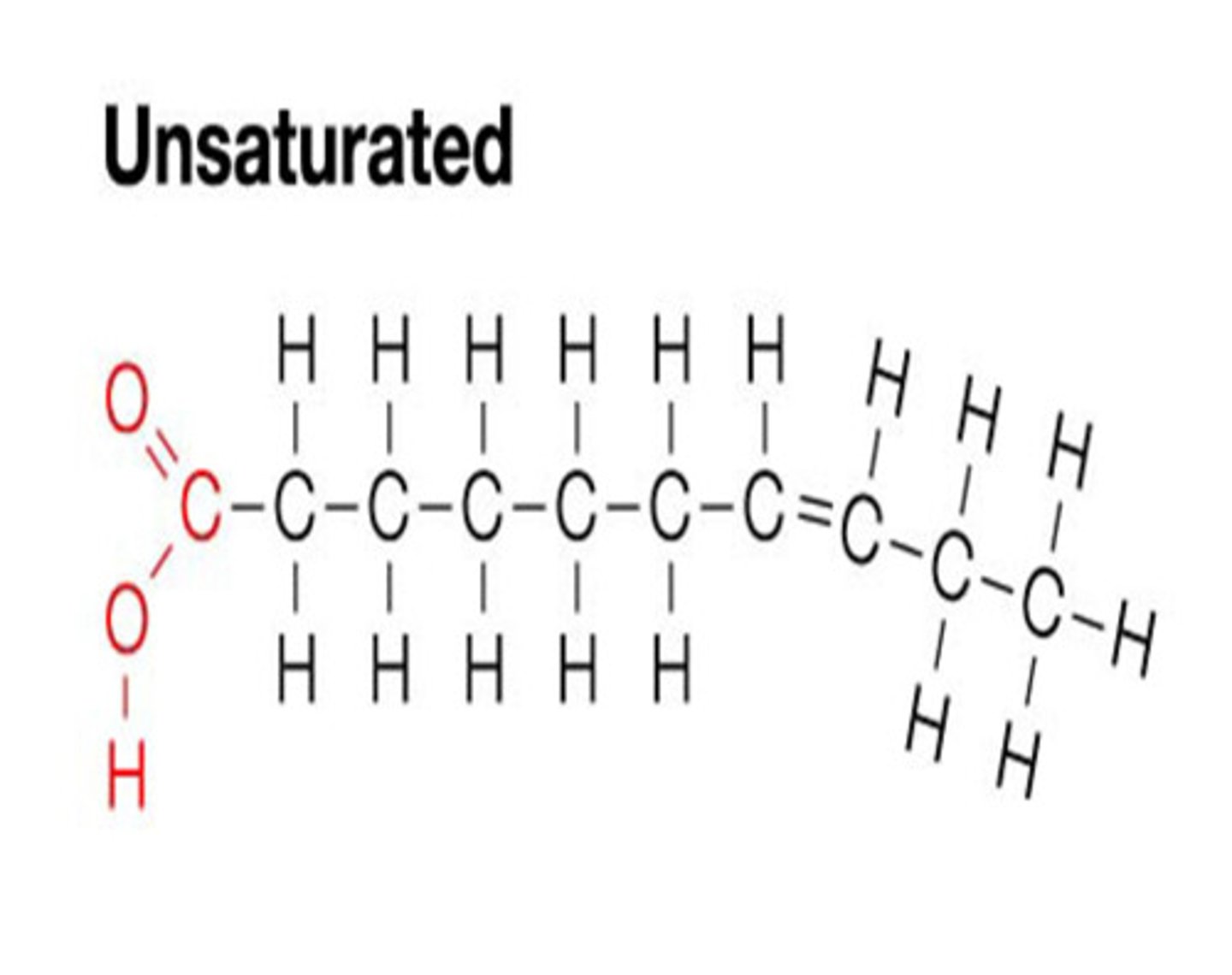
Unsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid with one or more double bonds. It contains less hydrogen than it possibly could.
Monounsaturated
1 double bond
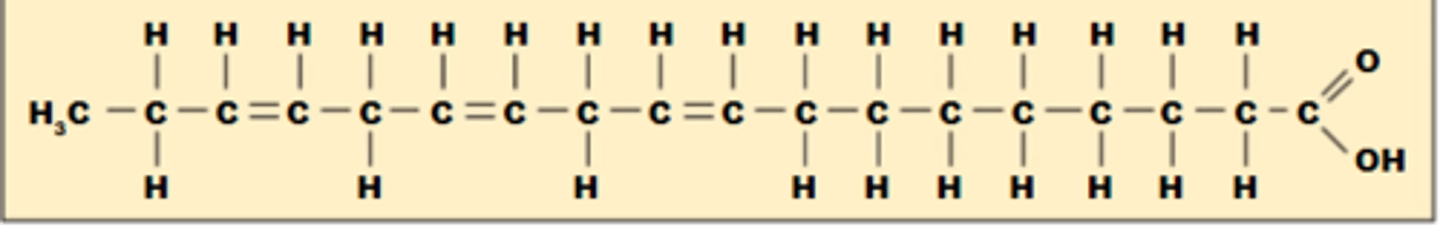
Polyunsaturated
more than 1 double bond
Appearance of a saturated fatty acid
Straight chain
Appearance of a monounsaturated fatty acid
One kink
Appearance of a polyunsaturated fatty acid
More than one kink (curve)
Purpose of triglycerides
used for energy storage and insulation in plants and animals
Adipose tissue
groups of cells that store triglycerides as fats
Storage and USES of lipids in animals:
Stored in adipose tissue
subcutaneous fats + under the skin
visceral fats = around major organs
protection
Use:
Seals + walruses have blubber whoch traps heat - insulator
camel hump- source of water
longterm energy source: lipid rich yolks for hen eggs
Properties of Triglycerides that make them good for long-term storage
Chemically stable- cant respire anaerobically
more compact as not associated with water molecules
Release 2X the amount of energy in cell respiration than carbohydrates.
storage in specialised adipose tissue
Metabollic water:
water produced due to respiration
not ingested as water but as other compounds that get respired
forms part of the dietry water intake
What animals need thermal insulation
Animals that maintain higher body temperatures than the temperature of their environment.
Name of adipose tissue in marine mammals
Blubber
Storage and uses of lipids in plants:
in seeds
to provide enrgy for growing seedling plant
olives, sinflowers, coconust
What are phospholipids usually surrounded by
aqueous solution
The double structure of the phospholipid bilayer is formed by
Hydrocarbon tails being attracted to each other
Steroids
a group of lipids
Steroids identifying features
4 fused rings of carbon atoms. 3 cyclohexane (6-sided) rings and 1 cyclopectane (5-sided) ring. 17 carbon atoms in total.
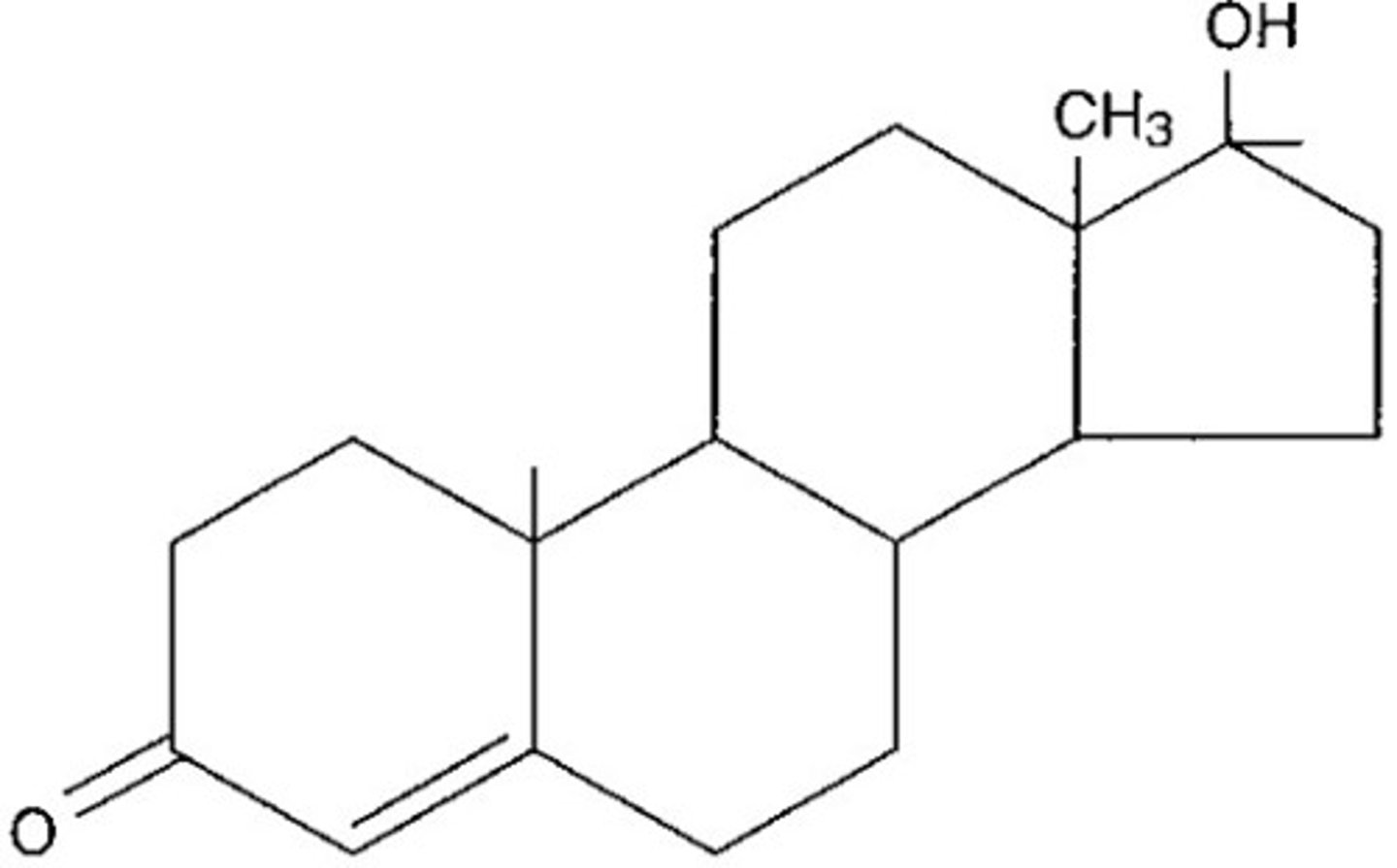
Are steroids hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or amphipathic
Hydrophobic
Can steroids pass through the phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion? Why?
Yes. They are non-polar.