Salivary glands
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
major salivary glands (3)
-parotid
-submandibular
-sublingual
How much saliva do the major salivary glands produce
90%
Functions of saliva (5)
- wetting
- lubricating
- digestive
- mineralization
- protective
What does the parotid gland secrete?
- produces a serous (watery) secretion
what percentage of the daily saliva volume is produced from the parotid gland
20 %
What is included in the secretion from the parotid gland
-SIgA
-defense chemicals
what percentage of the daily saliva volume is produced from the submandibular glands
65 %
what does the sublingual gland predominantly produce
-mucous saliva
what percentage of the daily saliva volume is produced from the sublingual gland
5 %
What does the submandibular gland secrete
-mixed serous and mucous secretion
What is the capsule of connective tissue of the salivary gland made up of? What is it continuous with?
-collagen fibers
-continuous with the connective tissue septa
What runs within the connective tissue septa
-blood vessels
-nerves
-excretory gland
What glands are mostly being activated when we are eating
parotid gland
Salivary gland structure
-composed of lobules within lobes
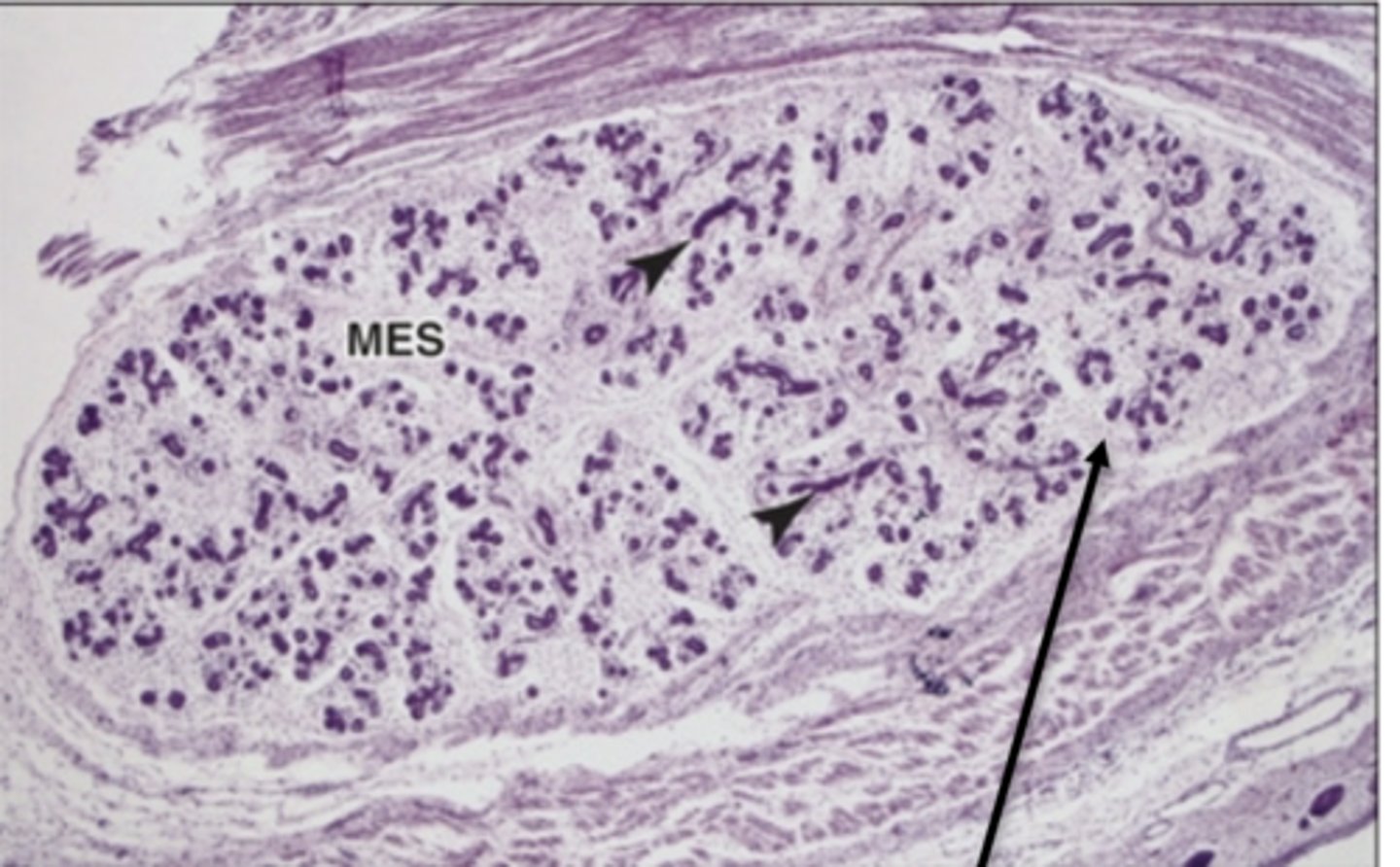
if salivary glands end in compound acinar glands, what do they secret
serous
if salivary glands end in tubules what do they secrete
mucous
serous cells secretion
-produce watery secretion with proteins
-alpha amylase
What secretes alpha amylase
serous cells
function of alpha amylase
digest dietary starch into maltose
shape of serous cells
-pyramidal
serous cell nucleolus shape? Polarized or non-polarized cells?
-round
-polarized cells
compound acinar gland
made of serous-secreting cells that dump into intercalated duct
Mucous cell shape
pyramid
mucous cell nuclei shape?
polarized or non-polarized cells?
-flattened nuclei
-polarized cell (nuclei near basal end)
What do mucous cells produce and where is it stored?
-mucus-rich secretion (mucin) stored in large light-colored vesicles
where are myoepithelial cells present
- in the serous acini (between serous cells and their basal lamina) as branched “basket cells”
-also along intercalated duct (spindle shaped)
what covers the acini and intercalated ducts surface area
myoepithelial cells
origin of myoepithelial cells around the intercalated duct
ectoderm (but resemble smooth muscle)
where does the Duct system of the salivary gland empty into
-empties into intercalated duct which flows into striated duct
Function of intercalated duct
-lining of cuboidal epithelial cells
-act as stem ells for both secretory end piece cells and for the ductal cells
Both ducts (striated and intercalated) of the salivary gland are _______ ducts
intralobular
What are striated ducts connected to
-connected to several intercalated ducts
Why are striated ducts striated
-caused by infoldings of the basal plasma membrane (for ion transport)
excretory ducts are _____ and have their own stem cells
interlobular
polar or nonpolar: intercalated duct cells
nonpolar
what cell? small diameter and drain individual secretory units
intercalated duct cell
what do intercalated duct cells synthesize and secrete
-lysozyme
-lactoferrin
what is the source of salivary gland stem cells
intercalated duct cells
Where are striated duct cells mainly found
-parotid and submandibular glands
polarized or nonpolarized: striated duct cells
polarized
role of striated duct cells
-assembly and transcytosis of SIgA
What two cells do excretory ducts contain
-goblet cells
-stem cells
what type of epithelium is found in excretory ducts
-pseudostratified to stratified
What is the parotid gland composed of
100% serous acini
What gland has the highest amount of amylase
parotid gland
When is saliva secreted from the parotid gland
-during eating (stimulated saliva)
When is the saliva mainly produced from the submandibular salivary gland
-mostly resting saliva
functions of the serous cells in the submandibular salivary gland
-secrete lysozyme to kill bacteria
When is the saliva of the sublingual salivary gland mainly produced
-resting saliva
what glands are branched tubuloacinar glands
all major salivary glands
Mucous minor salivary glands (2)
-palatine glands
-posterior lingual glands
serous minor salivary gland
glands of von ebner
Mixed minor salivary glands (3)
-anterior lingual glands
-buccal glands
-labial glands
New salivary gland that was discovered in 2020
-tubarial gland (minor salivary gland- mainly mucous gland)
function of tubarial gland
assist in swallowing
Where are minor salivary glands found
-submucosa
minor salivary glands produce 70% of _______ secretion
mucous
When is saliva produced in the minor salivary gland
Important contributors to unstimulated or resting saliva
are minor salivary glands surrounded by a connective tissue capsule
no
location of glands of von ebner
posterolingual in the tongue
Where are glands of von ebner secretions released
-in areas with significant numbers of taste buds
what do Von ebner glands secrete
-serous fluid with digestive enzymes and other proteins which assist in the perception of taste
what are von ebner glands associated with
-webers glands (mucous gland)
salivary gland development (6 steps )
1. bud formation (Eda)
2. cord growth (FGF)
3. branching of cords (sonic hedgehog)
4. lobule formation (EGF/FGF)
5. canalization of cords
6. cytodifferentiation: formation of acini
Differences between facial exocrine glands and exocrine glands located elsewhere in the body
-ectomesenchyme reacts differently than mesenchyme
-less reciprocal induction signals received from ectomesenchyme
-higher degree of epithelial interactions in salivary glands
teeth and sweat glands have less reciprocal induction signals, instead they are more affected by _________
hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
oral ectoderm derived organs (2)
-tooth
-salivary glands
What regulated the morphogenetic (shape) events of various ectodermal organs
mesenchyme
what determines if a gland with be mucous or serous
epithelial cells
what cell is important in bud formation during salivary gland development
ectodysplasin A (Eda)
function of sonic hedgehog
-epithelial cell proliferation, survival and differentiation
what is important in Embryonic submandibular salivary gland cord growth and branching morphogenesis
sonic Hedgehog
FGF funciton
-stimulates secretion of collagen- cleft formation
EGF function
stimulates epithelial proliferation and differentiation
what is important for branching to occur in the salivary gland development
FGF
What is defective in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
-Eda (bud formation)
-FGF (cord growth)
salivary gland development:
What simulates bud formation?
-stimulated by Eda from ECM on epithelium
salivary gland development stage: oral epithelium form a bud growing into ECM
bud formation
salivary gland development stage? bud growing into ECM because of FGF from ECM
cord growth
origin of parotid gland epithelium
ectoderm
origin of submandibular and sublingual glands epithelium
-endoderm
salivary gland development stage? clefts develop in the bud forming two or more bud
-branching of cords
What growth factors result in clefts from changes in epithelial cell shape
-Shh
-TGFb
what role does fibronectin and collagen III play in the branching of cords
-cleft formation
salivary gland development stage:
result of repeated branching and budding along major branches of the cord
What is this stimulated by?
lobule formation
-FGF, EGF
salivary gland development: lobule formation: what is important in acinar formation
E-cadherin
________ is a requirement in branching morphogenesis
fibronectin
collagen III funciton in development
cleft formation
fibronectin function in development
cleft formation
collagen IV funciton of development
-branching (acinar morphogenesis)
proteoglycans function of development
-branching
laminins function of development
Basement membrane assembly
- Lumen formation
- FGFR signaling
- Acinar formation
How can branching be inhibited
-treatment of collagenase --> no clefts form
How to block the formation of terminal end buds
-using antibodies to block collagen IV
What do all ducts form before?
the formation of
acinar cells and secretory granules.
what stem cells undergo cell proliferation? What do they differentiate into?
cells of the bulb region
-differentiate into acinar cells and ductal cells
what cells arise from the stem cells of the terminal bulbs
-myoepithelial cells
important growth factors of minor salivary glands
-Eda
-sonic hedgehog (Shh)
-FGF
mutations of minor salivary glands cause
-hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
unconditional reflexes of saliva production
-gustatory stimulus (taste)
-masticatory stimulus (chewing)
-olfactory stimulus (smelling)