Biochemistry Ch 7 Carbohydrates
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
What is the standard formula for carbohydrates?
Cn(H2O)n
How are carbohydrates produced? Products from what process?
Produced from CO2 and H2O via photosynthesis in plants
What’s the smallest sugar with a chiral carbon?
Glyceraldehyde
What’s are the major 3 functions of carbohydrates?
Energy source and energy storage
Structural component of cell walls and exoskeletons
Informational molecules in cell-cell signaling
Carbohydrates can be covalently linked to proteins forming products called what? (2 names)
Glycoproteins and proteoglycans
Carbohydrates typically have one or multiple chiral carbons?
Multiple
What are the monomers of carbohydrate polymers?
Monosaccharides
Does the way the monomer units are linked determine the sugar’s properties/function?
Yes
Storage of low molecular weight metabolites in the polymeric form avoids what effect that would occur from storing them as individual monomer?
High osmolarity, which would cause cells to swell and lyse due to entry of water via osmosis
Sequences of complex polysaccharides are determined by what?
Intrinsic properties of the biosynthetic enzymes that add each monomeric unit to the growing polymer
Is synthesis of polysaccharides a template dependent process?
No
Polysaccharides assume the 3D structure with the highest or lowest energy conformations?
Lowest
Is molecular complementarity central to function of carbohydrates?
Yes
What is the name of sugar-binding proteins?
Lectins
How are monosaccharides classified?
Number of carbons (triose - 3, tetraose - 4, pentose - 5)
How many carbons are in heptose?
7
Oligosaccharides are named based on what?
Number of monosaccharides (disaccharide - 2, trisaccharide - 3)
What are two categories polysaccharides are classified by?
Homosaccharide (starch, glycogen)
Heterosaccharide (semi-cellulose)
Do monosaccharides exhibit isomerism?
Yes
How do constitutional isomers and stereoisomers differ?
Constitutional isomer differs in the order of attachment of atoms
Stereoisomers are connected in the same order but differ in spatial arrangement
Enantiomers and diastereoisomers are both types of stereoisomers how do they differ?
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images
Diastereoisomers are NOT mirror images
Epimers and anomers are different forms of which class of isomers?
Diastereoisomers
How do epimers and anomers differ as types of diastereoisomers?
Epimers differ at one of several asymmetric carbons
Anomers differ at a new asymmetric carbon atom formed from ring closure (alpha vs beta)
An aldose is a carbohydrate with what functional group?
Aldehyde
A ketose is a carbohydrate with what functional group?
Ketone
Aldoses and ketoses can be interconverted but in the process form what type of intermediate?
Enediol Intermediate
Can aldoses and ketoses be interconverted?
Yes
Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxy acetone are related how?
They are structural isomers. Both C3H6O3 but connected differently.
In sugars with many chiral centers which one designates the isomer as D (right) or L (left)?
The chiral carbon furthest from the carbonyl carbon.
D sugars and L sugars are what type of isomers?
Enantiomers (nonsuperimposable mirror images)
Most sugars in living organisms are D or L?
D
Do L- and D- glucose have the same water solubility?
Yes
What requirement must be met for a carbon to be considered chiral?
Four different groups attached to the carbon atom
What simple sugar occurs in the L form?
L-arabinose
How do optically active isomers affect light?
They rotate the plane of polarized light by a characteristic amount
Rotation of plane poralized light by chiral molecules can be split in two categories called what? And what direction do they rotate light?
Levorotatory (L) - left (counterclockwise)
Dextrorotatory (D) - right (clockwise)
Can chiral molecules rotate the plane of polarized light?
Yes
D and L conformations are determined when the aldehyde is positioned at the top or bottom relative to the determining chiral carbon?
Top
How many carbons and how many chiral centers are in Glyceraldehyde?
3 carbons and 1 chiral center
What is the reference carbon?
The anomeric carbon. I.e. the chiral center most distant from the carbonyl carbon
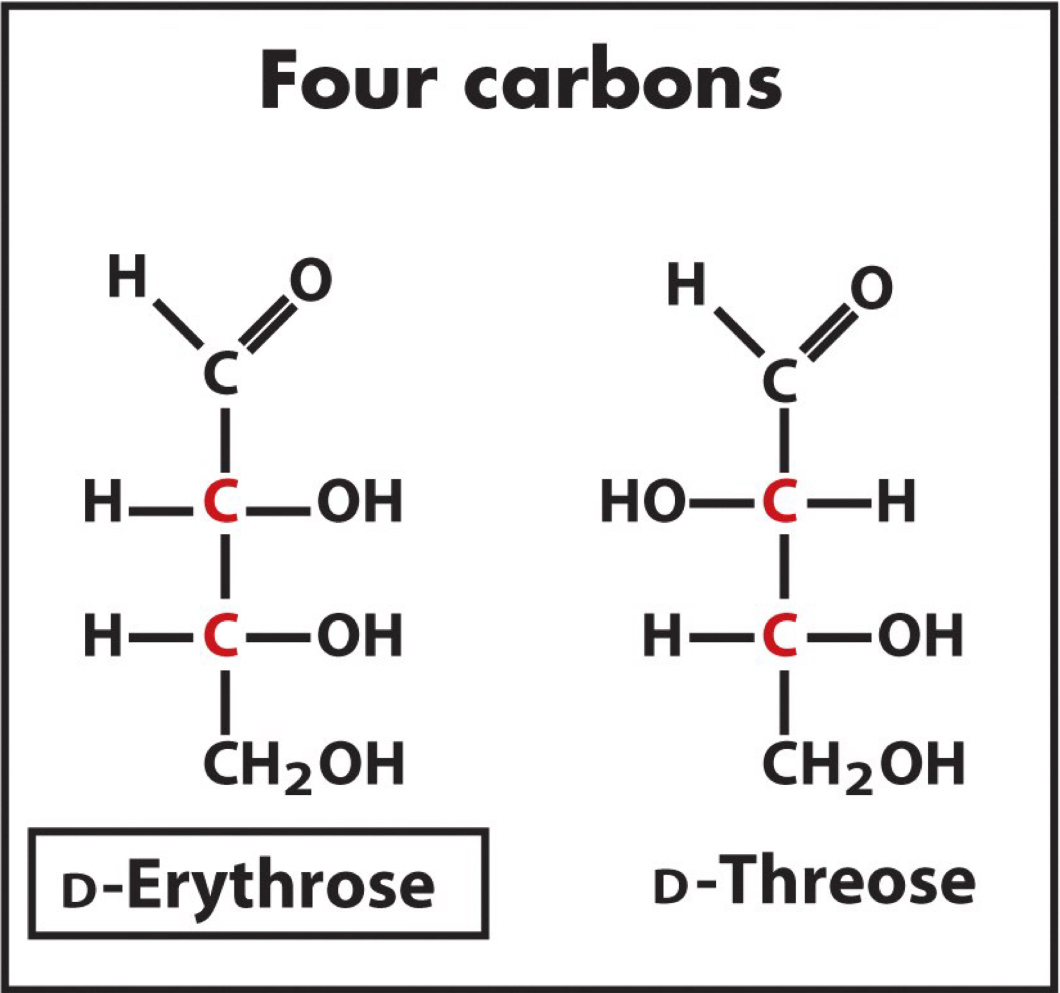
What is the relationship between these two isomers? Why?
They are diastereomers, specifically epimers, because they are not mirror images and they vary at only one chiral center.
Do diastereomers, including epimers and anomers, vary in their physical properties (i.e. water solubility and melting temp)?
Yes
What is the relationship between D-Mannose and D-Galactose in relationship to D-Glucose?
They are both epimers of D-Glucose
What carbon is the epimer between D-Mannose and D-Glucose?
C2
What carbon is the epimer between D-Galactose and D-Glucose?
C4
What is the relationship between chiral centers (n) and the number of stereoisomers?
A molecule with (n) chiral centers will have 2^n stereoisomers
4 chiral center = 16 stereoisomers (Aldohexoses)
How are fructose and glucose related?
Fructose is the ketose form of glucose which is an aldose
What is the standard five carbon sugar?
Ribose
What is the standard six carbon sugar?
Glucose
What five sugar structures do we need to memorize?
Ribose
Glucose
Galactose (epimer of glucose)
Mannose (epimer of glucose)
Fructose (ketose form of glucose)
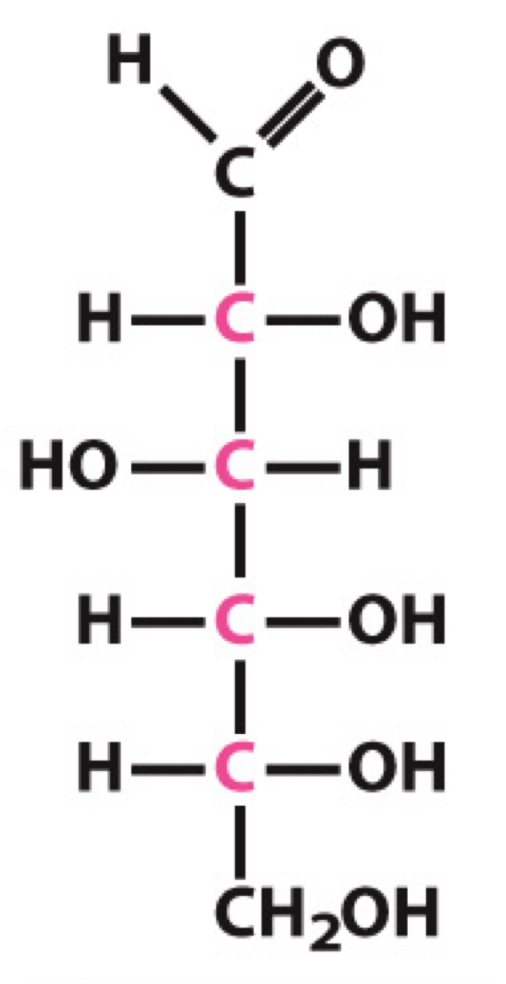
What sugar is this?
D-Glucose
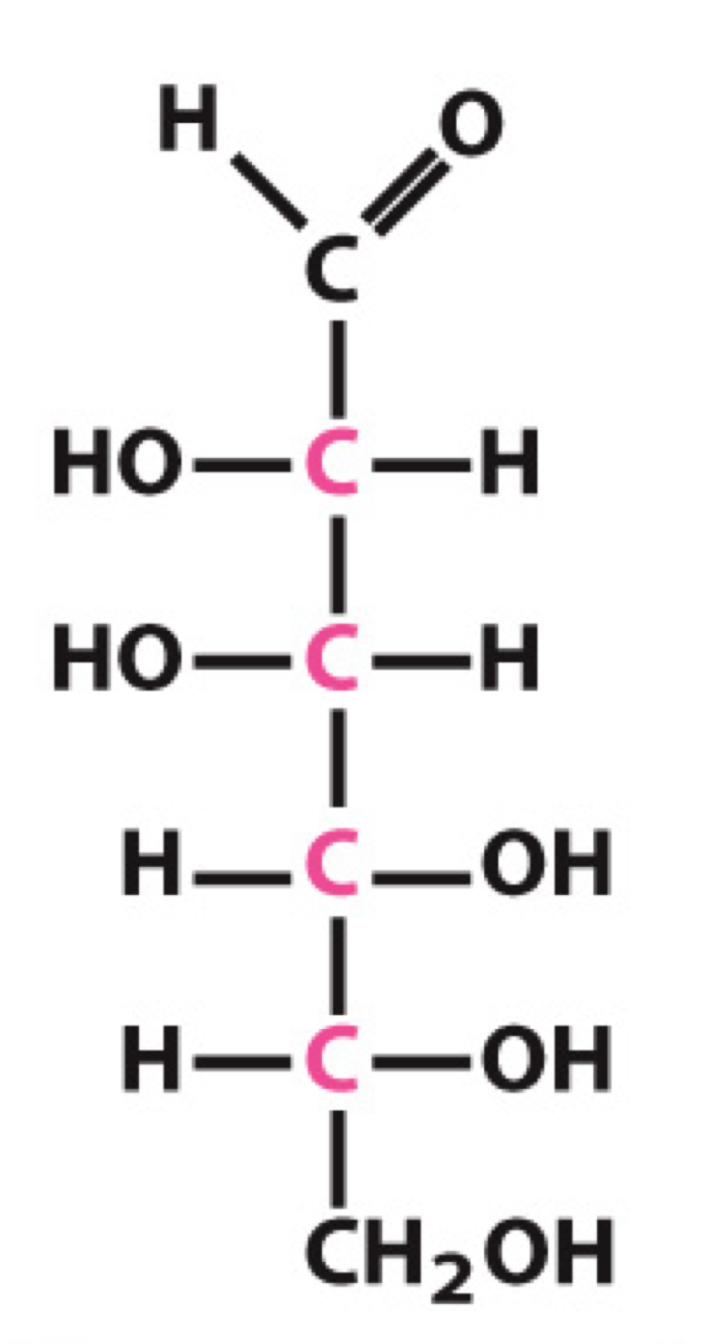
What sugar is this?
D-Mannose
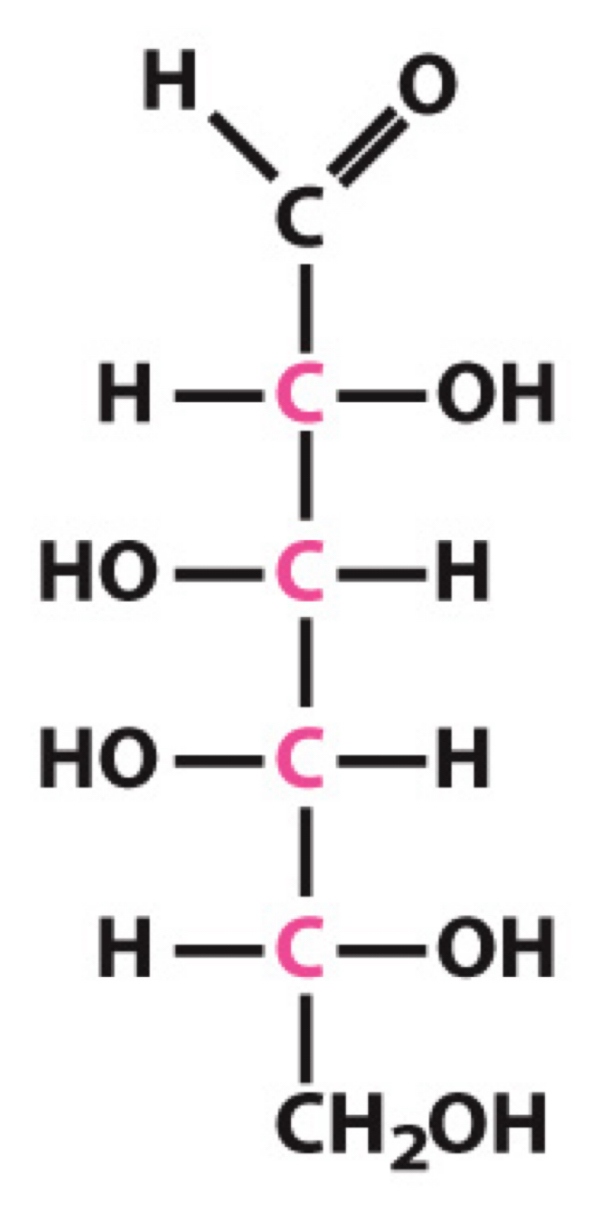
What sugar is this?
D-Galactose
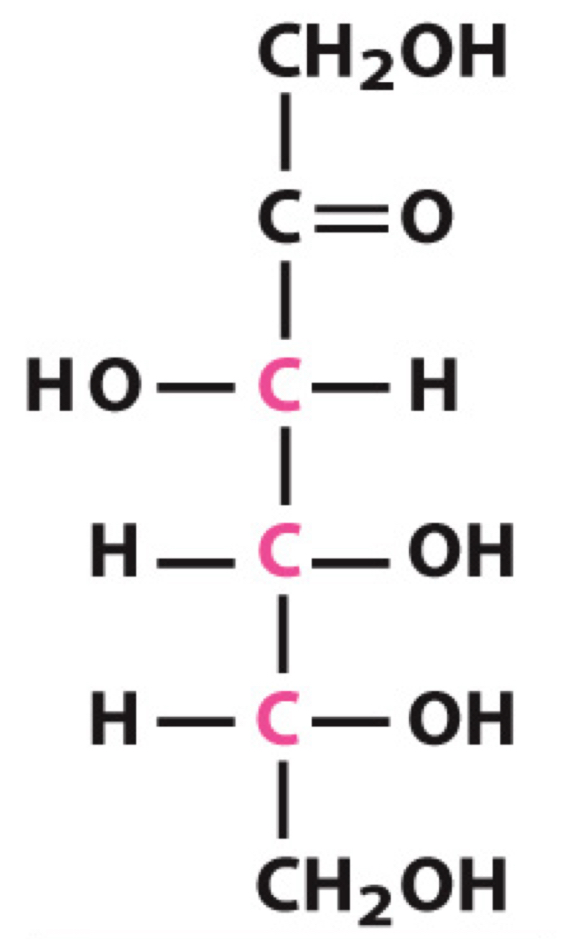
What sugar is this?
D-Fructose
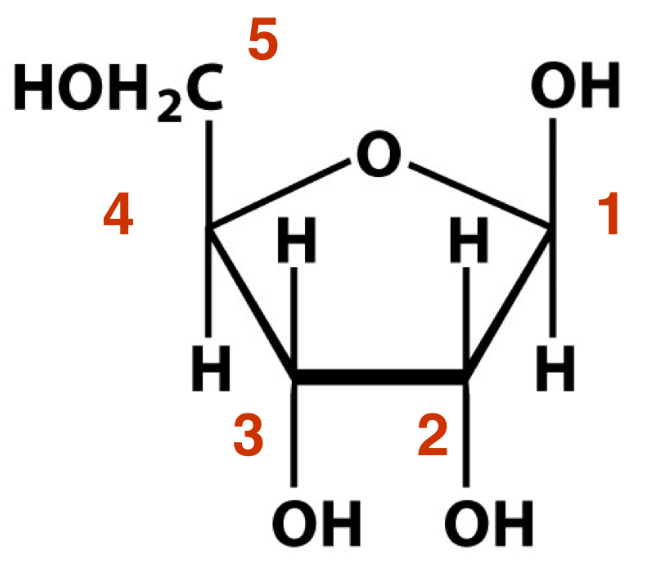
What is this sugar?
Beta-D-Ribose
Do chiral molecules have a plane of symmetry?
No
A mirror image isomer of a chiral molecule is called what?
An enantiomer
A non-mirror-image isomer of a chiral molecule is called a what?
A diastereoisomer
In aldoses at what carbon is the aldehyde functional group located?
C1
In ketoses at which carbon is ketone functional group located?
C2
Are the carbons of aldehydes and ketones, nucleophilic or electrophilic?
Electrophilic
Can aldoses and ketoses react with alcohols?
Yes
The oxygen atom of an alcohol is nucleophilic or electrophilic?
Nucleophilic
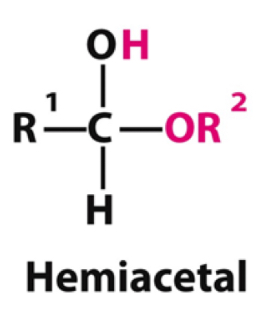
When aldehydes are attacked by alcohols once they form what type of product?
Hemiacetal
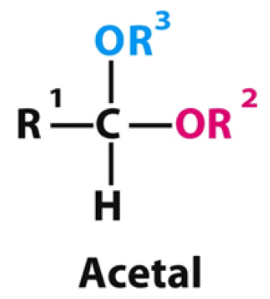
When an aldehyde is reacted twice with an alcohol what type of product is formed?
Acetal
When a ketone is attacked one by an alcohol what type of product forms?
Hemiketal
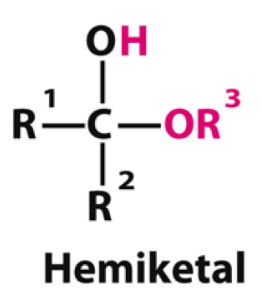
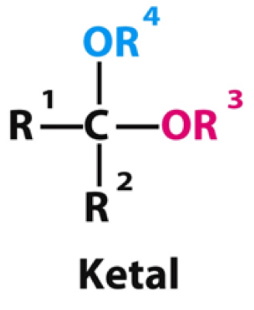
When ketones are attacked twice by alcohols what type of product is formed?
A ketal
Why is the ability of ketones and aldehydes to react with alcohols important in carbohydrates?
It allows them to switch from the linear form to the cyclic form and back
How are cyclic sugars that only vary in their alpha vs beta configuration at the anomeric carbon related?
They are anomers
Where do anomers differ?
At the anomeric carbon
Do pentoses and hexoses readily undergo intramolecular cyclization?
Yes
When a monosaccharide is turned into the cyclic form which carbon becomes the anomeric carbon?
The carbon the previously bared the carbonyl
Which carbon determine alpha vs beta configuration?
Anomeric carbon
When is a cyclic sugar alpha?
When the OH group on the anomeric carbon is trans relative to the CH2OH group
When is a cyclic sugar beta?
When the OH group on the anomeric carbon is cis relative to the CH2OH group
Which carbon is the anomeric carbon in ketoses?
C2
Which carbon is the anomeric carbon in aldoses?
C1
Six membered oxygen containing rings are called what?
Pyranoses
Five-membered oxygen containing rings are called what?
Furanoses
The anomeric carbon is usually drawn on the left or right side?
Right
In the process of cyclization is the carbonyl carbon reduced or oxidized?
Reduced
Can alpha and beta forms be interconverted? Why?
Yes, because the orientation of the alcohol around the anomeric carbon is variable and transient
An attack between the C1 and C5 carbon will form what type of ring?
A pyranose (6 member O containing rings)
Formation of a hemiacetal will cause the carbohydrate to be in the linear or cyclic form?
Cyclic
Is pyranose and furanose a heterocyclic or homocyclic ring?
Heterocyclic
How does increasing temperature shift the equilibrium relative to the presence of pyranose and furanose
Shifts in the direction of the furanose form
Cyclization of glucose may take two different ways resulting in how many final configurations?
4 possible final configurations of glucose
What forms of ribose is the component of DNA and RNA backbone
Furanose form (specifically beta)
How are reducing sugars defined?
By the presence of a free anomeric carbon, not bound to another monosaccharide or larger.
What functional group can reduces Cu2+ to Cu+ via Fehling’s test?
Aldehydes
What functional group reduces Ag+ to Ag0 via Tollens’ test?
Aldehyde
What is the purpose of Fehling’s test and Tollen’s test?
Allows the detection of reducing sugars
Modern detection techniques for reducing sugars uses what two type of tests?
Colorimetric test and electrochemical test
Does the ring form of a sugar exist in equilibrium with the open-chain form?
Yes
The process of interconversion between the linear and cyclic conformations is known as what?
Mutarotation
Are monosaccharides reducing sugars?
Yes
What type of method is used to quantify reducing sugars?
Enzymatic methods
How does the enzyme glucose oxidase affect glucose?
Catalyzes its conversion to glucono-delta-lactone and hydrogen peroxide
How does hydrogen peroxide, a product of glucose oxidase reacting with glucose, affect organic compounds?
It oxidizes them into highly colored compounds. Concentrations of such compounds can then be measured colorimetrically.
Two sugar molecules can be joined via what type of bond?
Glycosidic bond