bipsychology test 1
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
research
Three dimensions along which biopsychological research varies:
pure applied
Neuroscience
the scientific study of the nervous system
biopsychology
the scientific study of the biology of behavior
DO Hebb
Proposed that psychological phenomena might be produced by brain activity
Helped discredit the notion that psychological functions were too complex to be derived from physiological activities
subjects
Three dimensions along which biopsychological research varies:
humans nonhumans
methods
Three dimensions along which biopsychological research varies:
experiments non experiment
experiment
Used to determine cause-and-effect relationships
Between- and within-subjects designs
Independent and dependent variables
confounded variable
an unintended difference between the conditions of an experiment that could have affected the dependent variable
can be diff to elimate
can make exp diff to interpret
non experiments
quasiexperimental studies and case studies
quasiexperimental studies
studies of groups of subjects who have been exposed to the conditions of interest in the real world
not true experiments as potential confounded variables are not contolled
no random assignment
case studies
focus on a single cas or subject
usually more in depth than other app
good source of testable hypothesis
major prob is generlizability
gernalizability
degree to which results can be applied to other cases
lester and gorzalka
demonstates the coolidge effect in female hamsters
potential confounds: males become more sexual fatigued
- recep in females may be due to novelty or inc secual vigor in new mate
- controlled for fatigue w familiar males
results: On the 3rd test, female hamsters were more sexually receptive to an unfamiliar male than to the male they had already copulated with during an earlier test
pure research
conducted for the purpose of acquired knowledge
applied research
intened to bring about some firect benefit to human kind
Physiological Psychology
the study of behavior as influenced by biology
Uses direct manipulation of the brain in controlled experiments
subjects are usually lab animals
strong focus on pure research
psychopharmacology
focuses on the manipulation of neural activity and behavior with drugs
uses substantial portion of applied research
neuropsychology
studies the psychological effects of brain damage in human patients
cn be studied in humans by experimentation; focuses on case studies and quasi-experimental studies
has focused on cerebral cortex
psychophysiology
studies the relation between ohysiological activity and psychological processes (attention, emotion, info processing)
typically uses noninvasive procedures (EEG, eye tracking, muscle tension)
cognitive neuroscience
focuses on the neural bases of cognition
often employs human subjects, but sometimes non human animals
uses functional brain imaging tech as key methods
comparative psychology
compares different spp to understand evolution, genetics, and adaptiveness of behavior
uses lab and ethological research
inv areas of reaseracth that oftenn use comparative analysis
- evolutionary psychology
- behavioral genetics
converging operations
using multiple approaches to address a single question
- strengths of one approach comnpensate for the weakenesses of the other
ex korsakoffs syndrome
korsakoffs syndrome
characterized by severe memory loss
initially believed to be a direct consequence of the toxic effect of alcohol on the brain
Largely caused by brain damage associated with thiamine deficiency, although the damage is accelerated by alcohol
scientific inference
The empirical method that biopsychologists use to study the unobservable
Scientists observe & measure the consequences of unobservable processes & use these measures as a basis for inferring what they cannot observe
trex coprolites
dichotomy
Two opposite parts of one whole
- physiological/psychological
- inherited/learned
- right/wrong
cartesian dualism
Descartes's view that all of reality could ultimately be reduced to mind and matter.
universe: universe consists of two elements: physical matter & human mind (soul, self, or spirit)
human mind: mind and brain viewed as separate entities
Physical matter (body, brain, other animals)- governed by laws of nature; scientific
Mind- lacks physical substance, controls behavior, obeys no natural laws; concern of the church
watson
a behaviorist, believed that all behavior was the product of learning (nurture)
ethology
the study of animal behavior in the wild, focused on instinctive (nature) behaviors
asomatognosia
deficiency in proprioceptive selfawareness (typically involves damage to the right parietal lobe.)
genetic makeup
experience
perception of current situation
nuture now emcompasses learning and env
sev factors interact to impact env
charles darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
evolution
gradual change frequency of different genes in a population or spp over the course of generations via natural selection
natural selection
inherited trailed associated with high rates of survival and reproduction are most likely to be passes on to future generations
fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and cont its genes to the next generation
inclusive fitness
sum of the direct fitness gained by the indv investment in itsown offspring and indirect fitness gained by its effects on the reproduction of kin
fossil
common ancestors
selective breeding
darwins edvidence
________ for evolution
struct sim suggest _______ ______
impact of _________ _________
& grant finches
homind
inc great apes and humans
family
homonin
humans and immediate ancestors ancestors
tribe
inc size
most in cerebrum
inc convolutions inc cerebral cortex
evolution of human brain (3)
encephalization
the degree to which brain size exceeds body size
exaptations
characteristic that evolved to perform one fuction but later performs a different function
ex feather (temp teg --> flight)
homologous structures
similar structures due to a common evolutionary orgigin
analogous structures
similar structures w.o a common origin
alleles
two or more alternative forms of genes
diploid
two alleles per trait
mitosis
- a form of cell division that results in daughter cells that have 23 pairs of chromosomes
replication
strands unwind; each nucleotide attracts its complementary base, making two DNA molecules identical to the original
Transcription
Messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesized from DNA
Translation
Ribosome synthesizes protein according to 3 -base sequences (codons) of mRNA
promoters (enhancers)
short segments of DNA that determine whether particular structural genes initiate the synthesis of proteins & at what rate
transcription factors
proteins that bind to DNA and influence the rate to which genes will be expressed https://www.youtube.com/watch?
epigenetics
Study of mechanisms that influence expression of genes without changing genes (DNA sequence is unchanged)
changes can be passes on
histone remodeling
modifications to a histone protein (around which DNA is coiled) that can either decrease or increase gene
DNA methylation
the attachment of a methyl group to DNA (cytosine in mammals) that reduces the expression of adjacent genes
epigenetic inheritance
exp on lab rats
feed vinclozolin to pregnant rats
induced changes that can be seen in generations
behavioral development
consequence of genetic potential interacting with the experience of indv organism
- selective breeding of mazz bright and maze dull
- devel of birdsong
ontogeny
development of an indv through their lifespan
phylogeny
evolutionary development of a spp thru the ages
sensory
exposure to conspecific song leads to memories that guide song development.
sensorimotor
birds must hear themselves practice singing for songs to develop properly
adult neurogenesis
the creation of new neurons in the brain of an adult
- male canaries grow new neurons ea spring to learn new songs
phenylketonuria (PKU)
single gene metabolic disorder
Build up of phenylalanine (amino acid) in body caused by defect in gene that helps create enzyme (phenylalanine hydroxylase) needed to break down this specific amino acid.
results in intellectual disability
nervous system
A communication network consisting of nerve cells (neurons), that carry messages both to and from the brain & spinal cord to other parts of the body
• gather and process information
• produce responses to stimuli
• coordinate the workings of different cells
cns
brain and spinal cord
pns
out of skull and spine
somatic ns
interacts with external environment
voluntary control of body mvm
afferent
sensory arrive
efferent
motor exit
autonomic ns
interact w internal env
invol control of visceral functions
sympathetic parasymphathetic
two kinds of efferent nerves
sympathetic ns
thoracic and lumbar
flight or fight
second stage neurons are far from target organ
parasympathetic
cranial and sacral
rest and restore
second stage neurons are near the target organ
12
how many pairs of cranial nerves
cranial nerves
Special group of nerves in the PNS that leave CNS from the brain through skull • Have specific sensory and/or motor functions
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
chemical protection of the brain
tightly packed cells of blood vessel walls prevent entry of many colecules
skull
meninges
csf
physical protection of brain
dura meter
arachnoid membrane
pia meter
meninges
dura meter
the tough outermost membrane of meninges
arachnoid membrance
weblike meninges
pia mater
adheres to cns surface meninges
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
fills the subarachnoid space, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the cerebral ventricles of the brain
fluid serves as cushion
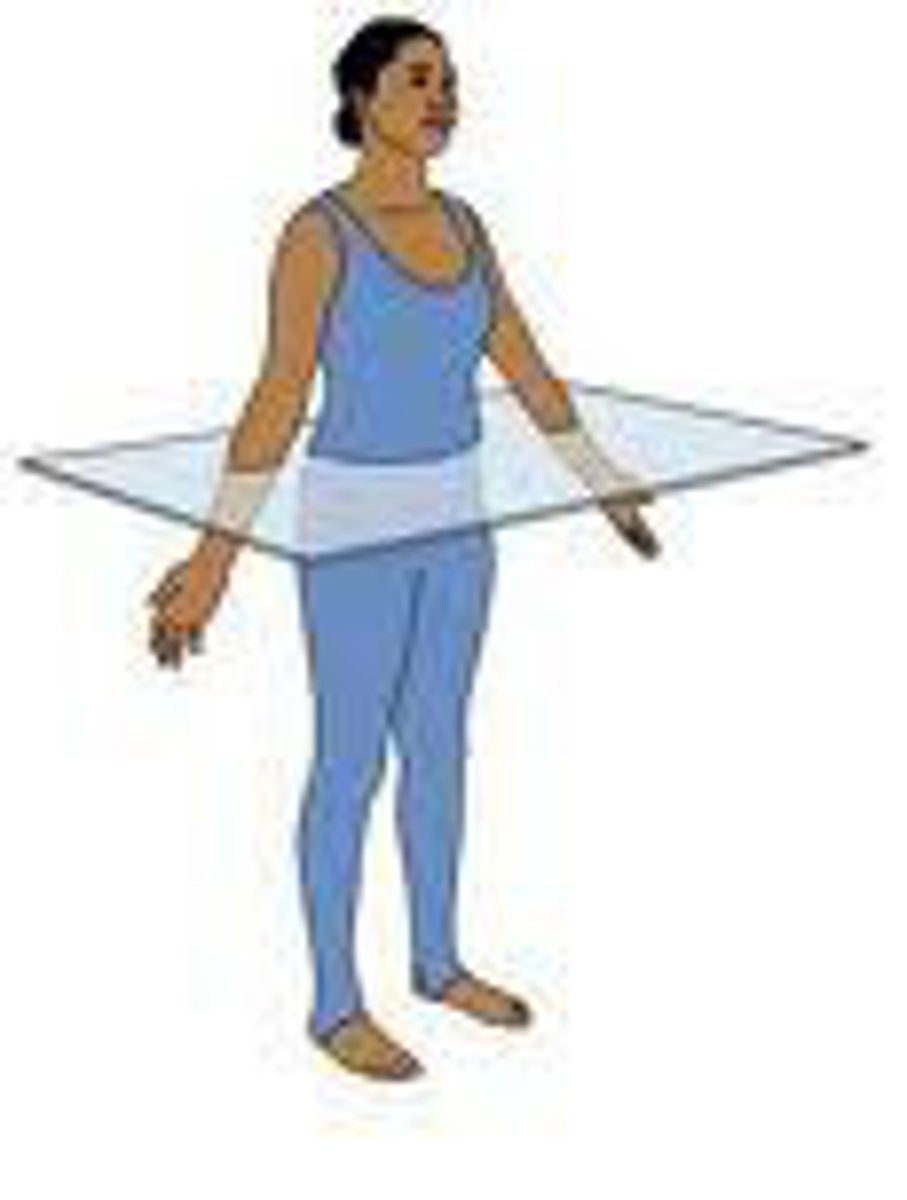
horizontal
slice parallel to the ground
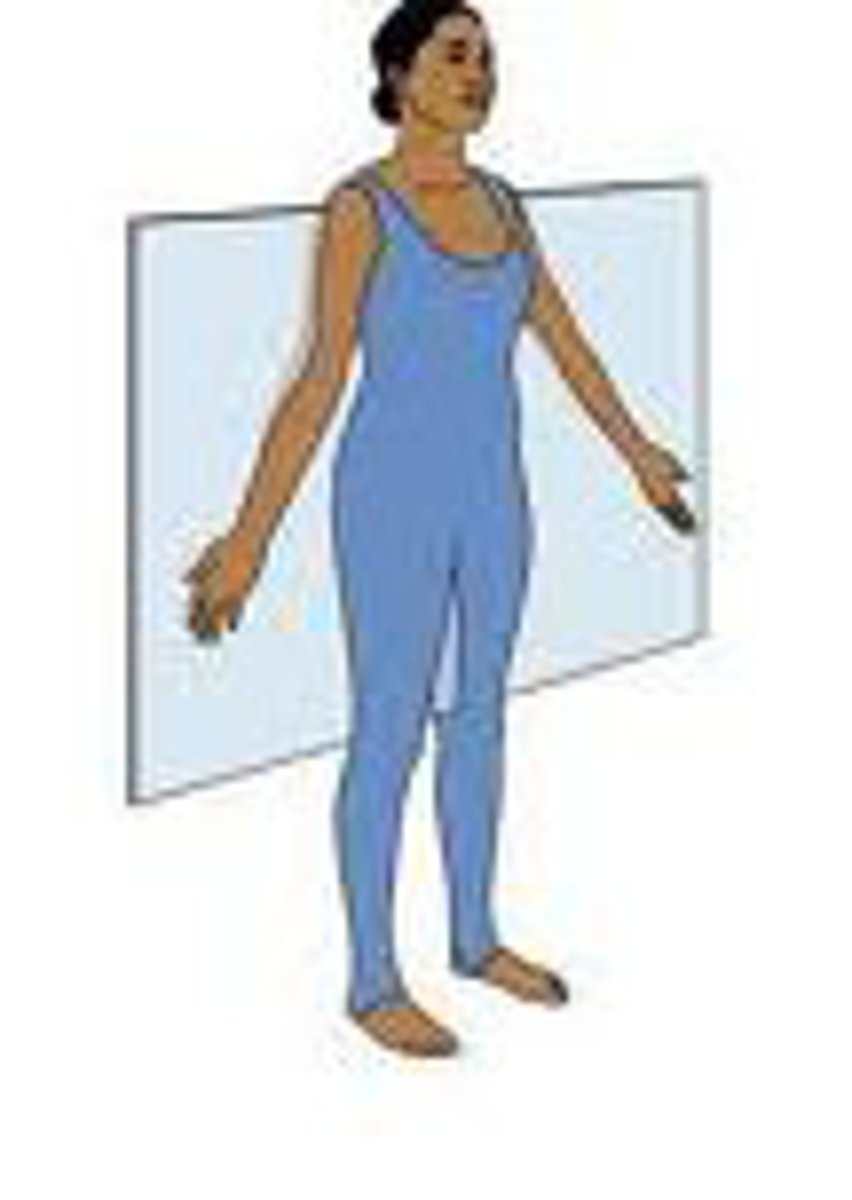
frontal
slicing bread or salami

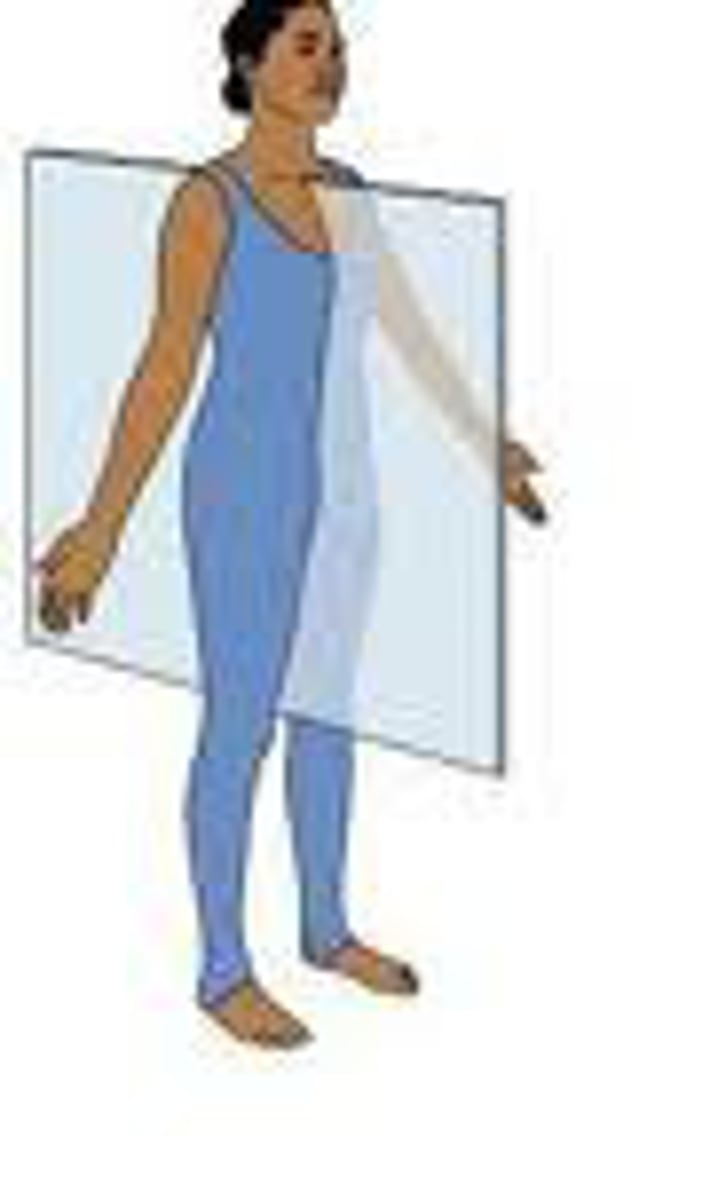
sagittal
midsagittal section separates the left and right halves
gray matter
inner component
prim cell bodies and unmyelinayed interneurons
white matter
outer area mainly myelinated axons
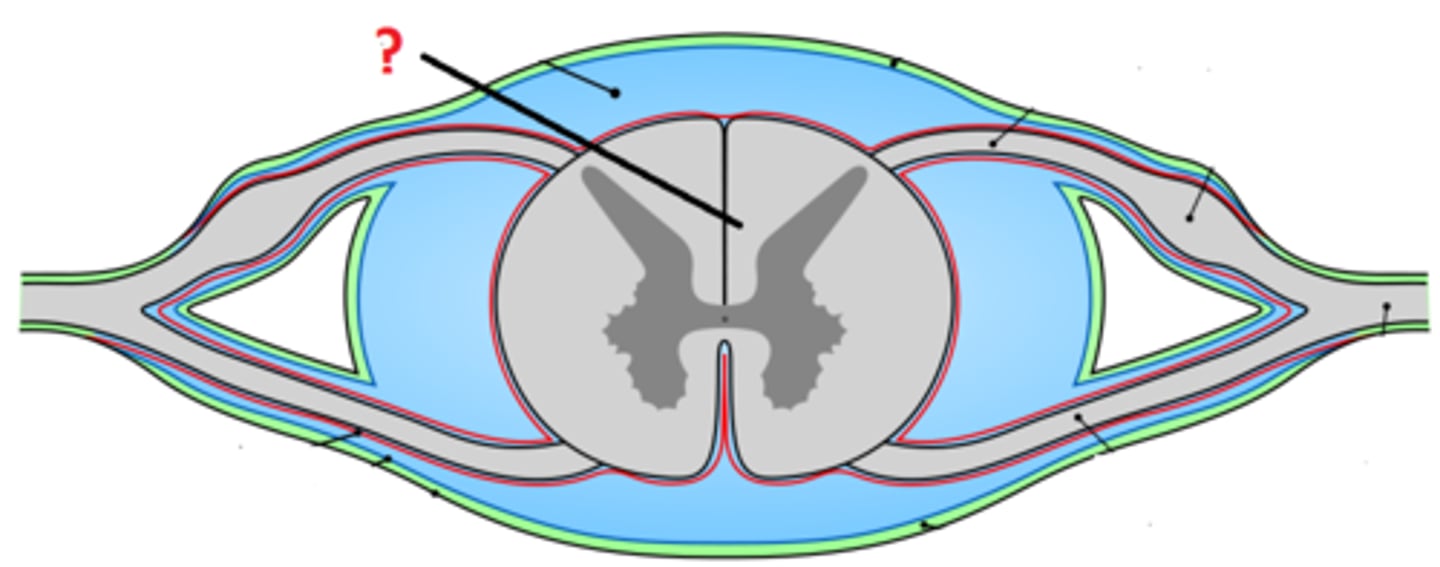
dorsal
afferent sensory
ventral
efferent motor
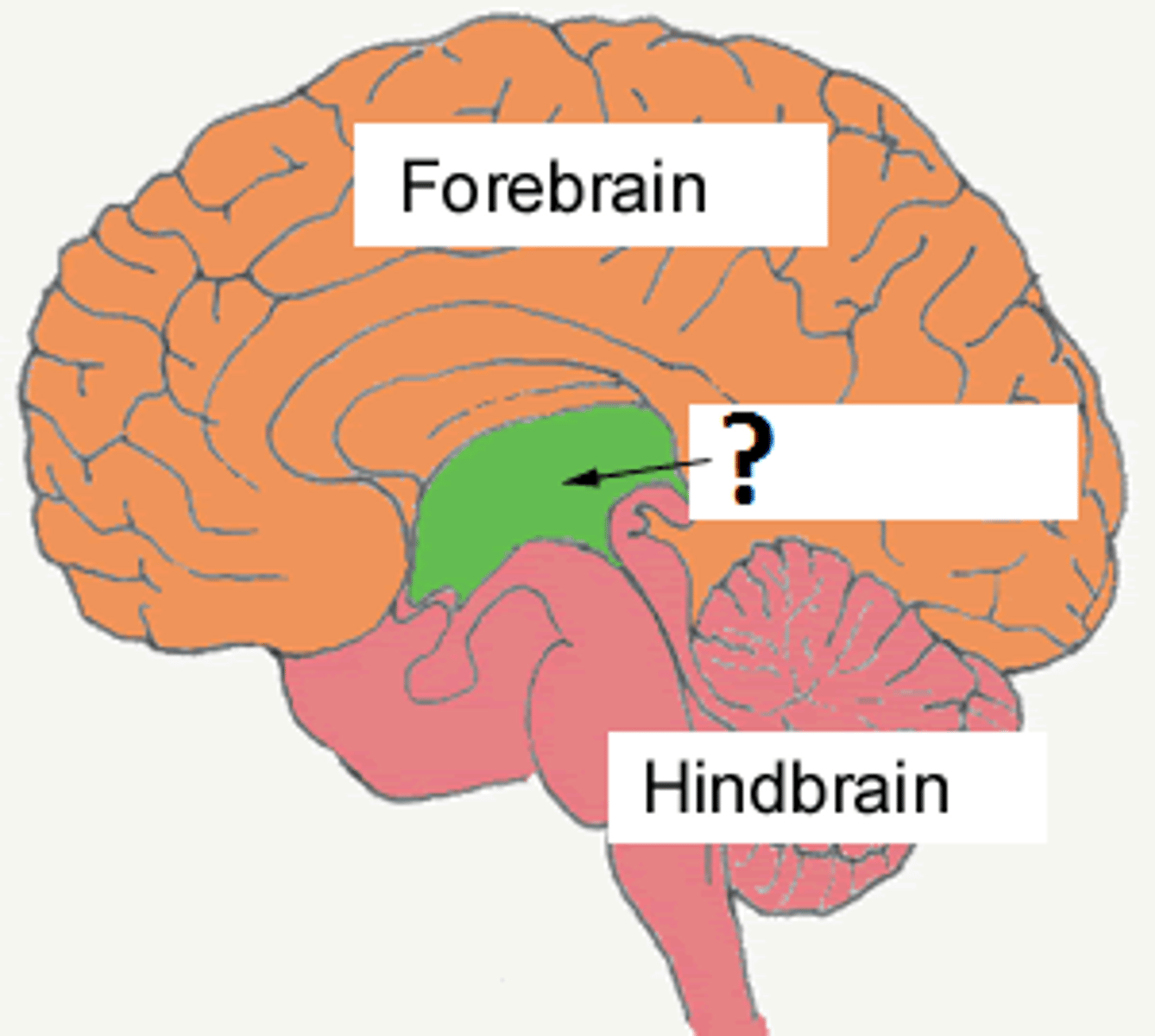
telencephalon
diencephalon
mesencephalon
metencephalon
myelencephalon
five major divisions of the brain
Telencephalon
diencephalon
major divisions of the brain
in forebrain
mesencephalon
major divisions of the brain
metencephalon
myelencephalon
major divisions of the brain of hindbrain
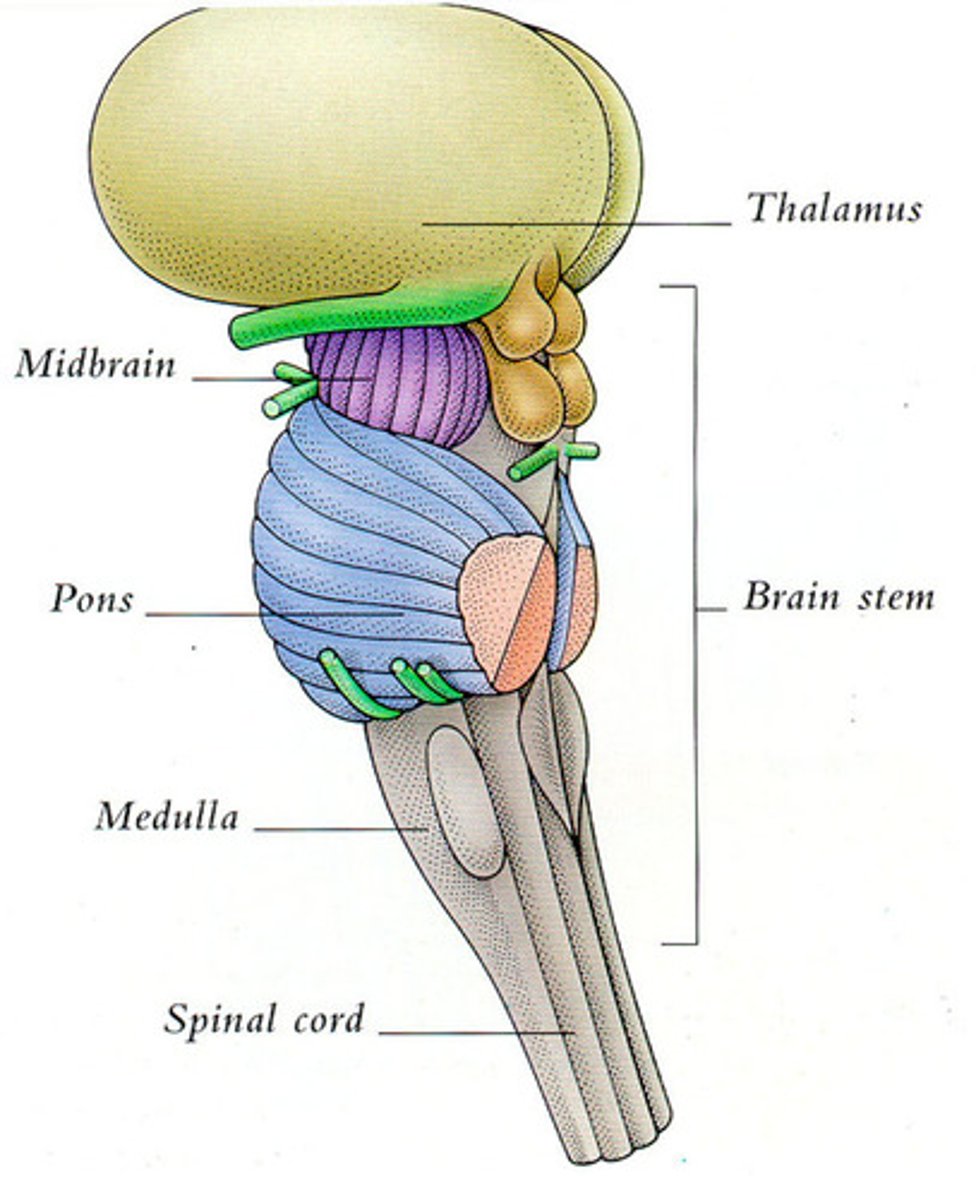
brain stem
regulates reflex activities that are critical for survival
cerebral hem sits on top of it
myelencephalon
divisions of the brainmedulla oblongata
composed largely of tracts that carry signals bw brain and body (auto fxn)
origin of the reticular formation'
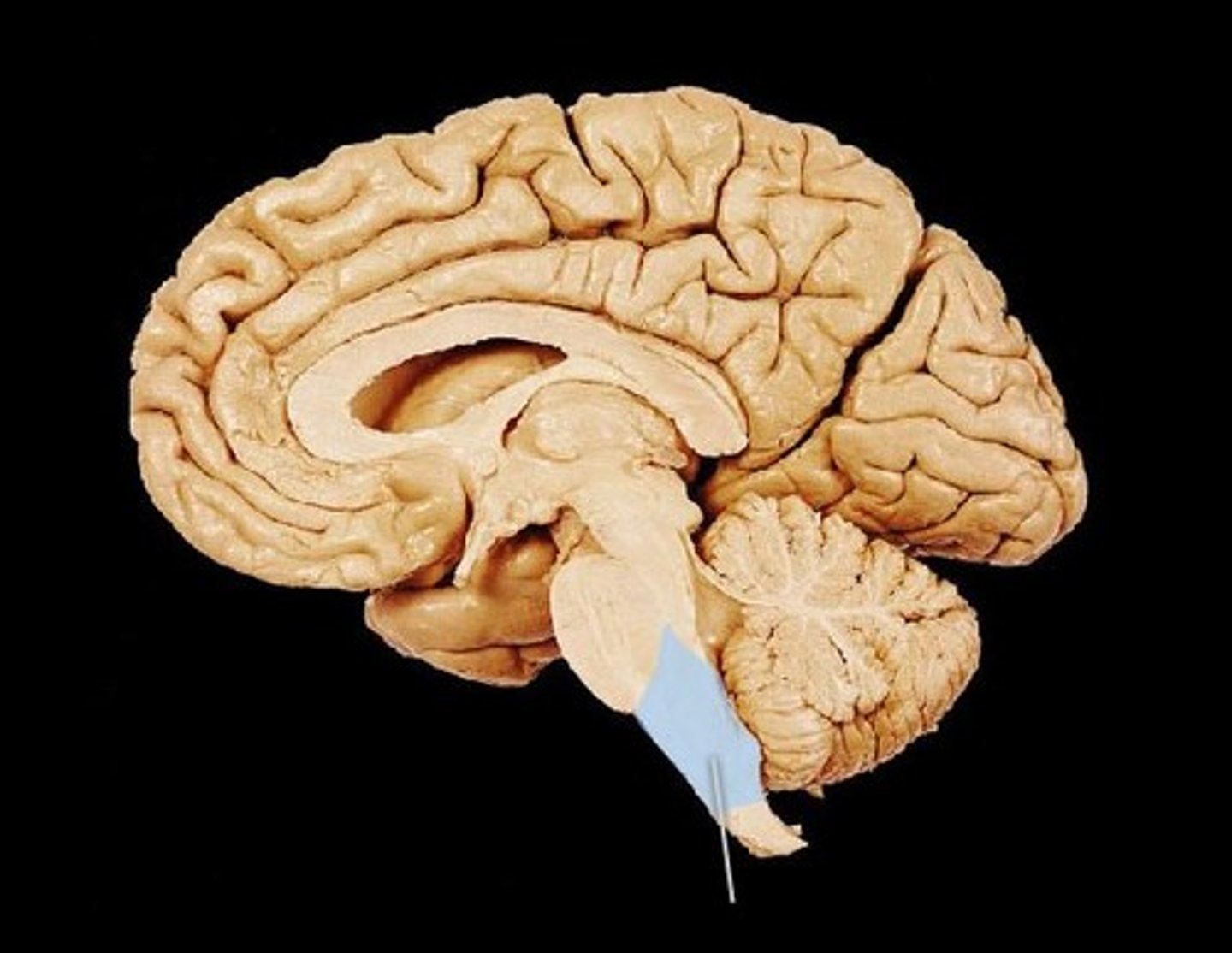
reticular formation
Network of nuclei that play a role in arousal
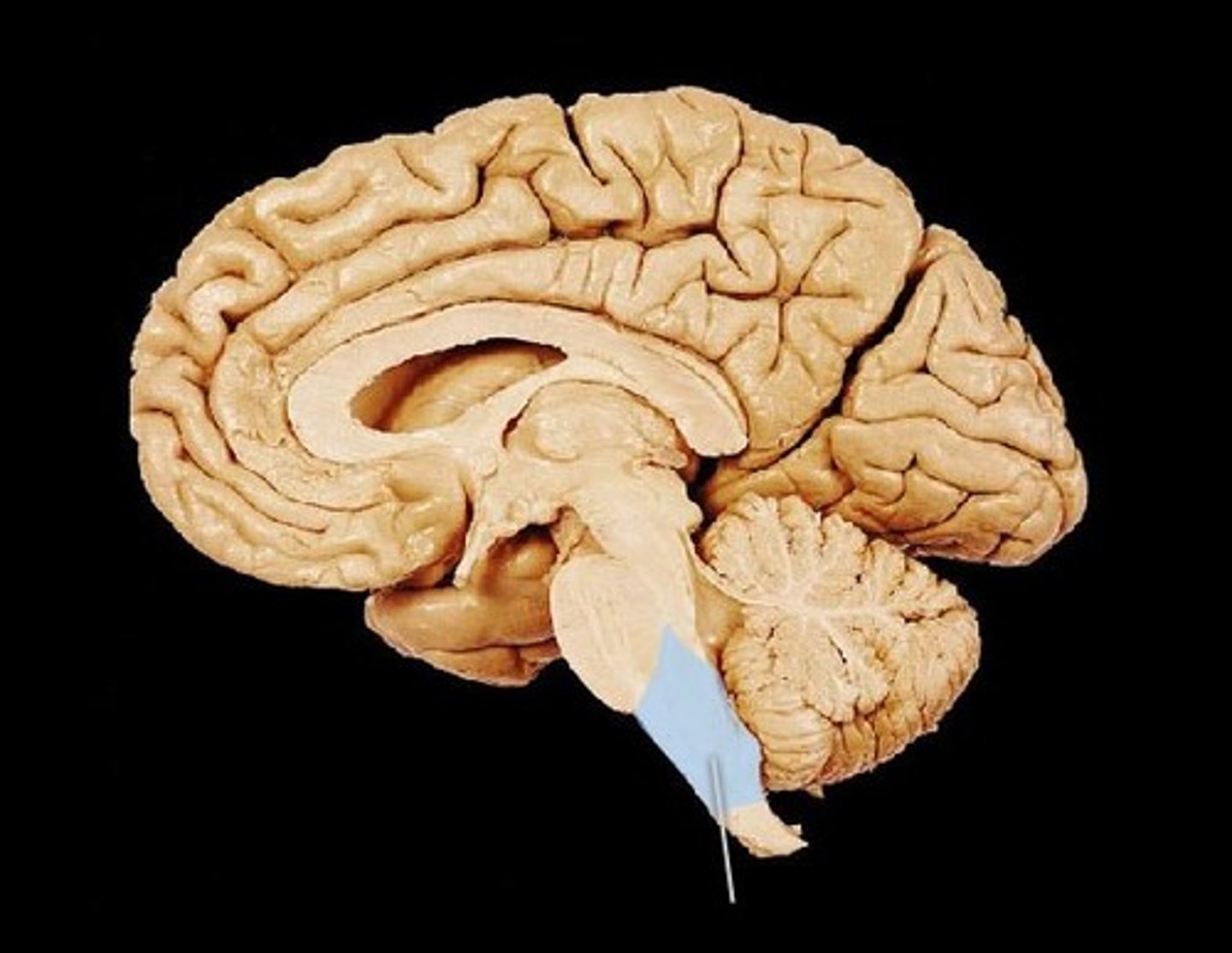
metencephalon
pons
cerebellum divisions of the brain
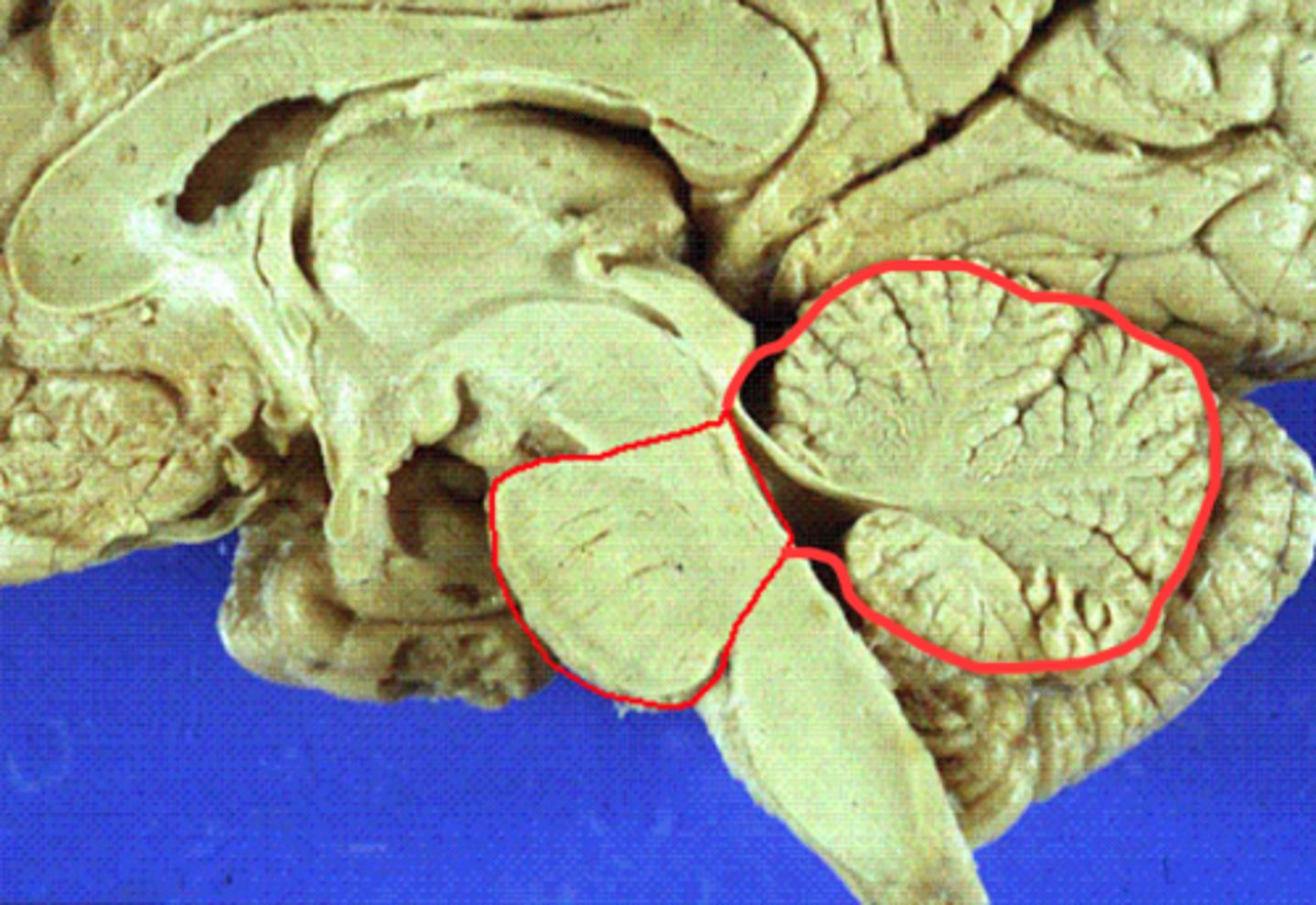
pons
replays messages from cortex to crebellum
imp for sleeping/dreaming
cnt sev cranial nerves
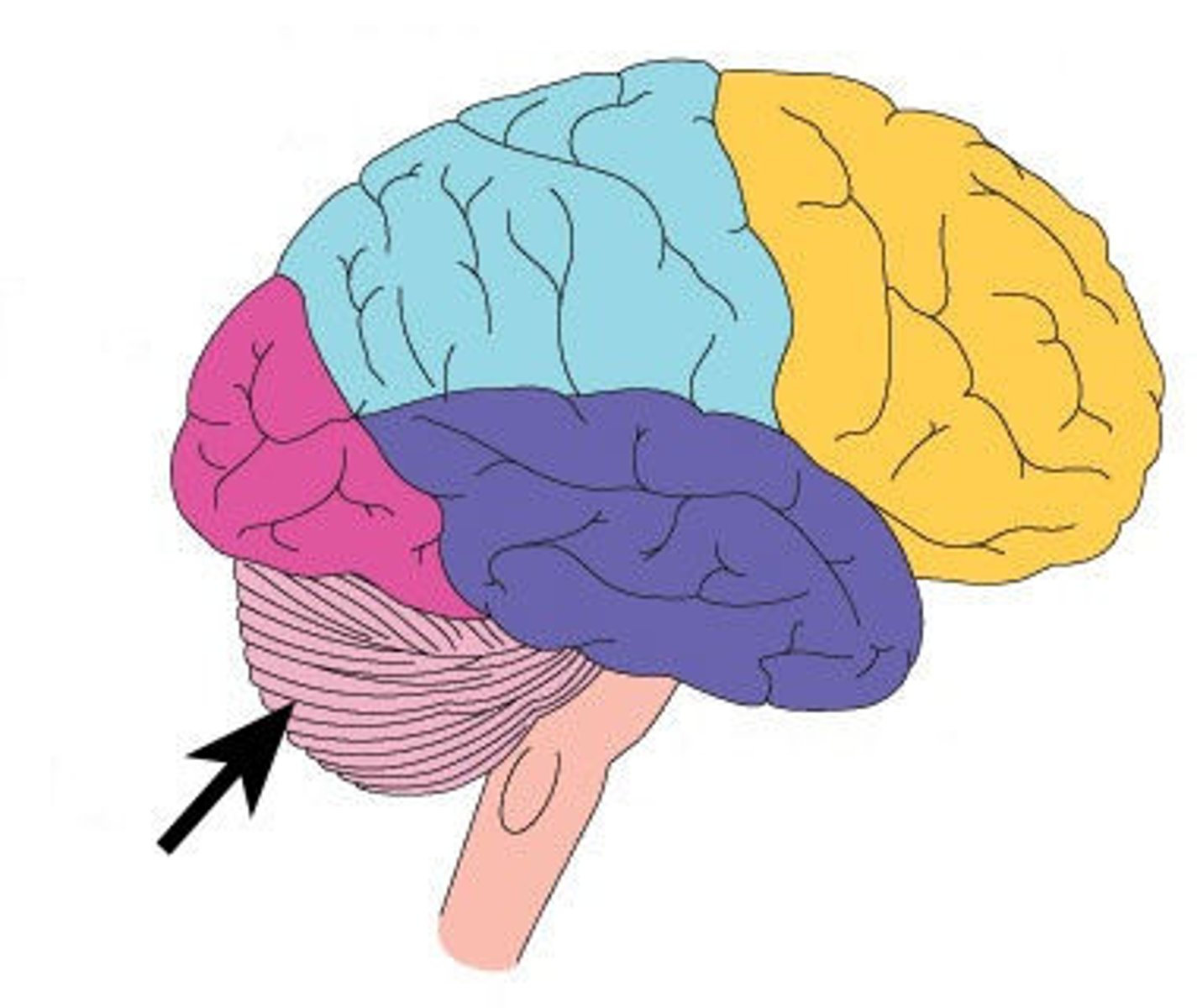
cerebellum
mvm
balance
memory for simple skills & acq reflexes
decision making & understanding words
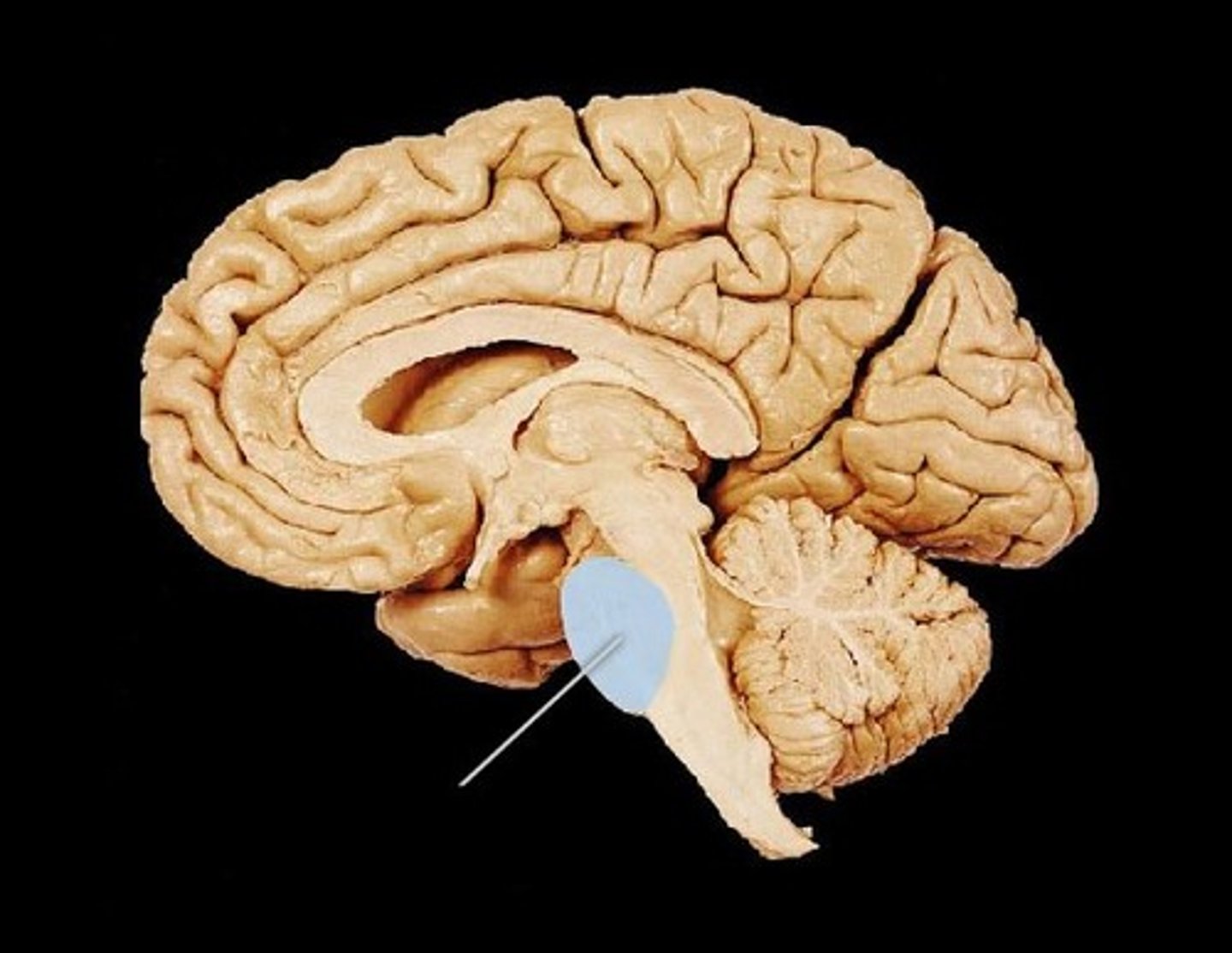
Mesencephalon
midbrain
divisions of the brain
tetum and tegmentum
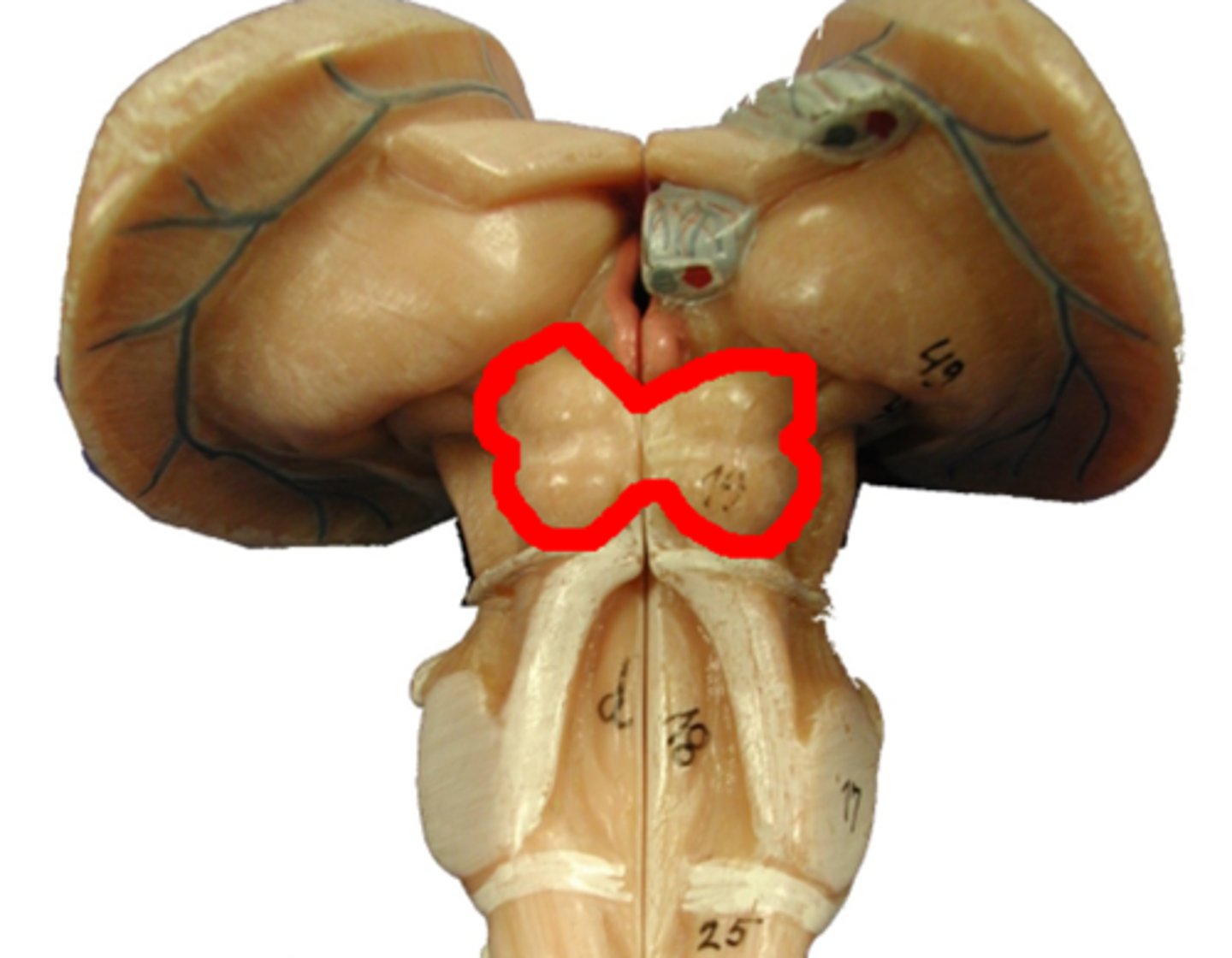
tectum
inferior colliculi (auditory fxn)
superior colliculi (visual motor fnx)