Bacterial Visualization, Bacteria Isolation, Environmental Factors, Culture Media
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
magnification
total magnification = ocular x objective
light microscope with oil- 1000x
-how big is it, how big it looks
-makes tiny microorganism big enough to see
contrast
reflects internal detail
light rays absorbed by, reflected by or transmitted completely through sample
different light intensities reach eye
staining increases contrast
-how well you can see it
-makes cells stand out from the background
-can i see it
resolution
ability to distinguish 2 close objects as separate
resolving power light microscope = 200nm
resolution inverse to wavelength of light
resolution decreases as wavelength increases
longer wavelength- less energy
resolution increases as wavelength decreases
shorter wavelength- more energy
resolution more important for visualization than magnification
stains increase contrast, increased contrast increases resolution
-how sharp the image is
-clear
-Can I see details
-shorter wavelength- better resolution
-staining increases contrast- improves resolution
streak plate technique
easiest, most common way to obtain isolated, single colonies
decreases number of bacteria on plate
streak plate prepared directly from mixed sample
inoculate mixed sample onto section 1 of plate with sterile loop
streak sample parallel to long axis of section
cover entire surface in section 1
transfer sample from section 1 to section 2
streak plate technique
sterilize loop
touch last inoculated area in first section
drag through section 1 into section 2
spread sample parallel to section 2 as above
do not go back into section 1
transfer sample from section 2 to section 3
sterilize loop- drag from section 2 to section 3 as above
transfer sample from section 3 to section 4
sterilize loop- drag from section three into section four
lazy loop in section 4
section 4 should contain the fewest bacteria colonies
Environmental conditions directly influence bacterial growth
temperature
maintain with incubators, water baths, refrigerators in lab
mesophiles (grow best at 37 °C)
grow best at body T
maximum growth, reproduction occurs at optimum temperature
E. coli optimum (37 C)- proteins begin to denature at 40 C+
thermophiles- heat resistant; grow best at 60+C/ grow in very hot environments
-how fast bacteria grow
too cold- enzymes work slowly
just right- maximum growth
too cold= slow, too hot= dead, just light=grow
pH
measure of hydrogen (H+) ions in solution
optimum pH for growth varies between species
6.5 to 7.5 average- fungi 4.5 to 6.0; blood 7.4 (7.2 and 7.6 toxic)
culture pH changes over time
metabolic byproducts accumulate as nutrients are used up
usually becomes more acidic- fewer species survive
buffers prevent abrupt changes in culture pH
buffers donate H+ ions or remove H+ ions
-how acidic or basic the environment is
-ph affects protein structure and enzyme function
-most bacteria grow best at neutral ph (6.5-7.5)
-metabolism changes ph over time - growth slows
-wrong ph- broken proteins
oxygen requirements
vary between species
oxygen can be reduced or removed completely in culture
thioglycolate broth- differential broth medium
Thioglycolate combines with oxygen
establishes oxygen gradient in culture
atmospheric O2 at top of tube, no O2 at bottom of tube
methylene blue- O2 indicator; green in atmospheric O2
green band at top of broth indicates amount of atm oxygen in tube
Brewer anaerobic jar (oxygen is removed by reacting with hydrogen)
combines oxygen with hydrogen to form water
forms anaerobic environment inside jar
candle jar (oxygen inside a sealed jar) “eats oxygen”
burning candle reduces oxygen concentration
forms microaerophilic environment inside jar
-removes oxygen
-
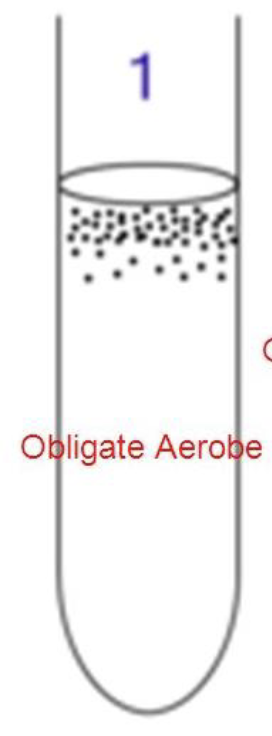
obligate aerobic species
needs oxygen/ must have oxygen - to survive
require atmospheric level of oxygen
example : Pseudomonas aeruginosa
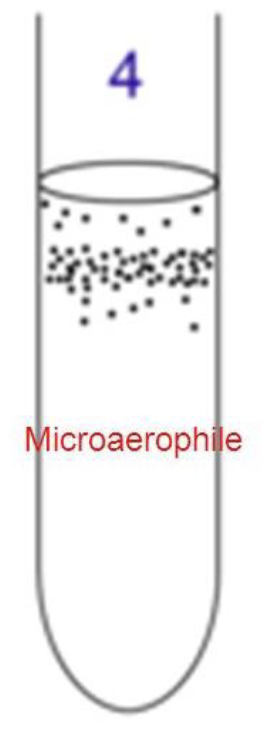
microaerophilic species
require oxygen but less than atmospheric level of oxygen
example : Micrococcus
-needs low oxygen
-too much oxygen damage them
-minimal oxygen

obligate anaerobic species
do not use oxygen- killed by oxygen (toxic)
Clostridium
-oxygen kills them

aerotolerant anaerobic species
do not use oxygen- not harmed by oxygen
example : Lactobacillus (lacto ignores oxygen)
-dont use oxygen but aren’t harmed by it
-oxygen doesn’t bother me
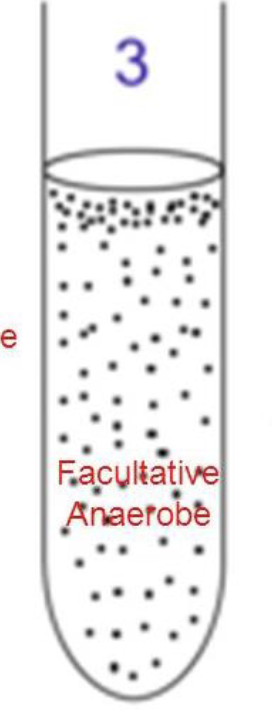
facultative anaerobic species
use oxygen if present- can live with or without oxygen
E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
-can survive without oxygen
“flexible with oxygen”
Culture media
iquid (broth) or solid (agar) containing nutrients and other agents required for growth
agar
polysaccharide from red algae
-food for bacteria
-agar= algae jelly
defined medium
exact chemical composition known to mg
-defined- detailed recipe
minimal defined, rich defined
minimal defined
medium
contains just enough nutrients to support growth
use to determine minimum growth requirements
minimum amounts vary depending on organism
Leuconostoc- limited metabolic capability (needy)
requires many substances to grow
E. coli- mostly self sufficient
requires only glucose, salts (independent)
rich defined
medium
abundant nutrients
exact amounts known- grows all species
rich= luxury buffet
undefined (complex) medium
abundant nutrients
exact composition unknown- grows all species
tryptic soy agar, nutrient agar
selective medium
contains inhibitory agent
grows species that tolerate inhibitory agent
species that do not tolerate inhibitory agent do not grow
-only the strong survive
-who grows
salt agar
only salt tolerant (can survive it) species in sample grow on salt
Staphylococcus,- grows on salt agar , Micrococcus, Bacillus
-salt kills most bacteria
-salt tolerant bacterian survive high salt
salt tolerant- salt doesn’t scare me
differential medium
grows all bacteria in sample
growth characteristics (appearance) on agar distinguish different species
differental- everyone grows but looks different
-all bacteria grow
blood agar
motility agar
thioglycolate broth
blood agar
grows all species
colonies look different on blood- Streptococcus species
motility agar
all species grow
distinguish motile bacteria from non motile bacteria
hioglycolate broth
all species grow
distinguish aerotolerance characteristics of bacteria
selective and differential medium
grows some species in the sample, inhibits others in the sample
distinguish species that grow by appearance on agar
selective- who grows
medium- how they look
mannitol salt agar
salt- selective agent
selects for salt tolerant species in sample
non salt tolerant species do not grow
mannitol- differential agent
distinguishes salt tolerant species by mannitol fermentation
yellow color- uses mannitol; Staphylococcus aureus
-high salt kills most bacteria
-only salt tolerant bacteria survive and all grow
MacConkey agar
selects for Gram negative bacteria in sample
inhibits Gram positive bacteria in sample
lactose- differential agent
some Gram negatives ferment lactose
E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter- form pinkish to reddish colonies
some Gram negatives do not ferment lactose
Shigella, Salmonella- form whitish colonies
-kicks out gram positive
non- lactose fermentes- white clear
enrichment procedure
not media
expose mixed sample to unusual treatments
endospore isolation- boil sample
only endospores survive
boil the sample
-only endospores survive
-endospore are heat- resistant
boil it- spores survive
-you treat the sample to kill most bacteria
the special ones survive

thioglycolate broth tube
differential broth medium
Thioglycolate combines with oxygen
establishes oxygen gradient in culture
atmospheric O2 at top of tube, no O2 at bottom of tube