Science Final Exam Notes
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam Tuesday at 9:30am
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Define Independent variable:
The one factor that is purposely changed by the scientist during an experiment
Define dependent variable:
The factor that changes in response to the Independent Variable; the variable that is measured during an experiment.
Define controlled varaible:
A factor in an experiment that is kept to be constant so that it doesn’t affect the outcome.
Explain the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
An Independent variable is what we will expect will influence the dependent variable.
And the Dependent variable is what happens as a result of the Independent variable.
What is the most reliable method for identifying a minerals unique characteristics?
Crystalline structure, geometric shape, and streak.
What is the least reliable method for identifying a minerals unique characteristics?
Color is the least useful property because many minerals may be the same color, and the same mineral may exist in many different colors.
What is the name of the scale that is used to rate the hardness of a mineral?
Mohs Hardness Scale
How do you perform a streak test? What items do you need to perform a streak test?
Rub a mineral across a white or black porcelain plate and observe the color of the streak that is left behind.
You need a porcelain plate and a sample of the mineral.
Define Fracture:
It is the texture/shape of a rock surface, that is formed when a mineral is fractured.
Define Cleavage:
It’s the tendency of a mineral to break along certain flat surfaces or planes which are flat, smooth lines due to weak, and atomic bonding.
List potential negative consequences associated with mining:
Deforestation
Pollution
Erosion
Contamination of wetlands/local streams
Health risks for workers.
What is the Density Triangle?
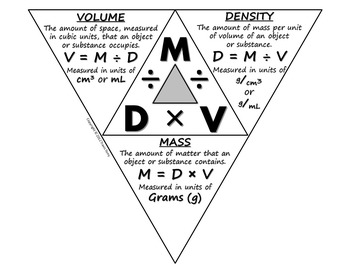
Density=Mass/Volume
Mass= Density x Volume
Volume= Mass/Density
Define Lithosphere:
It is the rigid outer layer of the Earth, it consists of the crust and the upper part of the mantle.
Tectonic plates that are part of the lithosphere:
North American, Caribbean, Antarctic, South American, African, Australian, etc
What is the key difference between Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift and the modern theory of plate tectonics?
The modern theory of plate tectonics explains a mechanism for how the continents move, but Alfred’s theory did not explain that.
Define Theory of Continental Drift:
The Continents on Earth’s surface once joined together into a supercontinent called Pangea, but have slowly separated over millions of years.
Define Theory of Plate Tectonics:
The Earth’s lithosphere is being broken up into large, rigid plates that move/interact with one another.
What geological feature is most likely to form at a divergent boundary of two oceanic plates?
The Mid Ocean Ridge and the Mid Atlantic Ridge
Mid Atlantic Ridge:
Boundary type: Divergent
Crust 1: Oceanic
Crust 2: Oceanic
Andes Mountains:
Boundary type: Convergent
Crust 1: Oceanic
Crust 2: Continental
Aleutian Trench:
Boundary type: Convergent
Crust 1: Oceanic
Crust 2: Oceanic
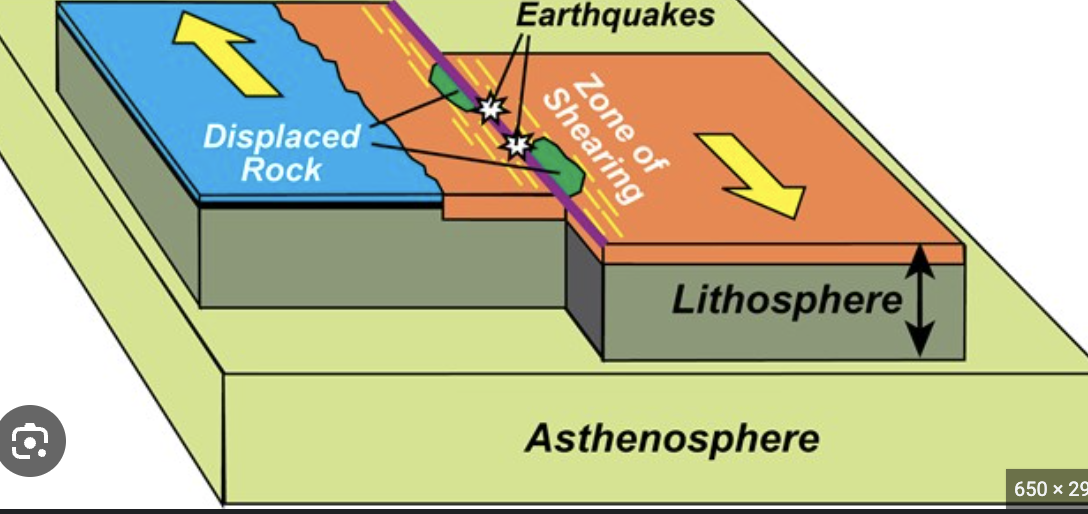
San Andreas Fault:
Boundary type: Transform
Crust 1: Continental
Crust 2: Oceanic
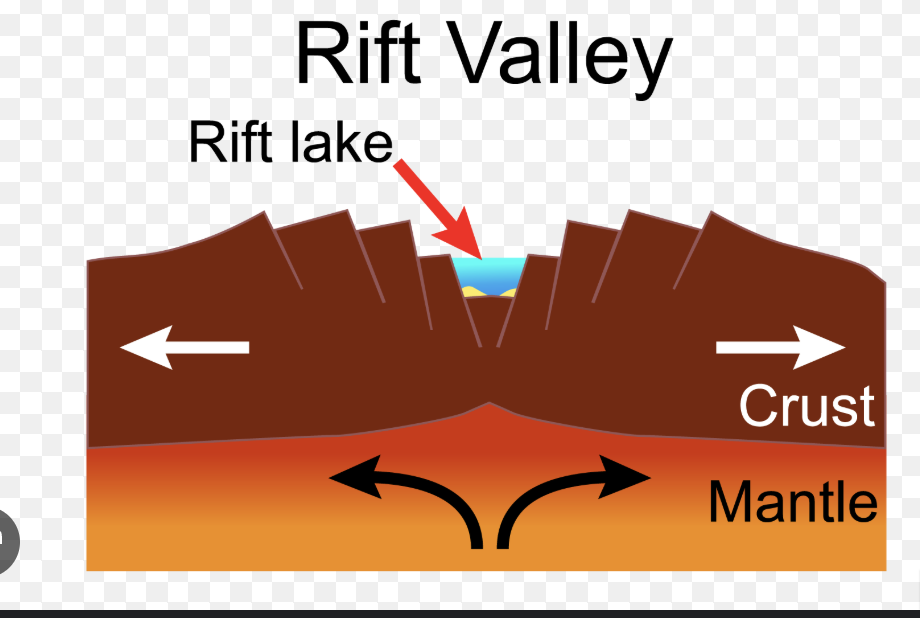
Draw arrows indicating the movement at divergent boundaries.
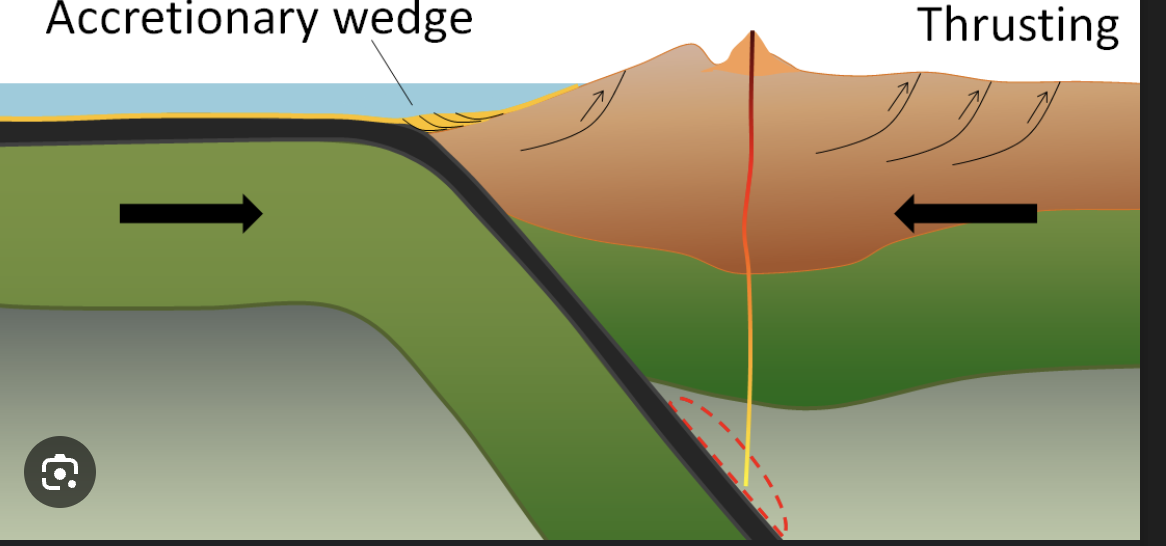
Draw arrows indicating the movement at convergent boundaries.
Draw arrows indicating the movement at transform boundaries.
How do the differing densities of oceanic and continental crust affect plate interactions?
Which crust is more dense? (Use the term subduct or subduction in your answer)
The Oceanic crust is more dense than the continental crust.
The Oceanic crust can subduct under the continental crust, creating volcanoes and earthquakes.
What one geological feature is common to all types of plate boundaries?
Earthquakes
What geological features occur at a continental collision (convergent plate boundary)?
Earthquakes and Mountains
What geological features occur at a continental divergent plate boundary?
Rift Valley and Earthquakes
What drives (causes) the movement of tectonic plates?
The Convection currents
What is the primary mechanism (cause) of convection currents in the Earth’s mantle?
High/Low heat, transforming from the core to the mantle, in which causes movement.
How does temperature affect rock material in the mantle? Does it change the density of the rock material? Does it affect movement?
Yes, the more there is heat the less dense it will be causing it to rise. But when it rises it’s cooling and gets more dense causing it to sink.
When hot mantle rises near the Earth’s crust, what typically happens?
It cause the plates to move, and it triggers convection/gets more dense.
Why do convection currents create continuous movement in the mantle?
Because it goes from heating to rising and cooling to sinking.
How do convection currents contribute to plate tectonics?
It causes movement in the Earth’s lithospheric plate.
Be able to label this diagram of Earth’s layers:
