Periodicity
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
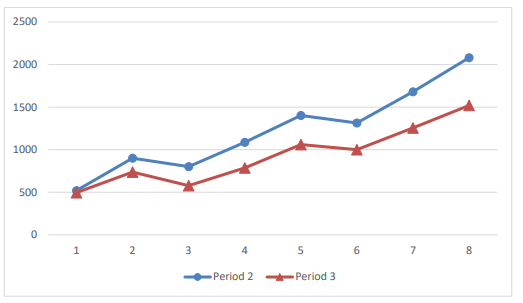
State and explain the general trend in first ionisation energies across a period.
First ionisation energies generally increase across a period. This is because
there are the same number of electron shells so the outer e-s experience a similar degree of shielding.
The nuclear charge increases and the atomic radius decreases
so the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons becomes stronger
requiring more energy to remove an electron
State and explain the trend in first ionisation energies down a group.
First ionisation energies decrease down a group. This is because
there are more electron shells so the outer e-s experience more shielding and the atomic radius increases.
Despite the increase in nuclear charge
the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons is weaker overall
requiring less energy to remove an electron.
What to mention in first ionisation energy questions?
State the trend
Shielding (outer electrons experiencing more/less)
Atomic radius (increases/decreases)
Nuclear charge (increases/decreases)
Electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons is (stronger/weaker)
Why is the first ionisation energy of the Gr3 element lower than Gr2 element of the same period?
Electron removed from the Gr3 element is from the p-subshell, whereas Gr2, it’s from the s-subshell
As the p-subshell is higher in energy than s, the p electron requires less energy to remove, thus the ionisation energy is lower
Why is the first ionisation energy of the Gr6 element lower than Gr5 element of the same period?
Electron removed from the Gr6 element comes from a doubly occupied p orbital, whereas Gr5 its from a singly occupied p orbital
The electron in the doubly occupied p orbital experiences more electron repulsion, so less energy is required to remove it, resulting in a lower ionisation energy
Write the 3rd ionisation energy of aluminium.

Equations that show the increase in reactivity down group 2:
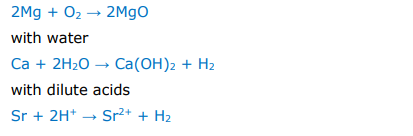
Appearance of halogens