Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
origin
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
usually the most stationary, proximal end of the muscle; also called the fixed end.
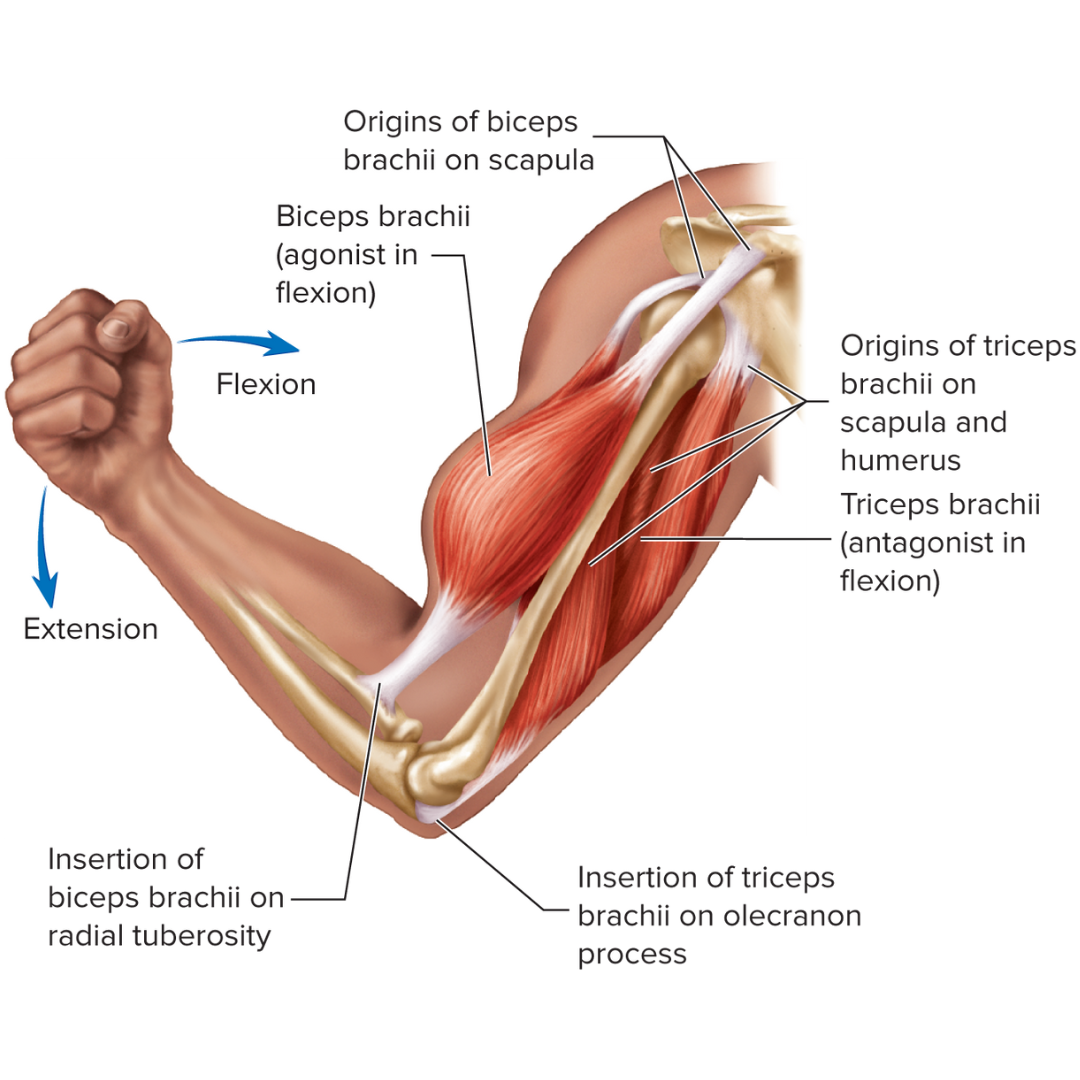
insertion
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
usually the distal end of the muscle attached to the bone being pulled toward the other bone of the joint; also called mobile end.
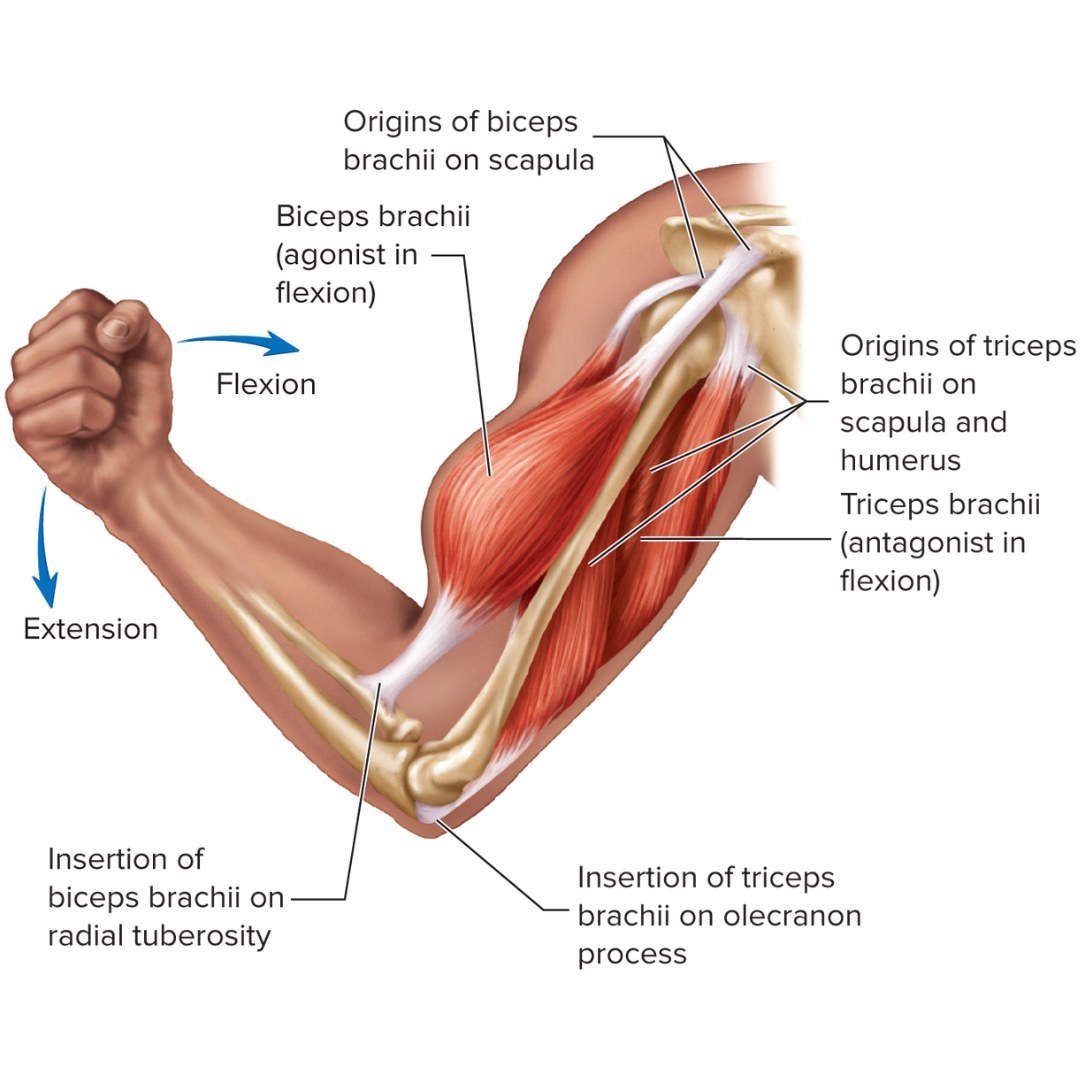
agonist
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
a muscle that contracts to provide the main force to move or rotate a bone through its joint
antagonist
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Muscle that works in opposition to another muscle
synergist
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Muscle that works with other muscles to cause a movement
fixator
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Muscle that stabilizes the origin of a prime mover
prime mover
General Principles of Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Muscle that plays a major role in accomplishing a movement
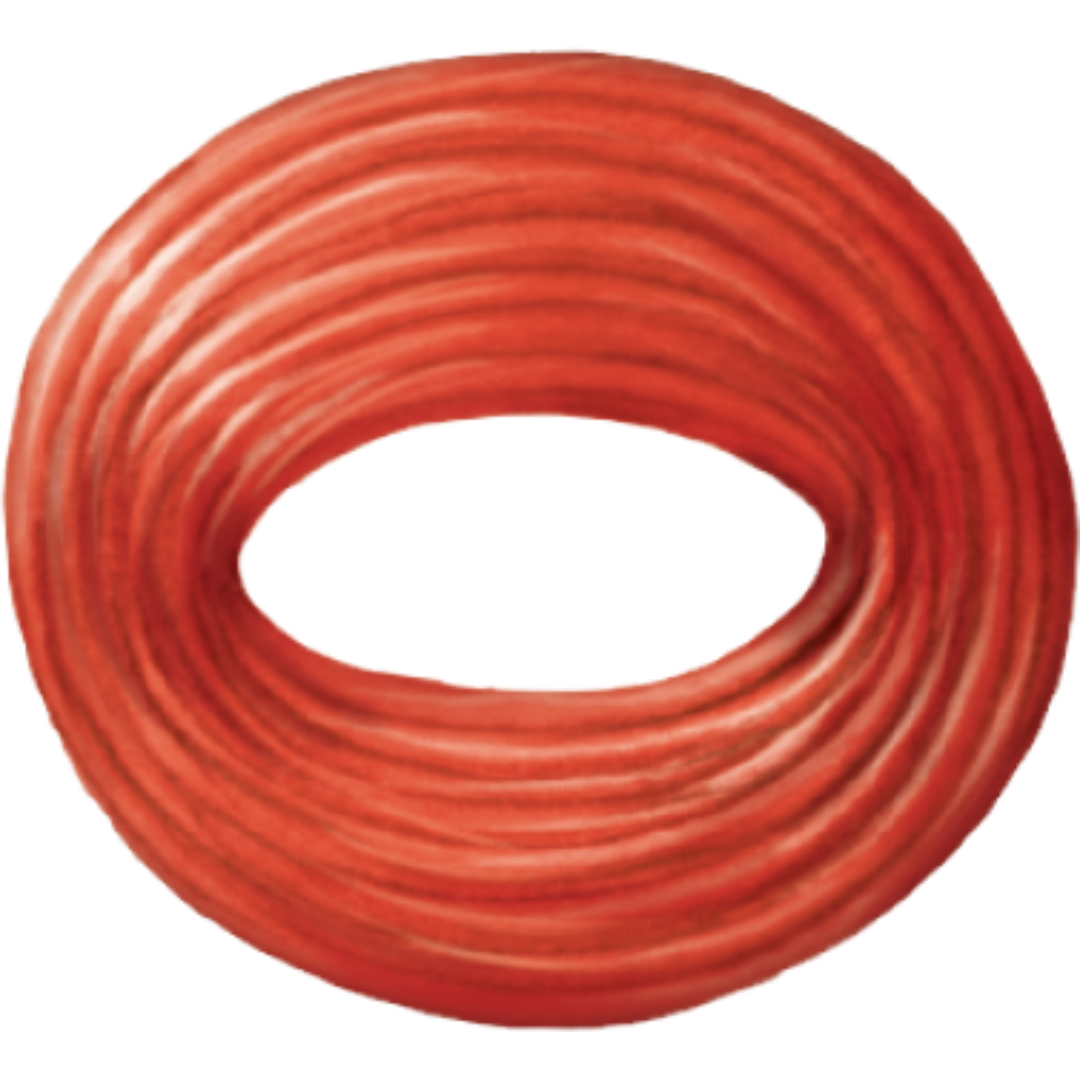
circular
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles are arranged in a circle around an opening, and act as sphincters to close the opening
Ex: Orbicularis oris, orbicularis oculi

convergent
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
broadly distributed fascicles converge at a single tendon
Ex: pectoralis major, pectoralis minor
parallel
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles lie parallel to one another and to the long axis of the muscle
Ex: trapezius, rhomboideus, rectus abdominus
pennate
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles originate from a tendon that runs the length of the entire muscle. There are three different patterns
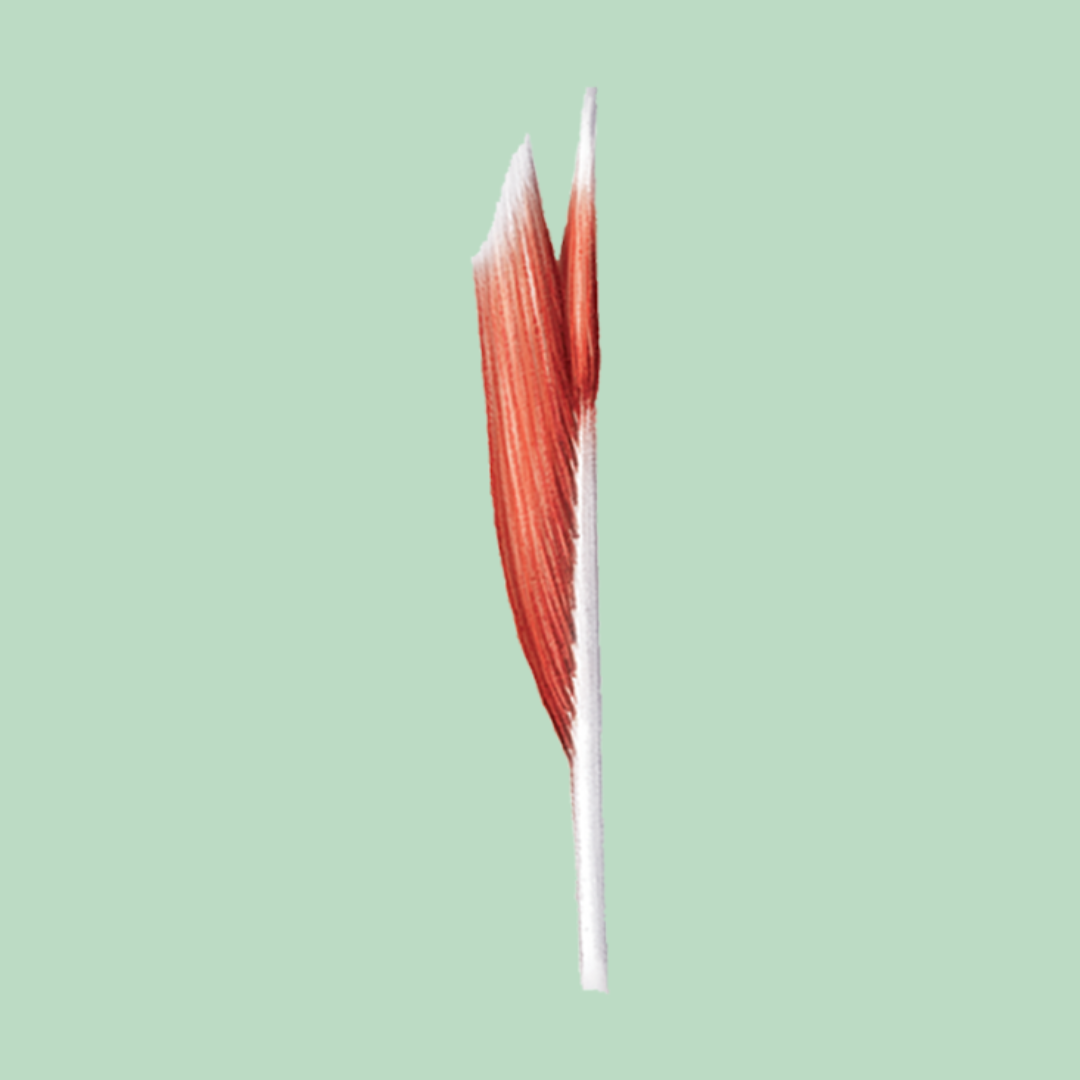
unipennate
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles are on only one side of the tendon
Ex: Palmar interosseus, semimembranosus

bipennate
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles are on both sides of the tendon
Ex: rectus femoris
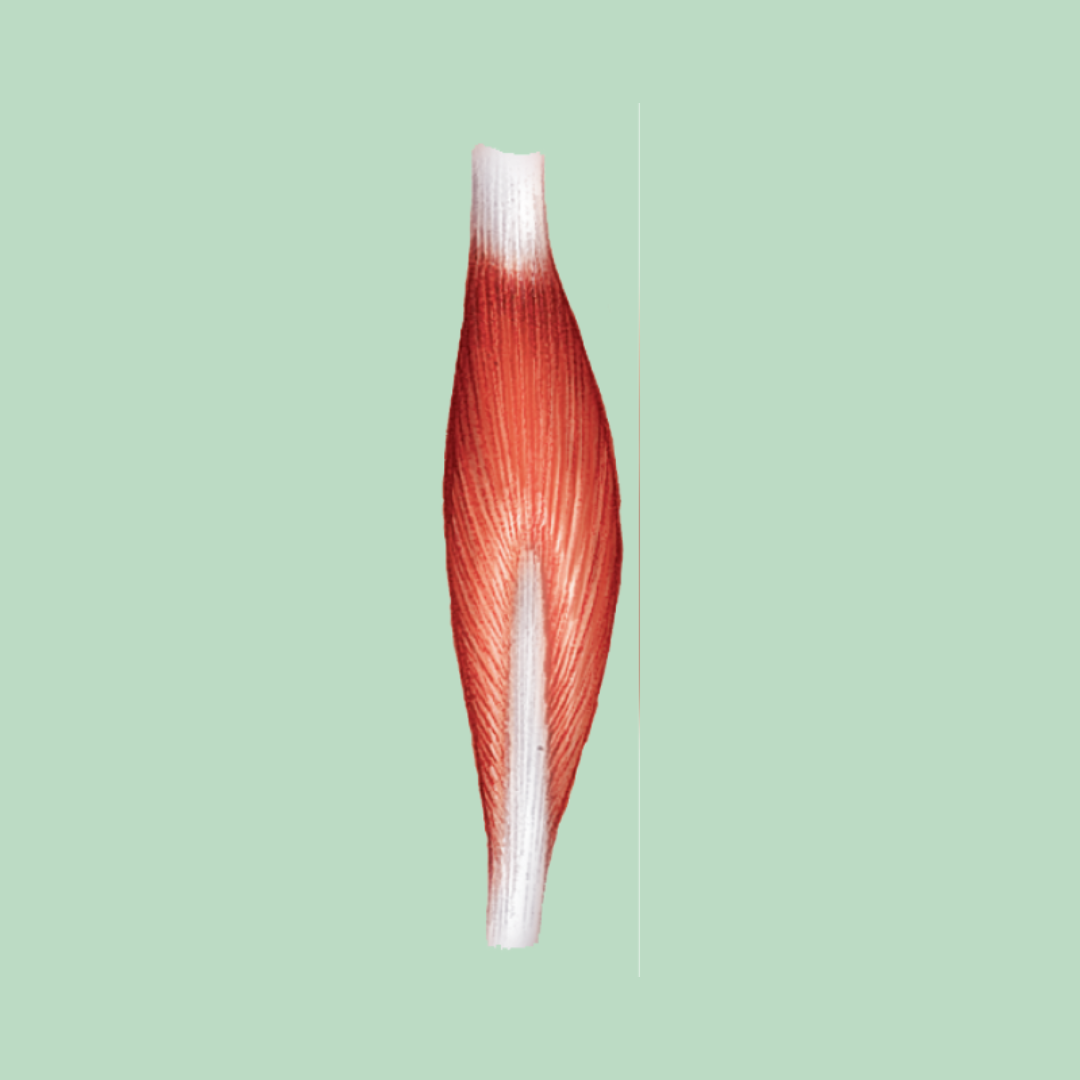
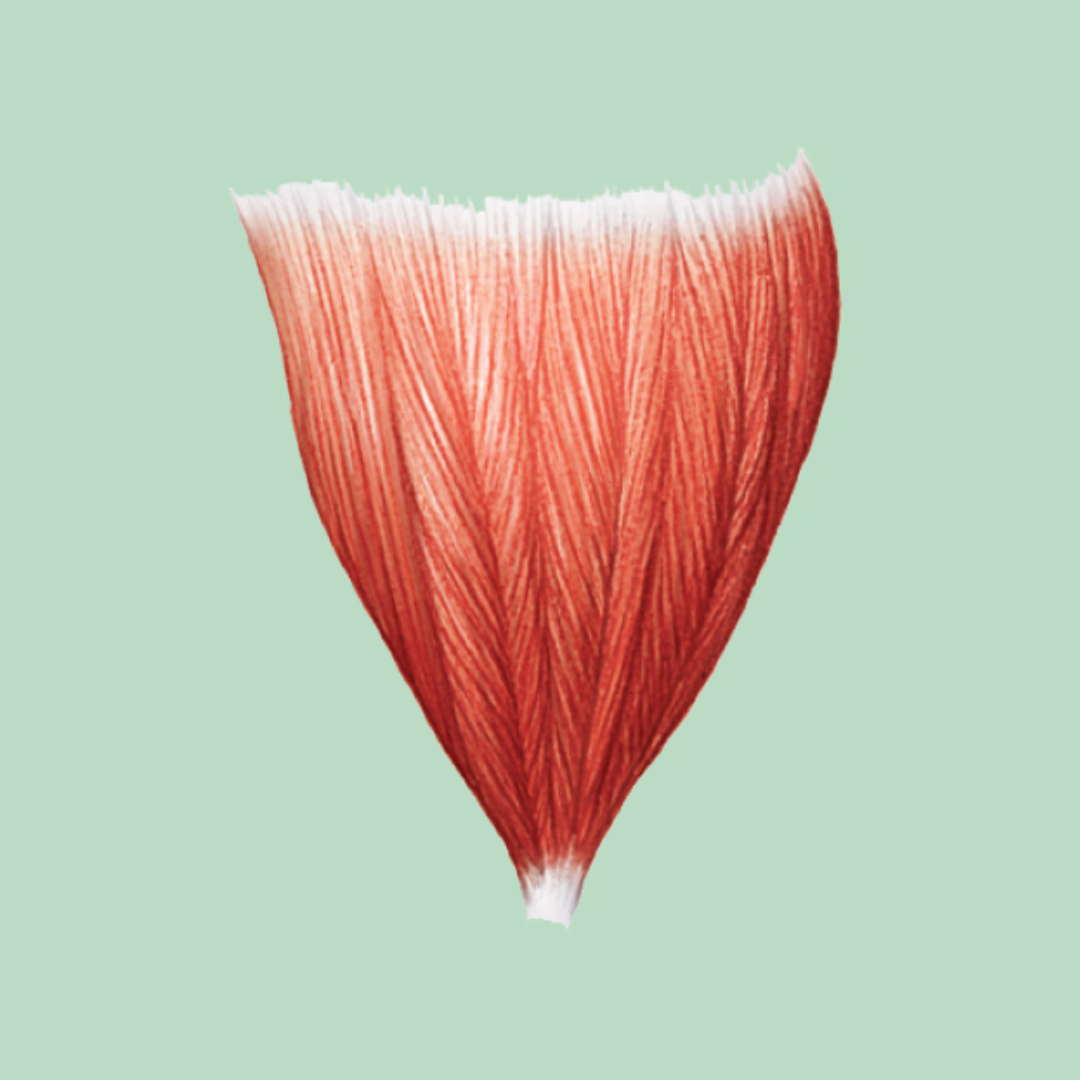
multipennate
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles are arranged at many places around the central tendon. They are spread out at angles to many smaller tendons
Ex: deltoid

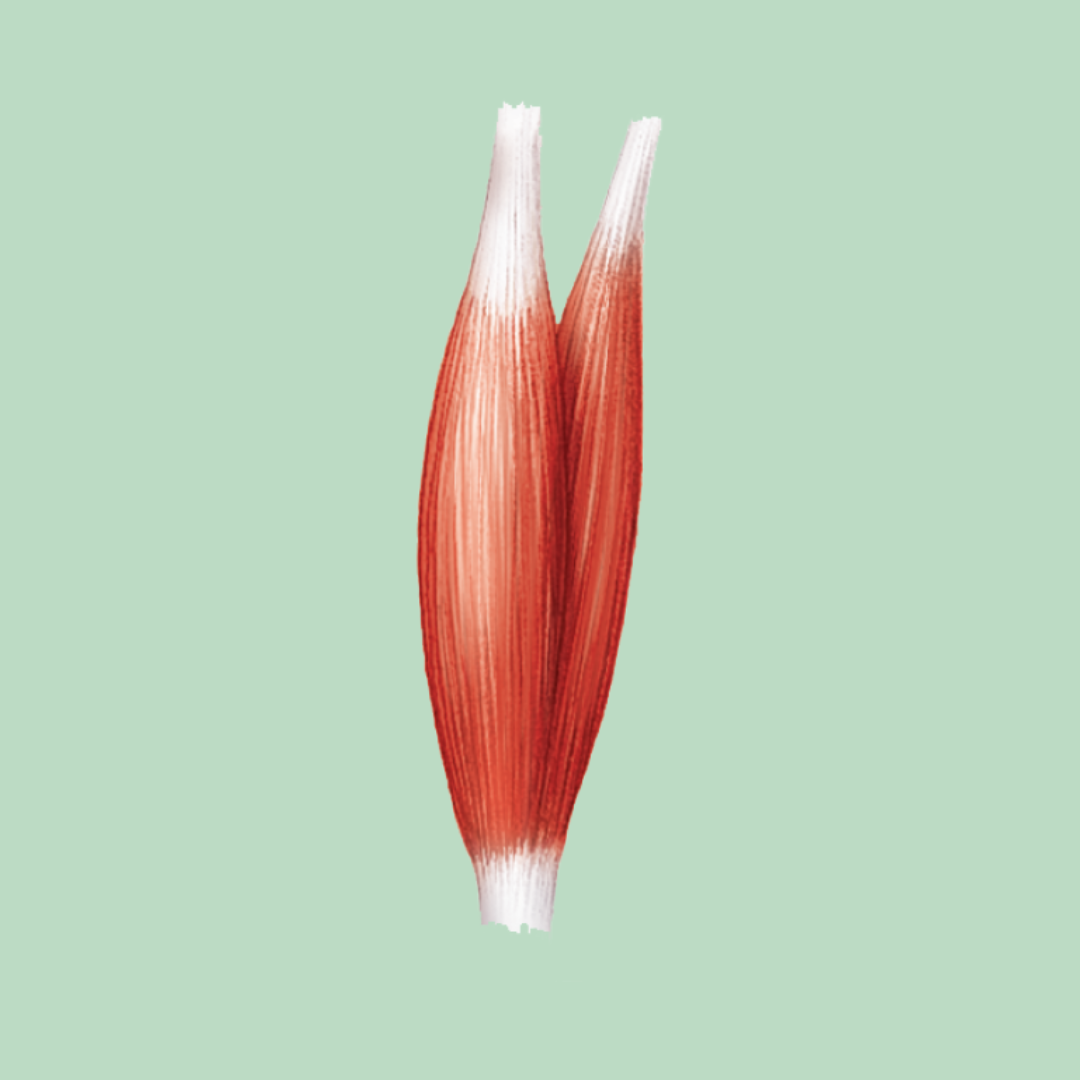
fusiform
Muscle Shapes / Fascicle Arrangement
fascicles lie parallel to the long axis of the muscle. The belly of the muscle is larger in diameter than the ends
Ex: Biceps bracii (two-headed; shown), Triceps brachii (three-headed)

pectoralis
Muscle Names
chest muscle
gluteus
Muscle Names
buttock muscle
brachial
Muscle Names
arm muscle
maximus
Muscle Names
large muscle
minimus
Muscle Names
small muscle
longus
Muscle Names
long muscle
brevis
Muscle Names
short muscle
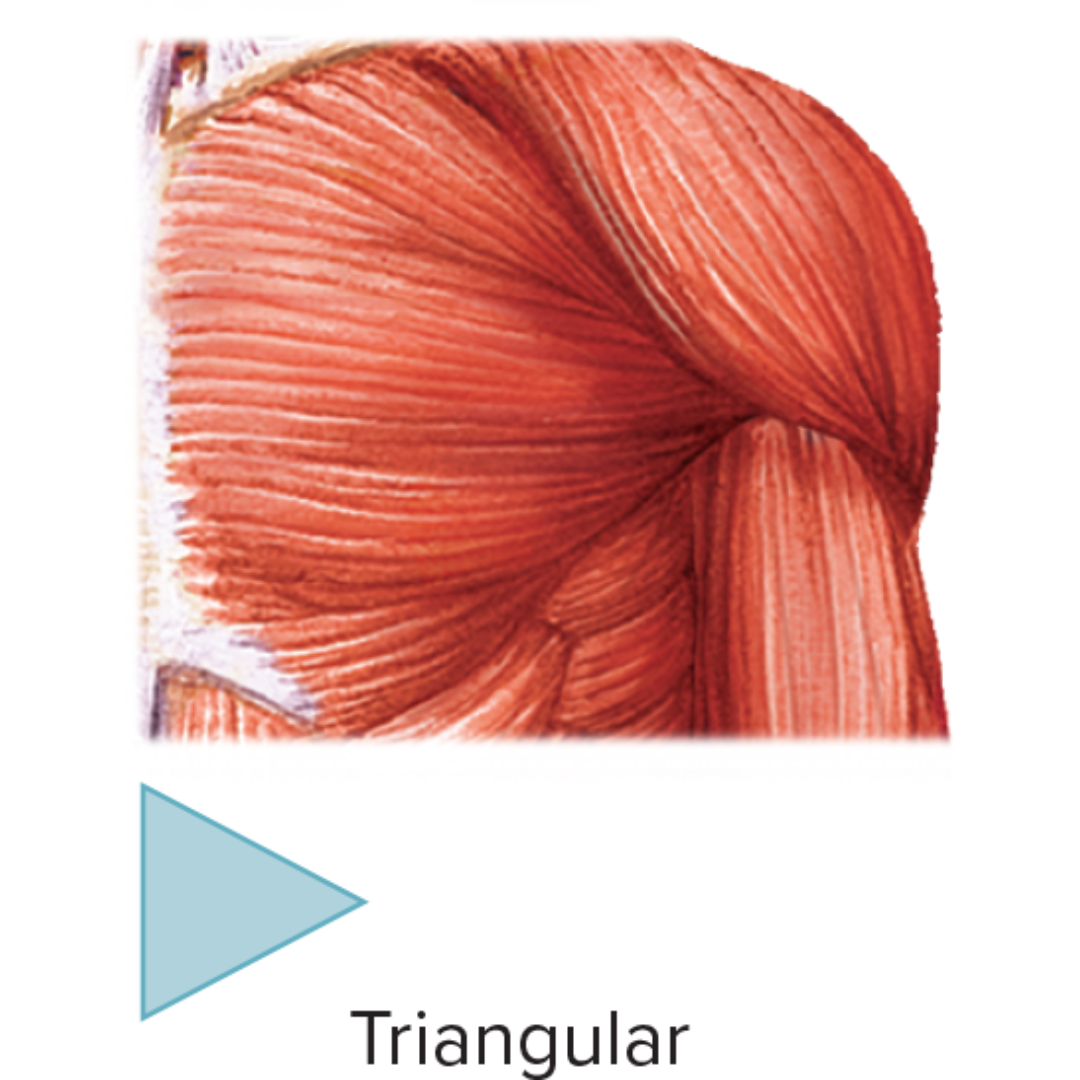
deltoid
Muscle Names
triangular muscle
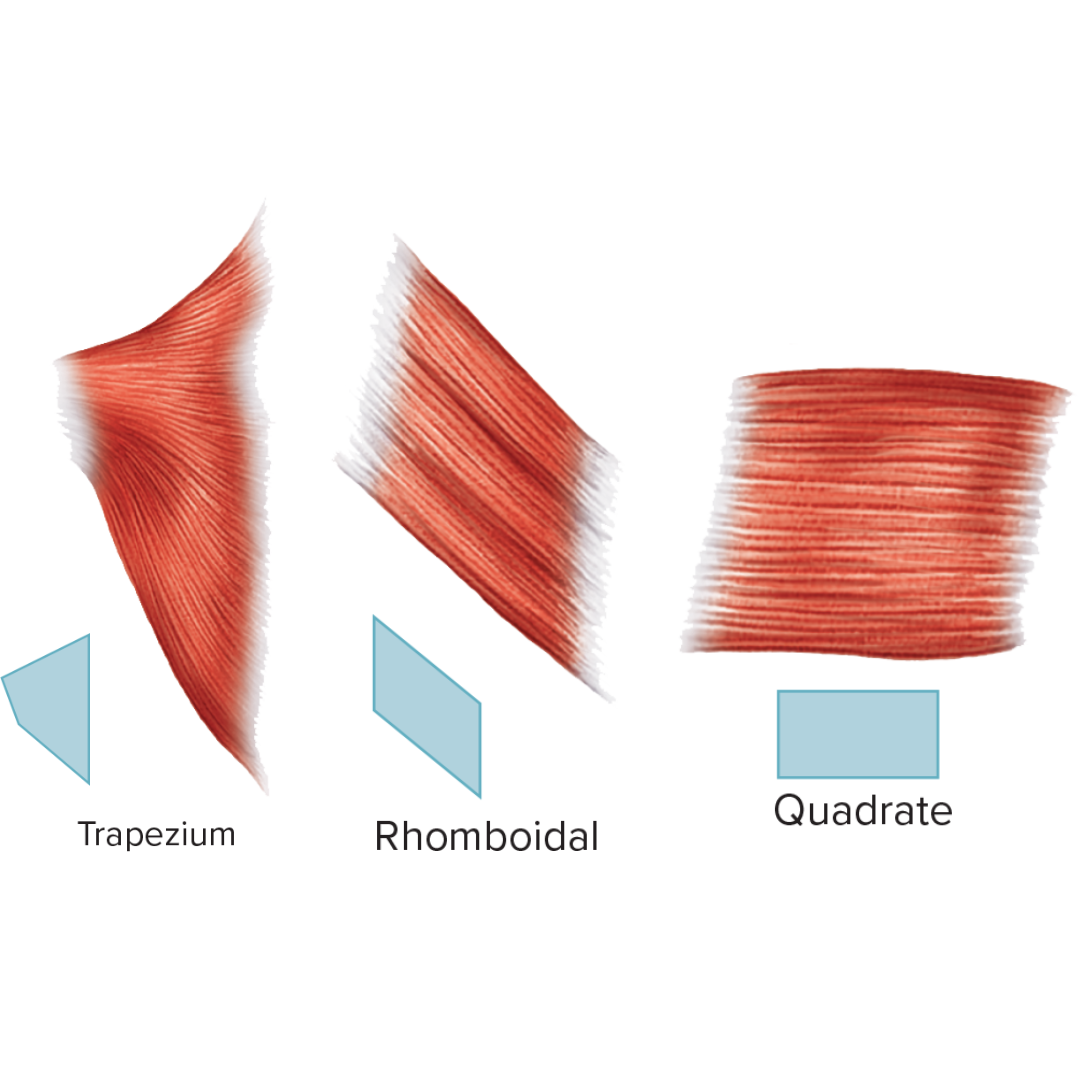
quadratus
Muscle Names
quadrate muscle
teres
Muscle Names
round muscle
rectus
Muscle Names
straight or parallel muscle
biceps
Muscle Names
muscle with two heads (origins)
triceps
Muscle Names
muscle with three heads (origins)