4- pulpal/periapical pathology + lesions
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
most common disease process that dentist encounters
inflammation
2 types of periapical inflammatory disease
rarefying osteitis
sclerosing osteitis
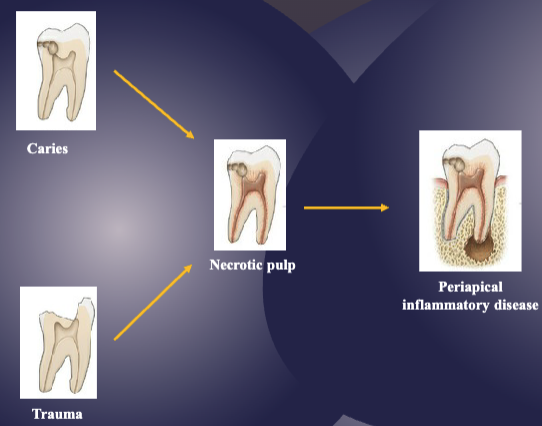
periapical inflammatory disease is a result of what
caries/trauma → necrotic pulp → periapical inflammatory disease
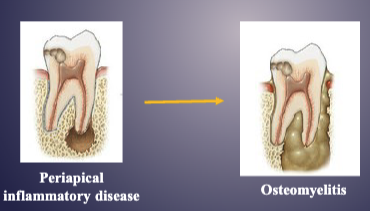
what happens once the disease spreads beyond the root apex
pericapical inflammatory disease → osteomyelitis
term for inflammation that is restricted to PDL
apical periodontitis
2 radiographic signs of apical periodontitis
widened PDL space
loss/thickening of lamina dura (radiopaque line that’s normally around the roots)
definition of rarefaction
loss of bone material
definition of osteitis
inflammation of bone
what’s rarefying osteitis
chronic inflammation associated w/ non-vital tooth

rarefying osteitis always involves 1 of which 3 things
abscess
granuloma
radicular cyst
what’s sclerosing osteitis
sclerosis: hardening of bone
increased radiopacity of bone w/ widened PDL

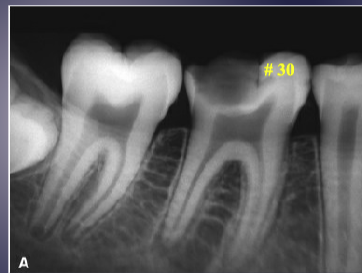
differentiate the pathology for #30 + #31
#30: apical rarefying osteitis
#31: developing tooth w/ open root apex
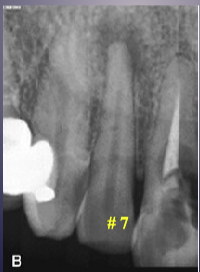
what’s the pathology of #7
apical rarefying osteitis

what’s the pathology of #30
apical sclerosing osteitis
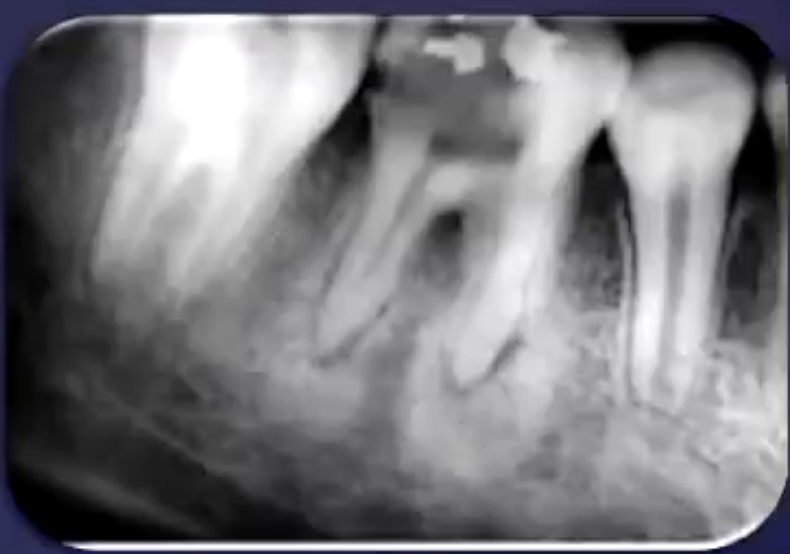
describe the pathology
apical sclerosing osteitis + radiolucency around PDL space
T/F: trabeculae can become thicker + increase in number in periapical inflammatory disease
true
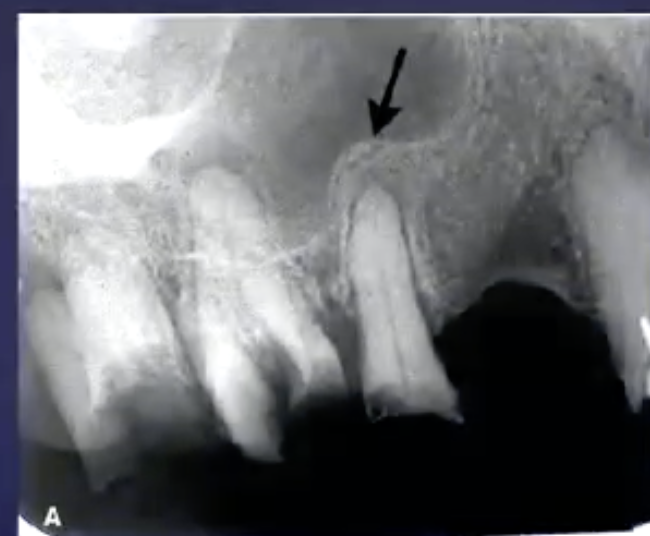
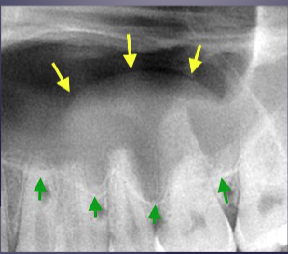
what’s the arrow pointing to
periosteal new bone formation
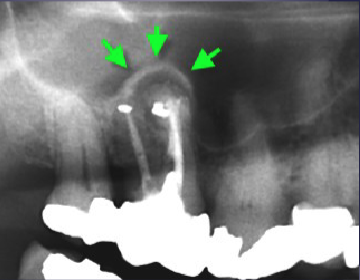
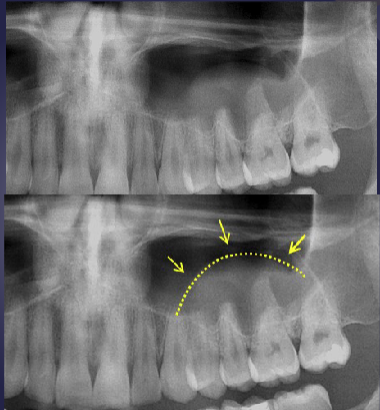
what are the arrows pointing to
“Halo sign”: elevation/displacement of max sinus floor
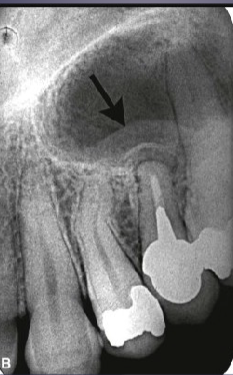
what’s the arrow pointing to
periosteal bone formation aka periostitis aka “onion skin” + mucosal thickening aka mucositis
T/F: you can have rarefying + sclerosing osteitis at the same time
true
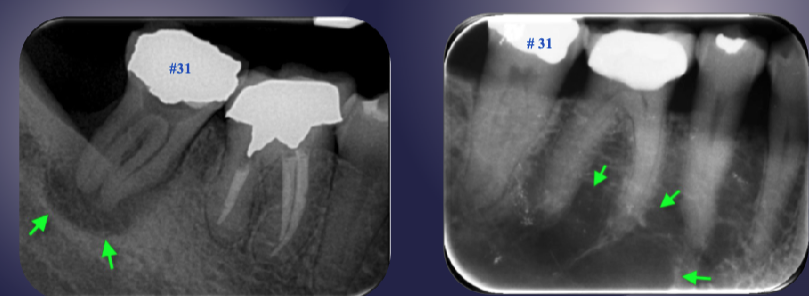
differentiate the pathology of the 2 images
left: loss of apical lamina dura + periapical radiolucency
right: normal lamina dura + radiolucency due to submandibular fossa
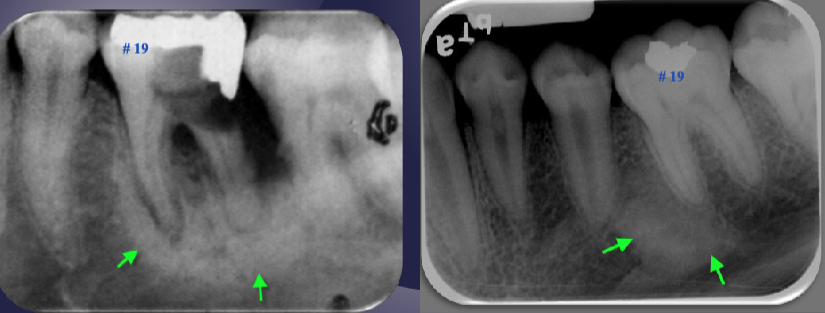
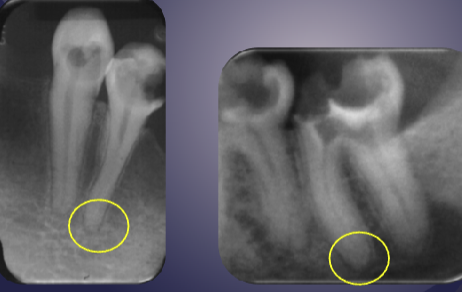
differentiate the pathology of the 2 images
left: widened PDL + periapical radiopaque area + non-vital tooth → sclerosing osteitis
right: normal PDL + periapical radiopaque area due to dense bone island + vital tooth → normal
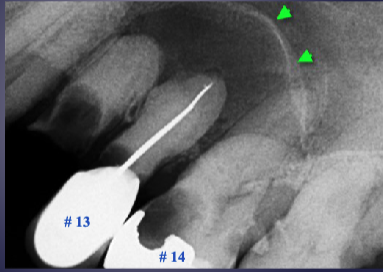
what’s the pathology
floor of max sinus elevated/displaced → rarefying osteitis
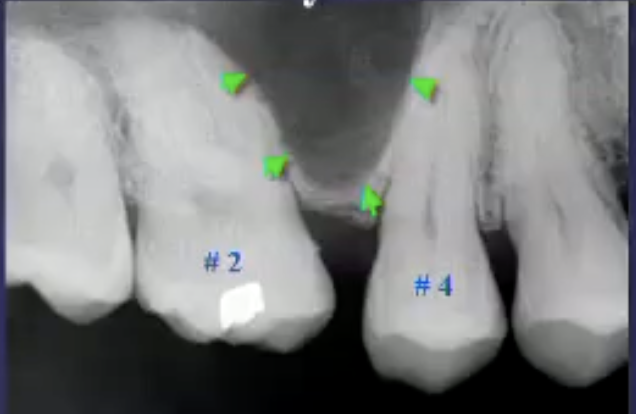
what’s the pathology
pneumatization of max sinus
what’s the pathology
mucus retention psuedocyst
5 potential pathologies as a result of periapical inflammation
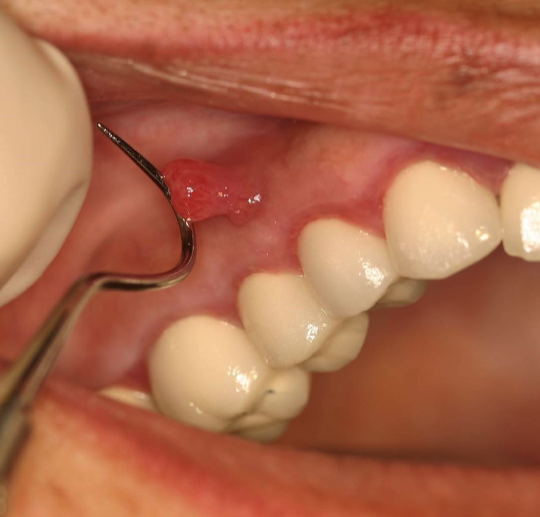
parulis: “gum boil”
periapical granuloma
periapical cyst
periapical abscess
condensing osteitis
3 clinical signs of parulis
dome-shaped yellow-pink papule
may/may not exhibit active suppuration (pus formation)
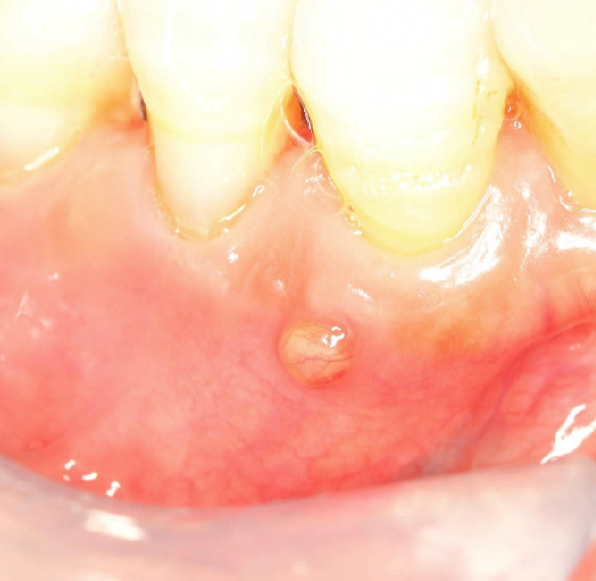
parulis is usually located where
on gingiva facial to non-vital tooth
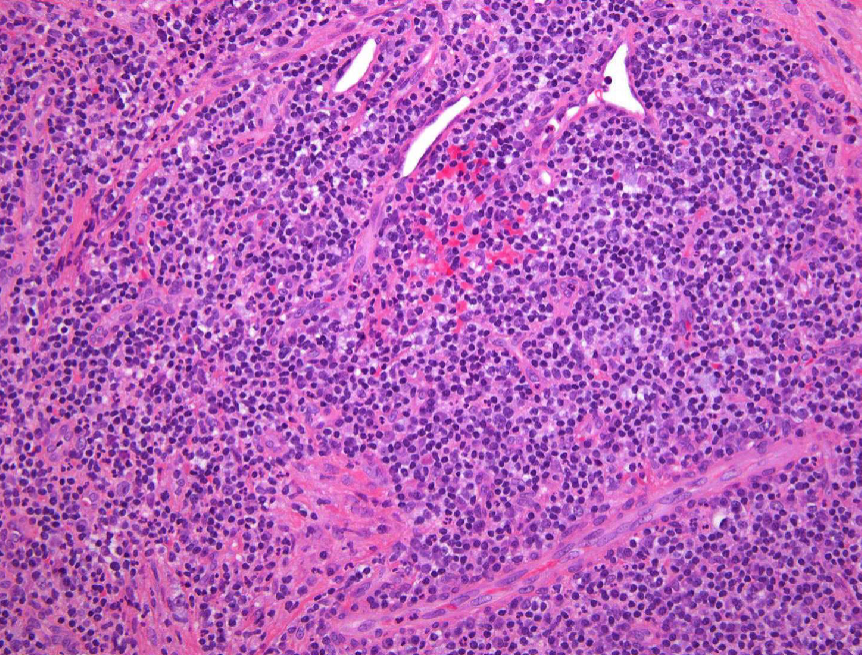
2 histopath features of periapical granulomas
granulation tissue surrounded by fibrous connective tissue
lymphocytic infiltrate may be intermixed with neutrophils, plasma cells, histiocytes, and occasionally mast cells or eosinophils
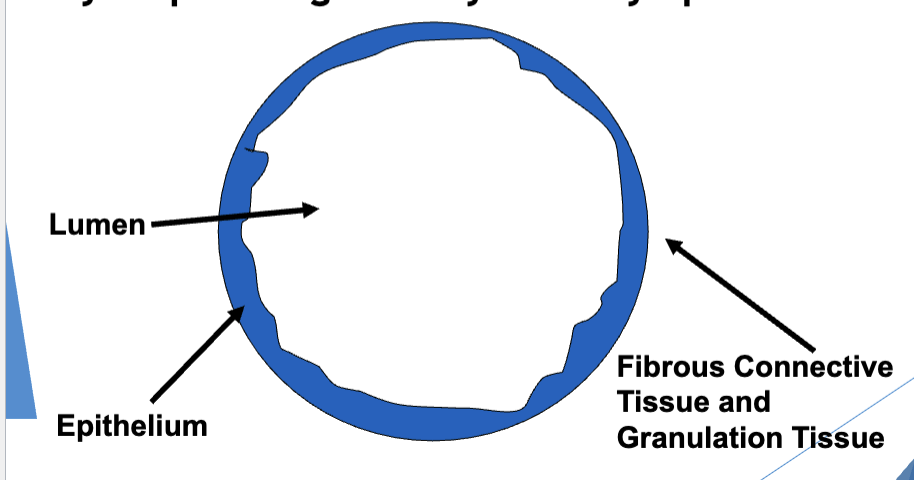
describe the 3 structural components of a cyst
outer → inner
fibrous CT + granulation tissue
epithelium
lumen
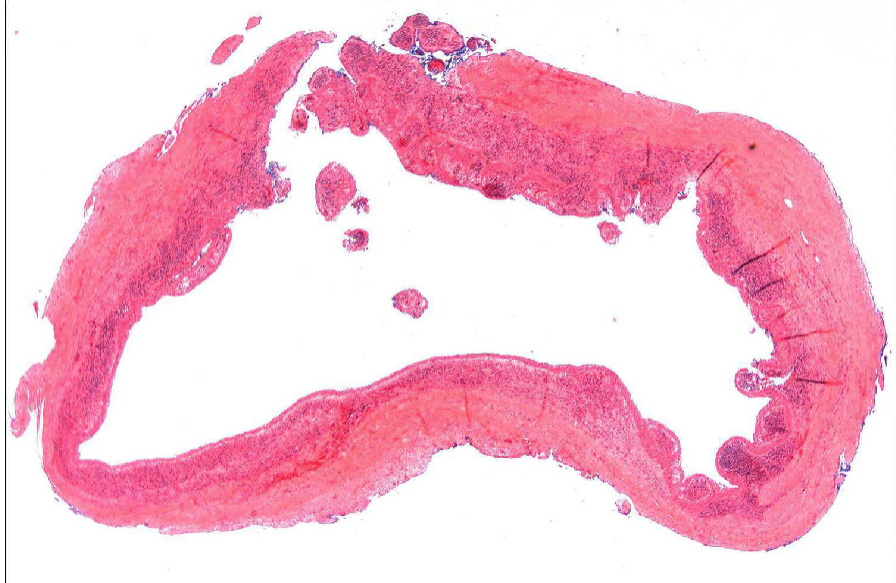
T/F: periapical cysts are the most common odontogenic cyst
true
how does the epithelium form the lining of a periapical cyst
usually derived from rests of Malassez or from lateral aspect of root at orifice of accessory canal
2 histopath features of periapical cysts
lining of cyst composed of stratified squamous epithelium
wall of cyst consists of dense fibrous tissue w/ inflammatory infiltrate
periapical abscesses are a result of
accumulation of acute inflammatory cells @ apex of a non-vital tooth
3 clinical features of periapical abscesses
headache, fever, malaise, chills
tenderness of affected tooth
possibility to spread through bone (osteomyelitis) or perforate cortex + spread through soft tissue (cellulitis)
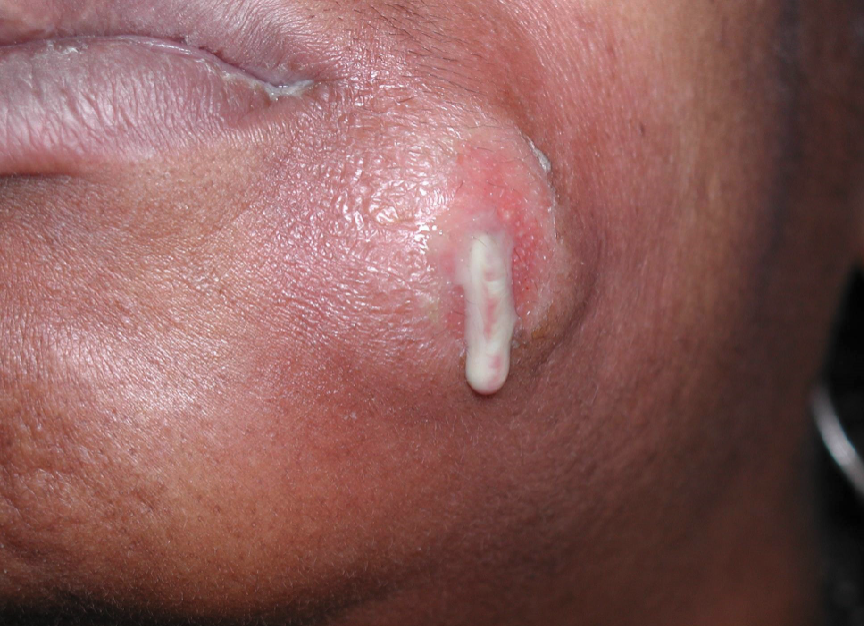
what’s a Phoenix abscess
type of periapical abscess, acute exacerbation of chronic periapical inflammatory lesion
2 histopath features of periapical abscesses
acute inflammatory cells, cellular debris, necrotic material, and bacterial colonies
Phoenix abscesses may include soft tissue component
3 tx options for periapical abscesses
Drainage
Elimination of infection
Antibiotics for medically compromised patients
2 tx options for condensing osteitis
endo therapy
ext
T/F: 85% of condensing osteitis cases will resolve or regress
true
2 tx options for non-vital teeth
RCT + biopsy of tissue
non-restorable → EXT + curettage of apical tissue
what happens if cortical plates have been lost after a non-vital tooth is treated
periapical fibrous scar formation
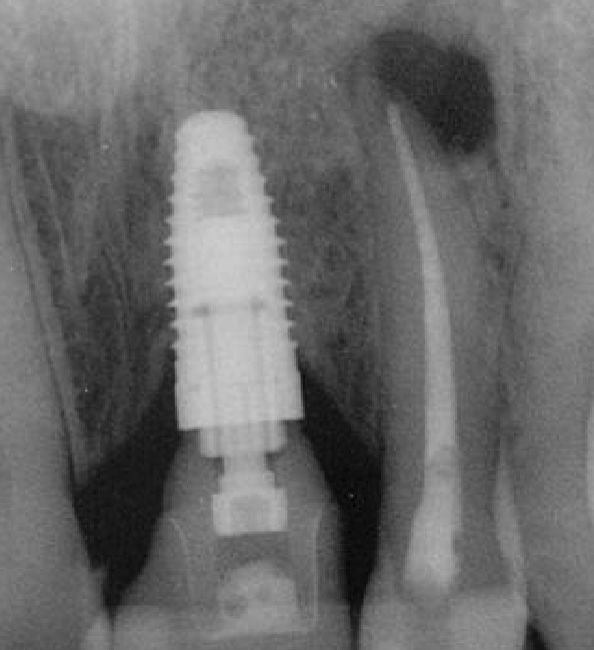
T/F: untreated cysts can turn into squamous cell carcinoma
true, but it’s rare
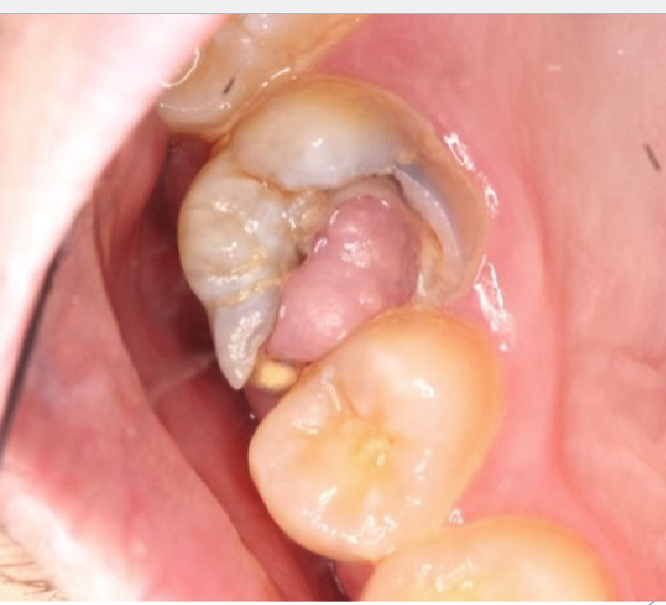
what is this
chronic hyperplastic pulpitis: hyperplastic granulation tissue extrudes from pulp chamber
chronic hyperplastic pulpitis usually happens in which age
children + young adults w/ large pulp exposures
2 tx options for chronic hyperplastic pulpitis
endo
ext
definition of osteomyelitis
inflammation that has extended from periapical region → marrow space, cortex, cancellous portion of bone + periosteum
6 types of osteomyelitis
acute osteomyelitis
chronic osteomyelitis
acute suppurative osteomyelitis
acute pyogenic osteomyelitis
proliferative periostitis
periostitis ossificans
acute osteomyelitis usually affects which 2 areas
mandible
premolar-molar area
6 clinical features of acute osteomyelitis
pain
swelling
redness
fever
purulent discharge
mobility in involved teeth
what happens if acute osteomyelitis is not treated
chronic osteomyelitis, but can also occur de novo
T/F: acute osteomyelitis does not radiographically manifest in the early stages
true
once past the early stages, the periphery of acute osteomyelitis presents w/ what 3 radiographic features
poorly defined
non-corticated
gradual transition to normal trabeculae
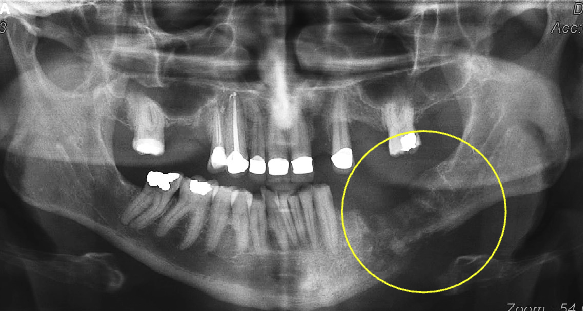
once past the early stages, the internal structure of acute osteomyelitis presents w/ what 3 radiographic features
decreased bone density
loss of trabeculae sharpness
mixed radiolucent- radiopaque areas: “moth-eaten” appearance w/ irregular outline
sequestrum: islands of necrotic bone
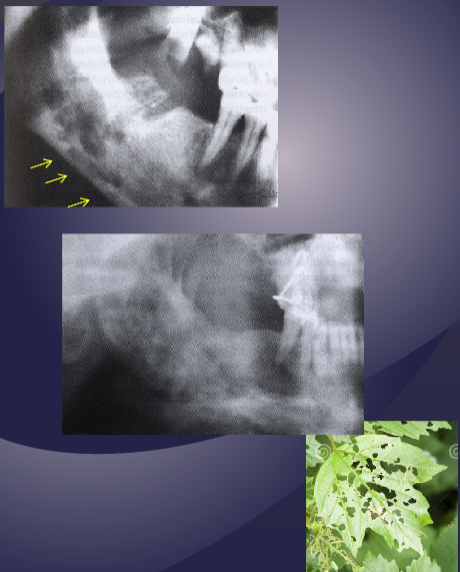
what is the black arrow pointing to
large sequestra caused by acute osteomyelitis
4 radiographically visible effects on surrounding structures due to acute osteomyelitis
bone formation aka periosteal stimulation aka “onion skin” pattern
bone resorption
fistula
pathologic fracture
what are the arrows pointing to
fistula due to acute osteomyelitis

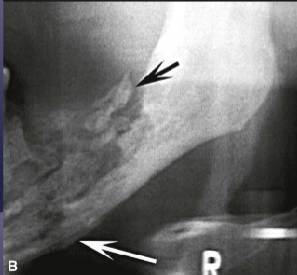
what is the white arrow pointing to
periosteal reaction due to acute osteomyelitis
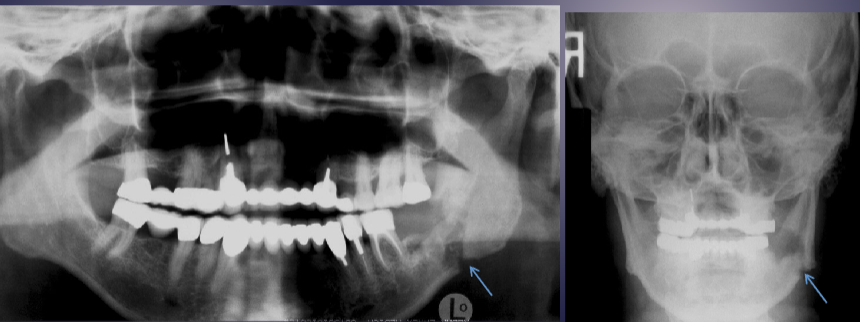
what are the arrows pointing to
pathologic fracture of the L mandible due to acute osteomyelitis
chronic osteomyelitis is called diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis when it has which 3 features
proliferation of bone
subperiosteal bone deposition on large segment of mandible
slight jaw enlargement
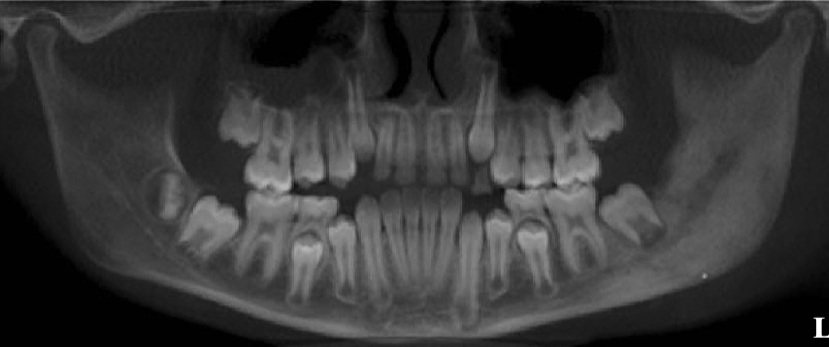
what’s the pathology of the L mandible
diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis of L angle-ramus of mandible
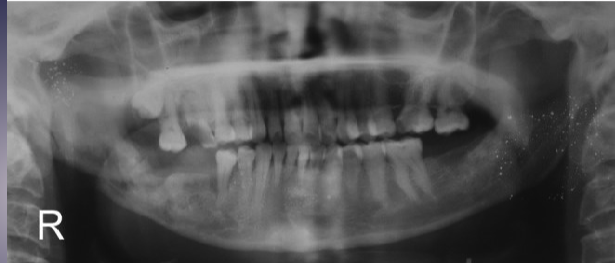
what’s the pathology of the R mandible
osteoradionecrosis (ORN), radiographically similar to osteomyelitis
T/F: bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaws (BRONJ) is radiographically indistinguishable from osteoradionecrosis + osteomyelitis
true
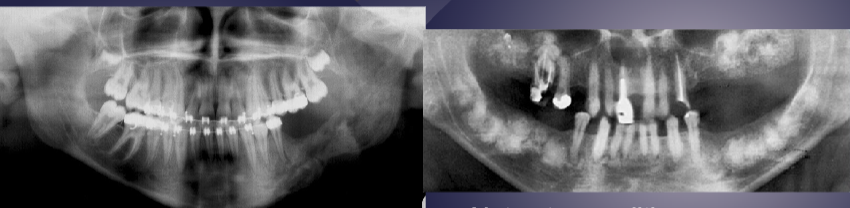
differentiate between the 2 radiographs
L: osteomyelitis w/ ill-defined, mixed lesion of L body + ramus of mandible, “moth eaten” appearance
R: well-defined radiopaque lesions in max + mand, not osteomyelitis
3 types of soft tissue inflammation seen radiographically
pericoronitis
sinusitis + mucositis in max sinus
mucus retention “pseudocyst”
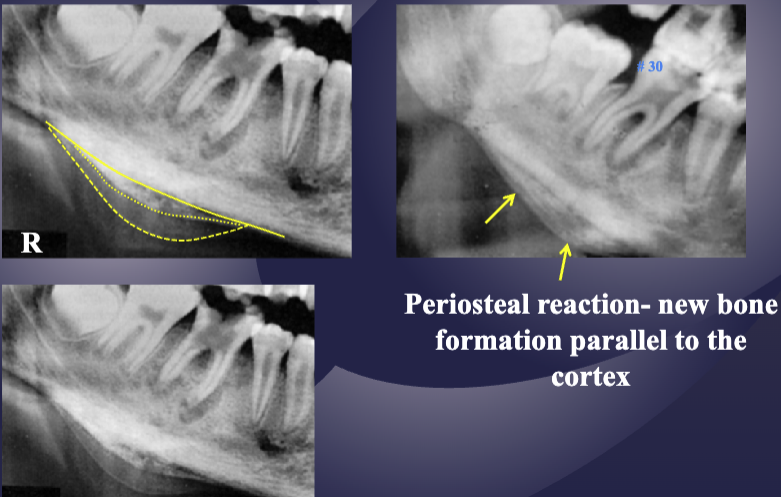
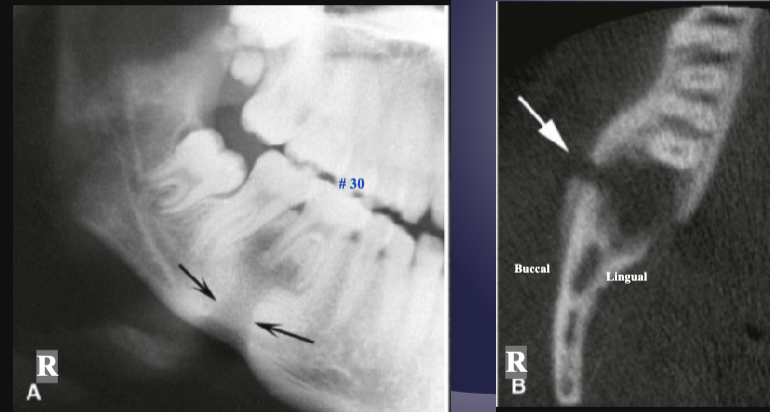
2 radiographic signs of pericoronitis
periosteal reaction
sclerotic bone reaction (radiopaque)
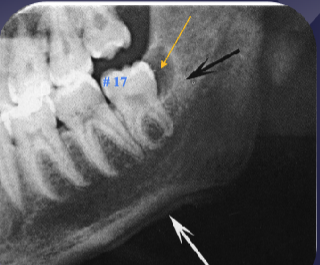
what are the white + black arrows
white: periosteal rxn
black: sclerotic bone rxn
of pericoronitis
sinusitis + mucositis in max sinus are shown radiographically via
sclerotic changes in boney walls
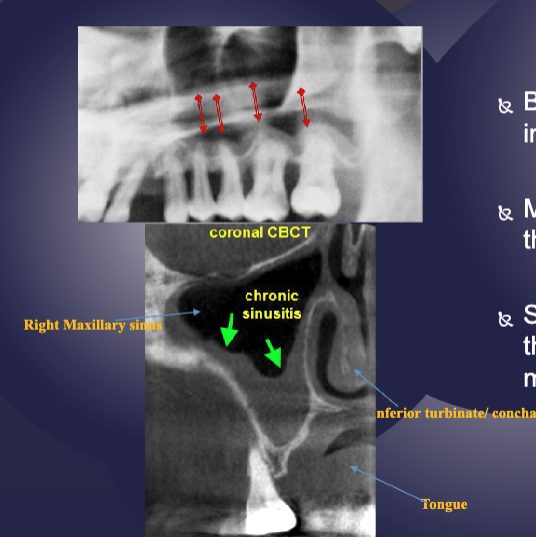
3 radiographic features of mucus retention “pseudocyst”
relative radiopacity on floor of sinus
well-defined, not corticated
dome-shaped