Chemistry topic 4
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
practice questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms

6 marks
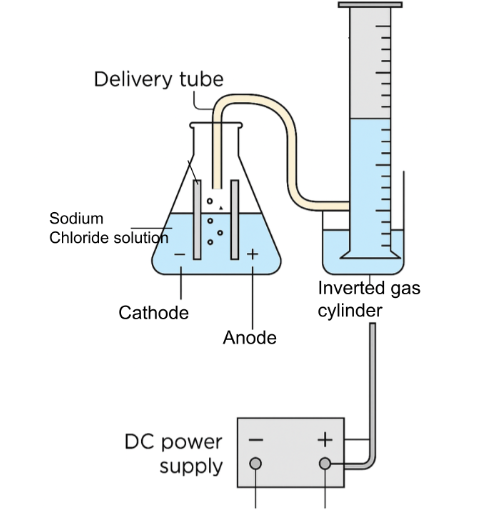
Set up the apparatus: Pour the sodium chloride solution into the beaker. Insert the two oppositely charged electrodes into the solution, ensuring they do not touch each other.
Connect to power supply: Connect the electrodes to a DC power supply using connecting wires and crocodile clips. Ensure the power supply is off before connecting.
Collect the gas: Invert a measuring cylinder over a trough of water to collect the gases produced.
Initiate electrolysis: Turn on the power supply and allow electrolysis to occur for a set period, e.g., 5-10 minutes, observing the water in the measuring cylinder dissipate
Measure hydrogen volume: After the set time, turn off the power supply and record the volume of hydrogen gas collected in the inverted measuring cylinder.

1 mark
1.0 to 2.9 is aprox 2 pH increase (2.9 rounds to 3), scale factor = 10 times 10, so we do 0.1 divided by sf of 100 ( less acidic so H+ ions decrease) which is 0.001 mol/dm³

1 mark
Copper is less reactive than hydrogen and cannot displace it

1 mark
Potassium is in group 1 which means it will react vigorously with hydrochloric acid, making it unsafe

3 marks
Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid meaning all the molecule fully ionises and all H+ ions dissociate . Ethanoic acid is a weak acid meaning it only partially ionises and only some of the H+ ions dissociate. This means that Hydrochloric acid has a higher pH because it has a higher concentration of H+ ion in solution that ethanoic acid.
Explain why Sodium Sulfate becomes more concentrated during the electrolysis process, 3 marks
Explain: At the Positive electrode Hydrogen (from water) and Sodium are attracted. Sodium is more reactive so Hydrogen is produced, At the Negative electrode Oxygen (from water) and sulfur are attracted, sulfur is not a halide so oxygen is produced
Answer: Water is being electrolyzed, This means the volume of the water will decrease and the volume of sodium sulfur will stay the same but the solution will become but be less dilute as solvent decreased