Test One Key Terms
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Homology / Homologous Characteristics
Characteristics are similar in two or more species because they are inherited from a common ancestor
Synapomorphy
A trait that is shared by a group of related species (evolved in the immediate common ancestor group)
Phylogeny
A visual representation of the evolutionary history of populations, genes, or species
Exaptation
A trait that is initially carries out one function and is later co-opted for a new function. The OG function may or may not be retained
Clades
Single branches in the tree of life that represent an organism and all of its descendants (like a starting point for two related species)
Outgroups
Groups of organisms (species) that are outside of the monophyletic group being considered. Used to infer the ancestral states of characters (used as a point of comparison)
Homoplasy
Describes a character state similarity not due to shared descent (produced by convergent evolution or evolutionary reversal)
Horizontal Gene Transfer
The transfer of genetic material other than from parent to offspring to another organism without reproduction, then passed down to descendants
Coalescence
The process by which, by looking back through time, the genealogy of any pair of homologous alleles merges in a common ancestor
Paralogs
Homologous genes that arise by gene duplication. Paralogs together form a gene family
Maximum Parsimony
A statistical method for reconstructing phylogenies that IDs tree topology that minimizes the amount of change or number of steps required to fit the data
Bootstrapping
A statistical method for estimating the strength of evidence that a particular branch in a phylogeny exists
Neighbor Joining
A distance method for reconstructing phylogenies. IDs tree topology with the shortest possible branch lengths
“MRCA”
Most recent common ancestor
Evolution
Change in frequency of heritable traits over time
Epigenetics
Heritable changes in a gene function that aren’t related to genetic differences
Example of horizontal gene transfer
Eastern emerald slug takes genetic information from leaves to produce chlorophyll to mimic a leaf (needs to eat the algae once)
Convergent evolution
The independent evolution of similar traits (homoplasious) from DIFFERENT ancestral conditions (EPAS1 vascular and altitude differences)
Parallel evolution
The independent evolution of similar traits from the SAME ancestral conditions (Lactose)
Example of homoplasious traits through reversal
leg reduction and loss in snakes, glass lizards, and worm lizards
Definition of Deep homology
Convergence of complex traits based on homologous elements
Example of deep homology
The convergence of opsins and crystallins for use in complex eyes (co-opted as well)
Bottleneck definition
A sudden decrease in population size resulting in drift
What restores diversity lost by drift?
Mutation and gene flow
Discrete / discontinuous genetics
Can be placed in categorial and distinct morphs of phenotypes (red, green, blue)
Discontinuous/discrete variation in a population often occur from a single gene with a few alleles. How can a complex system result in just two or three phenotypes?
Genetic or GxE threshold, variation in multiple genes interact but there is a tipping point.
VG + VE
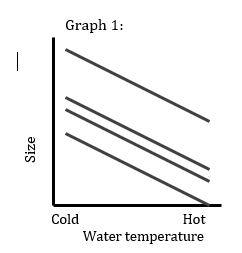
VG x VE
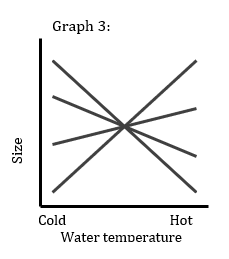
VE
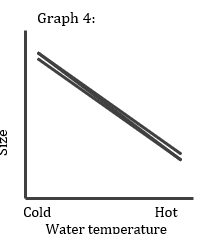
VE + VG x VE
Complex adaptations in mantis shrimp
Strong raptorial front “arms” and 16 photoreceptors which capture UV and polarized light
What is NOT an explanation for how convergent complex traits may be made more likely to occur?
Adaptive mutations
Describe how gene duplication may allow ability of novel, adaptive traits to evolve?
The original function is maintained by one paralog while the other is freed to accumulate mutations
How are h2 and H2 different?
H2 is more inclusive
What could result in a novel trait in a population?
Recombination or independent assortment (crossing of alleles), novel genetic - environment interaction, novel environment, gene flow
Carter, Goldizen & Heinsihn 2012 (our second paper) studied Namibian rock agamas and suggested that…
Behaviors were influenced by individual (likely genetic) differences, season, and plasticity (individuals’ different responses to season.)
Byrne & Corp 2004 (our first paper) found?
That evolutionary increases in neocortical size correlated with higher deception rates, suggesting that benefits of deception may have favored this brain growth.
DeWaal and Ferrari 2010 (our 3rd paper) argued that…
Focusing on deeply homologous neural elements like mirror neurons, can give us a better understanding of cognition than the “top-down” approach.
Why, in general, is the use of independent contrasts important?
Without them, we cant know if traits evolved together multiple times or if the tend to be paired together due to common decent.
What evolutionary processes best explain leglessness in snakes?
Changes in spatial and temporal expression of limb blocking and developmental genes
“Deep homology”, as seen in the evolution of complex eyes of vertebrates and cephalopods (like octopi), refers to…
Convergent complex traits whose similarities are due in part to the incorporation of homologous elements