CH 1 part 2, Done
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
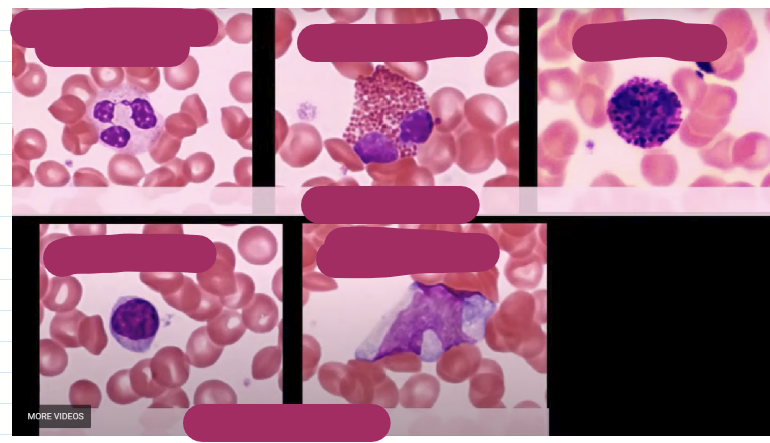
Granulocytes are
Neutrophil
Eosinophil
Basophil
Granulocytes are
Lymphocyte
Mnocyte
What does the OSHA Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard require for chemical safety?
What does SDS stand for?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard (HCS)
HazCom labeling requirements are rules for how every chemical must be labeled so workers know it’s safe to use.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
SDS are Official documents that explain hazards, safe handling, storage, and emergency steps.
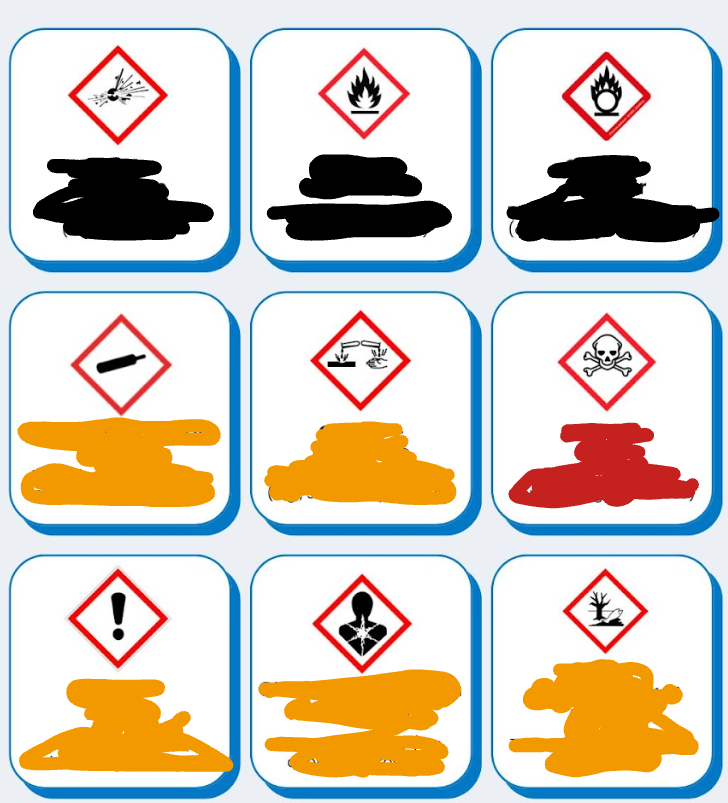

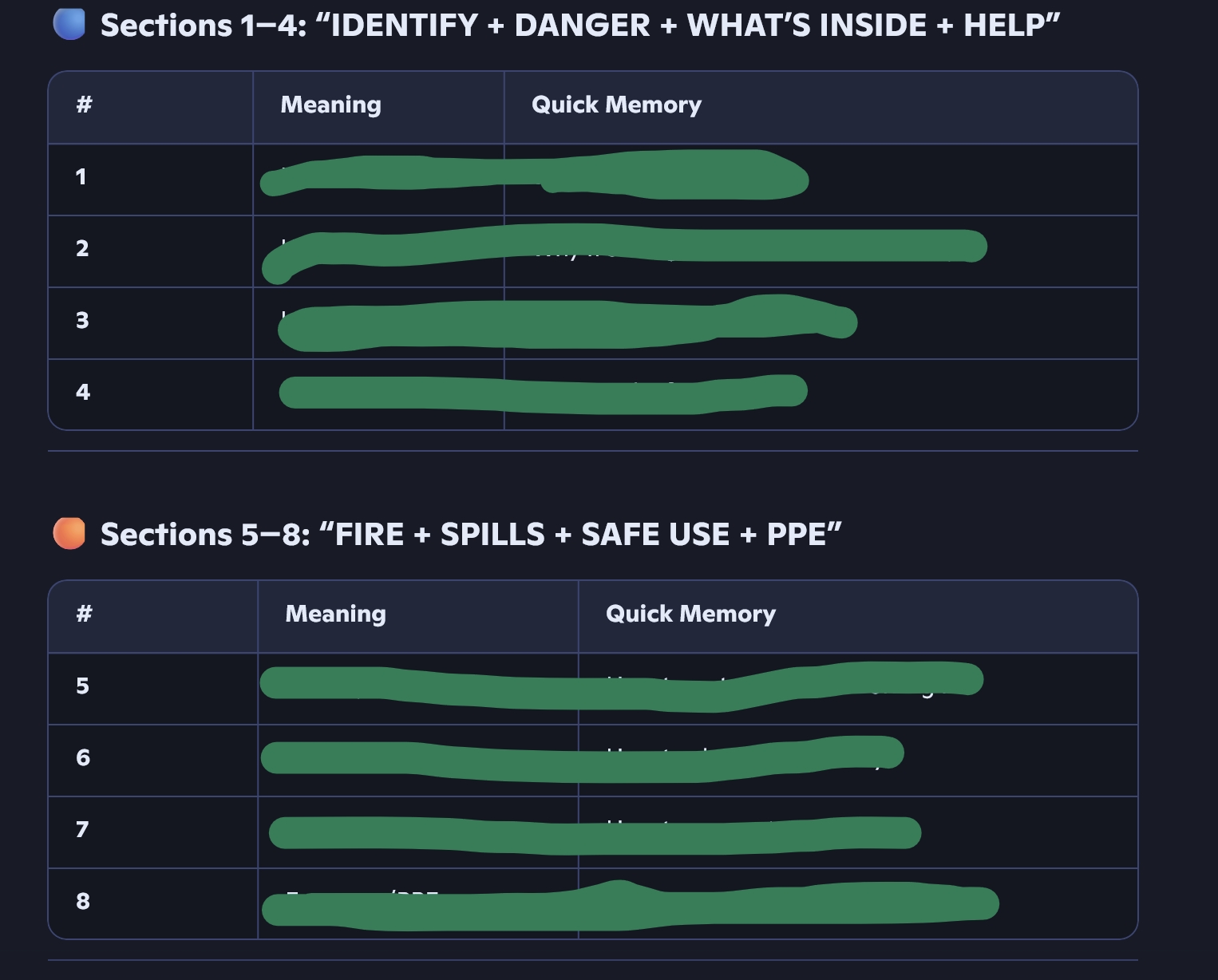
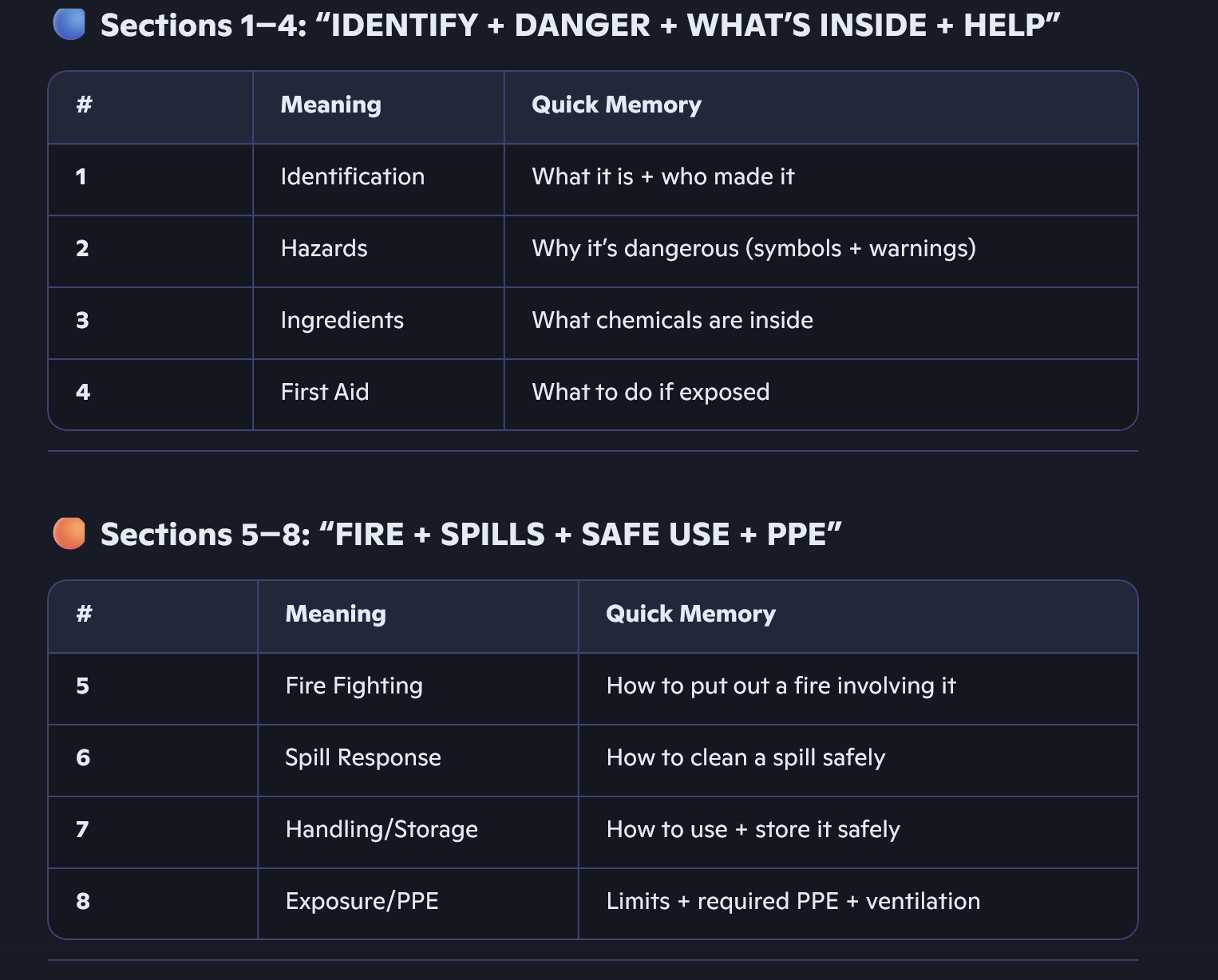
List the first 3 SDS sections and the acronym for all of them
Name the GHS hazard signs
SDS Sections
Chemical product and company Identification
Hazard Identification
Composition and information on Ingredients
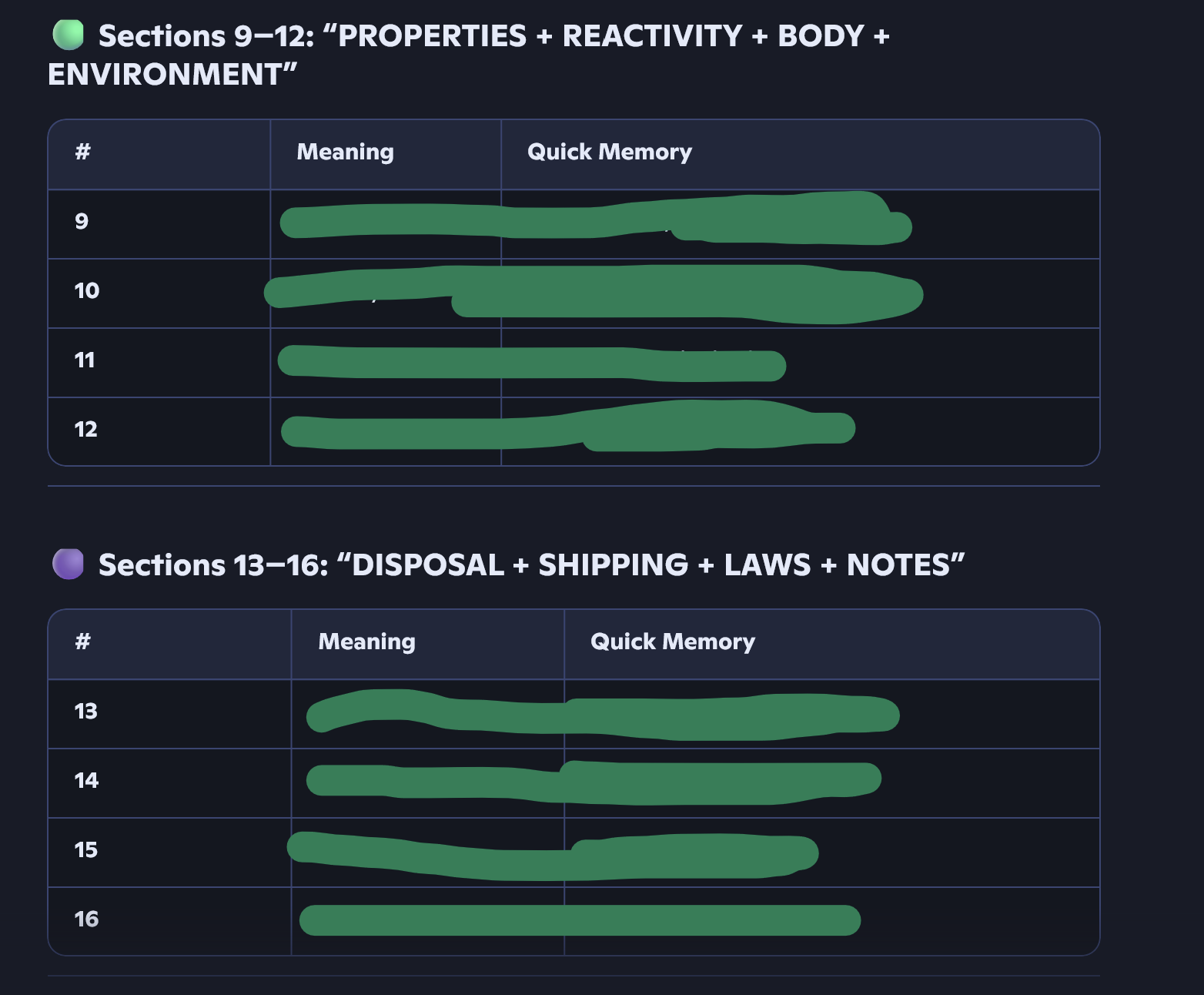
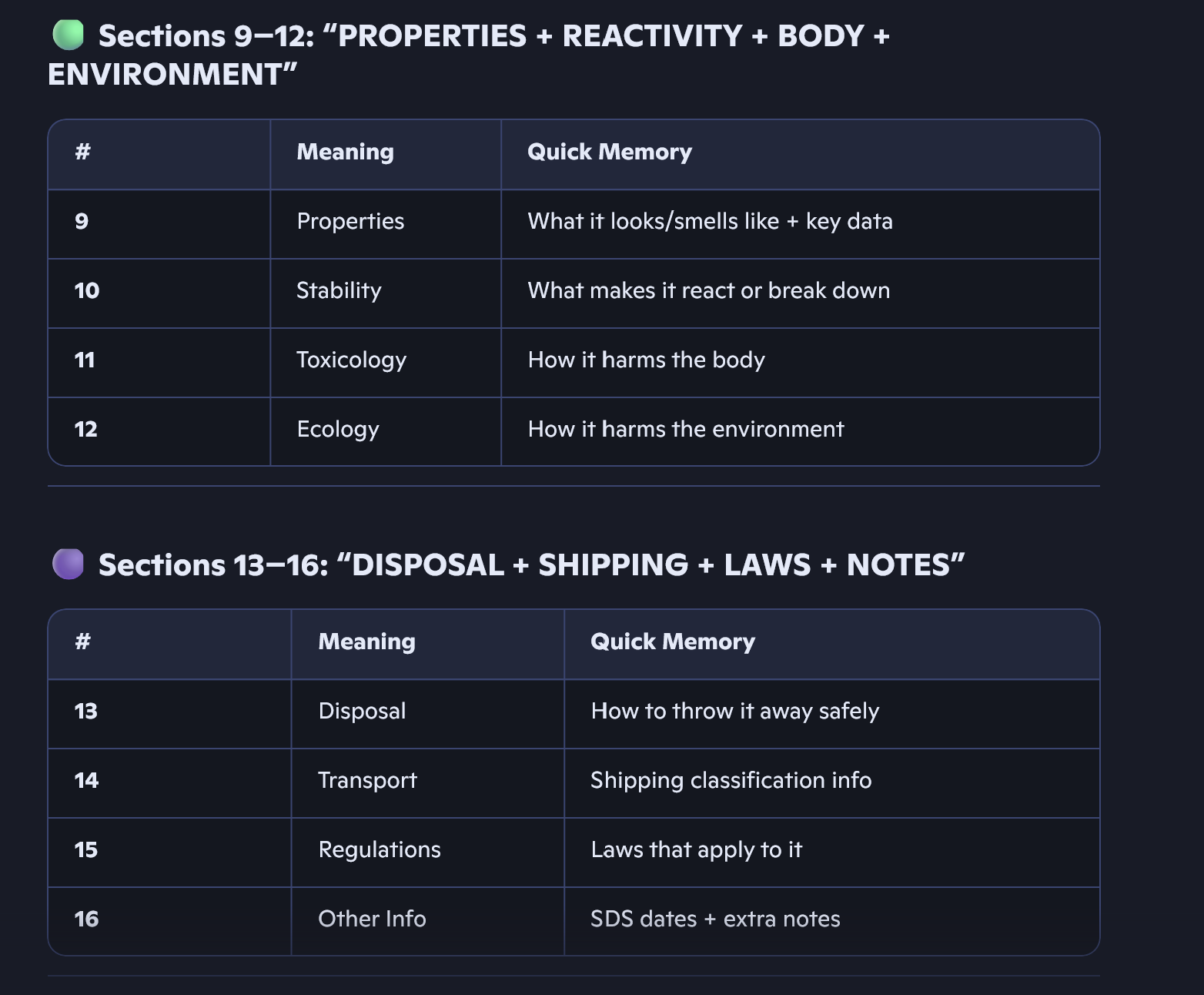
I have ingredients for fires, spills, handling PPE. Plus reactive toxicity.
Every day time runs out

What are the rules for when hazardous ingredients must be listed on an SDS?
At what concentration must a hazardous ingredient be listed?
What is the exception to the above rule in yellow?
SDS has to list ingredients that are hazardous (harmful to one’s health).
If the hazardous ingredient is over 1%, it MUST be listed.
If it causes cancer or major harm, it must be listed even below 1%
What four things must every hazardous chemical label include under HazCom law?
HazCom is a labeling rule (labeling requirement) that says every hazardous chemical (dangerous chemical) must have a label that includes:
Statement of warning (alert word like “danger” or “poison”)
Statement of hazard (what type of danger — toxic (poisonous), flammable (catches fire), combustible (can burn))
Precautions to eliminate risk (steps to stay safe and avoid accidents)
First aid measures for spills, accidents

What do the (National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) colors and numbers represent?
Blue
red
Yelllow
white
0 and 4
Blue is Health
Red is fire
Yellow is reactivity
White is Specific Hazard
0 is least hazard, 4 is the highest danger
List all the “Always” rules for chemical safety.
How long must you flush your eyes if exposed to chemicals?
Chemical Safety:
Always
Wear PPE (personal protective equipment)
Clean up chemical spills properly
Access SDS (Safety Data Sheet) to get guidance (instructions) on First Aid & spill clean‑up
Label secondary containers (any container you transfer chemicals into) with:
Name of chemical
All hazard info (danger details)
Expiration date
Flush eyes with water at least 15 minutes
List all the “Never” rules for chemical safety?
Chemical Safety:
Never
Store chemicals above eye level
Add water to acid
(causes violent reaction; always add acid to water instead)
Unknowingly mix chemicals together
Store chemicals in unlabeled containers
Pour chemicals into dirty containers
Use chemicals in ways they were not intended
What is the key electrical safety rule
what are the four steps for responding to a chemical spill?
Electrical Safety
Do NOT unplug equipment by pulling on the cord
(Always pull from the plug itself to avoid damage or electric shock.)
For chemical spill
Contain → Neutralize → Wipe → Disinfect

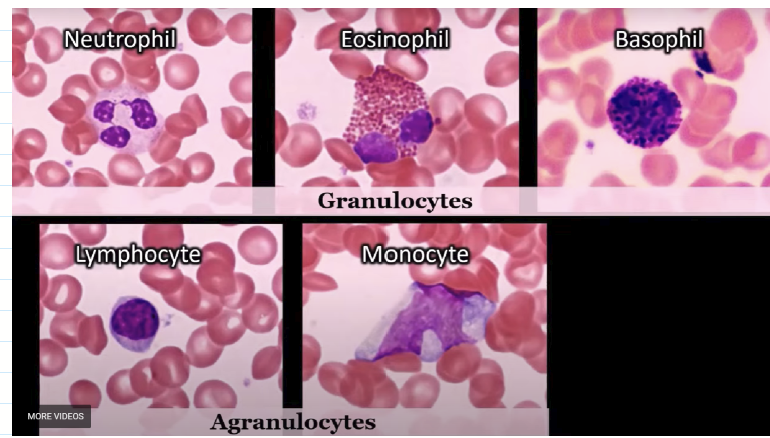
What four components are required for fire to occur, and what does the chemical reaction represent?
4 things are needed for fire to occur
Fuel
(Combustible material — something that can burn.)Heat
(Raises the temperature of the material until ignition (the moment it catches fire).)Oxygen
(Keeps combustion (burning) going.)Chemical reaction is everything above combined
(The process that actually produces fire — also called the “fire triangle” or “fire tetrahedron” when the reaction is included.)
What are the steps of RACE and when do we use it?
When should u use PASS and what does it stand for?
If a Fire Occurs — RACE
Rescue, Get people out of danger first.
Alarm
Confine, Close doors to keep the fire from spreading
Extinguish
To use fire Extinguisher- PASS
Pull
Aim
Squeeze
Sweep
What types of fires can Class ABC extinguishers handle
What is a Class A fire?
What is a Class B fire?
What is a Class C fire?
What does Class D cover?
What does Class K cover?
Healthcare facilities use Class ABC fire extinguishers which are Multipurpose extinguishers that can handle many types of fires.
Class ABC Extinguishers = can be used on ALL common fire types:
Class A
(Fires involving ordinary materials — paper, wood, cloth.)Class B
(Fires involving flammable liquids — gasoline, alcohol, oils.)Class C
(Fires involving electrical equipment — outlets, wiring, machines.)Class D : reactive metal
Class K: High temperature cooking oils, grease, or fats
What is the radiation hazard symbol

what does hemorrhage mean?
what are the treatment steps for hemorrhage?
External Hemorrhage = not normal or profuse bleeding
Hemorrhage = heavy, uncontrolled bleeding from a wound.
Treatment for hemorrhage —
Firm, direct pressure to the wound using clean cloth or gauze.
Use an ice compress for 5–10 minutes
Ice helps slow bleeding by tightening (constricting) blood vessels.
What causes shock?
Treatment rule for shock?
Shock: occurs when there is not enough blood coming back to the heart. This then causes low oxygen supply to body organs/tissues
Low blood return to the heart → weak pumping → low oxygen → organs fail (shock).
Treatment for shock
No fluids + don’t move them unless they’re in immediate danger.
What is a stroke?
Stroke: Blood clot in the brain
Clot = a clump of blood that blocks blood flow which stops oxygen from reaching brain tissue
What is CPR?
What is emergency cardiovascular care?
Who performs Hands‑Only CPR?
What does CAB stand for?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life‑saving action that keeps blood and oxygen moving when the heart stops.
Emergency cardiovascular care is help given during heart‑related emergencies
Hands‑Only CPR is for lay rescuers
Lay rescuers = regular people with no medical training
CAB = Compressions first, then Airway, then Breathing.
Compression is to push on the chest to keep blood moving
Airway: open the airway by tilting the head back)
Breathing is to give breaths if trained — otherwise hands‑only CPR is fine
How does timing affect CPR survival?
What are the key adult CPR numbers?
For every minute CPR is delayed, the chance of survival drops 10%
Immediate CPR doubles or triples the chance of survival
Adult CPR = 100–120 compressions/min + 30:2 ratio
You should push on the chest 100–120 times every minute — fast and steady.
Do 30 chest compressions, then give 2 breaths — if you are trained to give breaths.
What is ergonomics?
What is the key rule for back protection?
Ergonomics is keeping the body in a comfortable and neutral position
Neutral position is when joints are not twisted, bent, or strained; body aligned naturally
Back Protection
Use legs instead of back
Identify warning symbols & safety rules related to chemical, electrical, fire, & radiation hazards, and discuss actions to take if incidents occur.
Recognize symptoms of hemorrhaging, shock, stroke, and heart attack and describe the needed first aid.
List the main points of the American Heart Association CPR guidelines.
Describe the role of personal wellness as it relates to nutrition, rest, exercise, stress management, and ergonomics.