OXYGEN SATURATION & BP
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
pulse oximeter
noninvasive that measures O2 saturation
pulse oximeter step 1
sensor attached to finger
pulse oximeter step 2
diode emits light
pulse oximeter step 3
detector measures amount of light absorbed by Hb02
healthy person with no lung disease or anemia (low oxygen-rich blood) SpO2
92-100%
alternative probes for O2 saturations
forehead, toe, earlobe
hypoxia
O2 below 92%
supplemental (given) oxygen that increase O2 comes from?
MD or your provider
what is blood pressure?
force of blood against arterial walls
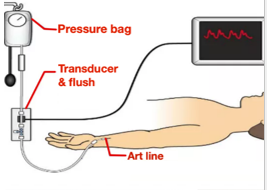
which line is BP measured?
via “A” line
BP is measured indirectly with
sphygmomanometer
INTERNAL factors influencing BP (one)
cardiac output
INTERNAL factors influencing BP (two)
volume of blood
INTERNAL factors influencing BP (three)
resistance/elasticity of vessels
INTERNAL factors influencing BP (four)
viscosity
sphygmomanometer is?
blood pressure cuff
Korotkoff sounds can be heard when?
auscultating manual BP
check BP at what level?
bare arm at heart level
where do you place the BP cuff?
+/-2.5 cm above brachial artery
patient position during BP
feet flat on floor and sit 5 min prior (relax)
systolic (systole)
maximal force against arterial walls during ventricular contraction
diastolic (diastole)
minimal force against arterial walls during ventricular relaxation
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic
pulse pressure measures?
amount of blood pumped out during systole
pulse pressure calculation
(120/80) → 120-80= 40 (pulse pressure)
normal pulse pressure
30-40
stroke volume
volume of blood (mL) ejected from ventricle during contraction
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
constant pressure that forces blood into tissues
mean arterial pressure (MAP) measurement is determined by the?
average over a cardiac cycle
MAP is looked at when we consider
low BP or unstable conditions/BP
mean arterial pressure (MAP) can tell us about
brain or organ perfusion (if they’re getting enough blood)
MAP value for adequate tissue/organ perfusion
greater or equal to 60 mmHg
EXTERNAL: factors that affect blood pressure (one)
exercise
factors that affect blood pressure (two)
emotions
factors that affect blood pressure (three)
meds
factors that affect blood pressure (four)
age **FIX ON TEMP FLASHCARDS**
factors that affect blood pressure (five)
circadian rhythm
factors that affect blood pressure (six)
gender
factors that affect blood pressure (seven)
position (feet uncrossed)
factors that affect blood pressure (eight)
digestion
factors that affect blood pressure (nine)
OBESITY
after usage, what should we do with BP equipment?
routinely inspect
BP cuff level (sphygmomanometer) should be at
zero
flat side of stethoscope
diaphragm
top side of stethoscope
bell
cuff (bladder) length
80% arm circumference
cuff width
40% arm length
BP cuff size (one)
long/xL
BP cuff size (two)
cone shaped - obese
BP cuff size (three)
standard adult/large
BP cuff size (four)
pediatric/small
BP cuff size (five)
newborn (extremely small maybe 6 in or less)
can also check BP on..?
legs
BP on leg is more common within?
baby/kids
BP cuff too small can result
falsely high BP reading
BP cuff too larger can result
falsely low BP reading
BP step one
arm relaxed
BP step two
arm at heart level
lower BP position (arm below heart) results in
higher readings
BP step three
wait 1-3 min before repeating on same arm (or 5 min)
BP step four
not over clothes
resting time before BP
at least 5 min
position of cuff bladder
bladder over brachial artery
cuff distance from auscultation site
2-3 cm
peak inflation level
20-30 mmHg above radial pulse disappearance
cuff deflation rate
2-3 mmHg/sec
systolic sound
first sound heard (Korotkoff phase 1)
diastolic sound
when sounds disappear (Korotkoff phase 5)
high bp
140/90 OR above
pre-high bp
121-139/81-89
normal bp
120/80 OR less
essential/primary HTN (not specific cause/”just because…”)
stressors, pain, dietary, genetics, etc.
secondary HTN (caused by condition)
renal, adrenal, pituitary, tumor
high BP term & reading
hypertension (above 140/90)
low BP term & reading
hypotension (below 90-95/60)
low BP can be caused by what events?
bleeding, dehydration, anemia, medications, fall risk
orthostatic hypotension
BP drops when standing up or sitting down
orthostasis def
BP drops by at least 20/10 mmHg (when they rise)
during orthostatic hypotension , when BP goes down
pulse goes up
orthostatic hypotension are what measurements?
serial measurements of pulse and BP
orthostatic hypotension related factor (one)
suspect volume depletion
orthostatic hypotension (two)
history of syncope (fainting)
orthostatic hypotension (three)
risk for falls
how to check orthostatic hypotension?
lying, sitting, standing BP and pulse
how long do we wait between readings for orthostatic hypotension
wait 2-3 minutes (lying, sitting, standing)
orthostatic hypotension documentation items
time, positions, readings, Pt report of symptoms
what age do we begin BP in children?
3 yo
why do we take vital signs in a sequence for pediatrics?
for accuracy (kids freak out so their BP rises)
VS sequence in pediatrics step one
respirations (least invasive, or not gonna upset pediatrics)
VS sequence in pediatrics step two
pulse
VS sequence in pediatrics step three
temperature
VS sequence in pediatrics step four
O2
VS sequence in pediatrics step five
blood pressure
what makes vital signs concerning?
vital sign trend changes (up or down)
vital signs presents a new finding can be
more concerning
more concerning: acute VS change vs chronic VS change?
acute VS (chronic VS have trends)
we use the PAINAD scale for…?
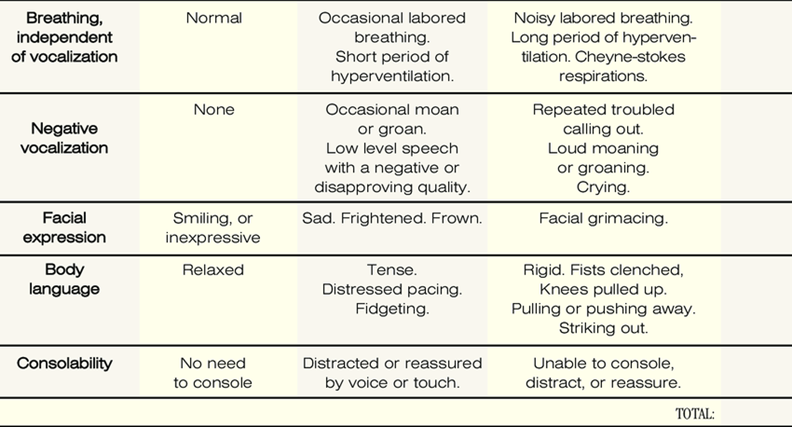
dementia patients (advanced dementia)
PAINAD scale is subjective or objective?
objective (done by nurse)