Physics of the Atom
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When would a nuclei be considered stable and unstable?
A nuclei is stable when there is a even number of protons and neutrons held by a strong nuclear force. A nuclei is considered unstable when they have either too many protons or too many neutrons.
What are the types of decay?
Apla, Beta - , and Beta +.
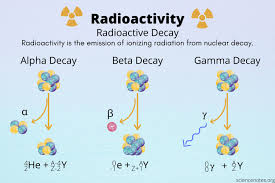
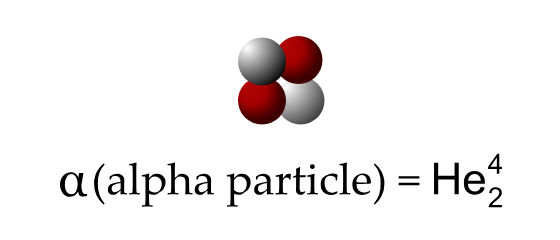
Explain what happens in Alpha Decay
In alpha decay, an unstable atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle, which consists of two protons and two neutrons (identical to a helium-4 nucleus). This process reduces the atomic number of the original element by two and the mass number by four, transforming it into a different element.
Explain what happens in Beta - Decay.
In beta - decay, a neutron transforms into a proton while emitting a beta particle (an electron) and a electron. This process increases the atomic number of the element by one, resulting in a different element but with the same mass number.
Explain what happens in Beta + Decay?
In beta + decay there is too many protons present. So a proton is converted to a neutron and a positron is emitted. This decreases the atomic number by one, resulting in a different element while the mass number remains unchanged.
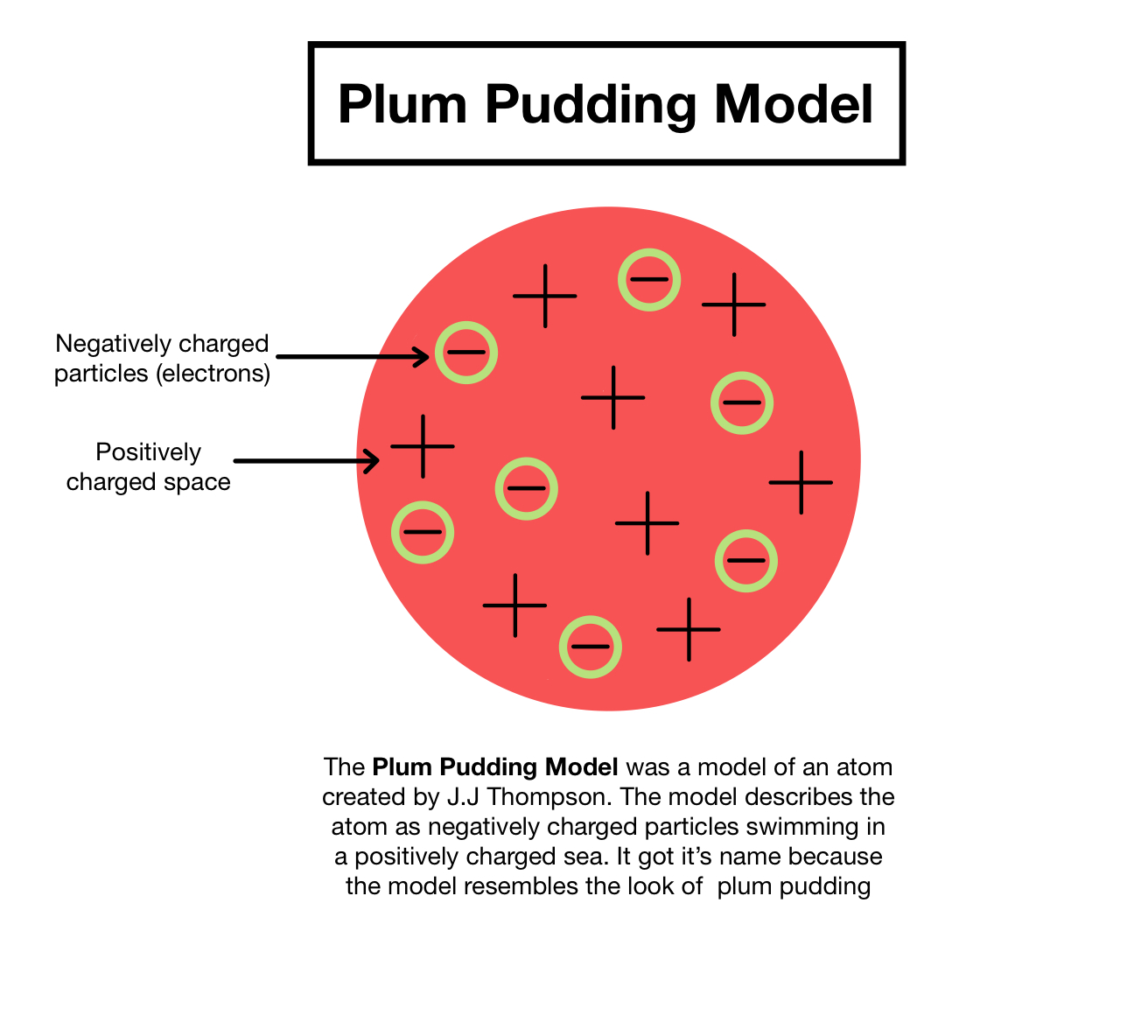
What did JJ Thompson propose and describe what it means?
JJ Thompson proposed that plum pudding model. The basic idea of the model was that the atom consist of negatively charged electrons in basically a positively charged ‘dough’ or ‘pudding’.
What did Ernest Rutherford and his students propose?
They were researching the plum pudding model. They fired alpha particles at a thin gold foil and observed that it passes through, however some bounced back. The plum pudding model was not able to explain the bouncing back of the alpha particles.
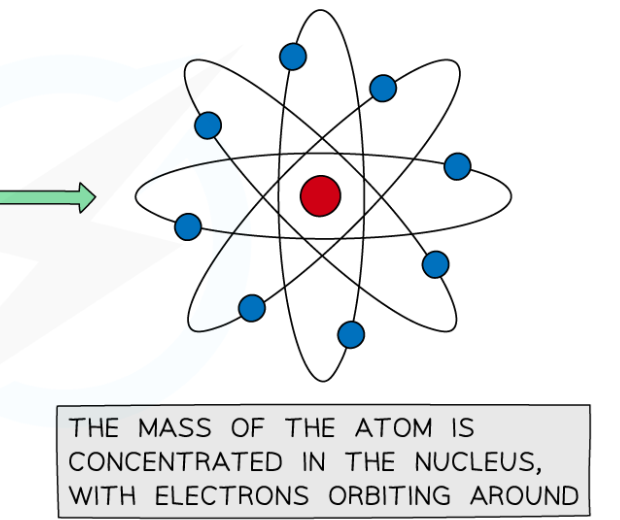
What were the conclusions of the Nuclear Model?
They concluded that the atom’s mass is concentrated at the centre known as the nucleus. The nucleus is positively charged and the negatively charged electrons orbit the nucleus at a distance.
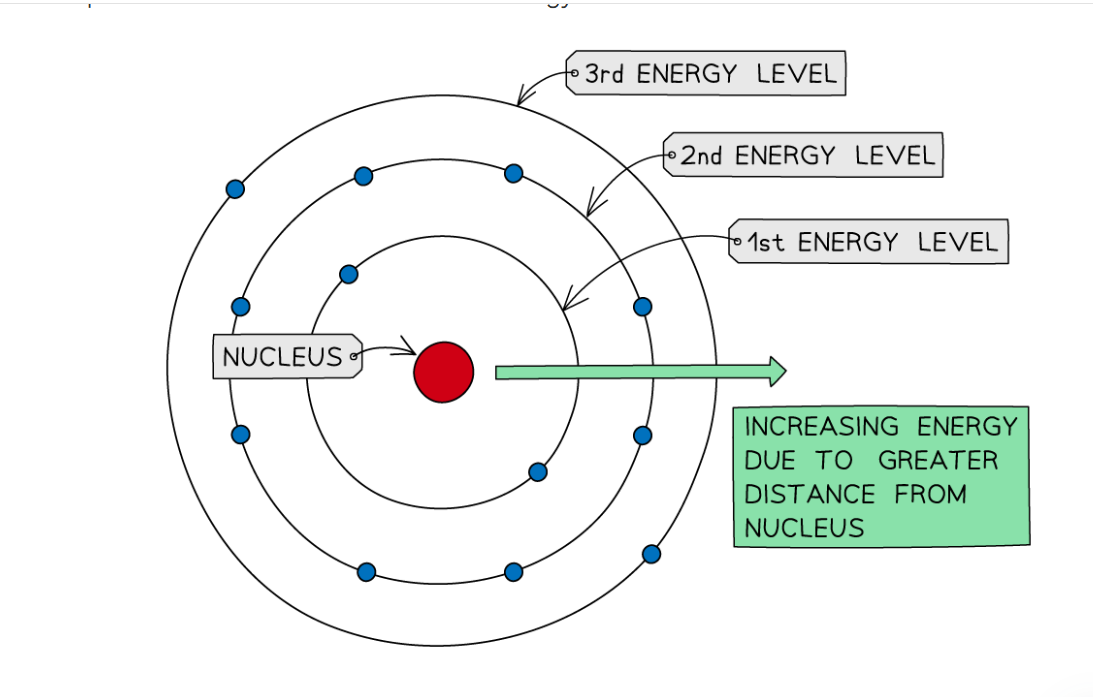
Explain the Bhor Model
He used the Nuclear Model to develop his model. He proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus at different distances called energy levels.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes are compounds that have the same amount of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.
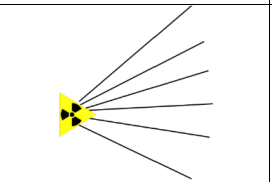
What is the range of alpha particles in air, behaviour in electric field, and the type of track created in the cloud chamber?
Range: Few centimeters ( 1cm to 5 cm),
Electric field: Bend towards the negative
Tracks: They have thick straight tracks (due to high ionisation).
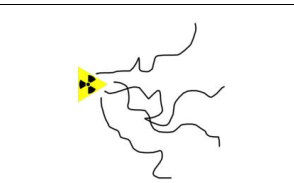
What is the range of beta particles in air, behaviour in electric field, and the type of track created in the cloud chamber?
Range: Few 10s of cm
Behavior in electric field: Bends towards the positive
Tracks created: Thin and twisted due to little ionisation
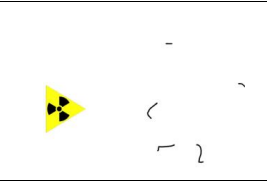
What is the range of gamma particles in air, behaviour in electric field, and the type of track created in the cloud chamber?
Range: Infinite
Behaviour in electric field: Undeviated
Tracks produced: short thin tracks
Speak to the penetrating power of Gamma, Beta, Alpha.
Gamma travel far and are stopped by lead. Alpha particles are stopped by paper. Beta particles are stopped by aluminium foil.
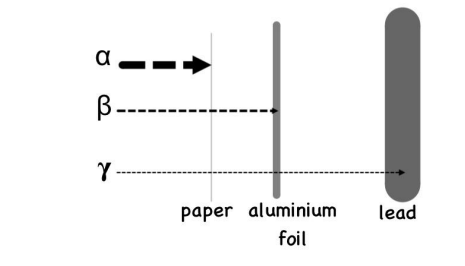
How does radiation cause ionisation?
The radiation causes the electrons to be knocked off. So they become charged particles called ions. Ionisation increases from gamma,beta to alpha.
Speak to the danger of Alpha, Beta, and gamma particles

ag