Anatomy & Physiology II - LAB 7 Digestive System
1/144
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
alimentary canal
mouth→anus
ingestion
eating
propulsion
movement of food thru the alimentary canal
peristalsis
propulsion of food that involves alternating waves of contraction & relaxation
bolus
food gets to mouth
chyme
food gets to stomach
feces
food gets to large intestine
mechanical breakdown
chewing, mixing food w/ saliva, churning food in stomach, & segmentation
segmentation
local constriction of intestines that mixes food with digestive juices
absorption
passage of digested fragments from lumen of GI into blood/lymph
defecation
elimination of indigestible substances via anus in form of feces
digestion
series of catabolic steps involving enzymes that break down food molecules into chemical building blocks
mesentery
double layer of peritoneum that extends to digestive organ from body wall
allows blood vessels, lymphatics, & nerves to reach digestive organs & holds organs in place, & stores fat
mastication
chewing
muscles involved in chewing?
masseter, temporalis, pterygoid
which cranial nerve controls chewing?
trigeminal (V)
what bones make the hard palate?
palatine bones & maxilla
specific term for swallowing?
deglutition
muscles that control swallowing
muscles of the pharynx
cranial nerves that control swallowing?
trigminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, hypoglossal
what macromolecule digestion begins in the mouth due to enzymes found in saliva?
salivary amylase
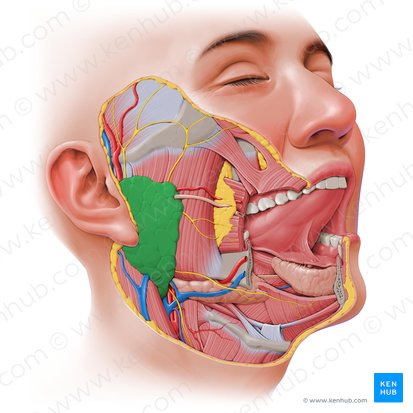
parotid gland
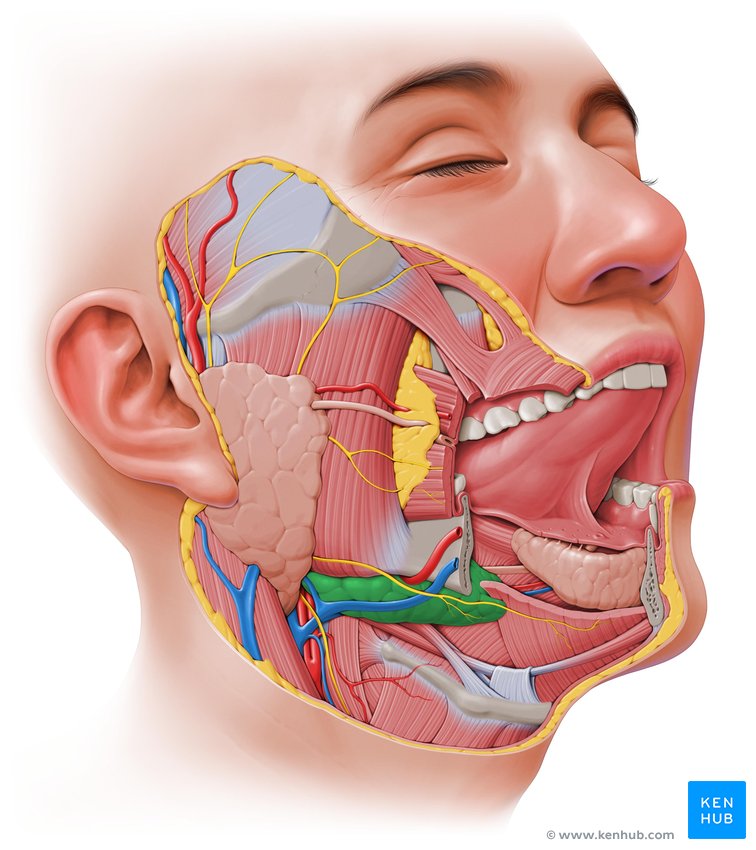
submandibular gland
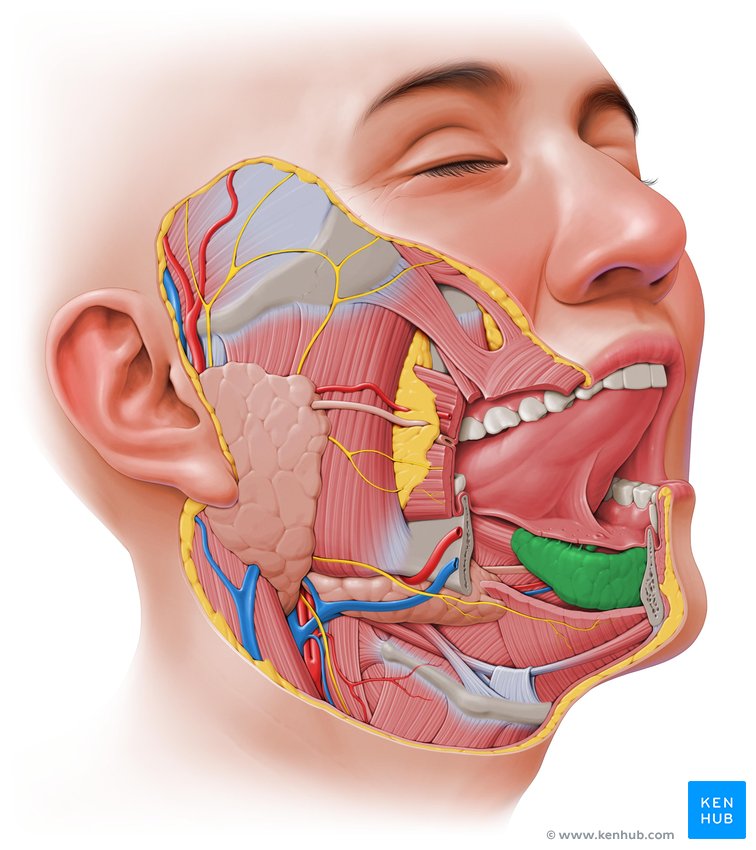
sublingual gland
xerostomia
dry mouth/cotton mouth
pH of saliva
6.75-7
cranial nerves of salivation?
facial & glossopharyngeal
esophagus
stratified squamous
emesis
vomiting
cholecystokinin (CCK)
Made: duodenal mucosa
Stim: fatty chyme
Target: stomach, liver, pancreas
Action: inhibits stomach’s secretion & potentiates secretin’s actions on those organs
glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)
Made: duodenal mucosa
Stim: fatty chyme
Target: stomach & pancreas (beta cells)
Action: inhibits HCl production & stimulates insulin release
gastrin
Made: stomach mucosa
Stim: food in stomach
Target: stomach (parietal cells), small intestine, ileocecal valve, colon
Action: increases HCl secretion & stimulates intestinal contraction
histamine
Made: stomach mucosa
Stim: food in stomach
Target: stomach
Action: activates parietal cells to release HCl
intestinal gastrin
Made: duodenal mucosa
Stim: acidic & partly digested foods in duodenum
Target: stomach
Action: stimulates gastric glands & motility
motilin
Made: duodenal mucosa
Stim: fasting, periodic neural stimuli release
Target: proximal duodenum
Action: stimulates migrating motor complex
secretin
Made: duodenal mucosa
Stim: acidic chyme
Target: stomach, pancreas, liver
Action: inhibits gastric gland secretion & gastric motility
serotonin
Made: stomach mucosa
Stim: food in stomach
Target: stomach
Action: contraction of stomach muscles
somatostatin
Made: stomach/duodenal mucosa
Stim: food in stomach; stim by sympathetic nerve fibers
Target: stomach, pancreas, small intestine
Action: inhibits gastric secretion of all products & inhibits pancreas secretion
vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
Made: enteric neurons
Stim: chyme containing partly digested contents
Target: small intestine, pancreas, stomach
Action: inhibits acid secretion & stimulates buffer secretion
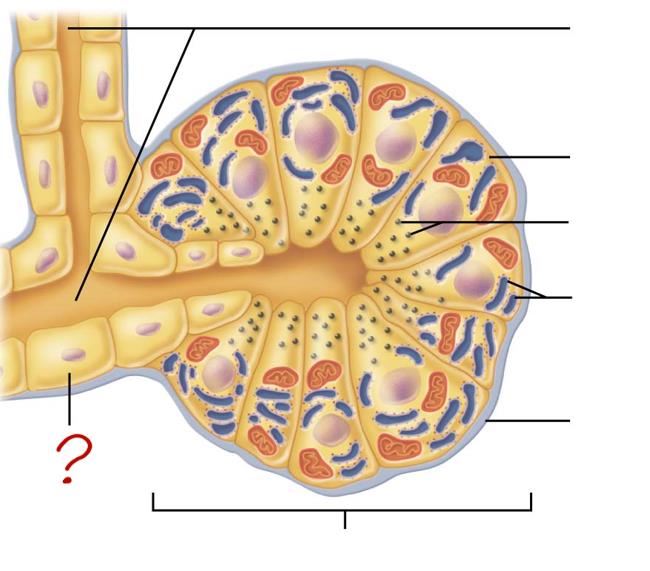
small duct
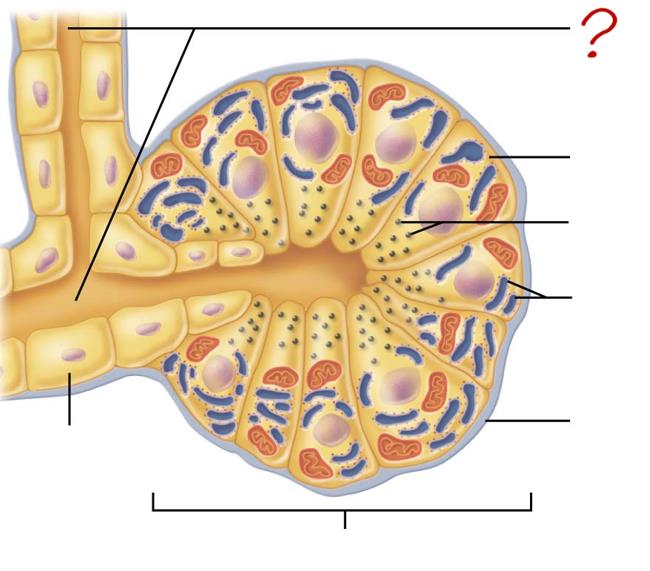
acinar cell
secretes enzymes
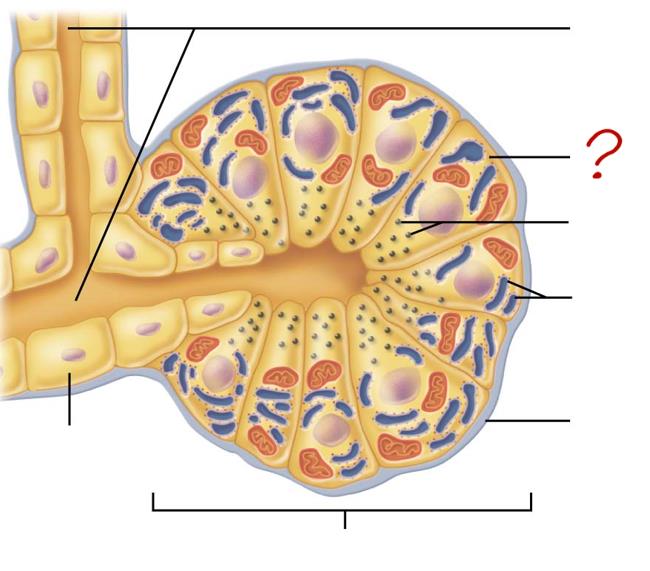
zymogen granules
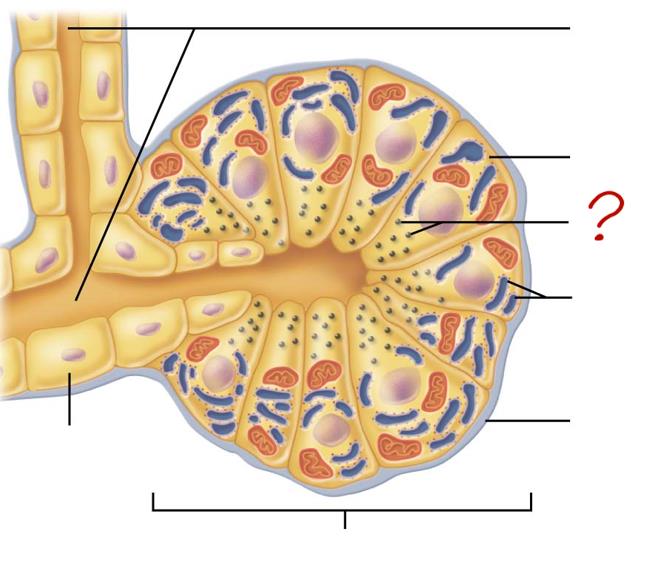
rough endoplasmic reticulum
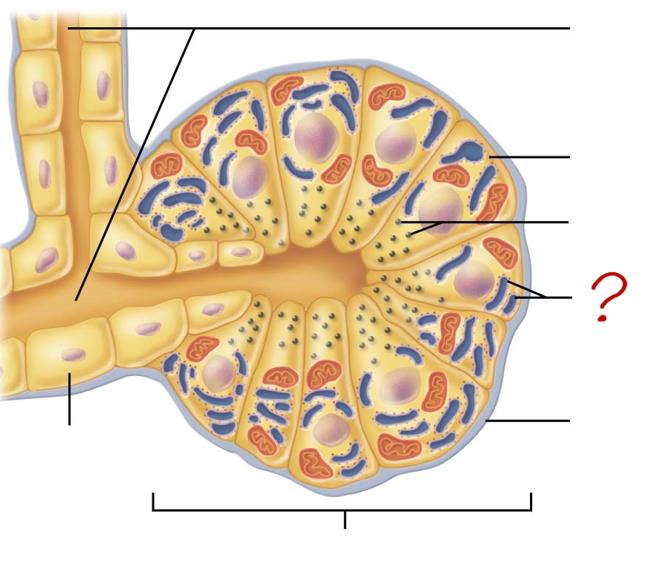
basement membrane
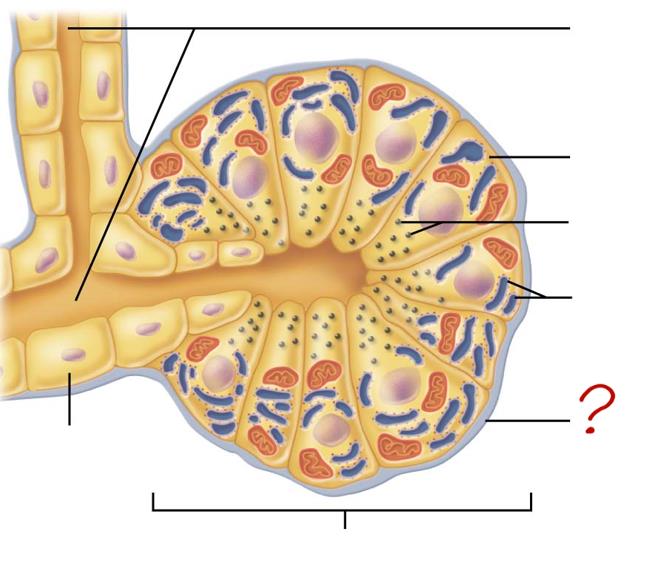
acinus
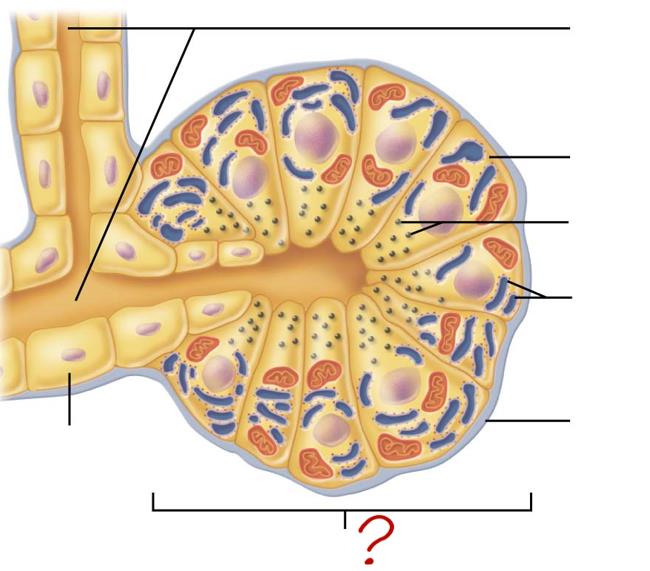
duct cell
secretes HCO3 & H2O
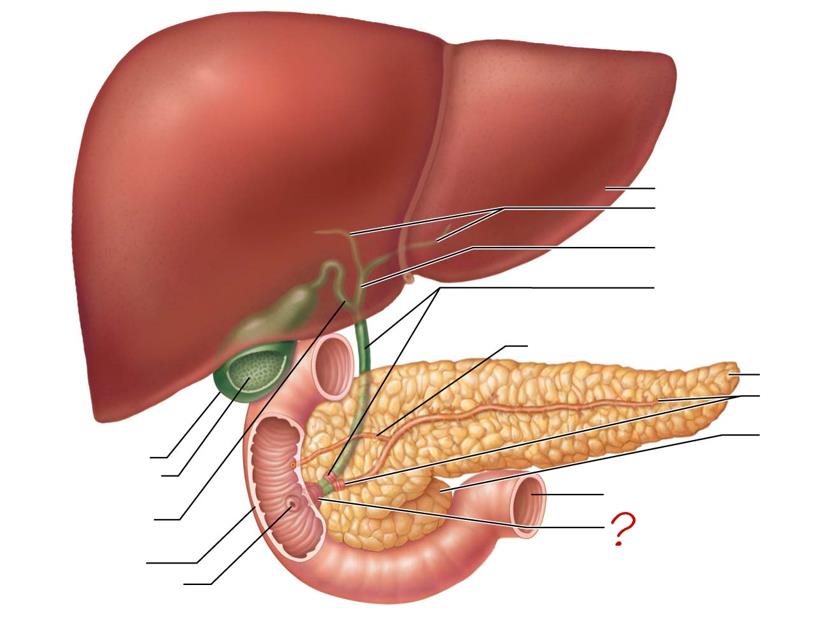
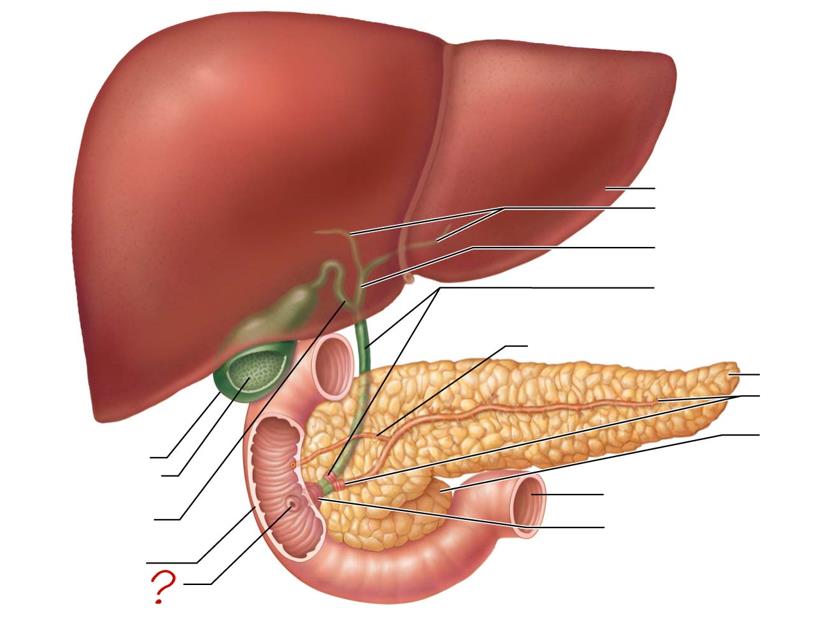
liver
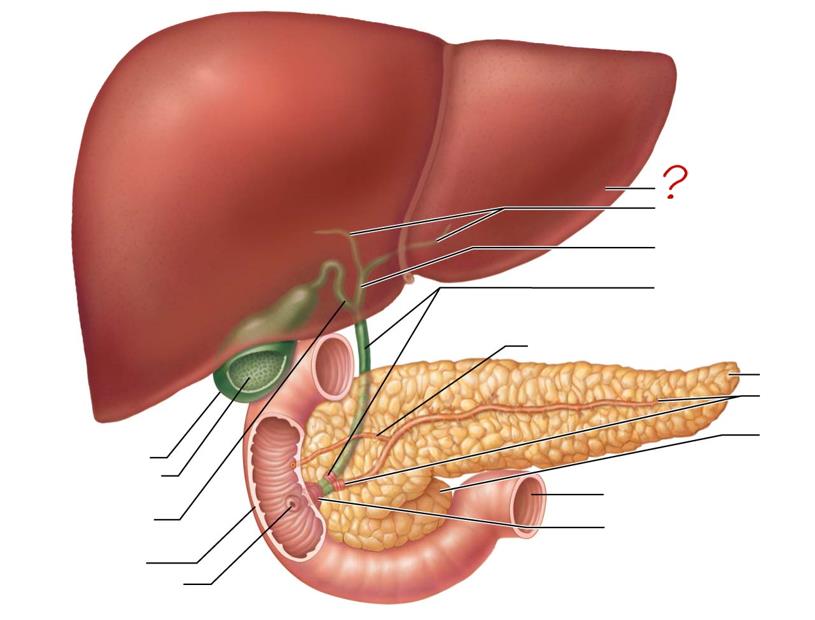
right & left hepatic ducts
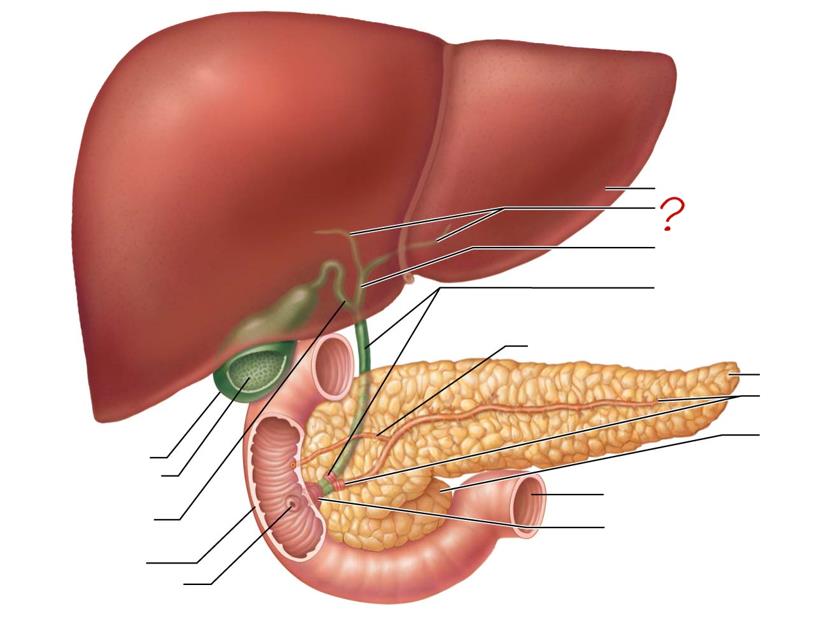
common hepatic duct
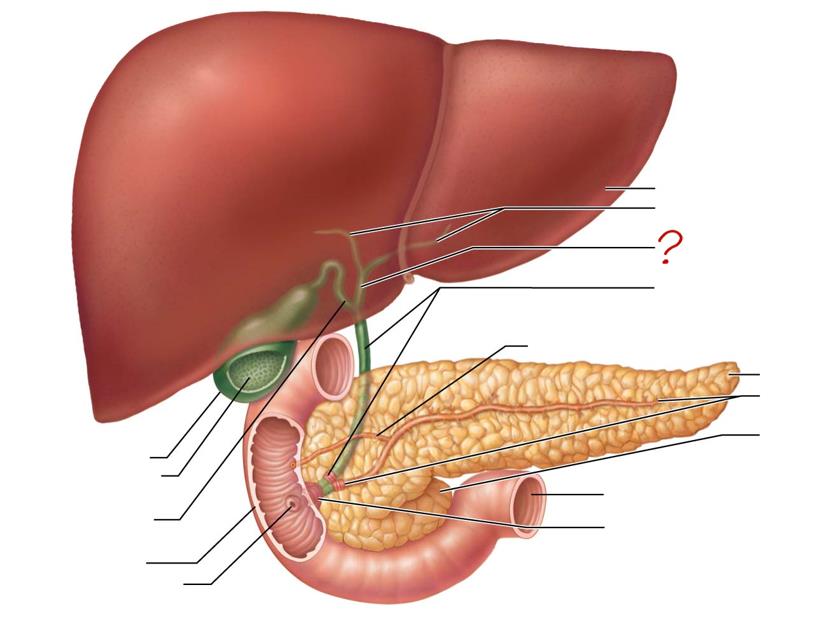
bile duct & sphincter
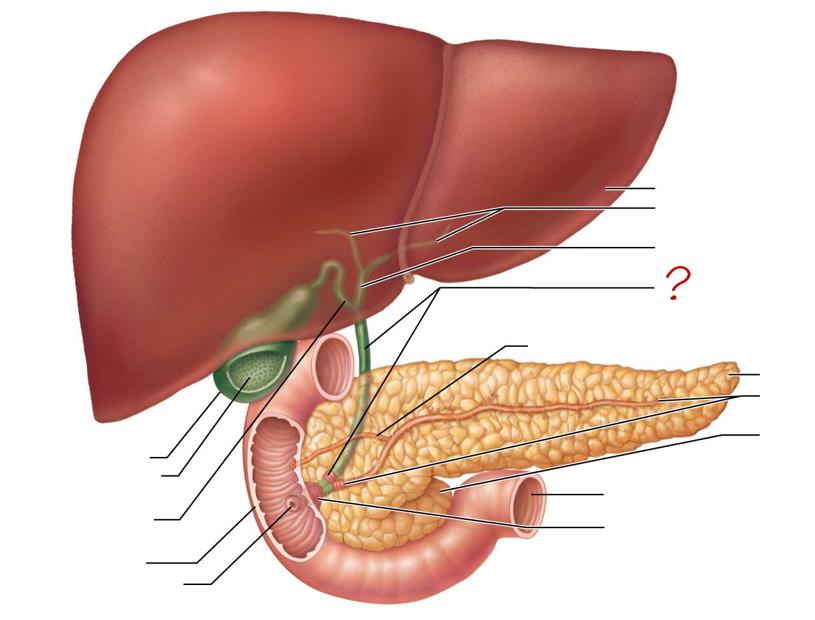
accessory pancreatic duct
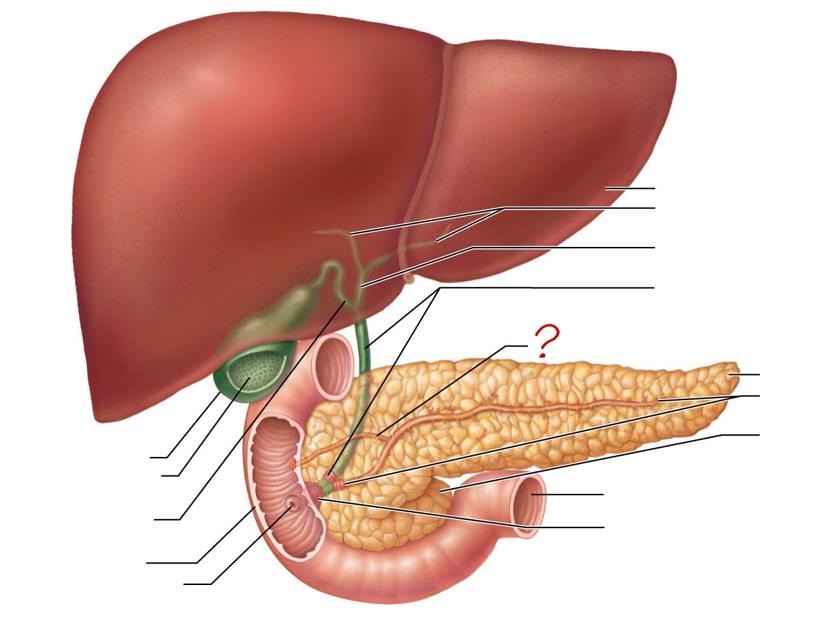
tail of pancreas
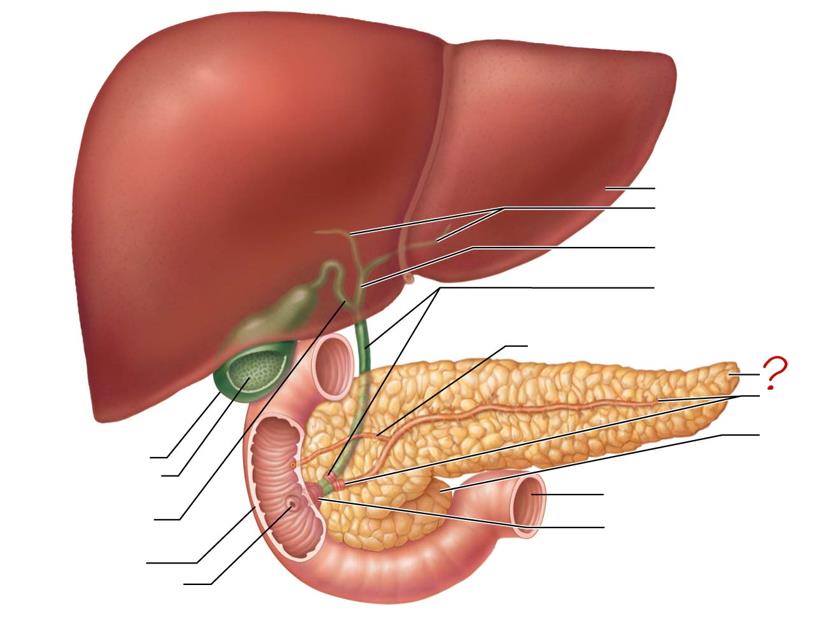
main pancreatic duct & sphincter
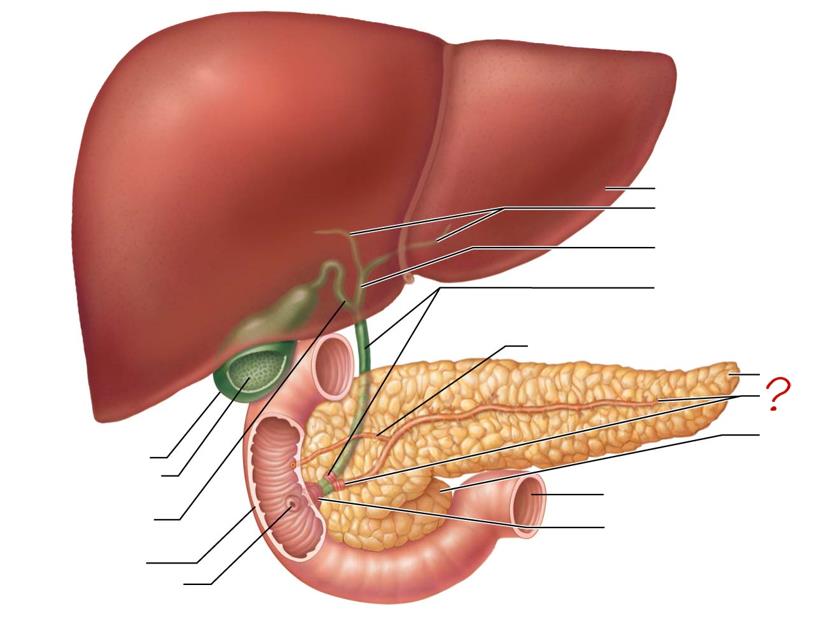
head of pancreas
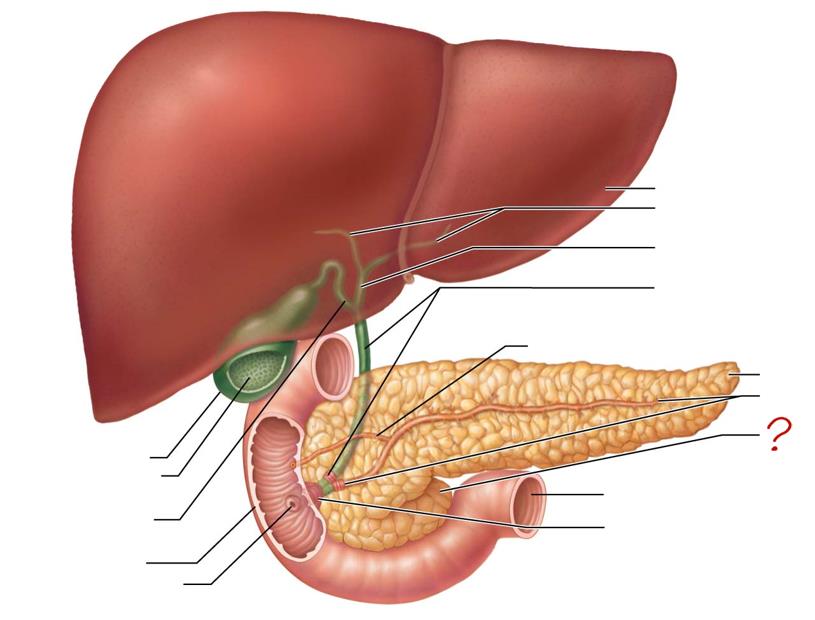
jejunum
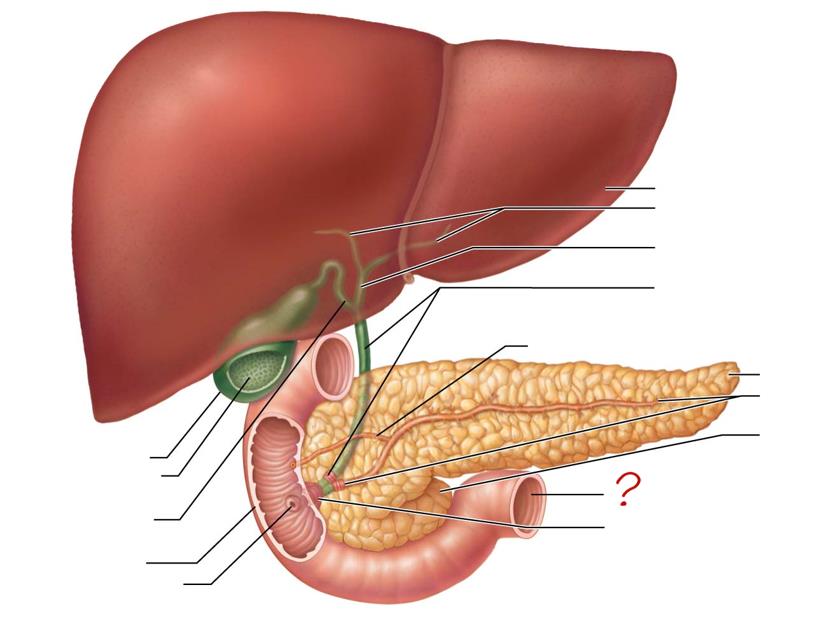
hepatopancreatic ampulla & sphincter
gallbladder
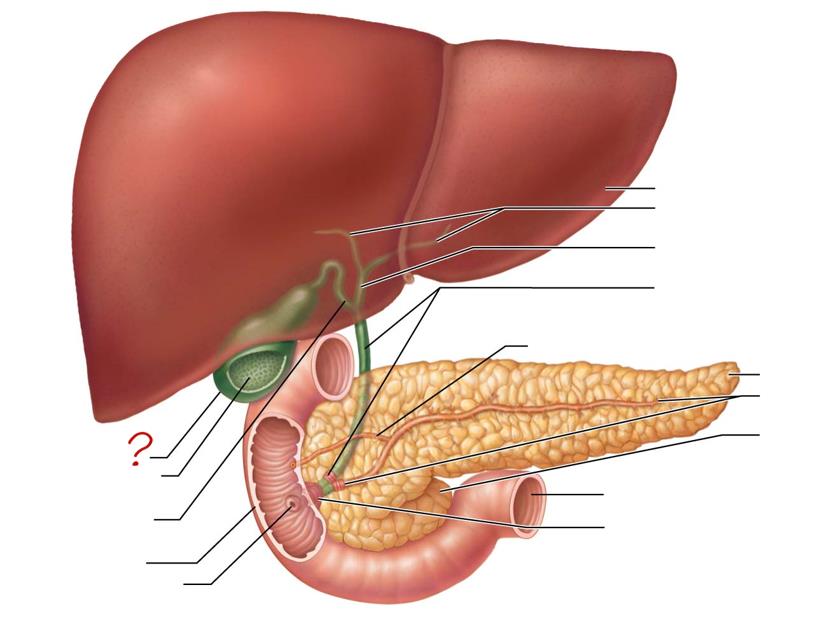
mucosa w/ folds
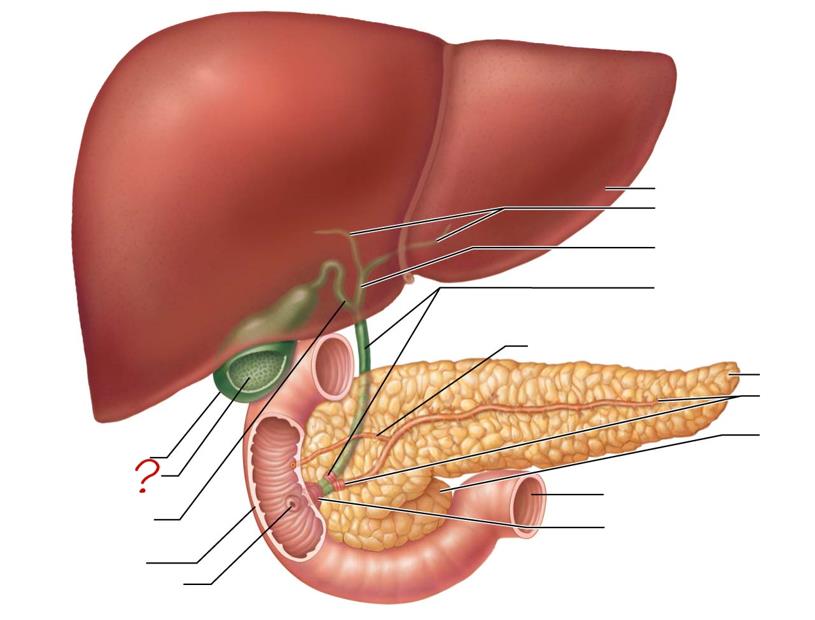
cystic duct
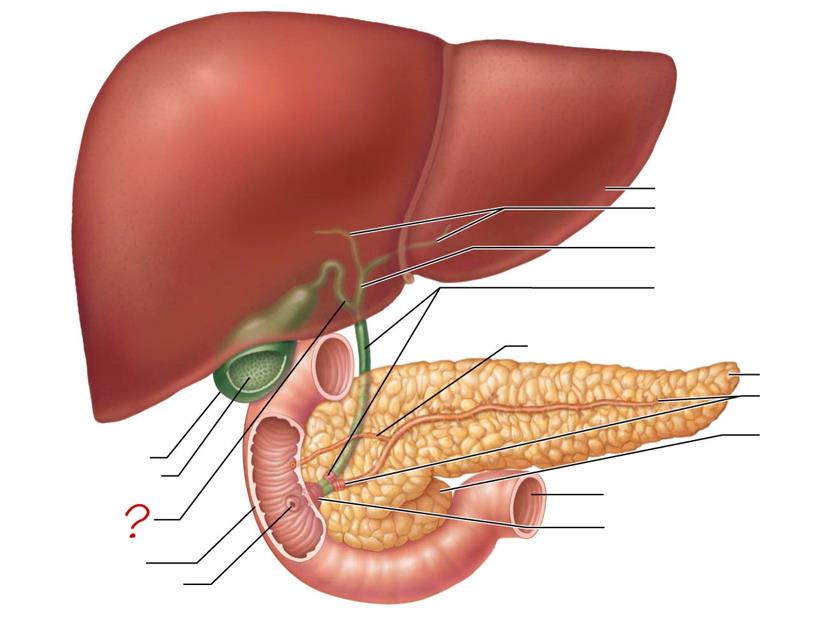
duodenum
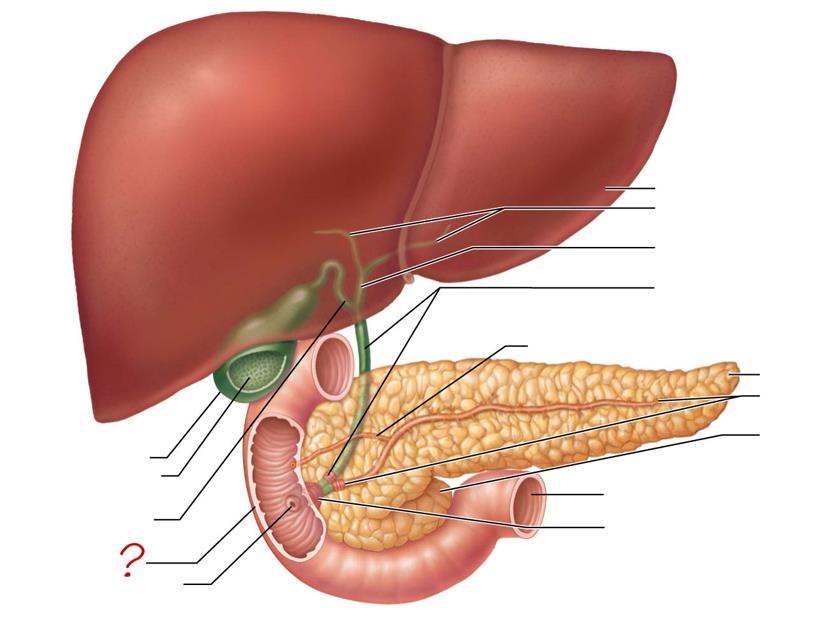
major duodenal papilla
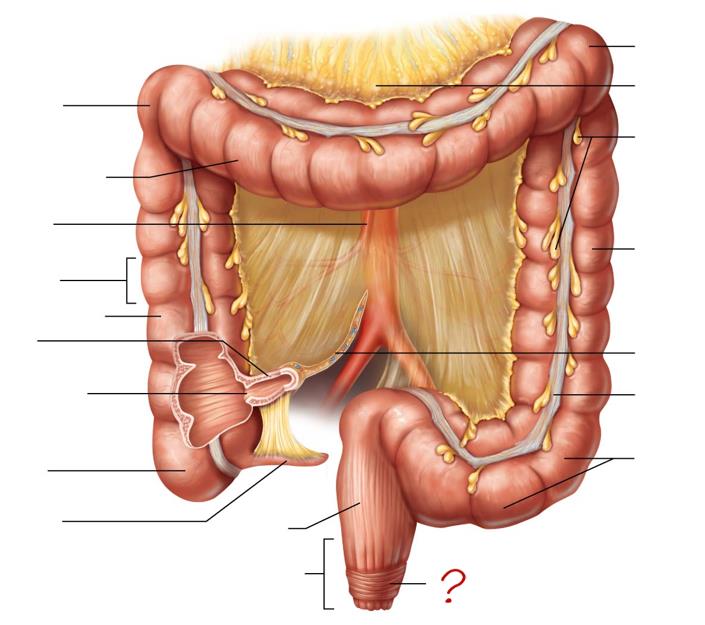
right colic (hepatic) flexure
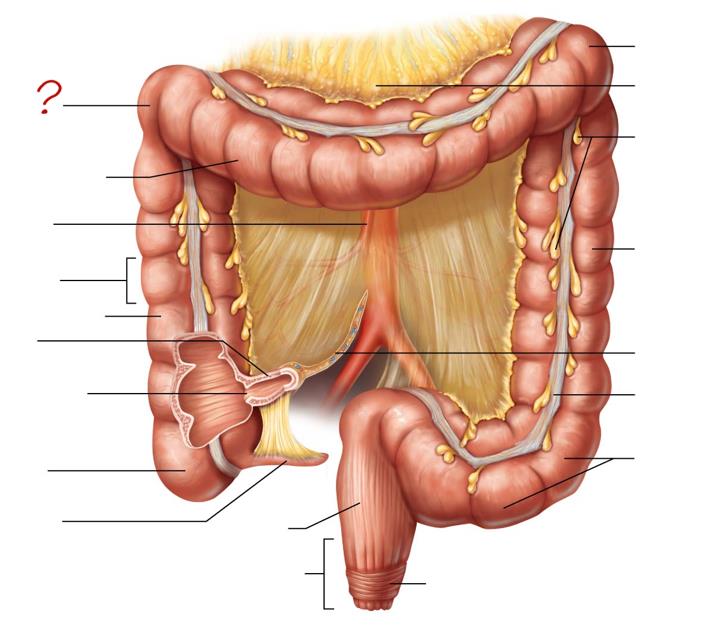
transverse colon
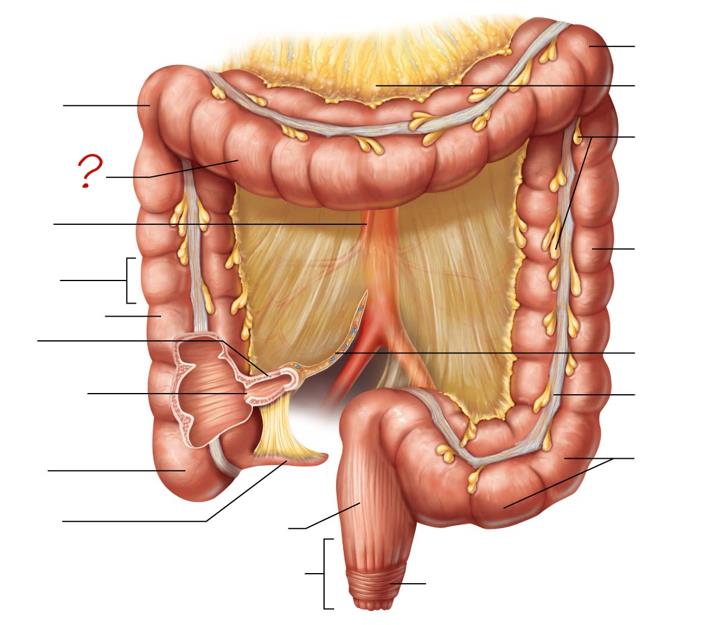
superior mesenteric artery
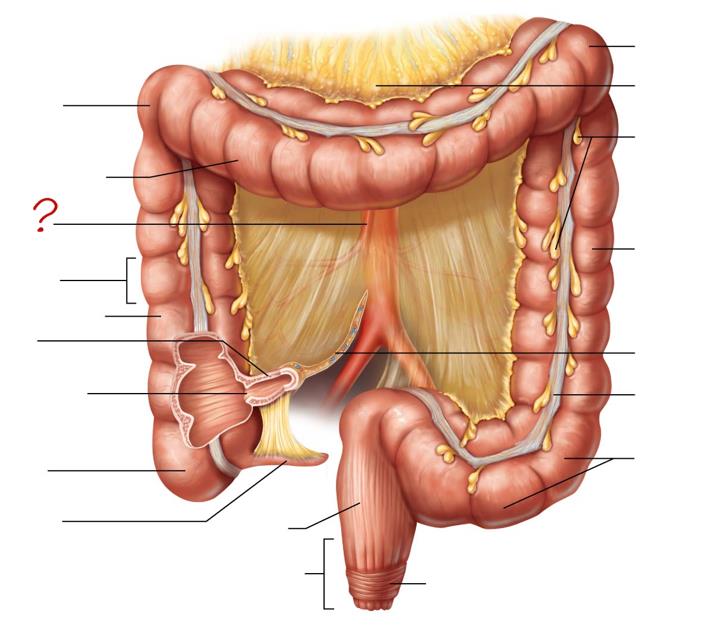
haustrum
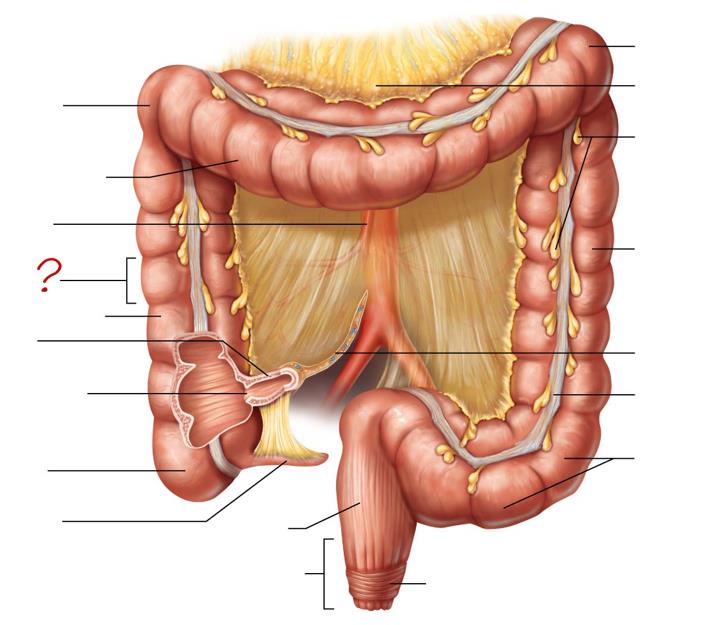
ascending colon
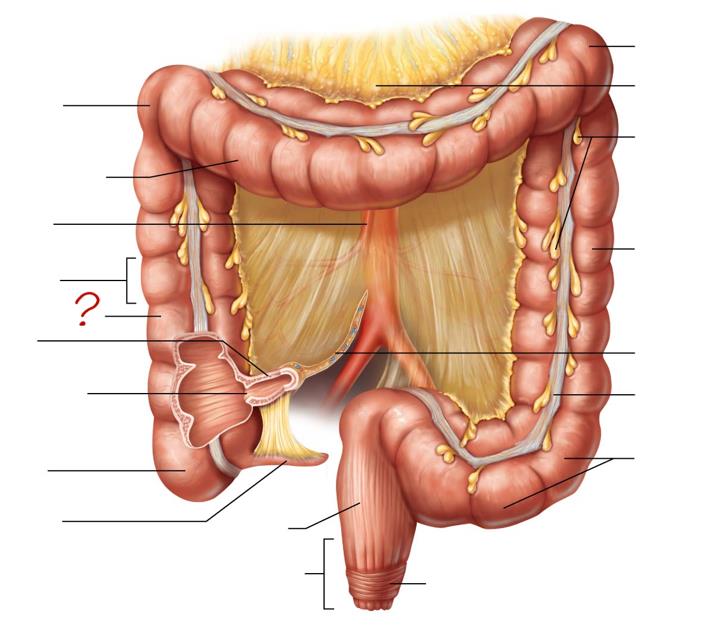
ileum
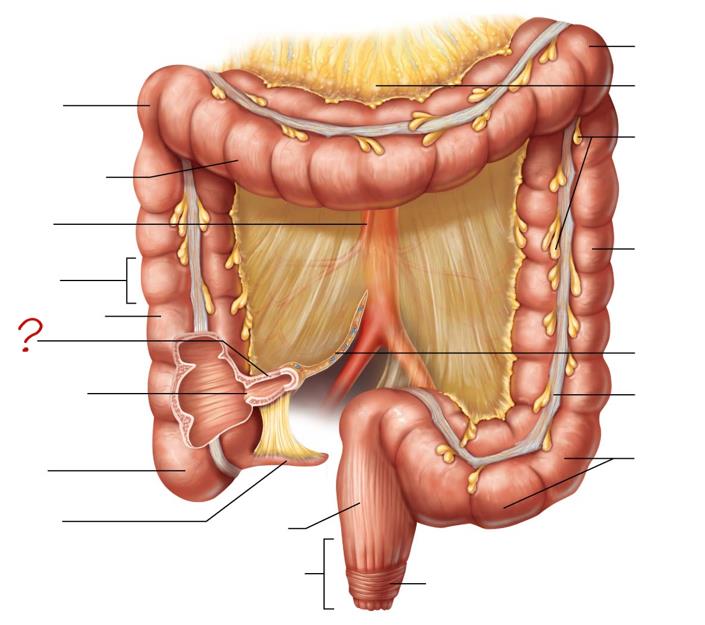
ileocecal valve
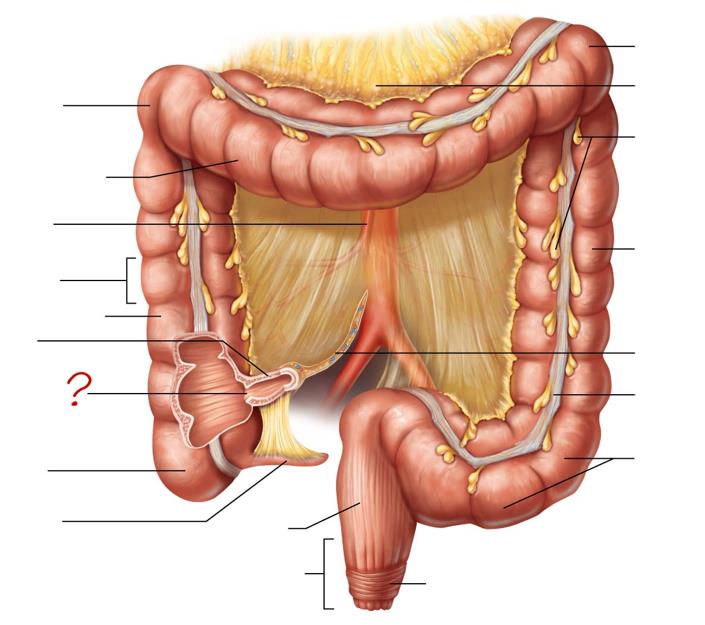
cecum
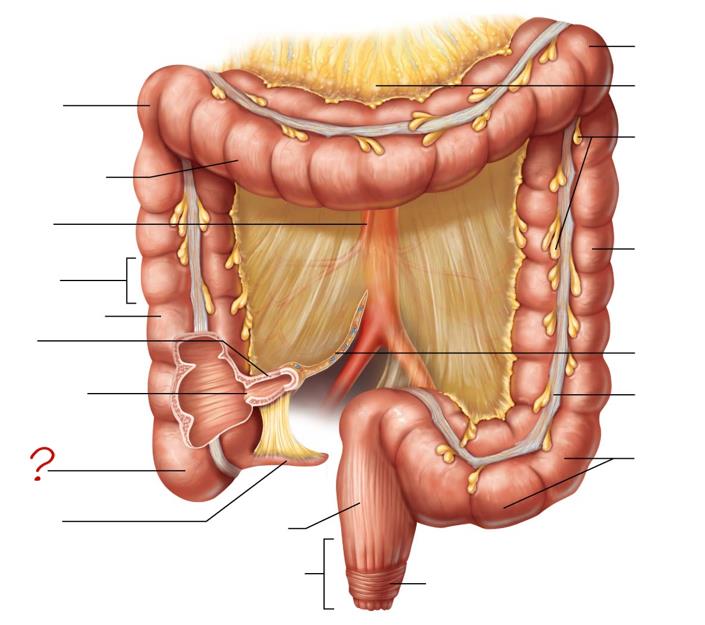
appendix
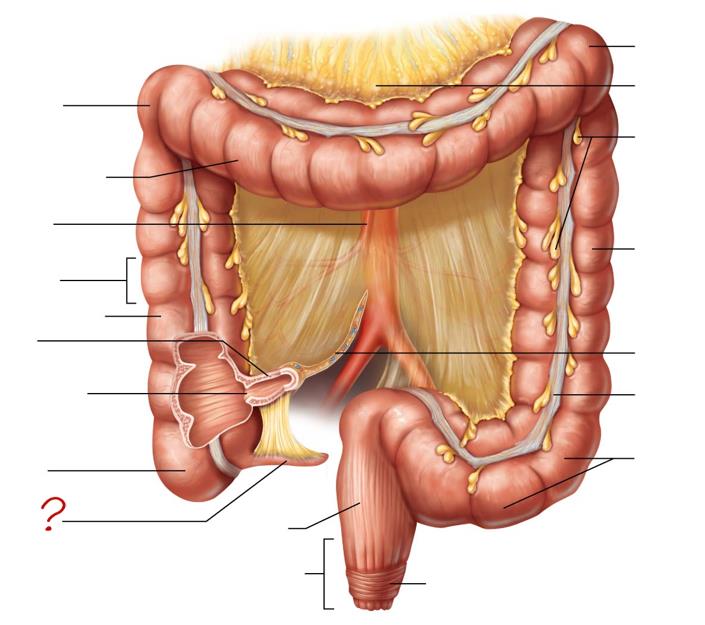
rectum
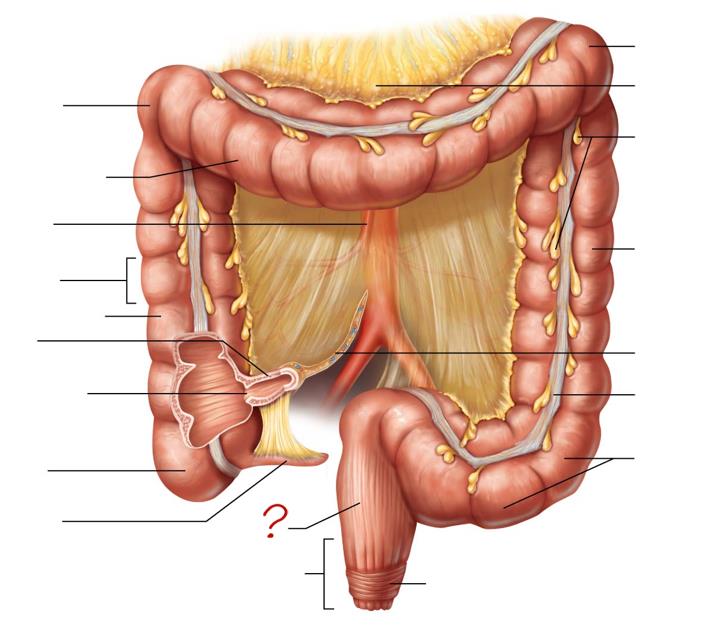
anal canal
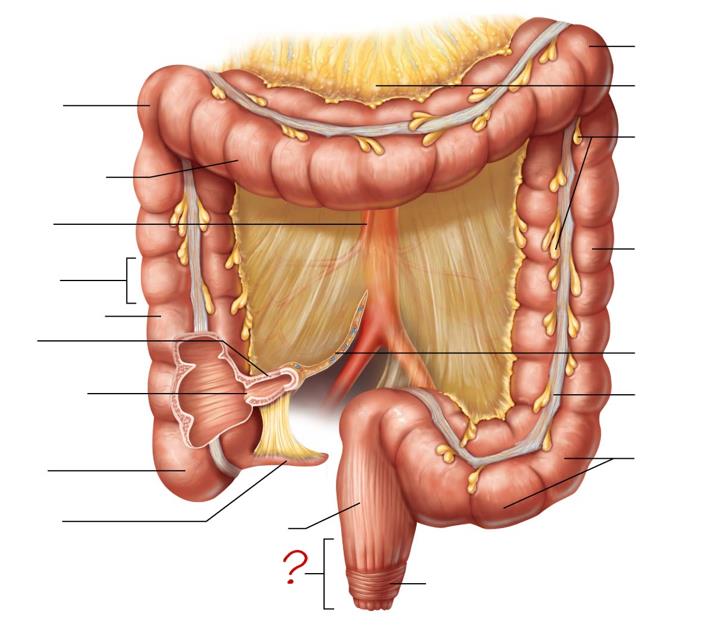
left colic (splenic) flexure
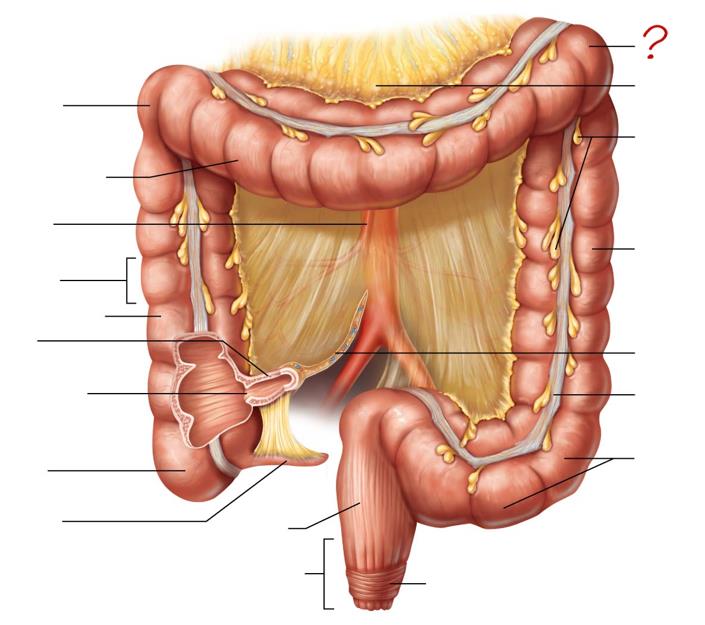
transverse mesocolon
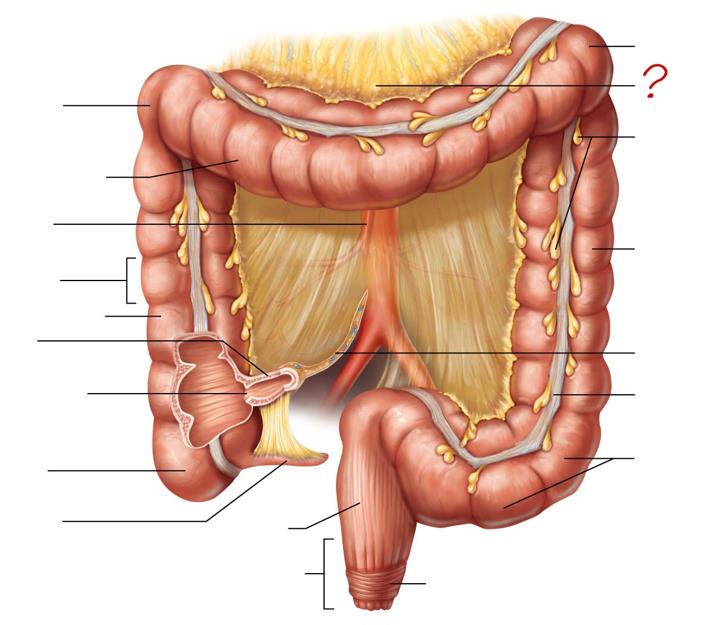
epiploic appendages
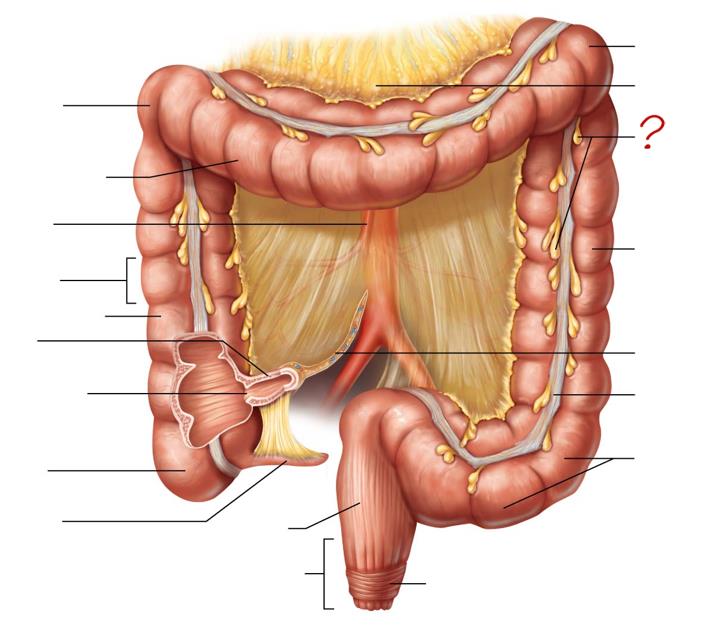
descending colon
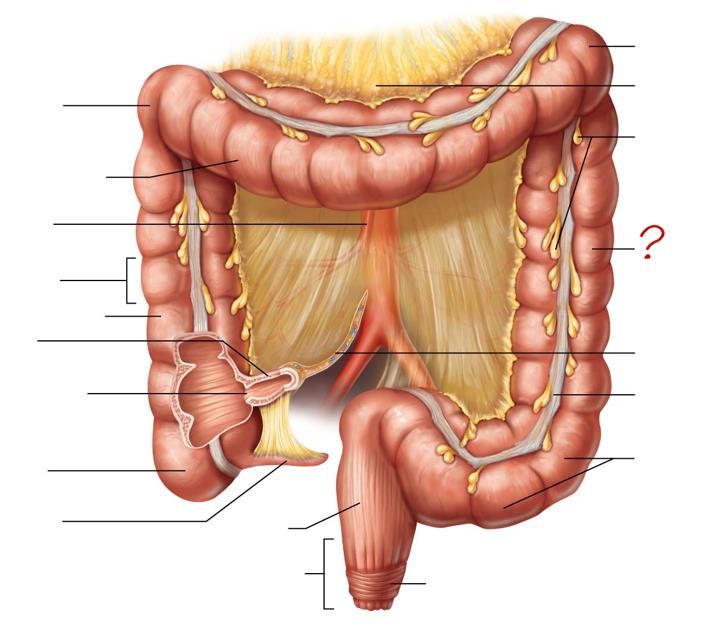
mesentery
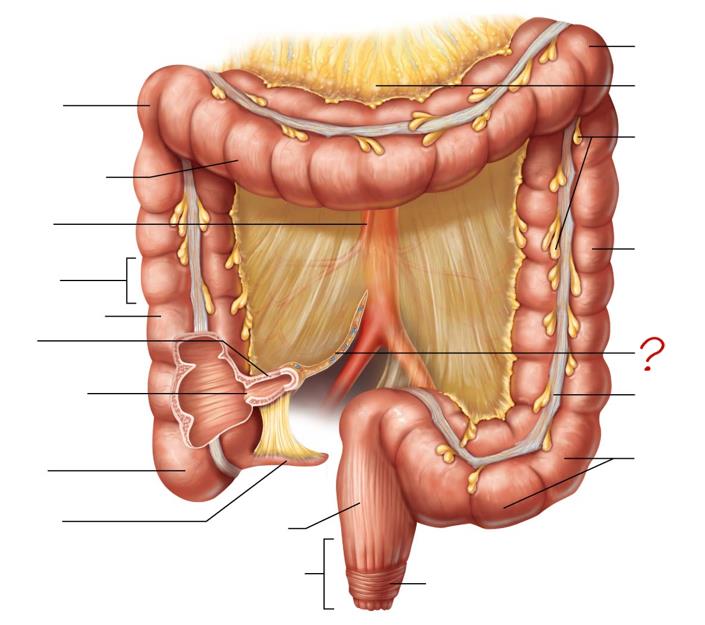
tenia coli
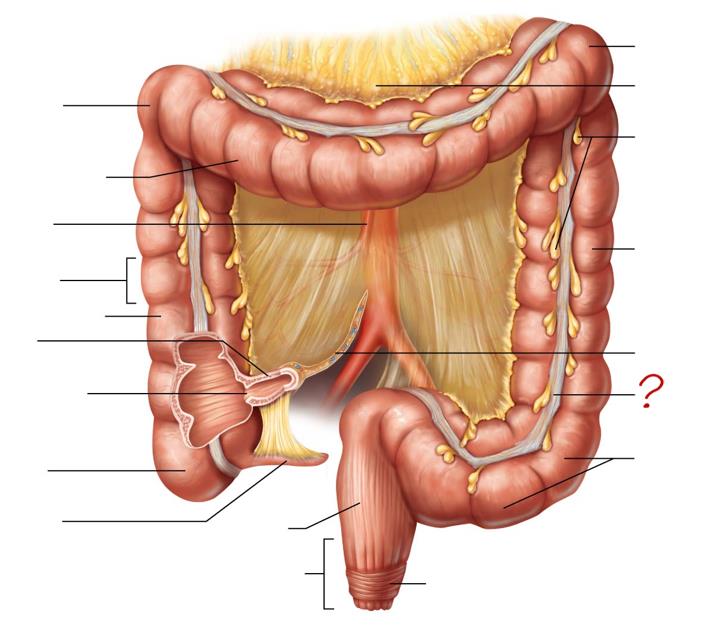
sigmoid colon
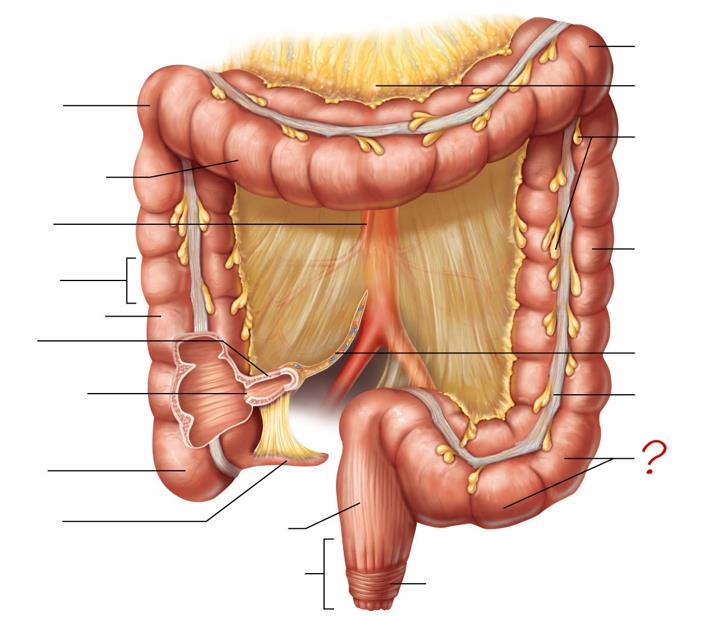
external anal sphincter
enterocytes
absorptive cells
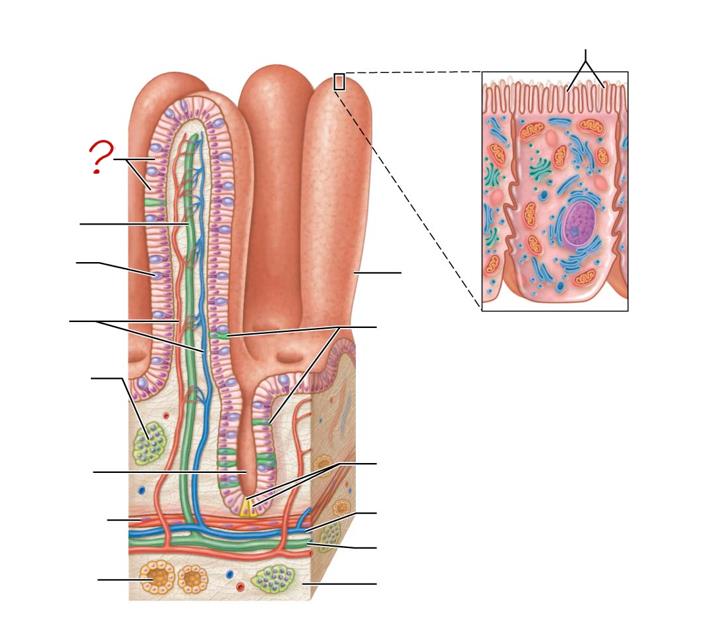
lacteal
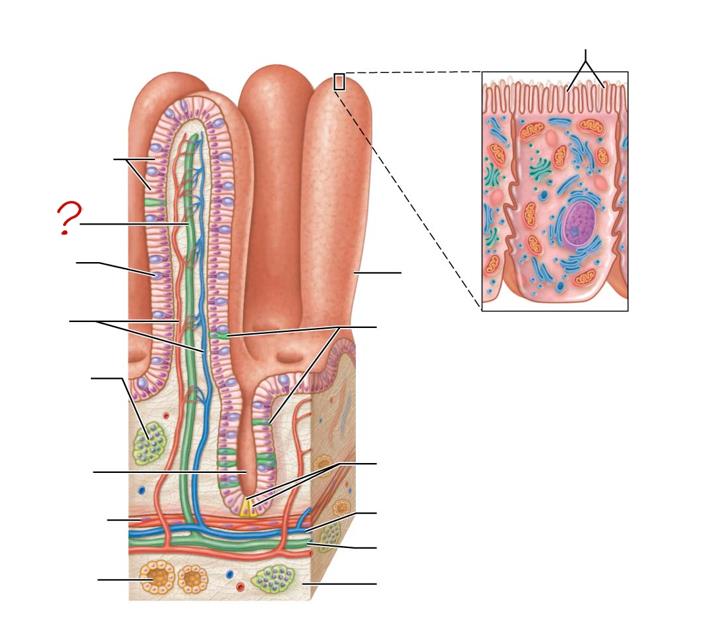
goblet cell
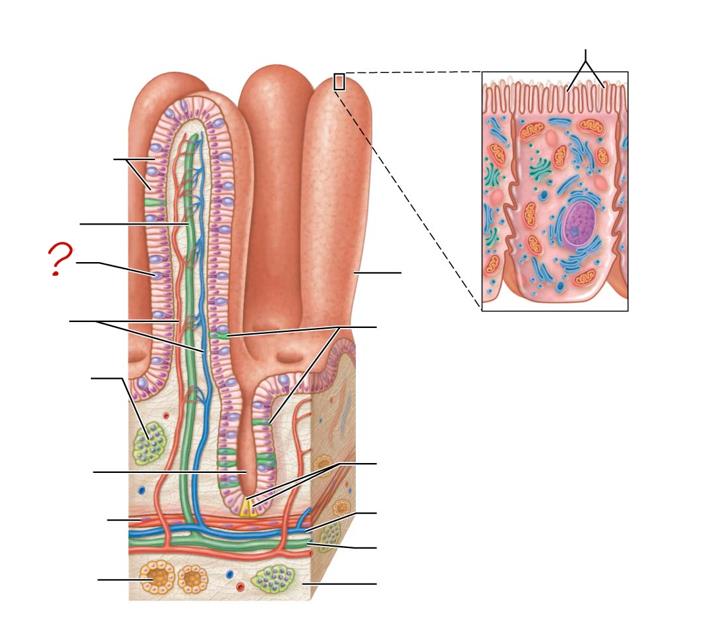
blood capillaries
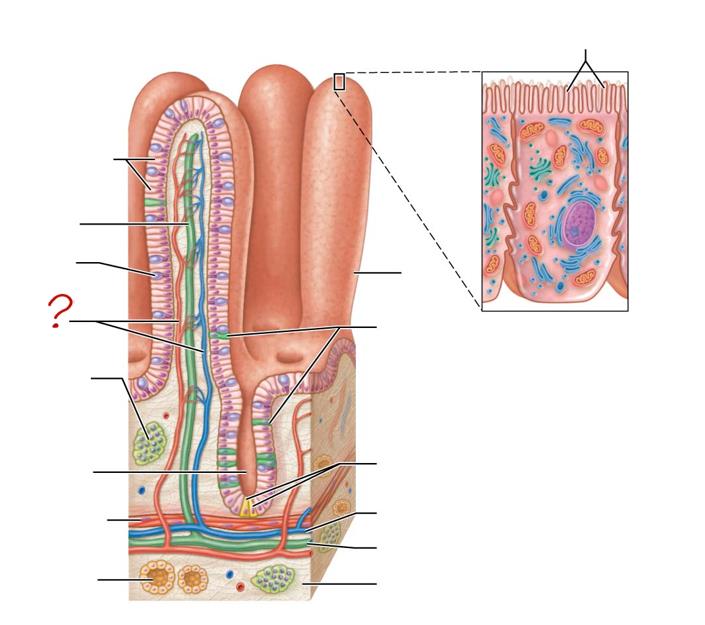
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
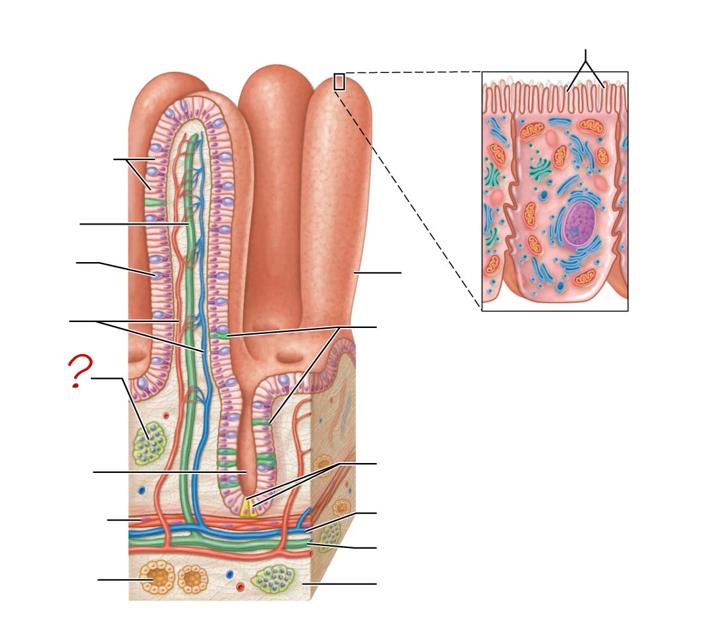
intestinal crypt
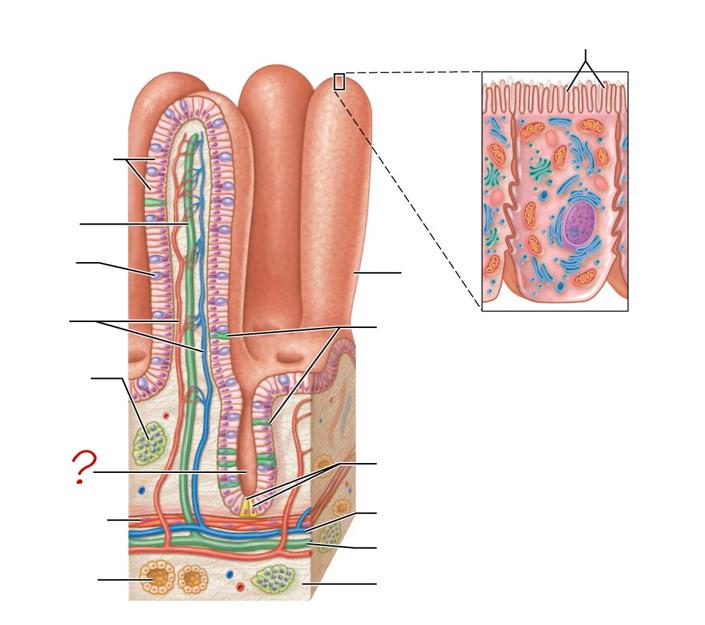
muscularis mucosae
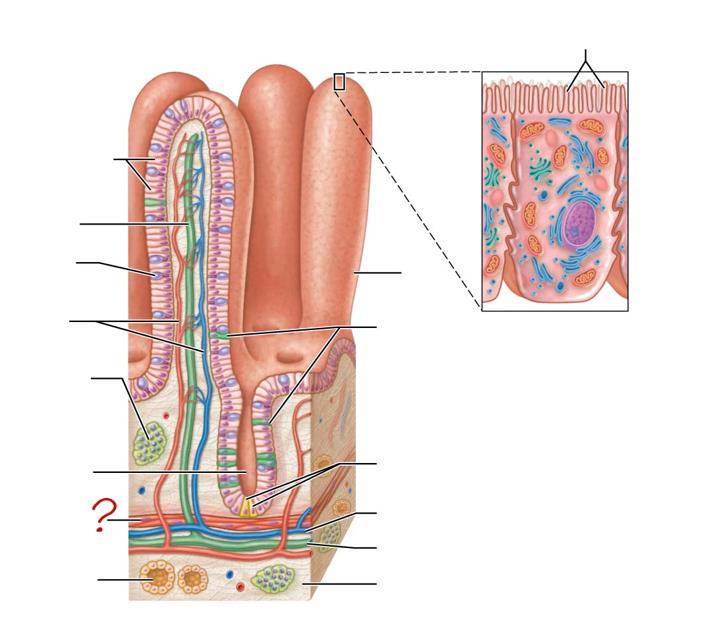
duodenal gland
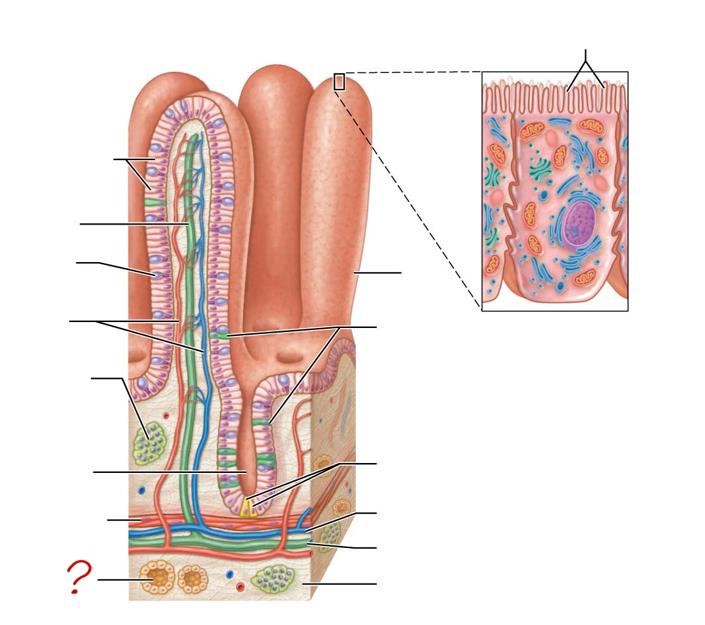
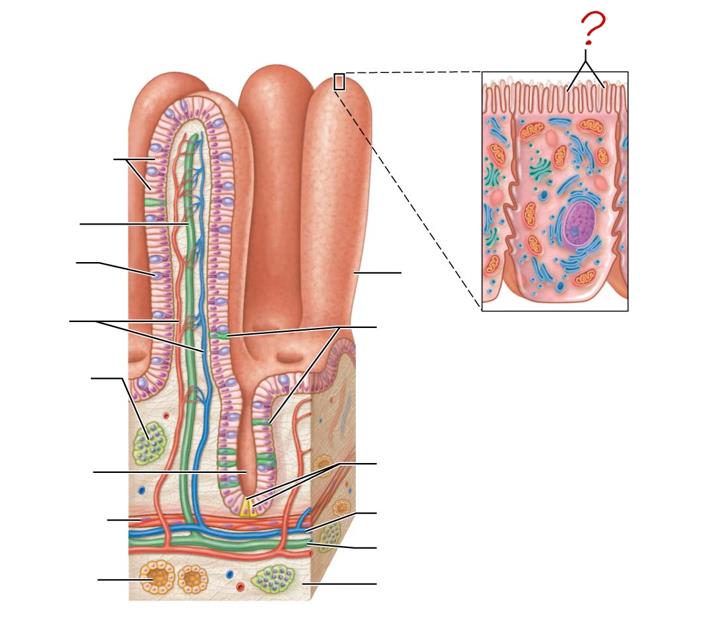
micovilli
brush border
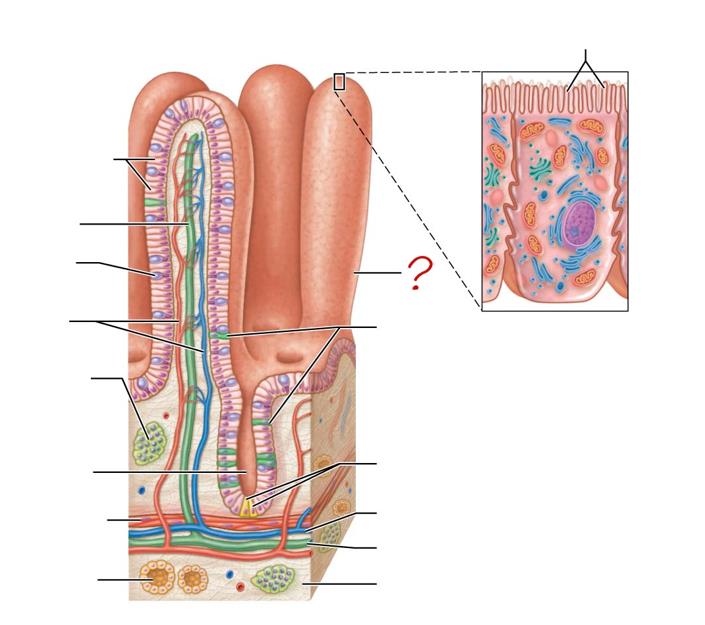
villus
enteroendocrine cells
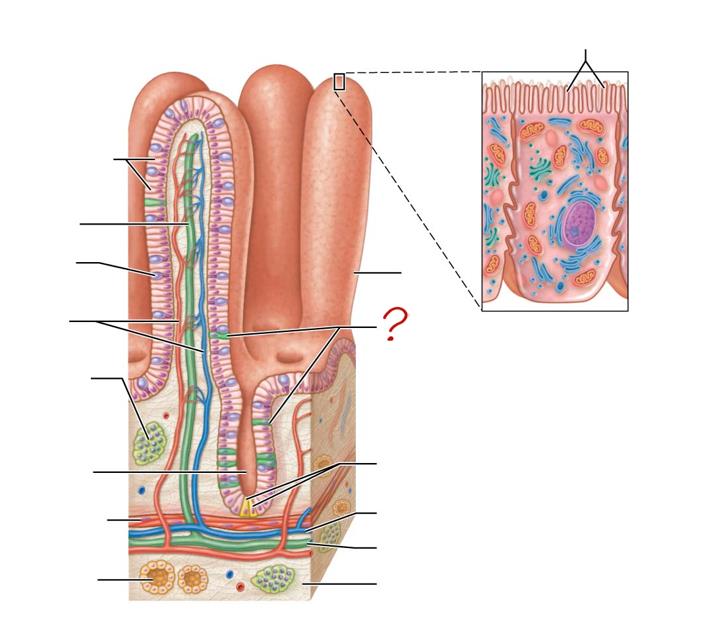
paneth cells
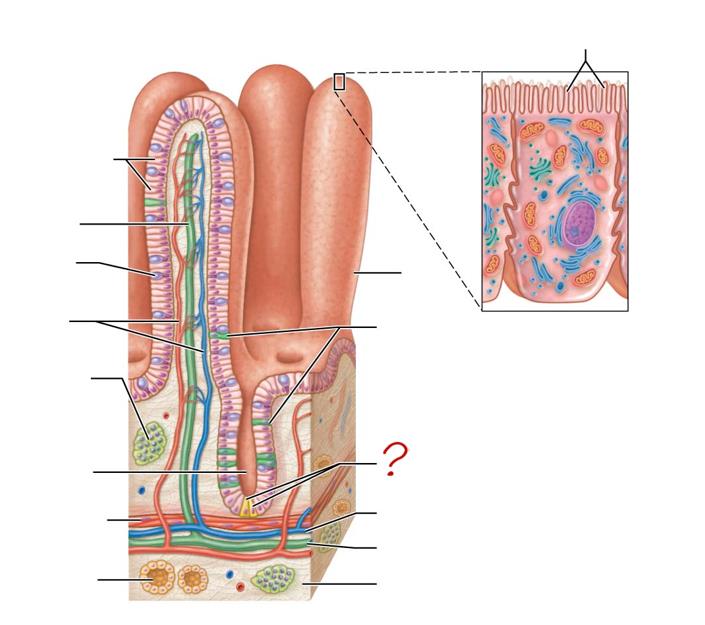
venule
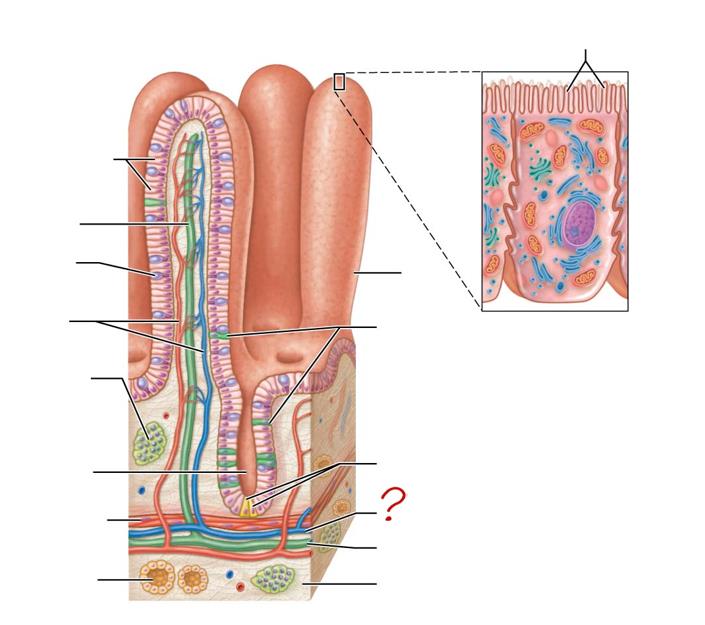
lymphatic vessels
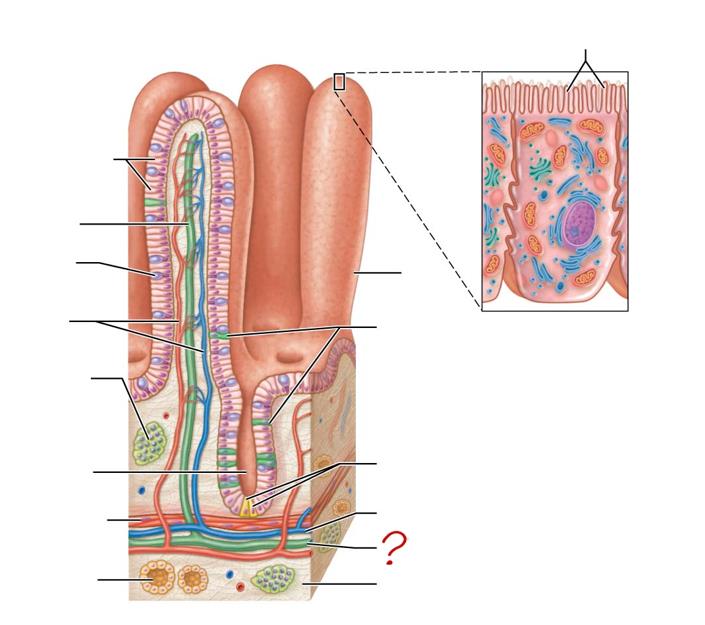
submucosa
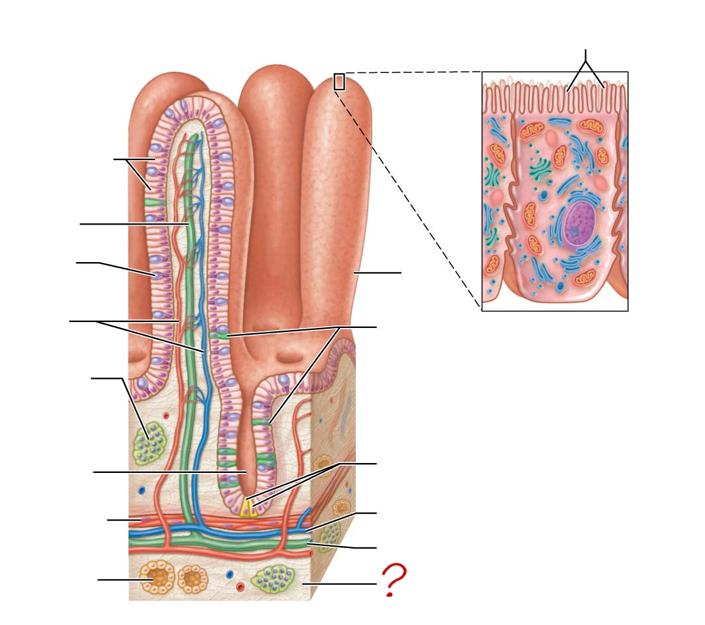
esophagus
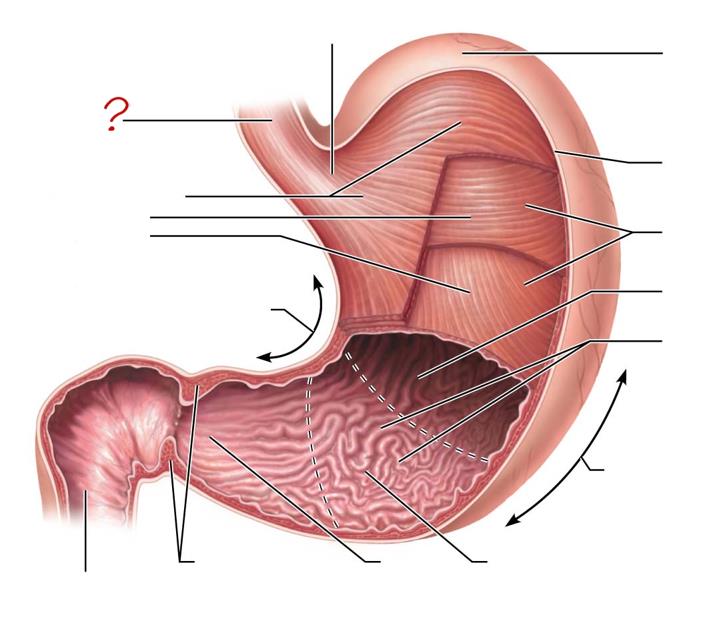
longitudinal layer
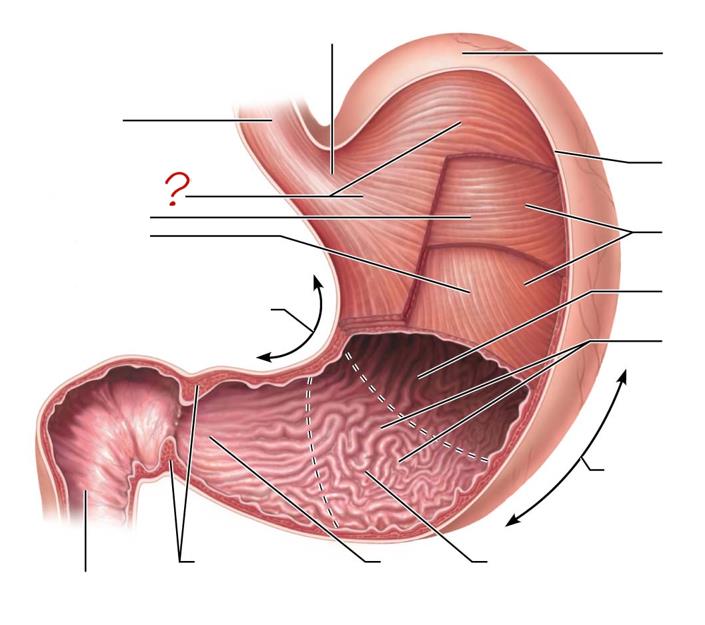
circular layer
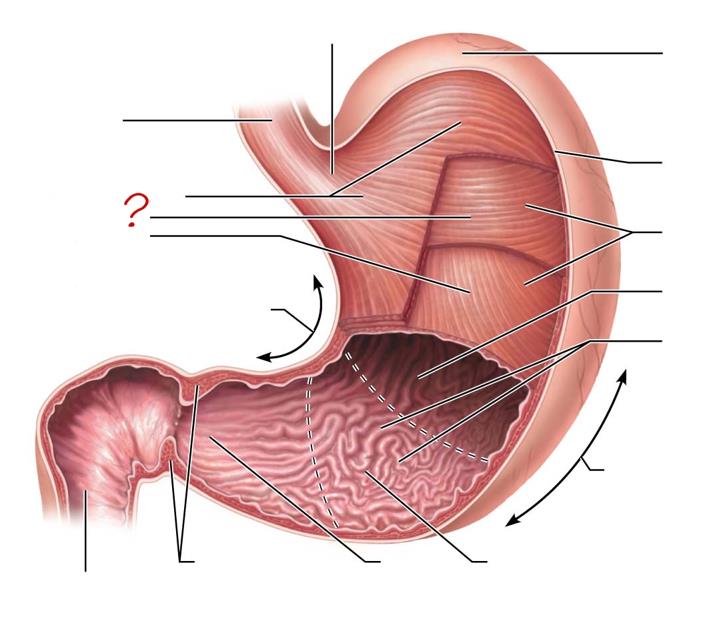
oblique layer
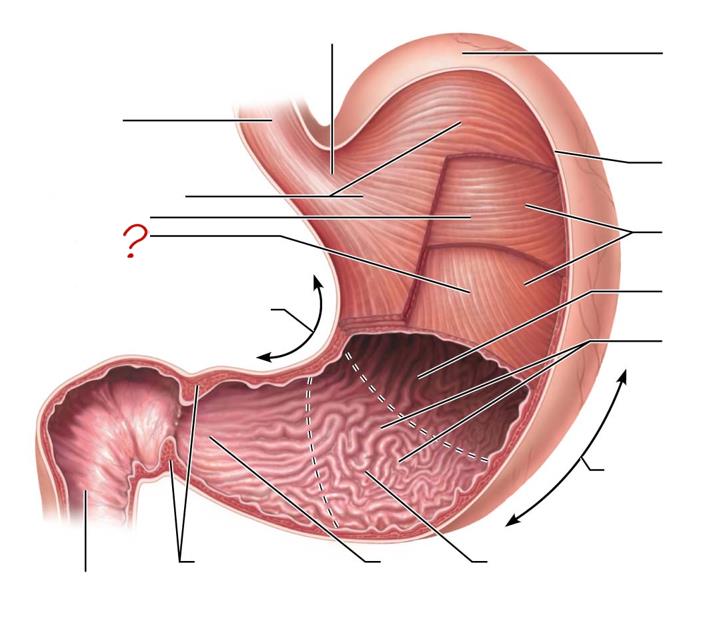
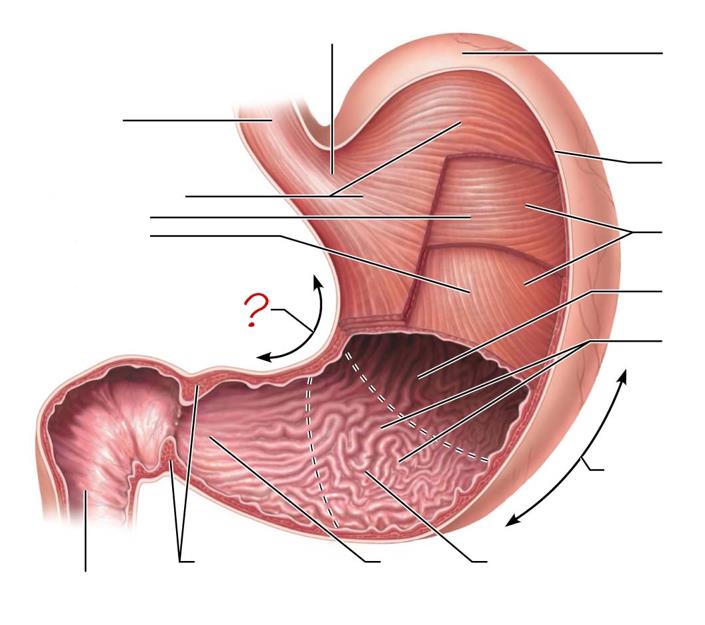
lesser curvature