Shoes + Modifications
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
A well designed shoe is the necessary foundation for many _________
many LE orthotics and for prosthetic alignment and an energy efficient gait
Components of a Good Shoe
minimizes stress on all portions of the feet
provides support, and acts as a shock absorber of ground reaction forces
your feet should not hurt every time you walk with your shoe
A well-designed shoe provides a:
a broad heel base, ankle collar, and close-fitting heel counter
Perfect Shoe - Harvards
Take a tracing of your foot with you. Place any shoe you think you might buy on top of the tracing. If the shoe is narrower or shorter than the tracing, don’t even try it on
Shop for shoes during the afternoon – your foot naturally expands with the use during the day
Wear the same type of socks to the store that you intend to wear with the shoes
Have a salesperson measure both of your feet – and get measured every time you buy new shoes. Feet change with age, often growing larger and wider. If one foot is larger than the other, buy a size that fits the larger foot
Stand in the shoes. Press gently on top of the shoe to make sure you have about a half-inch of space between your longest toe and the end of the shoe. This provides enough room for your foot to press forward as you walk. Wiggle your toes to make sure there’s enough room
Walk around in the shoes to determine how they feel. Is there enough room at the balls of the feet? Do the heels fit snugly, or do they pinch or slip off? Don’t rationalize that the shoes just need to be “broken in.” find the shoes that fit from the start
Trust your own comfort level rather than a shoe’s size or description. Sizes vary between manufacturers. And no matter how comfortable an advertisement claims those shoes are, you’re the real judge
Pay attention to width as well as length. If the ball of your foot feels compressed in a particular shoe, ask if it comes in a wider size. Buying shoes that are a half-size bigger – but not any wider – wont necessarily solve the problem
Feel the inside of the shoes to see if they have any tags, seams, or other material that might irritate your foot
Examine the soles. Are they sturdy enough to provide protection from sharp objects? Do they provide any cushioning? Take note of how they feel as you walk around the shoe store. Try to walk on hard surfaces as well as carpet to see how the shoe feels on both
Heel height can create stress on the?
forefoot during gait
Two primary determinants of proper shoe fit
shoe shape and size
Refers to the shape of the sole and the upper
Shoe shape
Proper shoe fit is achieved when the ___________
shoe shape is matched to foot shape
Shoe sieze is determined by _________, not by overall foot length
arch legnth
Shoe - Upper
The portion of the shoe over the dorsum of the foot
Vamp: anterior component
Quarter: the posterior component
In a laced shoe, the vamp contains the lace stays,
which have eyelets for shoelace
Blucher / Derby Shoe
lace stay is preferable; it is distinguished by the separation between the anterior margins of the lace stays and the vamp
The Blucher opening permits substantial adjustability, an important feature for the patient with edema
Oxford / Balmoral Shoe
lace stay is continuous with the vamp
Low Quarter vs High Quarter shoe
Low Quarter | High Quarter |
|
|
For individuals wearing orthoses and those with foot deformity, the _____ closure is preferable to the ____ closure
Blucher > Balmoral
Shoe - Sole
protects the plantar surface of the foot
heavy thick sole protects the foot against irregularities in the walking surface
The traditional sole consists of two pieces of leather sewn together with a layer of compressible cork in between
Shoe - Welt
inside piece of the external sole
Shoe - Insole
situated next to the foot
Shoe - outsole
portion that is most external
outer sole should not contact the floor at the distal end; slight rise of the sole is known as toe spring which allows a rocker effect at late stance
Shoe - Heel
The portion of the shoe adjacent to the outer sole
A broad, low heel provides greatest stability and distributes force between the back and front of the foot most evenly
A high heel places the ankle in greater plantarflexion range and forces the tibia forward
Compensation: either by retaining slight knee and hip flexion or by extending the knee and exaggerating lumbar lordosis
Wearing high heels accentuate your butt area making you look “sexier”
Purpose of Toe Box
in the vamp, protects the toes from stubbing and vertical trauma
Toe box - should be high enough to accommodate ________
hammer toe or similar deformity
Area that lies between the heel and the ball of the shoe
Shank
Shank - prevents _________
collapse of the material between the heel and the ball of the foot to provide extra support
sometimes made of steel
In most athletic shoes, the sole is _____ to provide maximal traction
sole
Rubber soles absorb shock, thereby, minimizing ________
heel impact forces
Found in the most posterior portion of the shoe all the way to the anterior portion of the heel
Counter
Purpose of Counter
stiffens the quarter and generally terminates in the anterior border of the heel
secure the shoe to the anatomic heel and provide stability to the posterior portion of the foot
Medial counter helps to support the ____________
support the medial arch of the shoe
Heel counter aids in controlling the ______
rearfoot
Shoes are contructed over a model of the foot, called a ______, which is styled from wood, plaster, or plastic
last
The LAST determines the _______ of the shoe
shape of the shoe
Types of Last
Conventional Last
Straight Last
Inflared Last
Outflared Last
Conventional Last
forefoot is directly slightly lateral to the midline
to accommodate the natural externally rotated position o
Straight Last
symmetric around the midline
Inflared last
directs the forefoot medially
counteract valgus position
Outflared last
directs the foot more laterally than a conventional last
counteracts a foot in varus position
is pain around the metatarsal heads that result from compression of the plantar digital nerve as it courses between the metatarsal heads
Metatarsalgia
Shoe prescription for metatarsalgia
Wide width to reduce pressure on the transverse metatarsal arch
Long fitting to eliminate plantarflexed MTP joints
Cushion soles to enhance shock absorption
A high toe box to allow forefoot flexion and extension
the configuration of the foot in which the second toe is either the same size as the great toe or slightly longer than the great toe
Morton Syndrome
Shoe Prescription for Morton Syndrome
Long medial counter for rearfoot support and stability
straight or flared last to accommodate foot shape
A high wide toe box to reduce compression across the transverse metatarsal arch
A large enough shoe size to accommodate the long second toe
A Thomas heel or wedge sole to support the medial longitudinal arch
A consequence of loss of the longitudinal arch in conditions such as pes planus or of undue stresses created in the forefoot with tightness of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles or an elevated longitudinal arch
Plantar Fasciitis
Shoe Prescription for Plantar fasciitis
Long medial heel counter to limit heel valgus and limits the stretching forces of the plantar fascia
A high heel to reduce tension on the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon and adequate length to minimize compression and promote supination from midstance to toe-off
Positions foot into plantarflexion
The types of shoe modifications that may be useful
include a posterior heel elevation to reduce tension
on the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon
pronation of the midfoot that results in a failure of the foot to supinate during midstance
Pes Planus
Shoe Prescription for Pes Planus
long medial heel counter, thomas heel (medial extension)
Firm wedge sole
Straight Last
Custom shoe for severe cases
Medial heel wedge → correct eversion and reduce pronation
Medial heel and sole flare in extreme cases
Orthosis Nomenclature
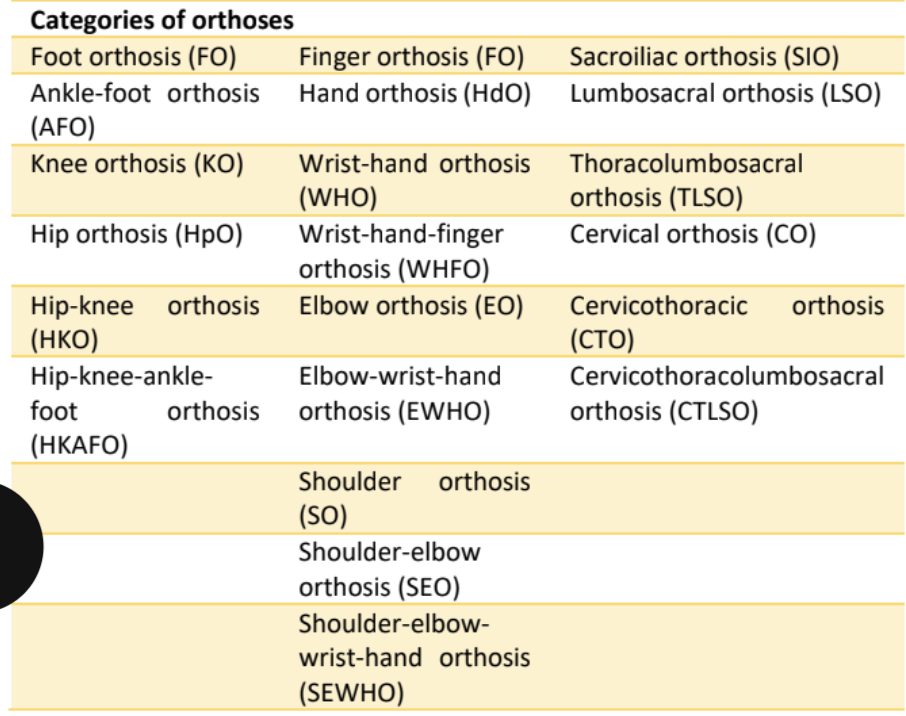
Clinical Objectives of Orthotic Treatment
relieve pain
manage deformities
prevent excessive ROM
increase range of joint motion
compensate for abnormalities of segment length or shape
manage abnormal neuromuscular function
protect tissues
promote healing
provide other effects
Functional Requirements of Orthoses
prevent, reduce, or stabilize a deformity
modify the range of motion of a joint
add to the length or alter the shape of a segment
compensate for weak muscle activity or control muscle hyperactivity
reduce or redistribute the load on tissues
Inserts are made of resilient materials to reduce ____________
reduce impact shock and shear → protecting painful or insensitive feet
General Disadvantage of Inserts
tends to reduce the shoe volume
Advantage of Inserts
does not alter the aesthetic appearance of the shoes
Full-length insert - tends to reduce ________ by improving proprioception from the increased foot contact area
reduce gait unsteadiness
Acts like a second skin if the patient has difficulty in positioning the feet in relation to its body position
Full-length insert
Full-Length insert - used to relieve pain and activity limitation in relation to patients who suffer from________
pes cavus
convex component that may be incorporated in an insert or may be a resilient domed piece glued to the inner sole so its apex is under the metatarsal shafts
Metatarsal pad
Metatarsal pad is effective in reducing __________
plantar pressure for patients who suffer from insensitivities
Longitudinal arch supports are intended to prevent _____________
depression of the subtalar joint and flattening of the arch
Longitudinal arch supports are helpful for patients suffering from ______
pes planus
allows minimum support that is positioned at the medial border of the insole with the apex between the sustentaculum tali and the navicular tuberosity
Scaphoid pad
aka navicular; in front of talus; primary keystone of medial longitudinal arch
Scaphoid
Scaphoid pad is given when?
there is presence of a decreased scaphoid bone to correct a flat medial longitudinal arch
weakness in the plantar muscles and other structures of the MLA
University of California Biomechanics Laboratory (UCBL) insert is for?
internal modification to address a midfoot issue (fracture, flat foot, posterior tibial malfunctino)
UCBL insert - used to realign a __________, immobilize ______, and correct ________
realign - flexible flat foot
immobilize - midfoot fracture
correct - posterior tibial malfunction
An external modification ensures _________
that the patient wears the appropriate shoes and does not reduce shoe volume
Heel wedge alters alignment of the ______
rearfoot
Medial heel wedge & Thomas Heel are intended for?
flexible pes valgus and correcting over-pronation
Medial heel wedge: attached to the medial part of the heel elevating the medial part of the foot to counteract _________
over-pronation and automatically position the forefoot to neutral
modification at the heel part where there are medial extensions; support a depressed scaphoid
Thomas Heel
Lateral wedge compensates for ________
fixed forefoot valgus allowing the entire distal foot to contact the floor
Lateral wedge counteracts a foot that is _______
Over-supinated
presence of an extension of the heel part on the lateral component, supporting the lateral longitudinal arch
Reverse Thomas Heel
Medial Heel wedge - To correct flexible:
pronation
eversion
pes valgus
pes planus
Medial heel wedge - to accomodate rigid:
supination
inversion
pes varus
pes cavus
Lateral heel wedge - to correct flexible:
supination
inversion
pes varus
pes cavus
Lateral heel wedge - to accomodate rigid:
pronation
eversion
pes valgus
pes planus
Cushion heel indication
indicated when the patient wears an orthosis with a rigid ankle
Shoe lift is commonly used for?
leg length discrepancies
raise one foot in order to shift balance
a flat strip of firm material placed posterior to the metatarsal heads
Metatarsal Bar - for pts with metatarsal pain
Metatarsal Bar - at late stance, the bar transfers stress from the ______ to the ________
metatarsophalangeal joints → metatarsal shafts
convex transverse band affixed to the sole proximal to the metatarsal heads; tends to create a smoother transition from heel strike to foot flat
Rocker Bar
Rocker Bar Indications
for patients with difficulties of transitioning from heel strike to initial contact, all the way to foot flat
pts with neurological / nerve impingement syndromes in LE
True/False: The rocker bar increases the distance the wearer must travel during stance phase, improving late stance, as well as shifting load from the metatarsophalangeal joints to the metatarsal shafts
False; Reduces the distance
Purpose of Ankle joint rocker
inhibits demand for motion in ankle joint
weak ankle proprioception / ankle pain
Met-head rocker - reduced ground-reactive forces to the ______
ball of the foot
Heel rocker - reduces ground-reactive forces to the _____
heel
Lisfranc rocker - reduces propulsive force to ______
midfoot
for pts with midfoot fracture / pes cavus / pes planus with difficulty transitioning
Healing rocker - holds foot in what position?
dorsiflexed to offload forefoot
pts with mild drop foot deformity