Smooth Muscle Cells: Structure, Function, and Regulation in Vascular Physiology
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
theme 1 CML
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
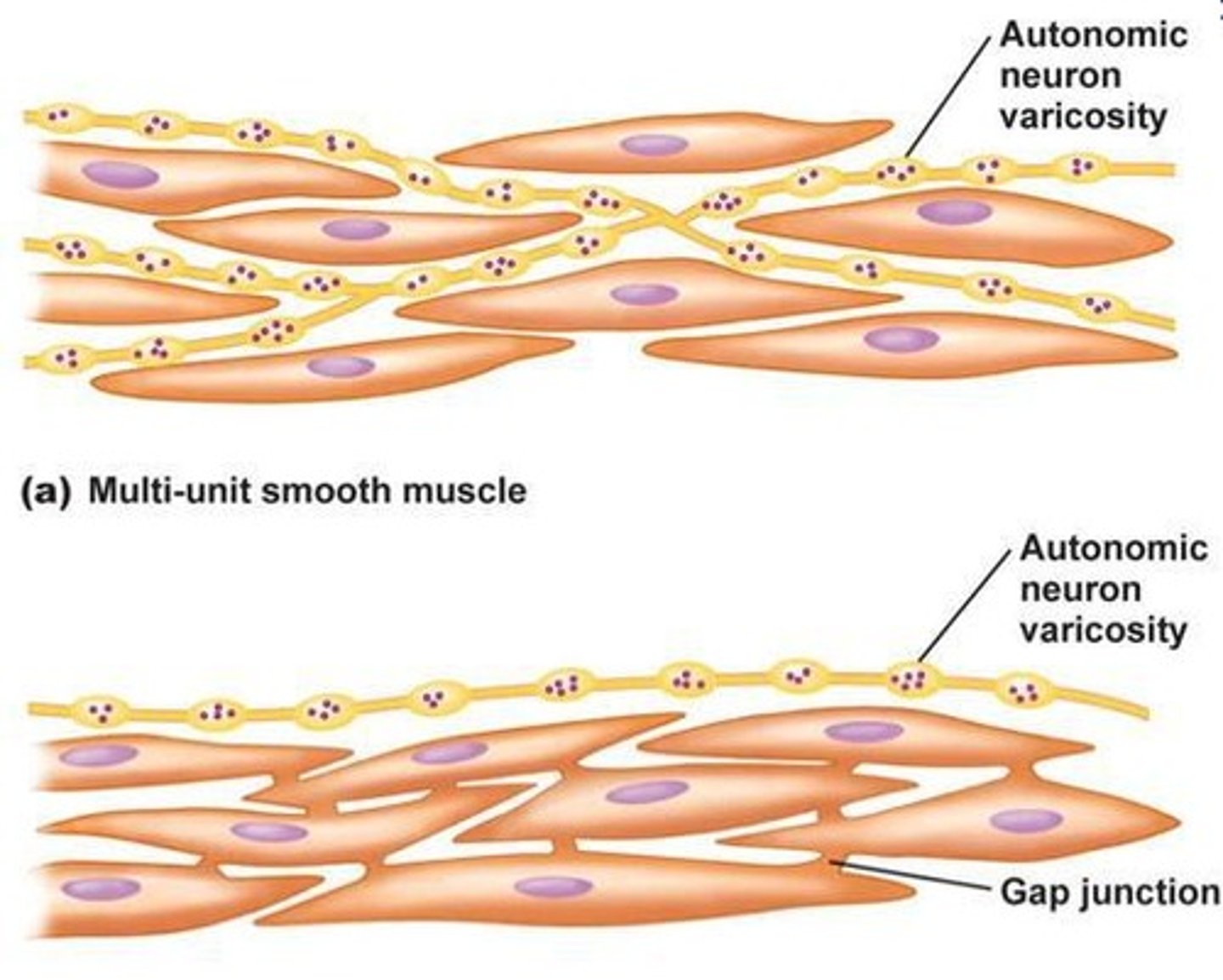
What are the two types of smooth muscle cells?
Multi-unit smooth muscles → autonomic neuron varicosity surrounding each CML (so independent)
each cell must receive a signal
noradrenaline from orthosympathetic nervous system
acetylcholine from parasympathetic system
unitary smooth muscles → gap junctions between CML so they are all connected
one activation activates all of them
What are the primary vasoconstrictors affecting smooth muscle cells?
Catecholamines, angiotensin II, ATP, endothelin, and TXA2.
What factors can lead to vasodilation in smooth muscle cells?
Tissue metabolism (adenosine) and neuronal nitric oxide (NO).
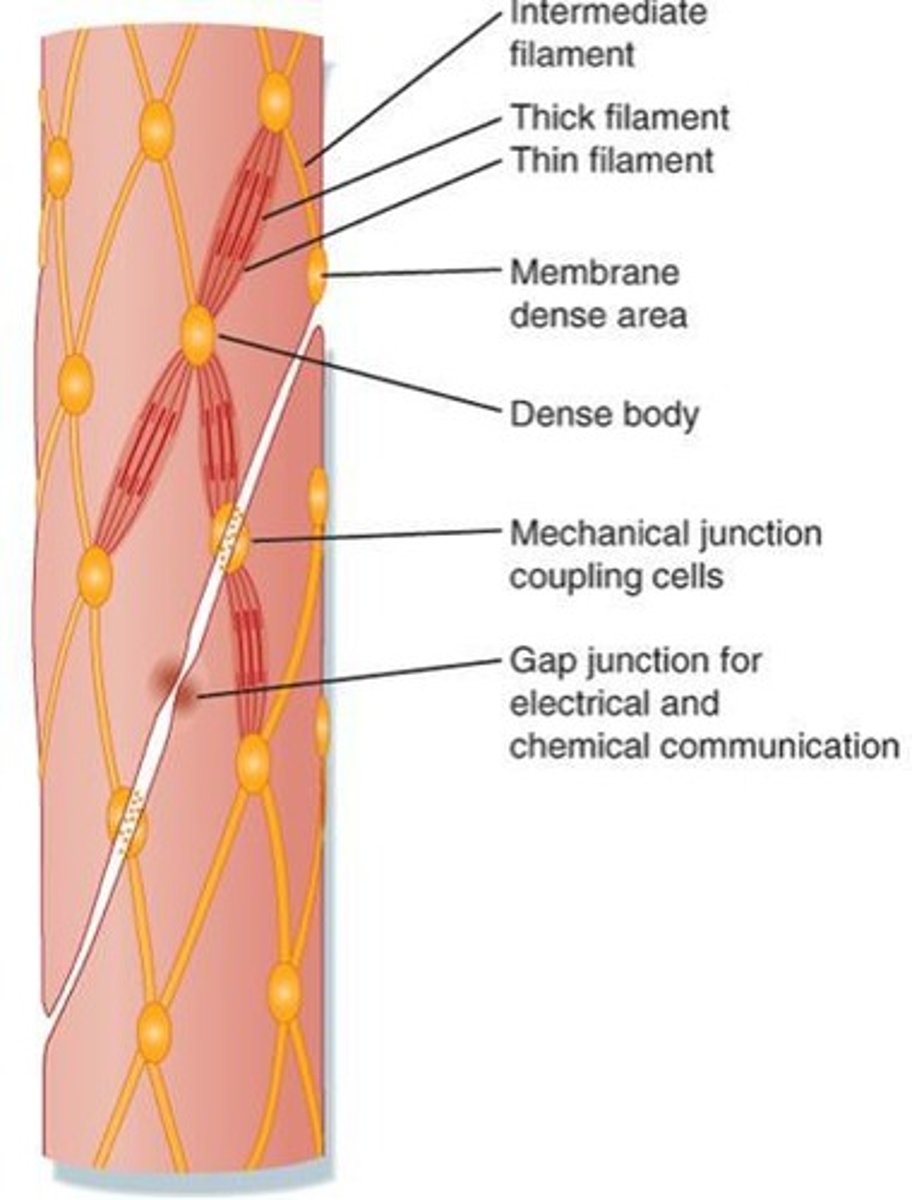
What is the role of dense bodies in smooth muscle cells?
Dense bodies anchor thin filaments in smooth muscle cells.
What are the two states of smooth muscle myosin molecules?
Inactive state (relaxation) and active state (contraction).
What is the significance of excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle?
It links the electrical activity of the muscle to its contraction.
What type of channels are involved in excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle?
Stretch-activated channels and calcium channels.
What is the threshold potential for action potentials in smooth muscle cells?
Approximately -50 mV.
What are the types of action potentials observed in smooth muscle cells?
Slow depolarization waves and spike potentials.
What role do potassium channels play in smooth muscle cells?
They help maintain resting potential and regulate action potentials.
What is calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in smooth muscle cells?
A mechanism where calcium influx triggers further calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the function of IP3 in smooth muscle cells?
It induces calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What are store-operated channels (SOC) in smooth muscle cells?
Channels that open in response to depletion of calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum.
What are the characteristics of purinergic ionotropic receptors?
They are sensitive to agonists and play a role in smooth muscle contraction.
What is the role of mechanoreceptors in smooth muscle cells?
They respond to mechanical stress and activate signaling pathways.
What is the significance of the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel family in smooth muscle?
They are involved in various calcium signaling pathways and responses to mechanical stress.
What is the role of integrin complexes in smooth muscle cells?
They are involved in anchoring contractile units and facilitating communication between the cell and extracellular matrix.
What is the structural organization of contractile units in smooth muscle cells?
They consist of cytoskeletal actin, contractile actin, myosin, and dense bodies.
What is the function of calcium channels in arterial smooth muscle cells?
They facilitate calcium influx, which is crucial for muscle contraction.
What are the two types of smooth muscle activity patterns?
Tonic smooth muscles (sustained contraction) and phasic smooth muscles (rhythmic contraction).
What is the role of nitric oxide (NO) in smooth muscle function?
It acts as a vasodilator, relaxing smooth muscle cells.
How do action potentials in smooth muscle cells differ from those in skeletal muscle?
They are typically slower and can involve various types of ionic channels.
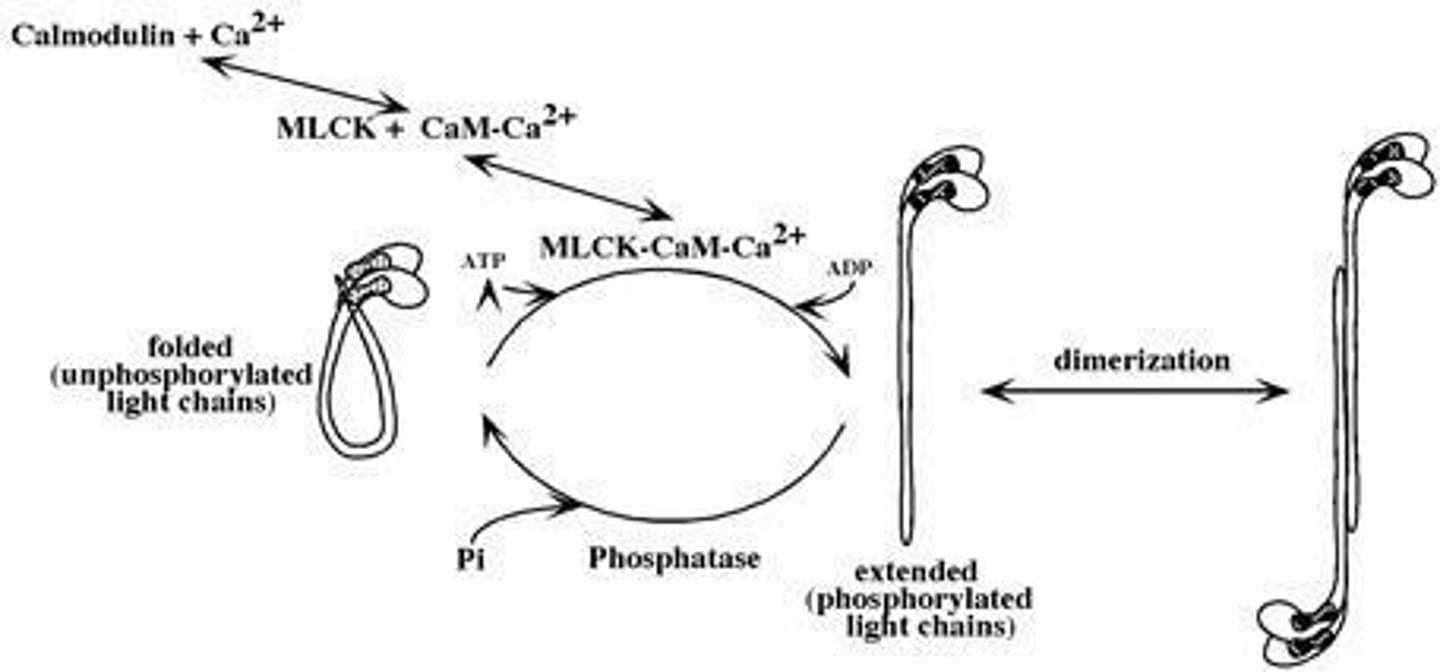
What is the significance of the myosin light chains (MLC) in smooth muscle contraction?
They are phosphorylated to activate myosin ATPase, leading to contraction.
What is excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle?
The process by which an electrical signal (excitation) leads to muscle contraction through calcium signaling.
What are ionotropic receptors?
Receptors that mediate fast synaptic transmission by allowing ions to flow through their channels.
What role do stretch-activated channels play in smooth muscle?
They open in response to mechanical deformation, contributing to calcium influx and muscle contraction.
What is calcium-induced calcium release (CICR)?
A mechanism where calcium entry into the cell triggers further release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is pharmacomechanical coupling?
A process where chemical signals (like hormones) induce muscle contraction through calcium signaling without direct electrical stimulation.
What is L'IP3-induced calcium release?
A pathway where inositol trisphosphate (IP3) stimulates the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is capacitative calcium entry?
A process by which calcium enters the cell after depletion of calcium stores in the endoplasmic reticulum.
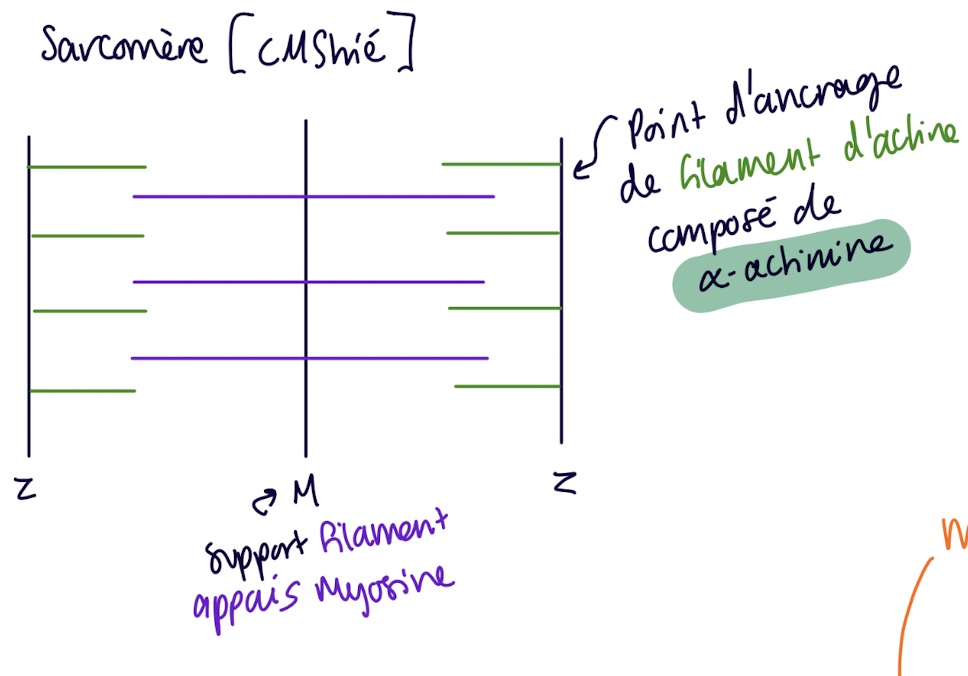
what does a sarcomere look like
z = point d’ancrage de filament d’actine
M = support filament eppais mysosine
What is the role of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) in smooth muscle contraction?
MLCK phosphorylates myosin light chains, enabling interaction with actin and resulting in contraction.
What does myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) do?
MLCP dephosphorylates myosin light chains, leading to muscle relaxation.
What is the smooth muscle contraction-relaxation cycle?
The alternating process of contraction and relaxation in smooth muscle, regulated by calcium levels and MLCK/MLCP activity.
What is the significance of RhoA/Rho-kinase in smooth muscle?
RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway enhances MLCK activity, promoting contraction and influencing vascular tone.
What are the effects of nitric oxide (NO) on smooth muscle?
NO induces vasodilation by increasing cGMP levels, which activates MLCP and promotes relaxation.
What is the role of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) in smooth muscle?
ANP promotes vasodilation through cGMP signaling, leading to relaxation of smooth muscle cells.
How do vasoconstrictor agonists affect smooth muscle?
They activate pathways that increase intracellular calcium and promote contraction, such as through alpha-adrenergic receptors.
What is the role of sympathetic nervous regulation in blood vessels?
Sympathetic activation typically leads to vasoconstriction through norepinephrine acting on alpha-adrenergic receptors.
What is the primary effect of parasympathetic nervous regulation on blood vessels?
It induces vasodilation primarily through NO release from endothelial cells.
What is the function of calcium pumps like SERCAs and PMCAs in smooth muscle?
They help remove calcium from the cytoplasm, contributing to muscle relaxation.
What is the significance of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) in smooth muscle metabolism?
The PPP provides NADPH for biosynthetic reactions and helps maintain redox balance in smooth muscle cells.
What is the role of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) in smooth muscle contraction?
GEFs activate RhoA, promoting contraction through the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway.
What is the effect of beta-adrenergic receptors on smooth muscle?
Activation of beta-adrenergic receptors leads to vasodilation via increased cAMP levels.
What are the main vasodilators acting on smooth muscle?
Acetylcholine, bradykinin, histamine, and nitric oxide are key vasodilators that increase intracellular cAMP or cGMP.
What is the role of phospholipase C (PLC) in smooth muscle contraction?
PLC generates inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), leading to calcium release and contraction.
What is the function of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers in smooth muscle cells?
They help regulate intracellular calcium levels by exchanging sodium ions for calcium ions across the membrane.
What is the role of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in smooth muscle relaxation?
cGMP activates protein kinase G (PKG), which promotes MLCP activity and leads to relaxation.
What is the effect of adrenomedulin on smooth muscle?
Adrenomedulin acts as a vasodilator, increasing cAMP levels and promoting relaxation.
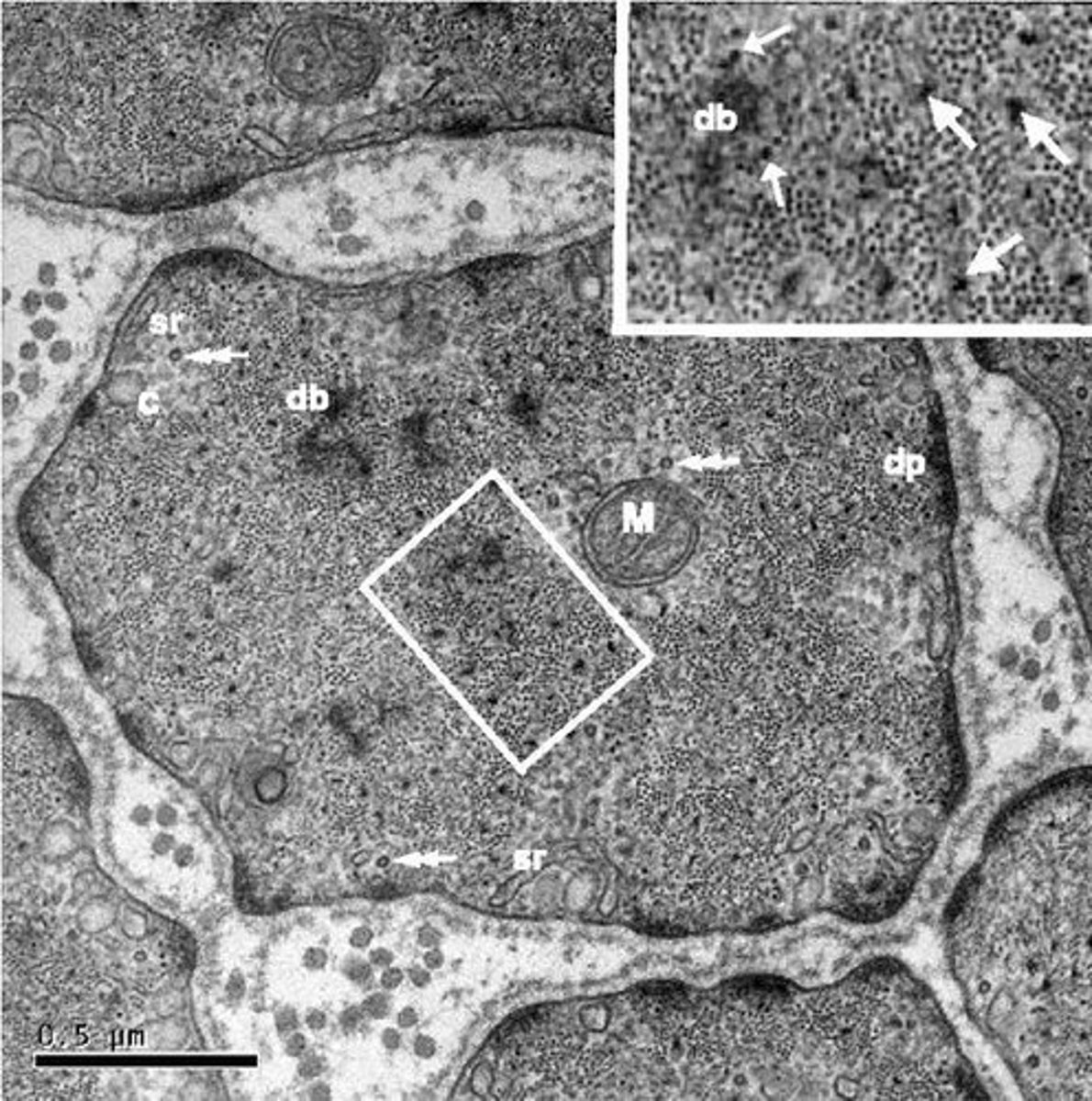
what is observed in a CML under micrscopy
mitochondria
Dense body db → corps dense aux e- → zone d’ancrage des filaments fins active
dense plate dp → plaque dense aux e-
sarcoplasmique reticulum
caveaola
microtubules