Exam #2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
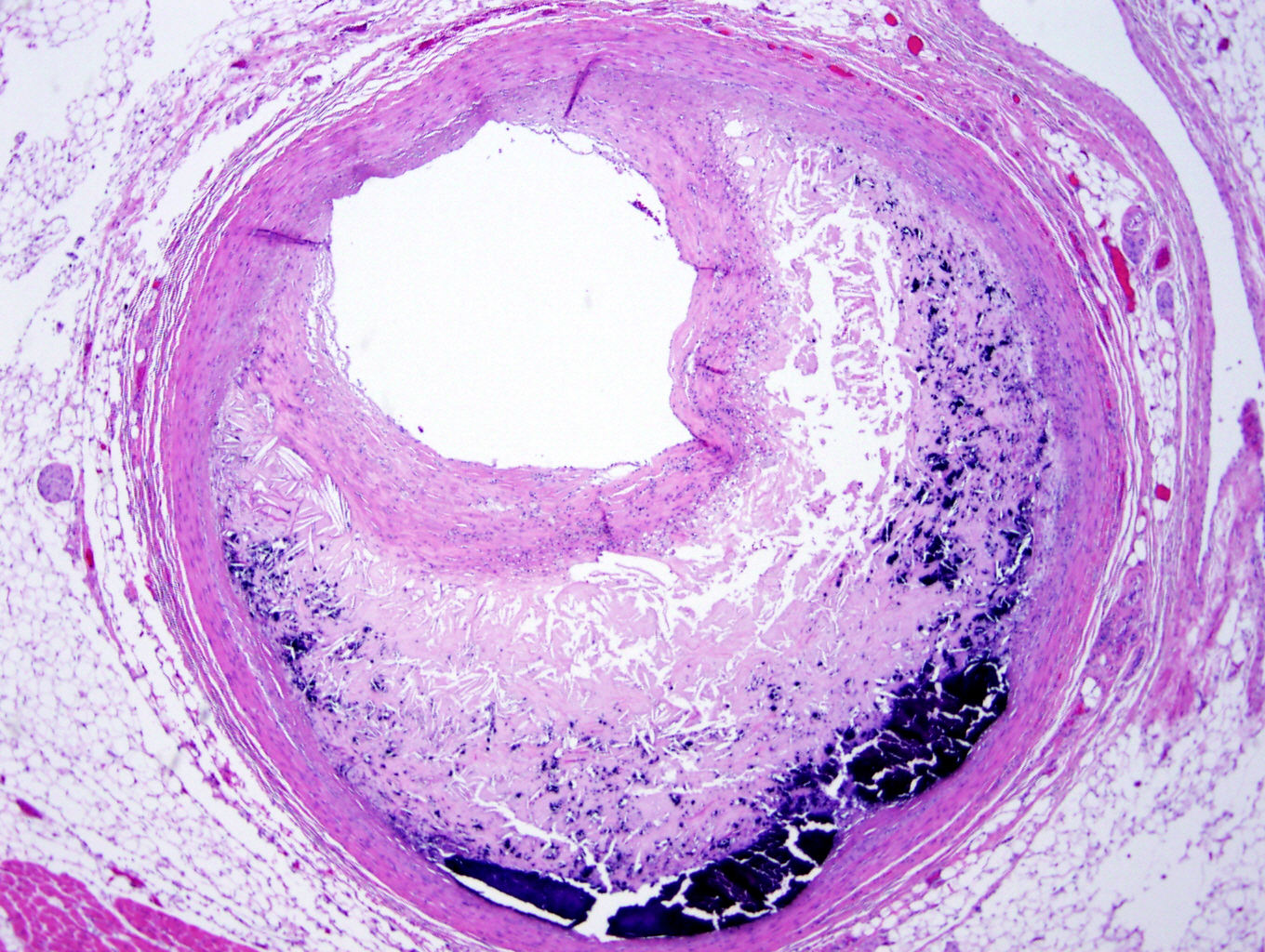
What histological slide is this for?
Atherosclerosis
What are the three tunics?
Tunica Externa
Tunica Media
Tunica Intima
What are the 2 major structures found in the fetal cardiac circulation (before birth)?
The Foramen Ovale
The Ductus Arteriosus
What is the function of the foramen ovale?
It allows blood to cross the atria and bypass pulmonary circulation during fetal development.
What is the function of the ductus arteriosus?
It allows the oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the lungs in utero.
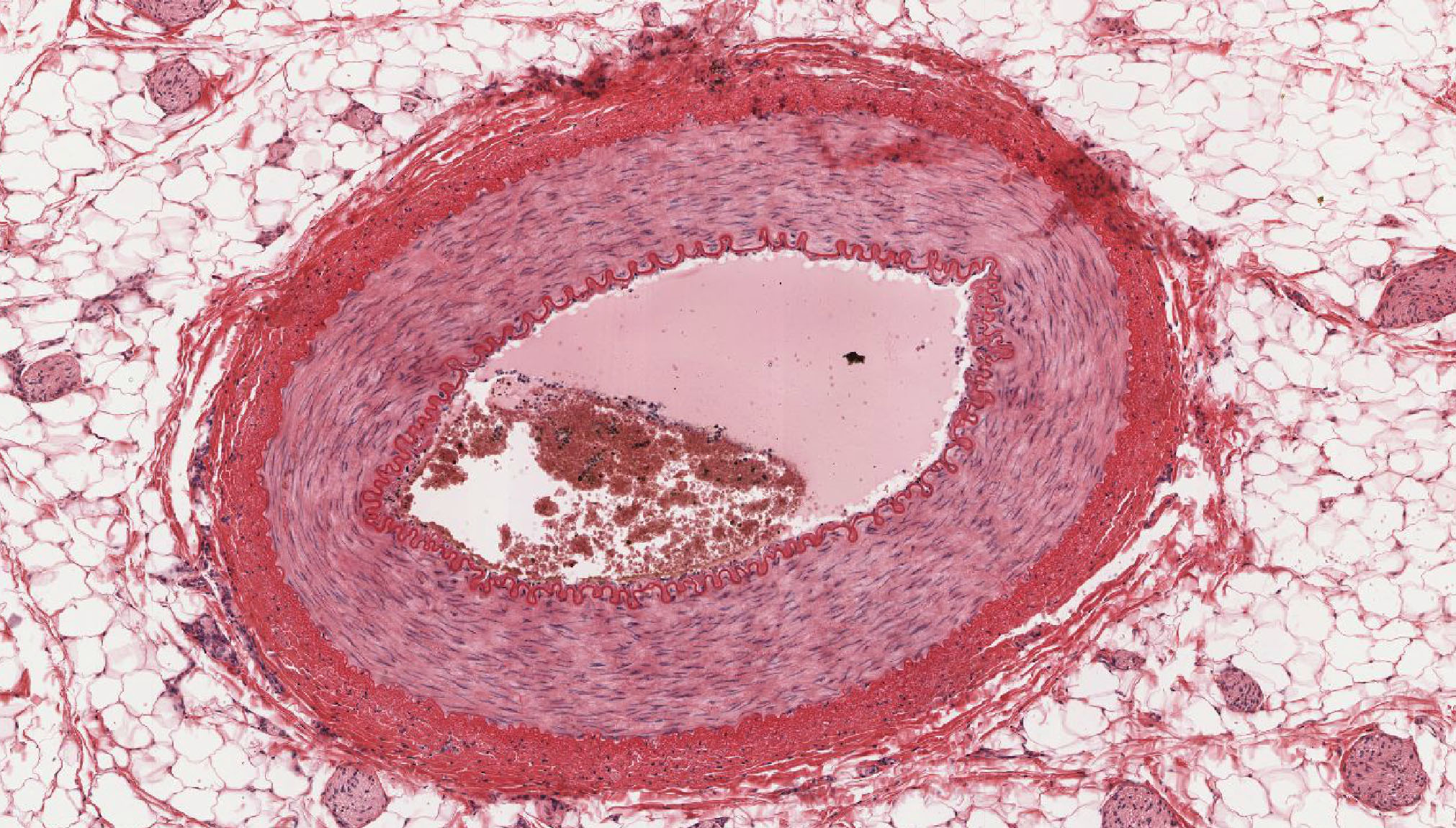
What histological slide is this for?
Artery
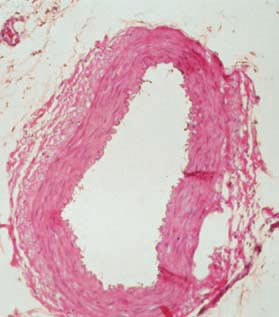
What histological slide is this for?
Vein
Why do doctors use ECG?
It is a quick test to check the heartbeat; it can help diagnose heart attacks and irregular heartbeats, called arrhythmias.
What is an ECG?
A test that measures the electrical activity of the heart.
What is the definition of auscultation?
A method of listening to the internal sounds of the body, typically using a stethoscope, to assess the condition of the heart, lungs, and other organs.
What does P of an EKG (ECG) mean?
In cardiology, the P wave on an electrocardiogram(ECG) represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole.
What does QRS complex of an EKG (ECG) mean?
The QRS complex represents the depolarization of ventricles. It shows the beginning of systole and ventricular contraction.
What does T of an EKG (ECG) mean?
The T wave on an ECG (electrocardiogram) represents the repolarization of the ventricles in the heart.
What is occurring to the heart when one hears the “lub-dub” sounds during auscultation of the heart?
The "lub-dub" sounds heard during heart auscultation are primarily caused by the closure of the heart valves during the cardiac cycle.
What is the average blood pressure?
120/80 mmHg
What is a heart murmur?
Heart murmurs are sounds — such as whooshing or swishing — made by rapid, choppy (turbulent) blood flow through the heart. The sounds can be heard with a device called a stethoscope.
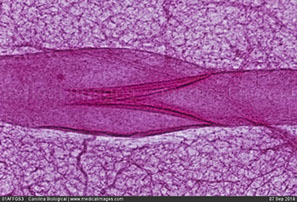
What histology slide is this for?
Lymphatic Valve
What type of cells are found in the red pulp of the spleen?
Unlike white pulp, which mainly contains lymphocytes such as T cells, red pulp is made up of several different types of blood cells, including platelets, granulocytes, red blood cells, and plasma.
What type of cells are found in the white pulp of the spleen?
It contains antigen-presenting cells(APCs), such as dendritic cells and macrophages. Some of the white pulp's macrophages are of a specialized kind known as metallophilic macrophages.
What is the function of the lymph nodes?
The lymph nodes filter out harmful substances and waste products.
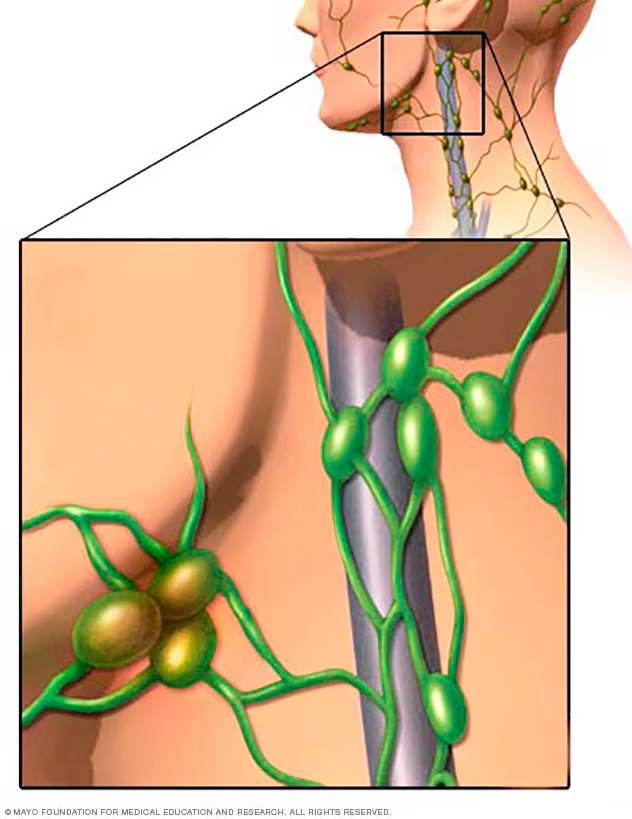
What are these?
Lymph nodes
Where are tonsils located?
Tonsils are fleshy pads located at each side of the back of the throat.
What is the function of tonsils?
Because of their location at the throat and palate, they can stop germs entering the body through the mouth or the nose. The tonsils also contain a lot of white blood cells, which are responsible for killing germs.
What is the function of the right lymphatic duct?
The right lymphatic duct is a main lymphatic vessel that forms part of the one-way route of the lymphatic system, carrying lymph from the periphery of tissues into the venous blood at the junction of the right jugulo-subclavian confluence.
What is the function of the left lymphatic duct?
The thoracic duct carries chyle, a liquid containing both lymph and emulsified fats, rather than pure lymph. It also collects most of the lymph in the body other than from the right thorax, arm, head, and neck (which are drained by the right lymphatic duct).
Which blood vessels do the two ducts drain in?
Two main ducts in your upper chest empty lymph into your subclavian veins. These are your right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct. These ducts are like highway on-ramps or merging points where lymph rejoins your bloodstream.
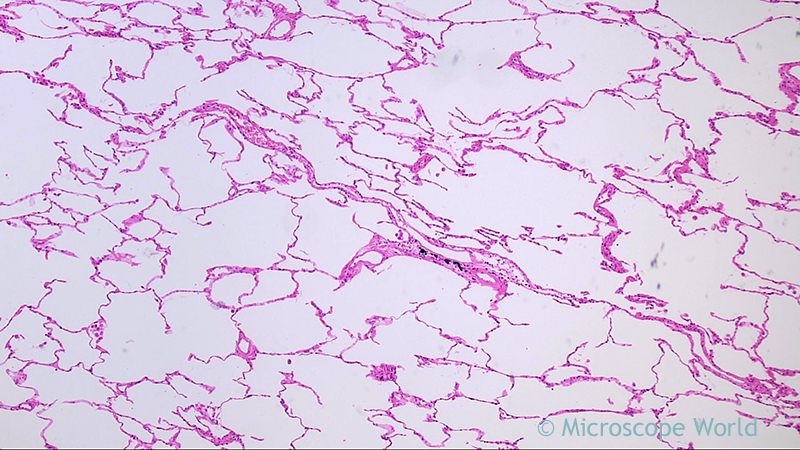
What histology slide is this for?
Lung tissue
What physiological conditions occur during asthma?
In asthma, the dominant physiological event leading to clinical symptoms is airway narrowing and a subsequent interference with airflow.
What are the accessory organs of the digestive system?
The accessory organs include the teeth, tongue, and glandular organs such as salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What is the approximate length of the small intestine?
Although the small intestine is narrower than the large intestine, it is actually the longest section of your digestive tube, measuring about 22 feet (or seven meters) on average, or three-and-a-half times the length of your body.
What are the the divisions within the large intestine?
The large intestine includes the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum.
What characterize acid reflux?
The main symptom of GERD is heartburn, often described as a fiery feeling in one's chest, and regurgitating sour or bitter liquid to the throat or mouth.
What is the function of the spleen?
It fights invading germs in the blood (the spleen contains infection-fighting white blood cells) it controls the level of blood cells (white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets) it filters the blood and removes any old or damaged red blood cells.
What is the function of the esophagus?
The primary function of the esophagus is to transport food entering the mouth through the throat and into the stomach.
What is the function of the stomach?
The primary functions of the stomach include the temporary storage and partial chemical and mechanical digestion of food.
What is the function of the small intestine?
The small intestine's principal function is to break down food, absorb nutrients the body needs, and excrete unnecessary components.