Brent – Lower Limb & Movement Analysis Flashcards
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This flashcard set breaks down Brent’s functional movements during squatting and caregiving tasks, focusing on joint actions, involved muscles (with origin and insertion), phases of movement, and stabilising structures. It also includes motor control system concepts (sensory input, integration, and motor output) to link anatomy and physiology with coordinated functional movement. Each card isolates key details — from specific muscle functions to joint capsule structures — to help you memorise and apply knowledge for practical exams or assessments.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
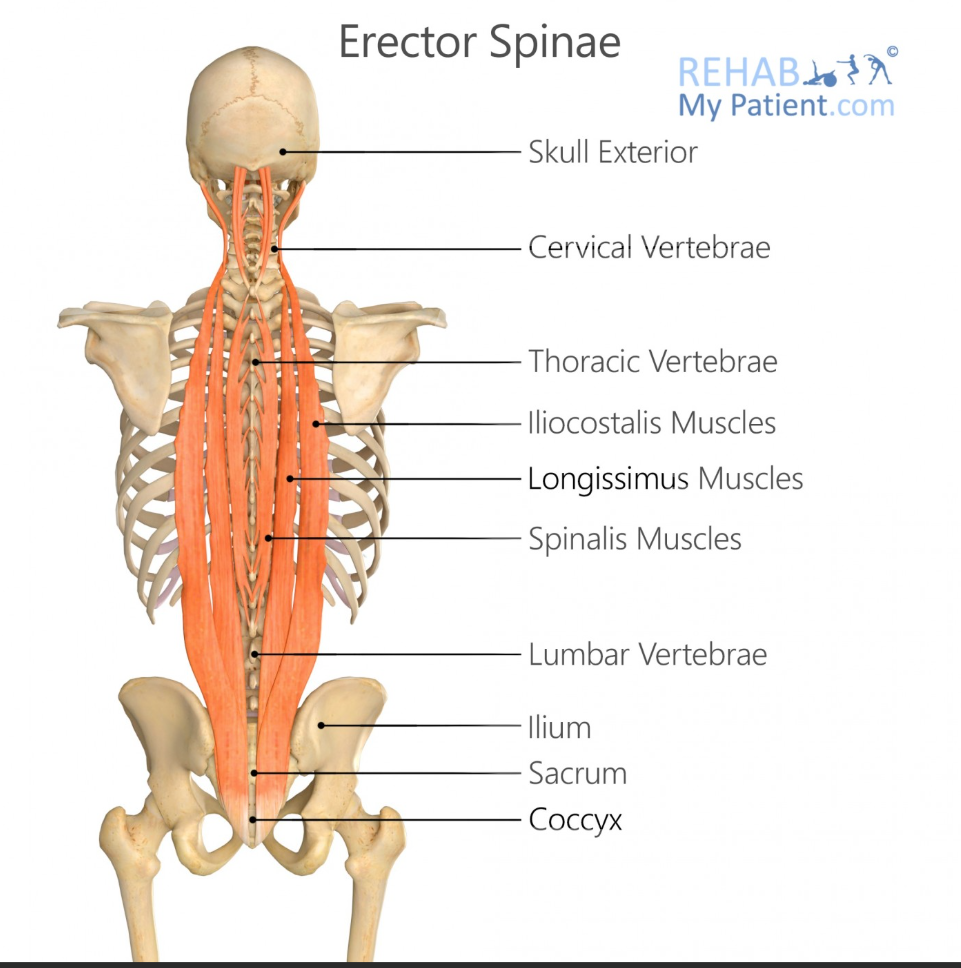
Erector Spinae
what is the name of the group of muscles that have ‘Iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis’ in them
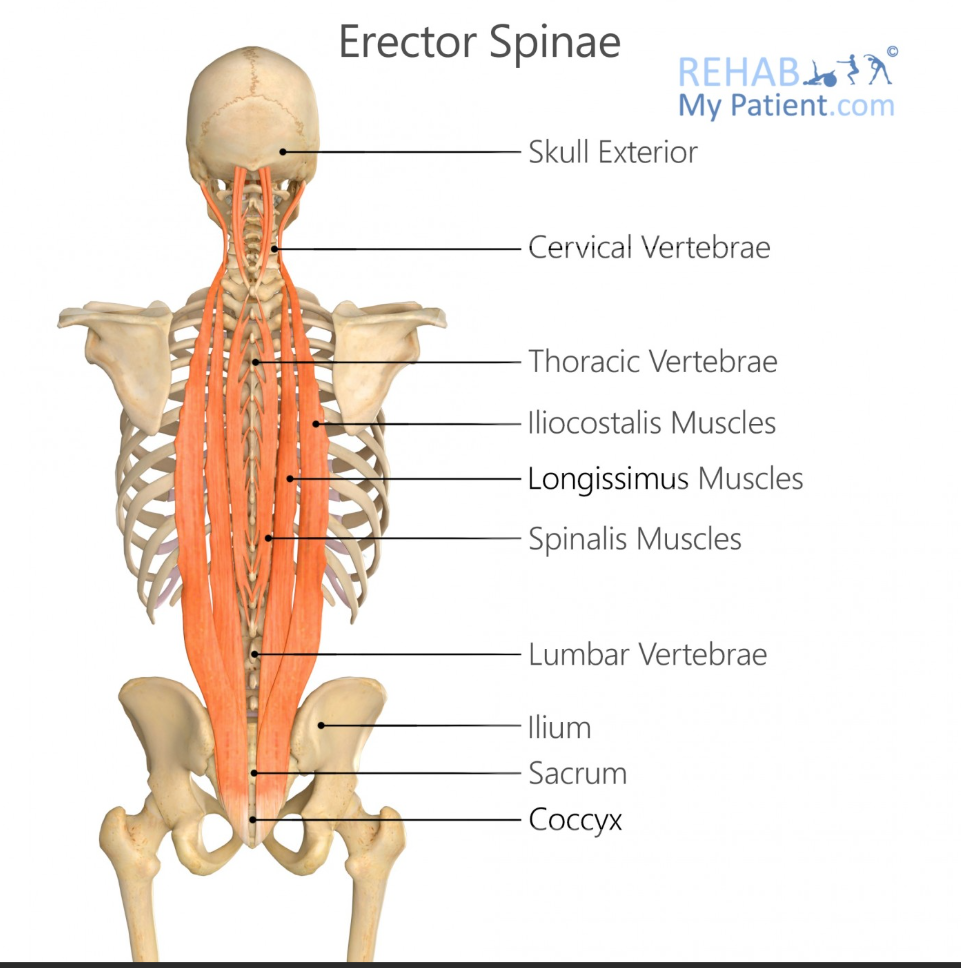
Iliocostalis Origin
Sacrum, iliac crest, lumbar vertebrae
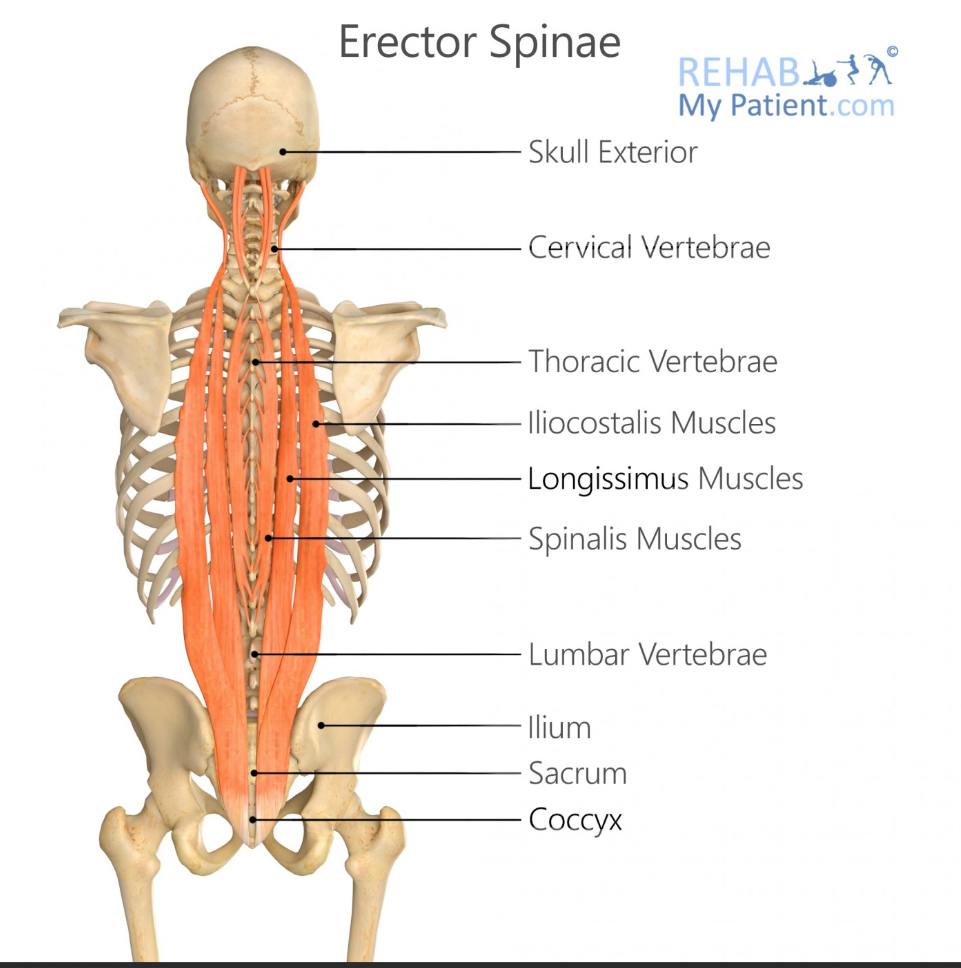
Iliocostalis Insertion
Ribs and cervical vertebrae
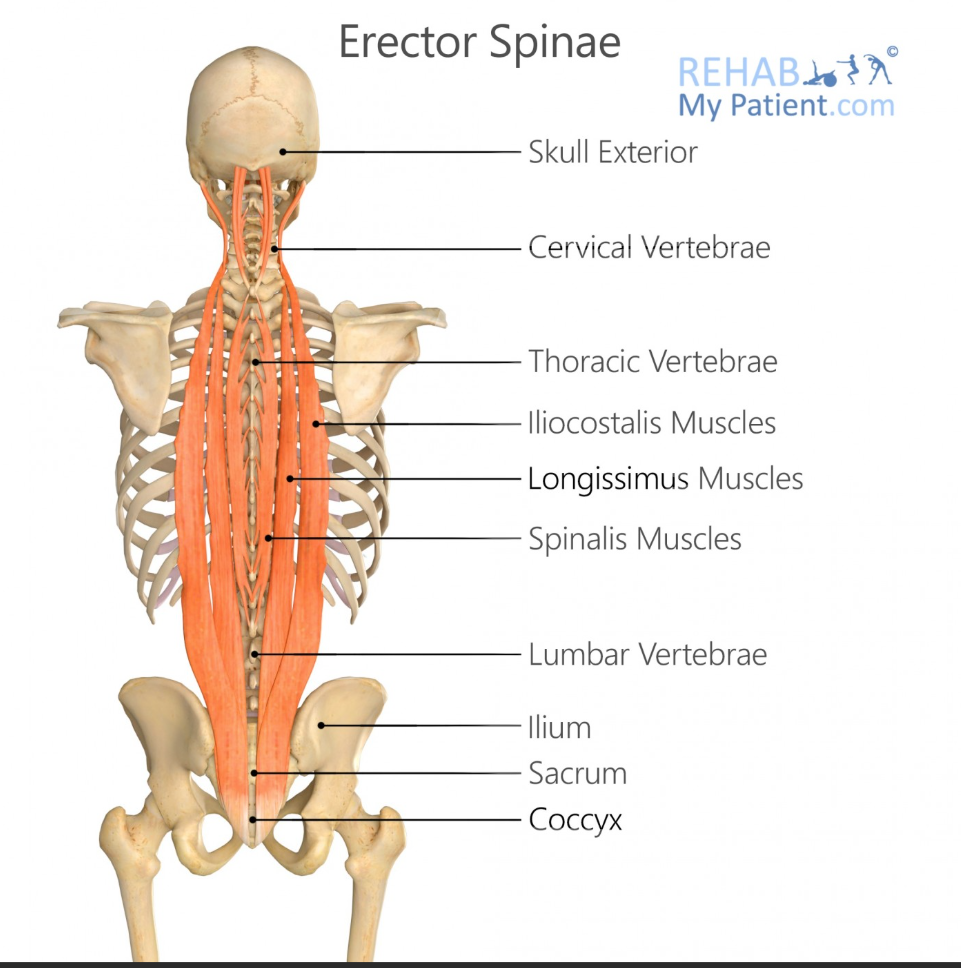
Longissimus Origin
Sacrum, lumbar vertebrae, thoracic transverse processes
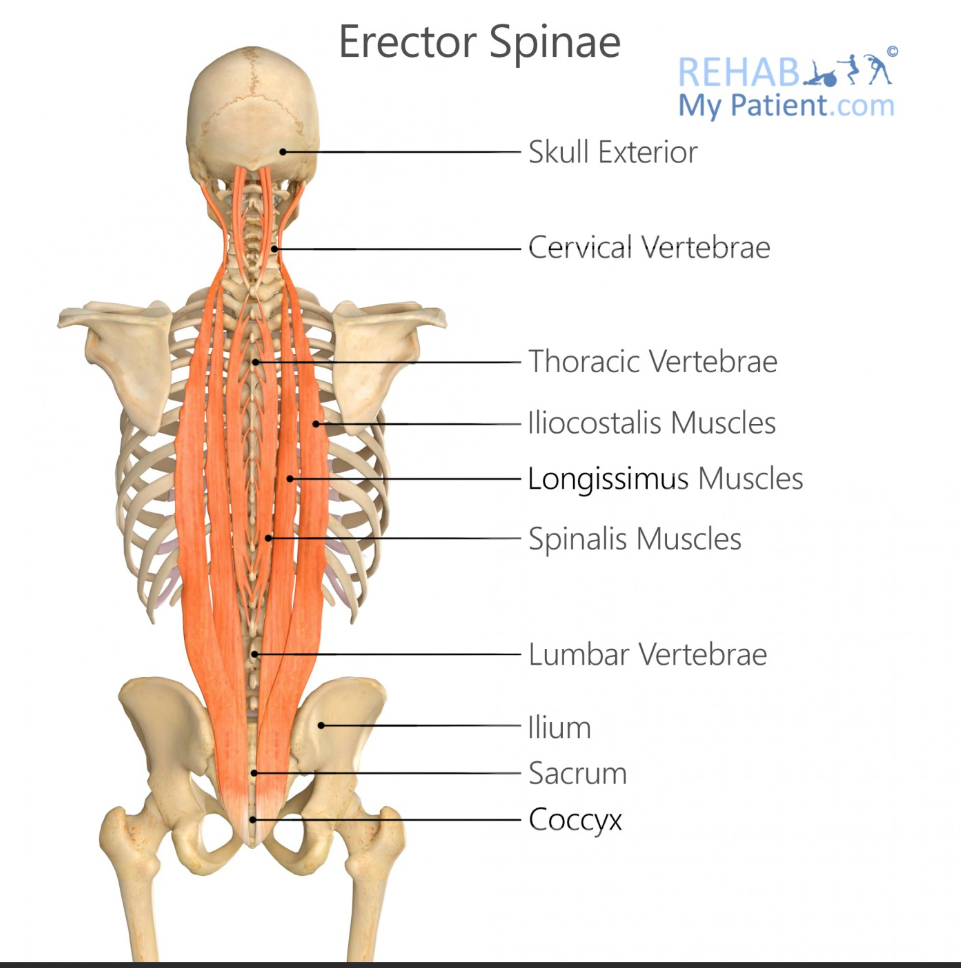
Longissimus Insertion
Thoracic and cervical transverse processes, mastoid process
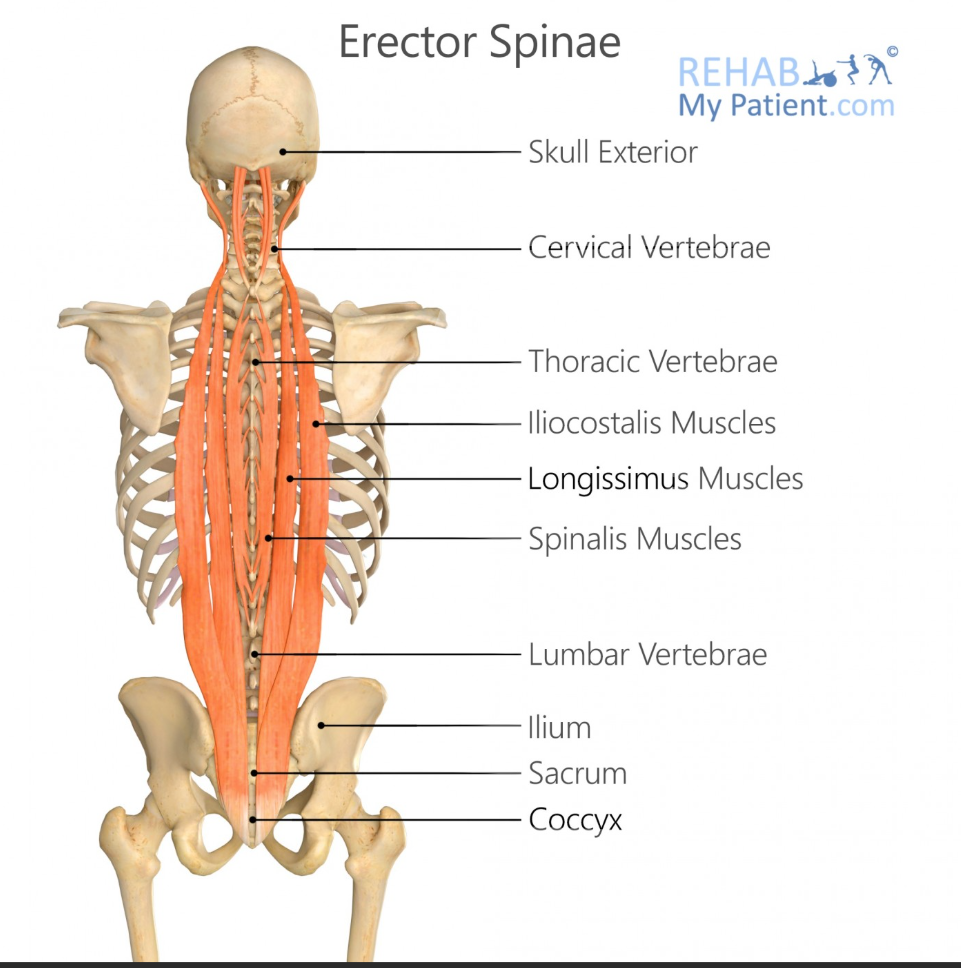
Spinalis Origin
Lumbar and thoracic spinous processes
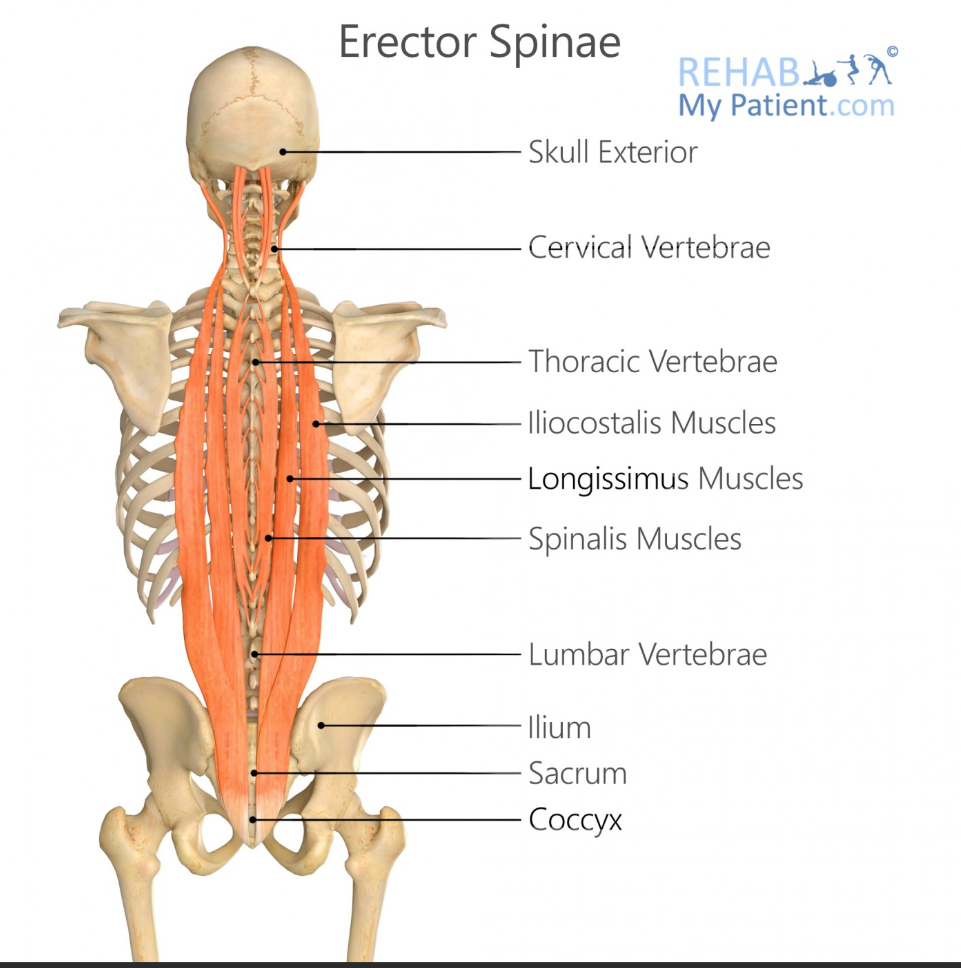
Spinalis Insertion
Thoracic and cervical spinous processes
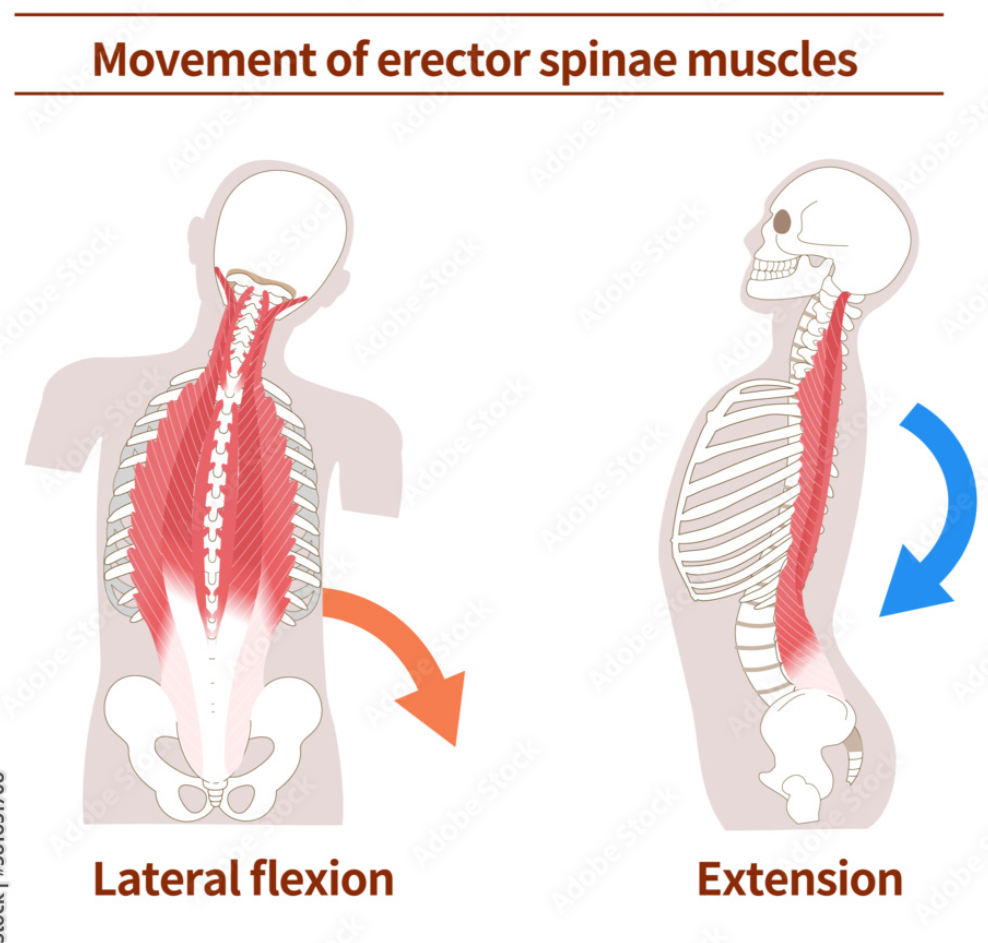
Main Action of Erector Spinae
Trunk extension and lateral flexion
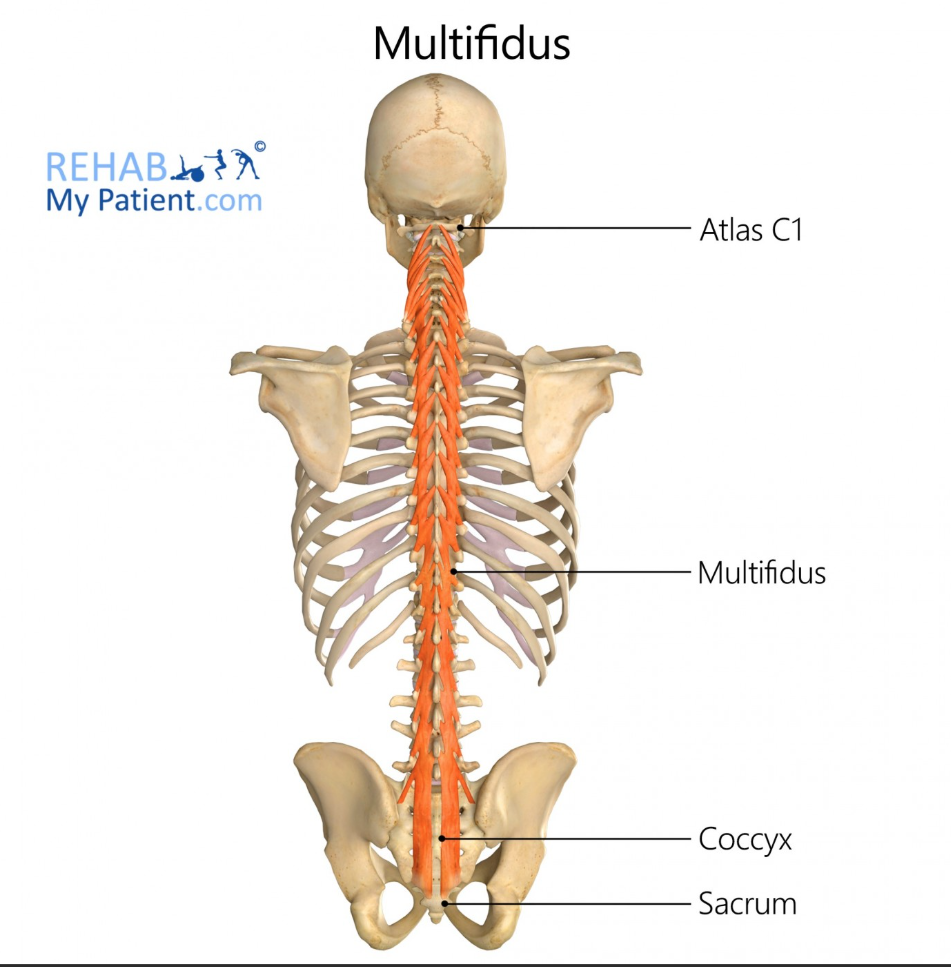
Multifidus Function
Segmental stabilization of the spine
Multifidus Origin
Sacrum and transverse processes of vertebrae
Multifidus Insertion
Spinous processes 2-4 levels above
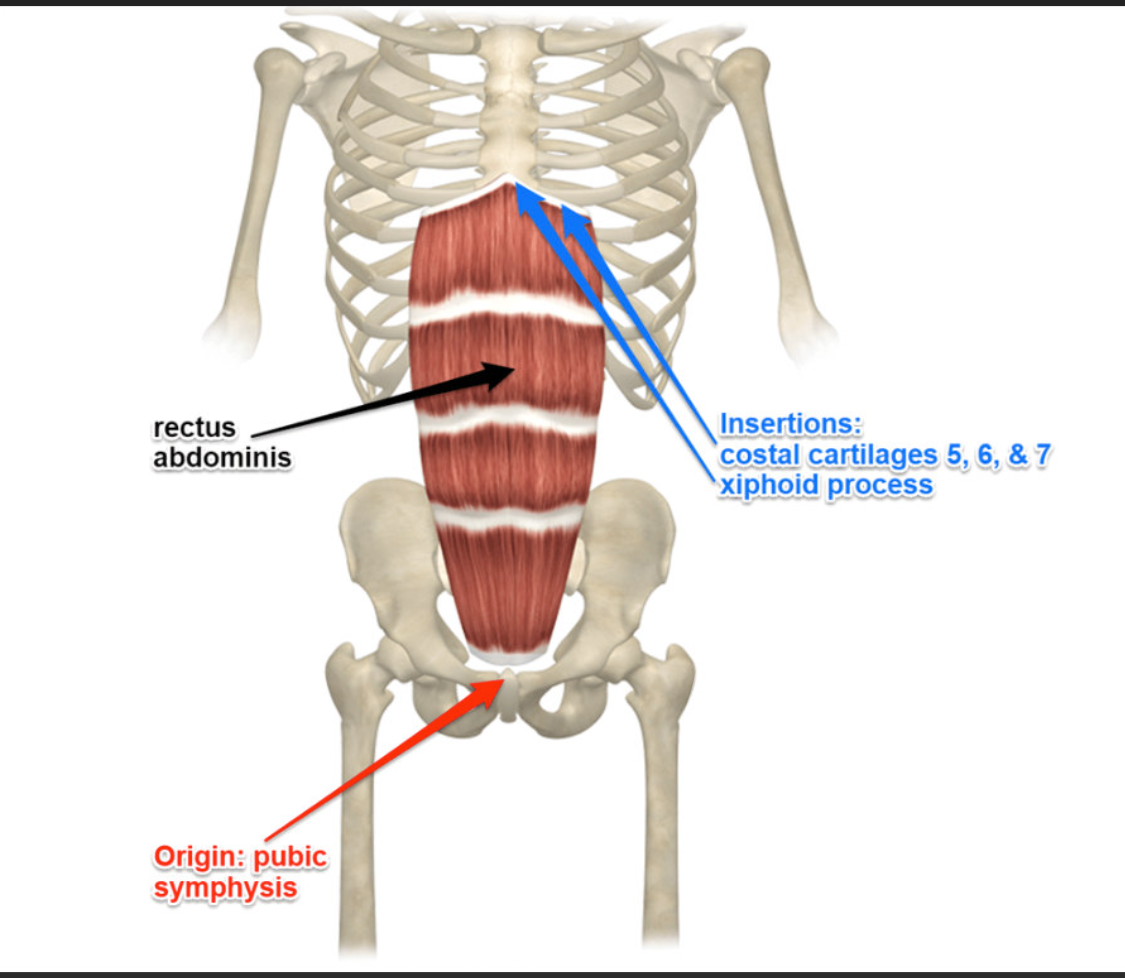
Rectus Abdominis Function
Flexes the trunk
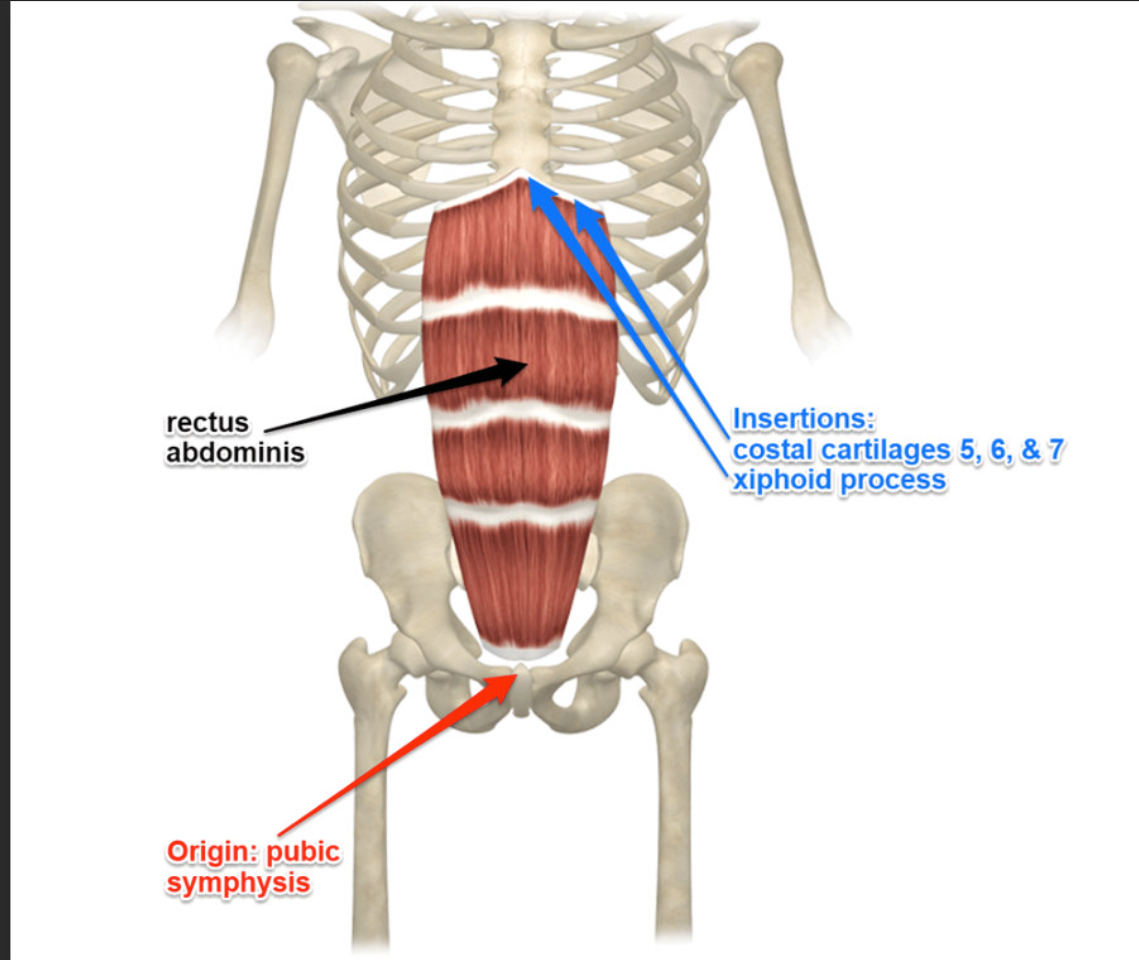
Rectus Abdominis Origin
Pubic crest and pubic symphysis
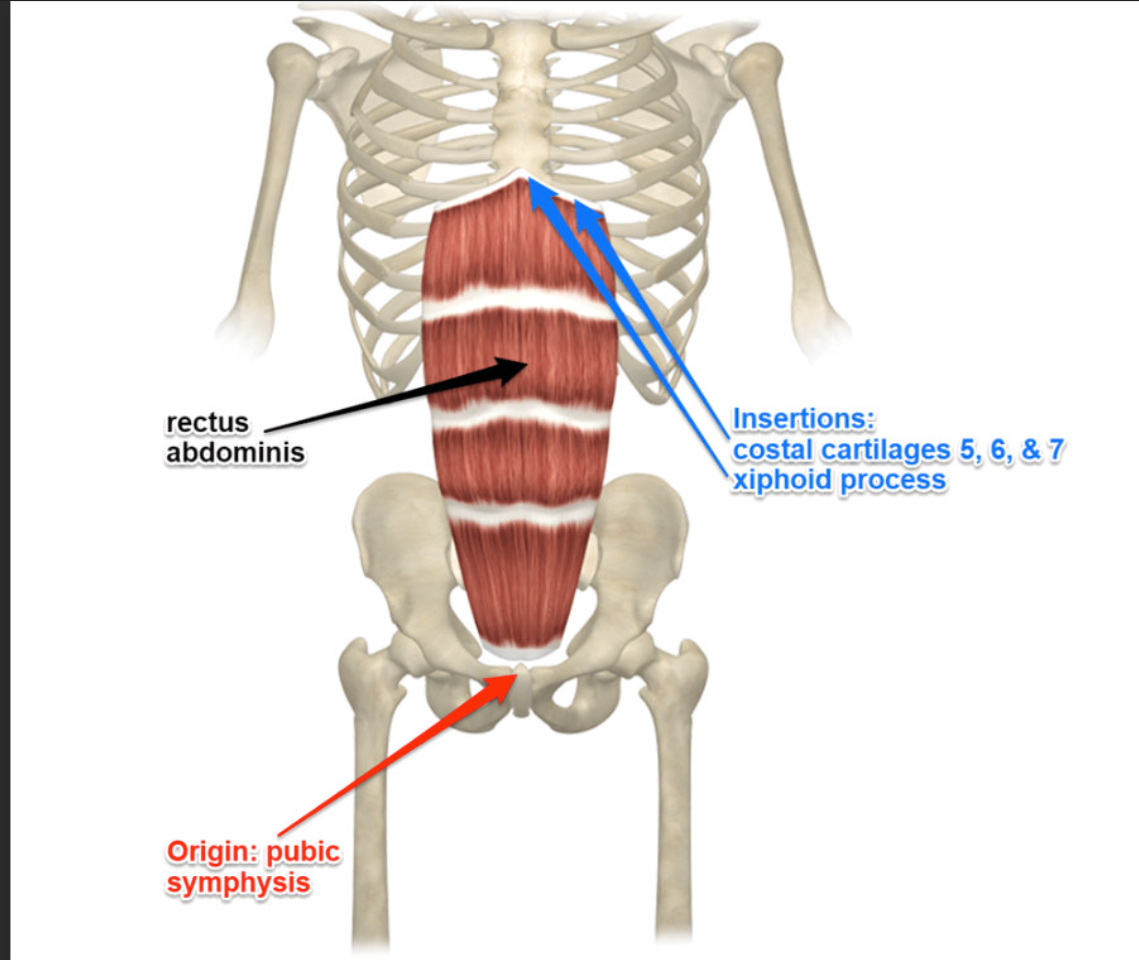
Rectus Abdominis Insertion
Xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs 5-7
External Obliques Function
Rotate and laterally flex the trunk
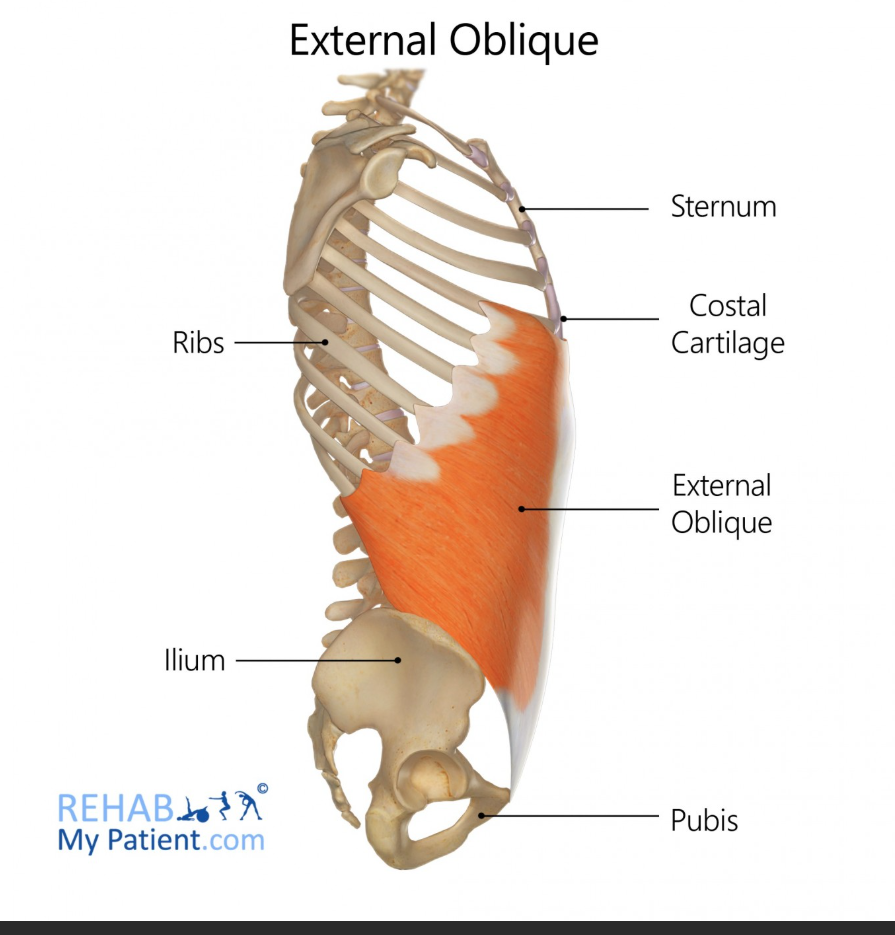
External Obliques Origin
Ribs 5-12
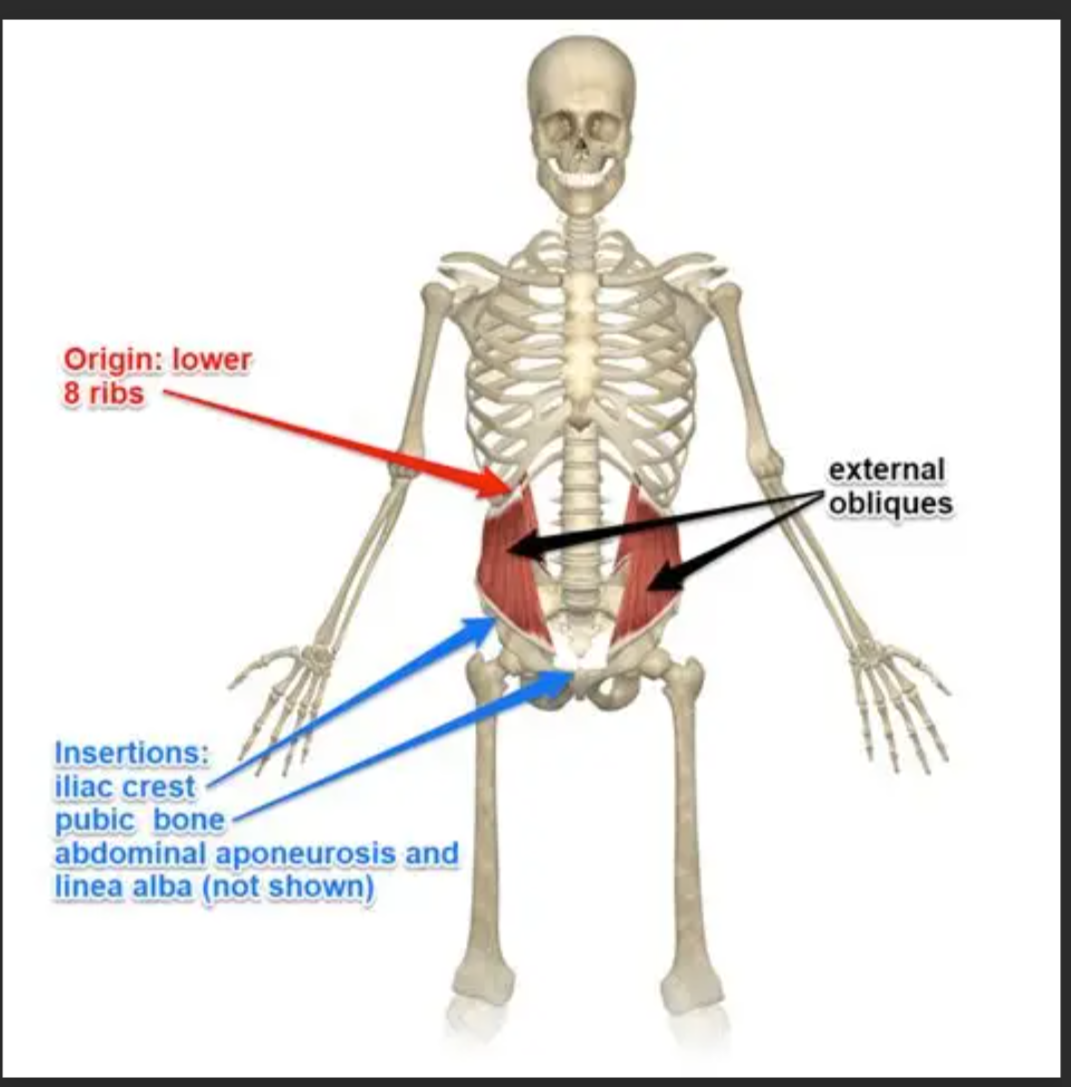
External Obliques Insertion
Iliac crest and linea alba
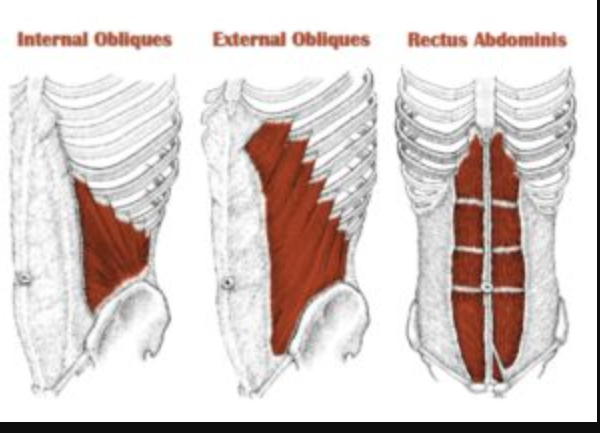
Internal Obliques Function
Assists in trunk flexion, rotation, and stabilizes pelvis
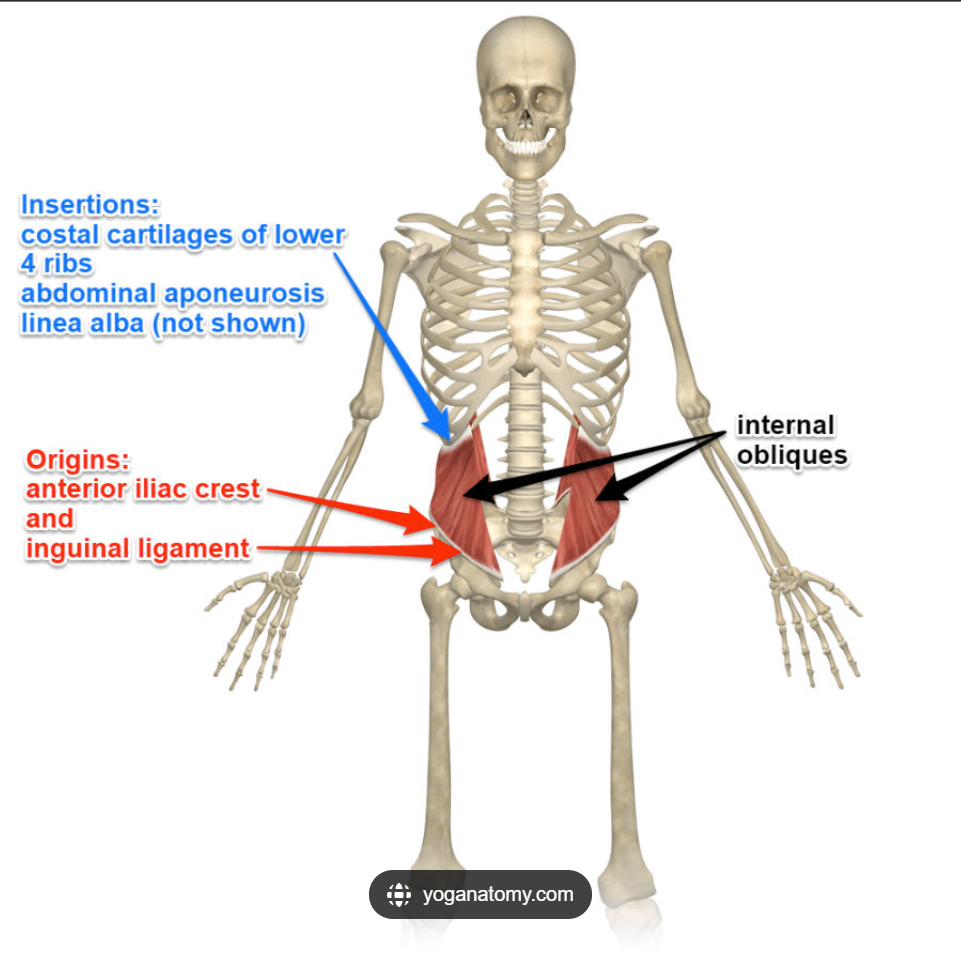
Internal Obliques Origin
Iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia
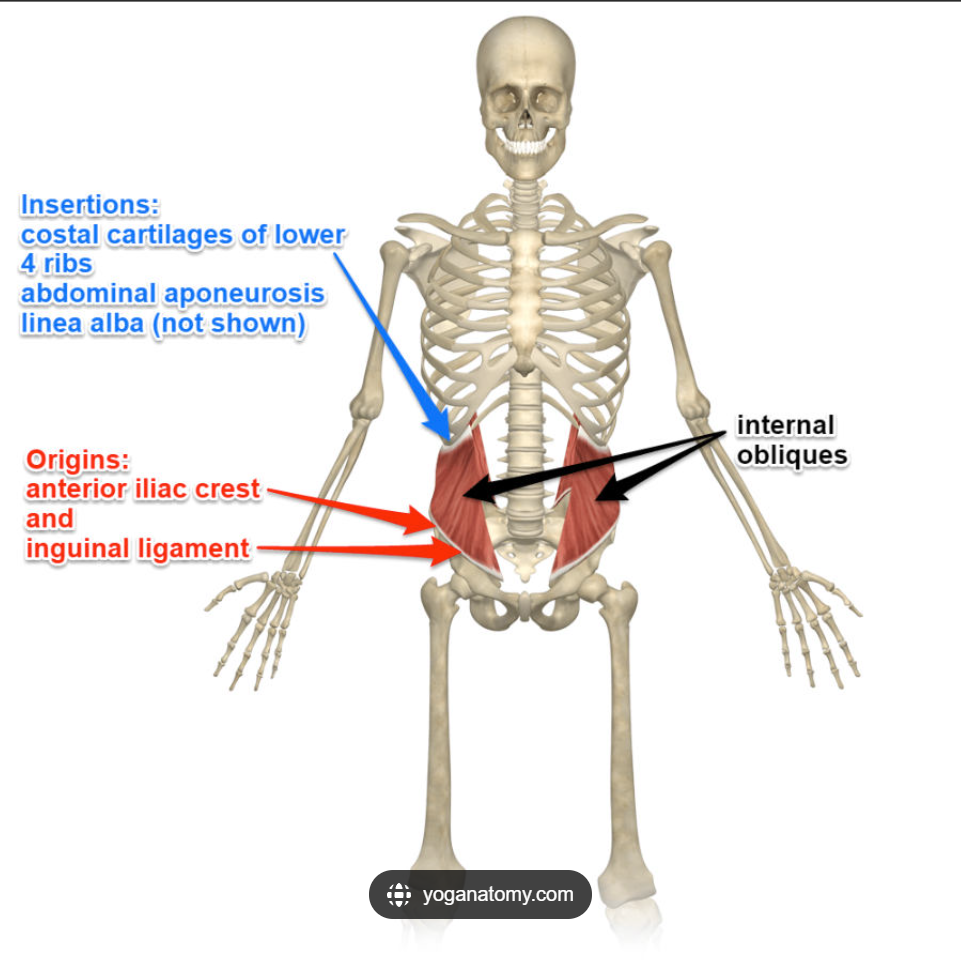
Internal Obliques Insertion
Ribs 10-12, linea alba, pubis
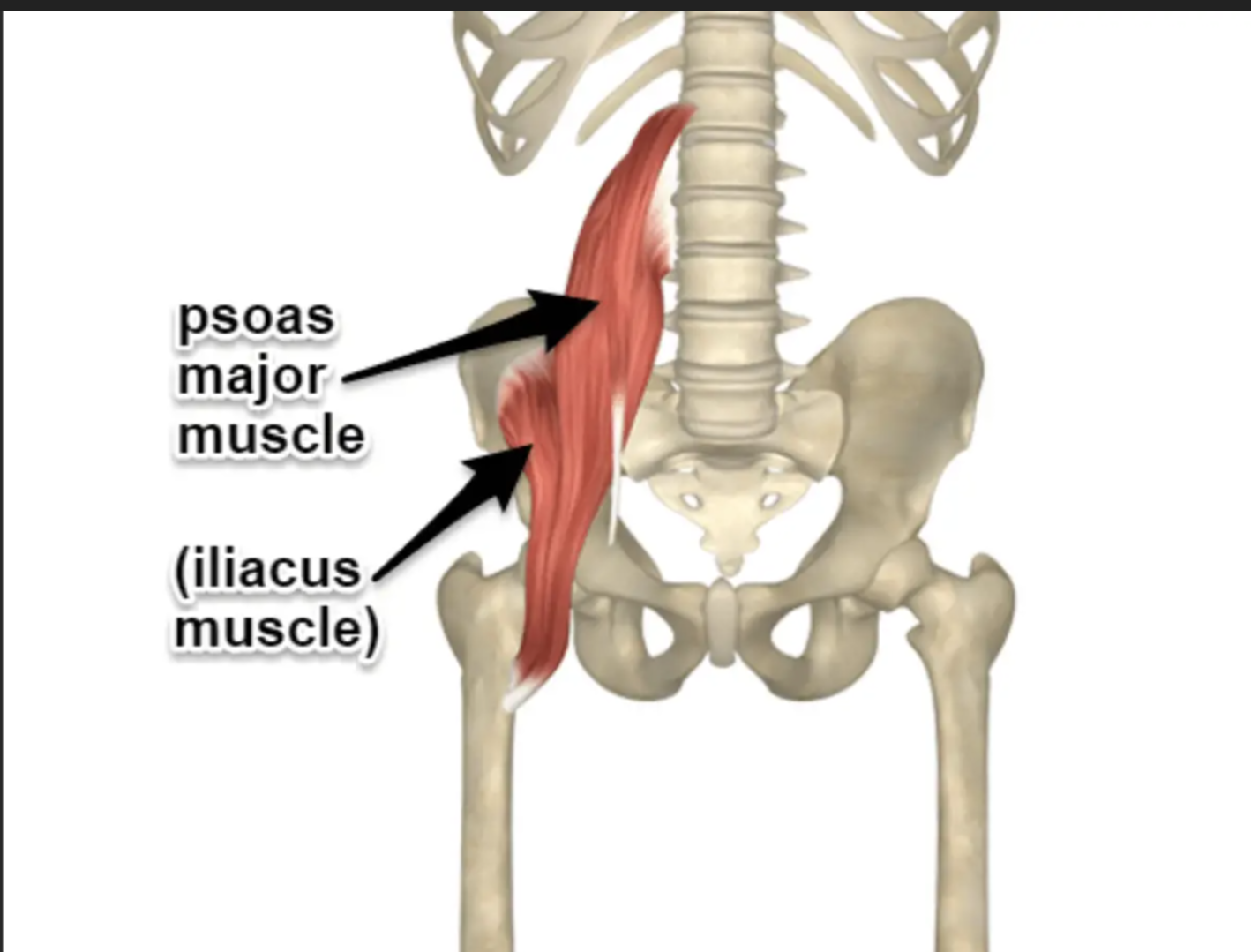
Iliopsoas Function
Main hip flexor
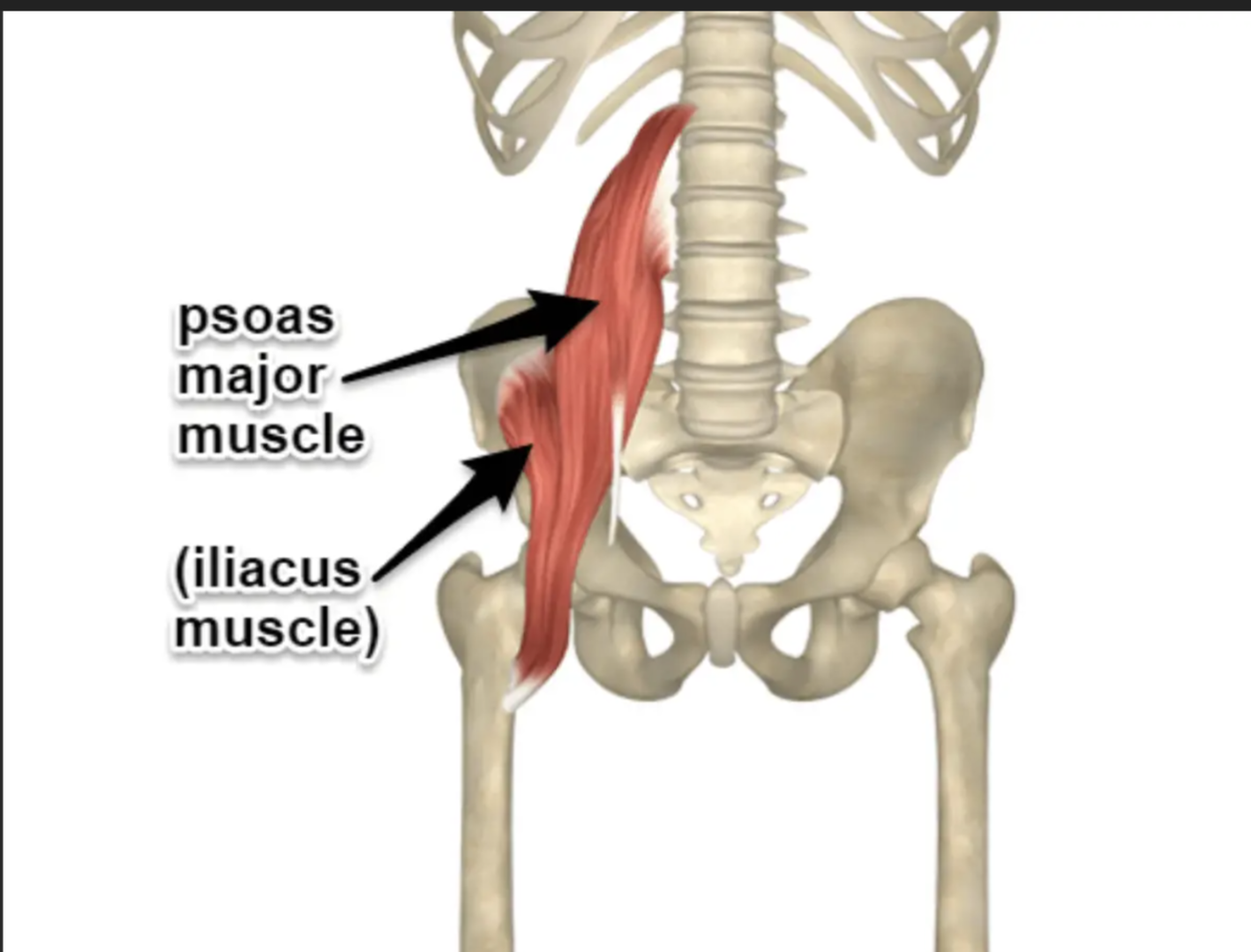
Psoas Major Origin
Lumbar vertebrae
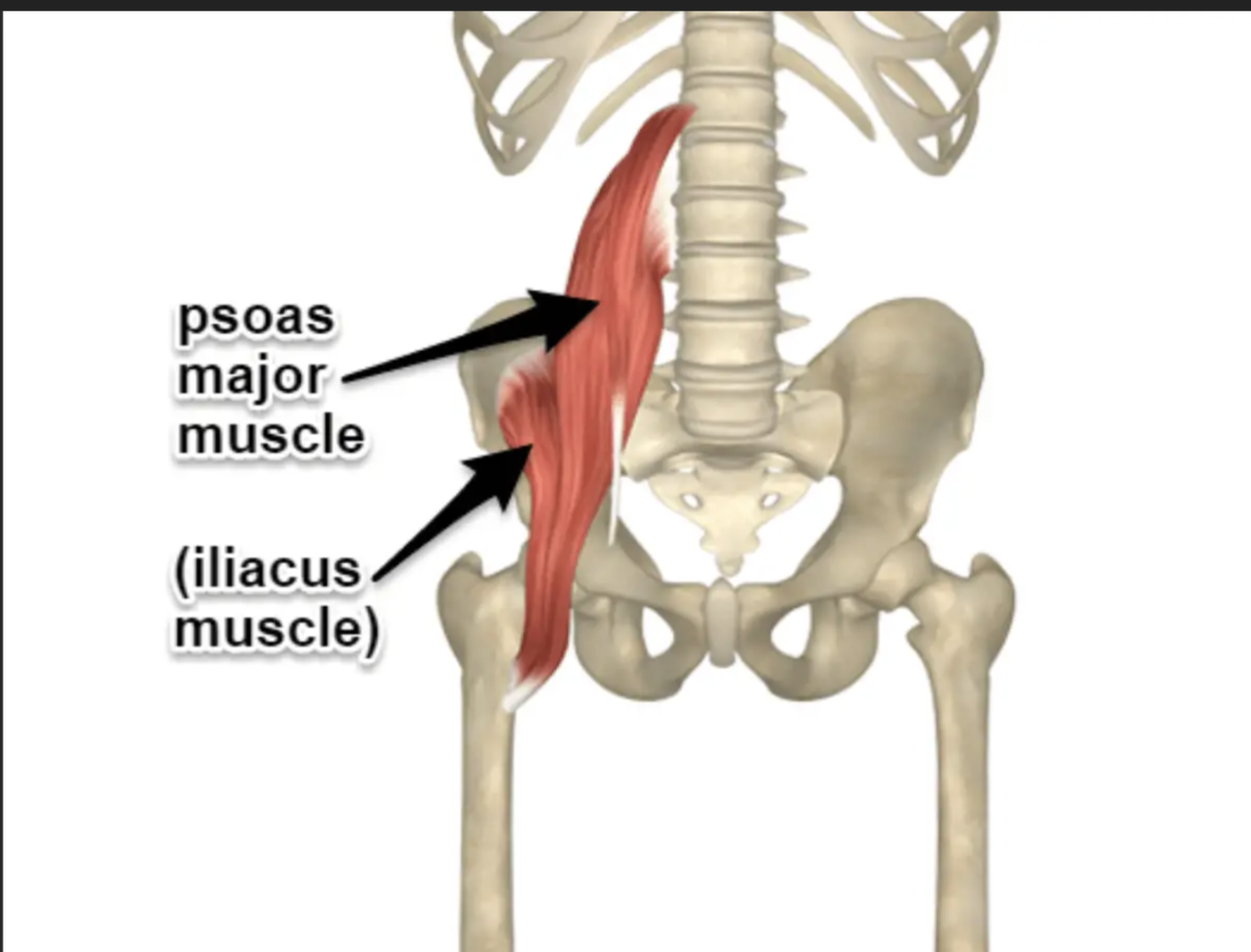
Iliacus Origin
Iliac fossa
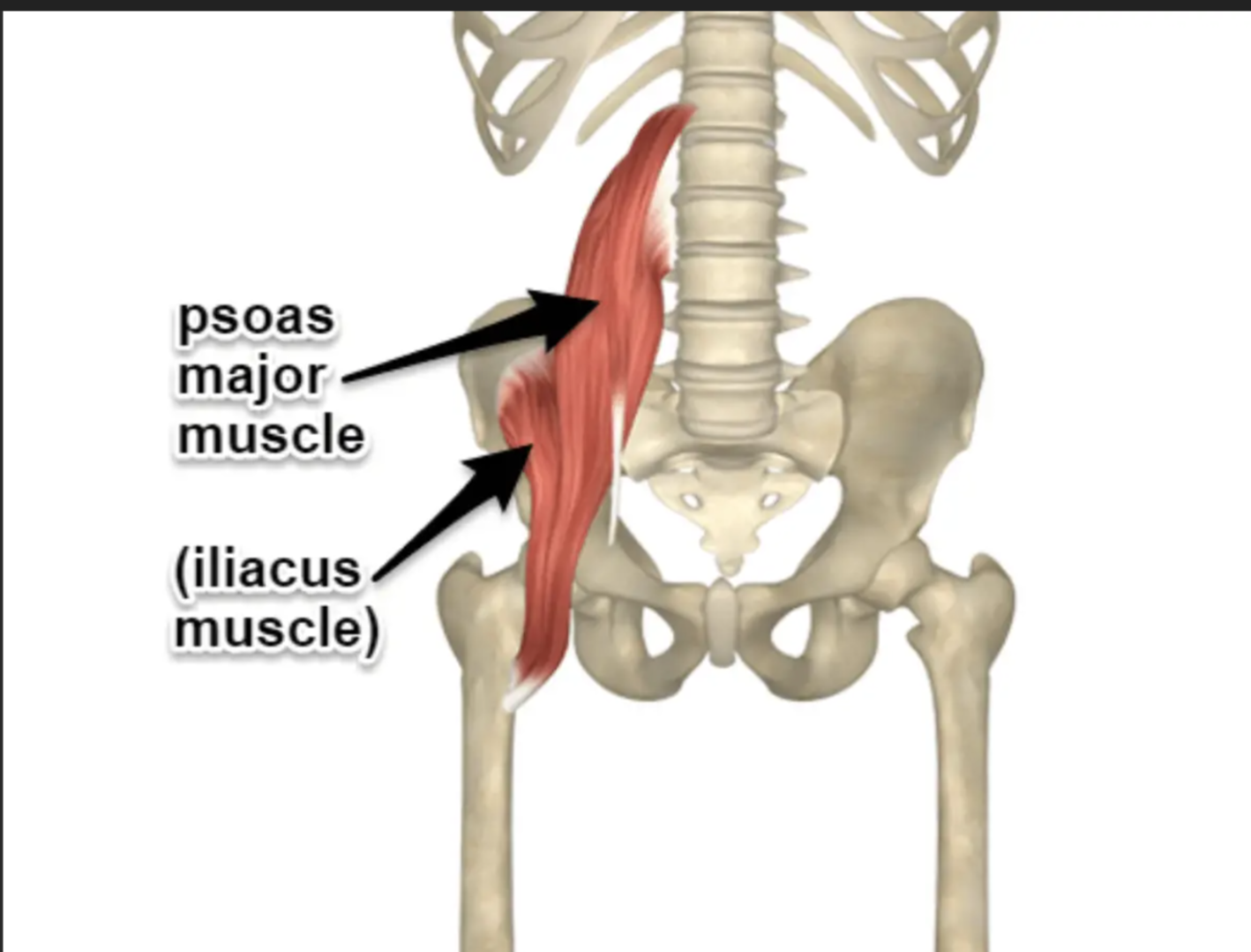
Iliopsoas Insertion
Lesser trochanter of femur
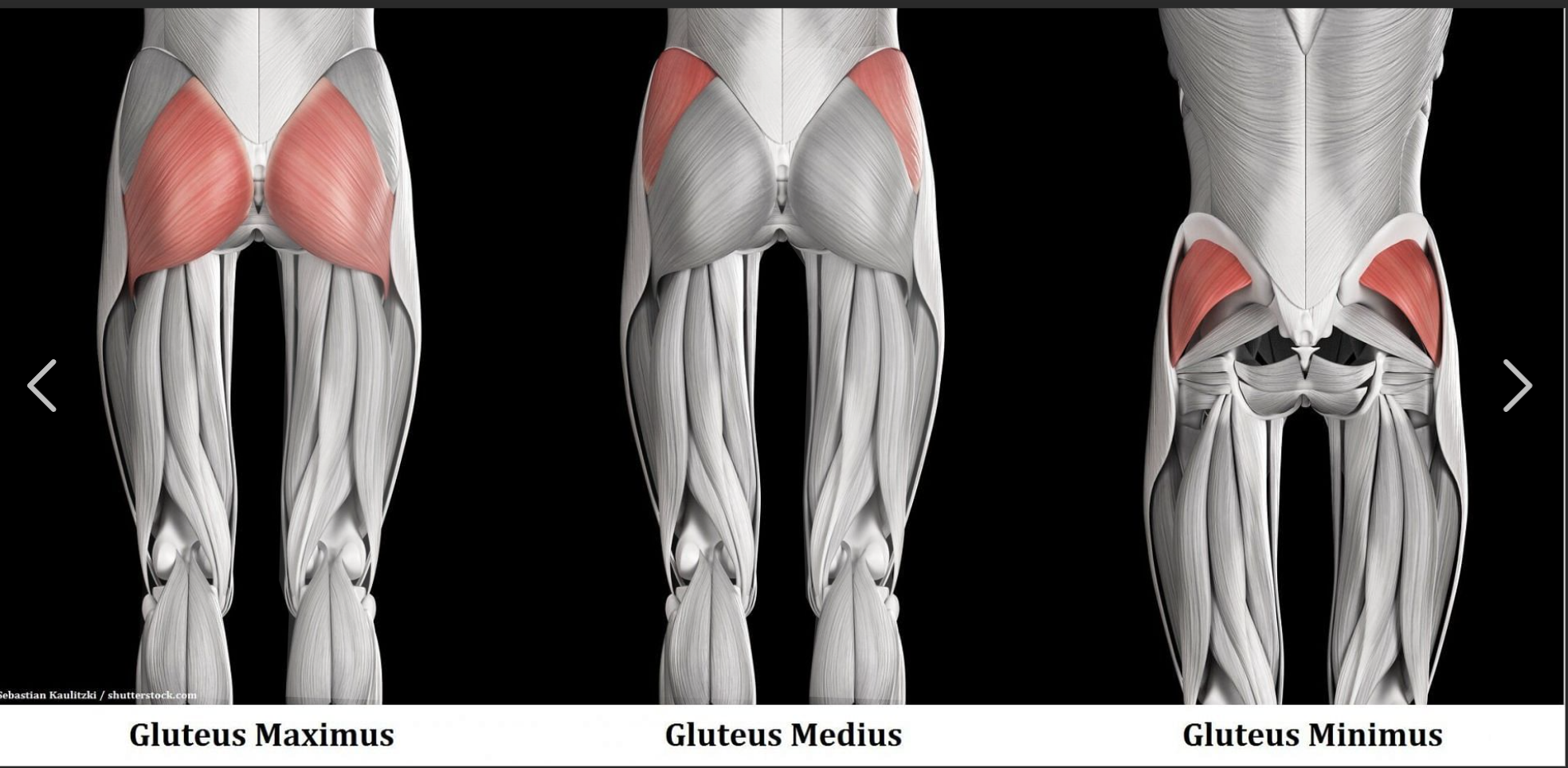
Gluteus Maximus Function
Extends the hip during lifting
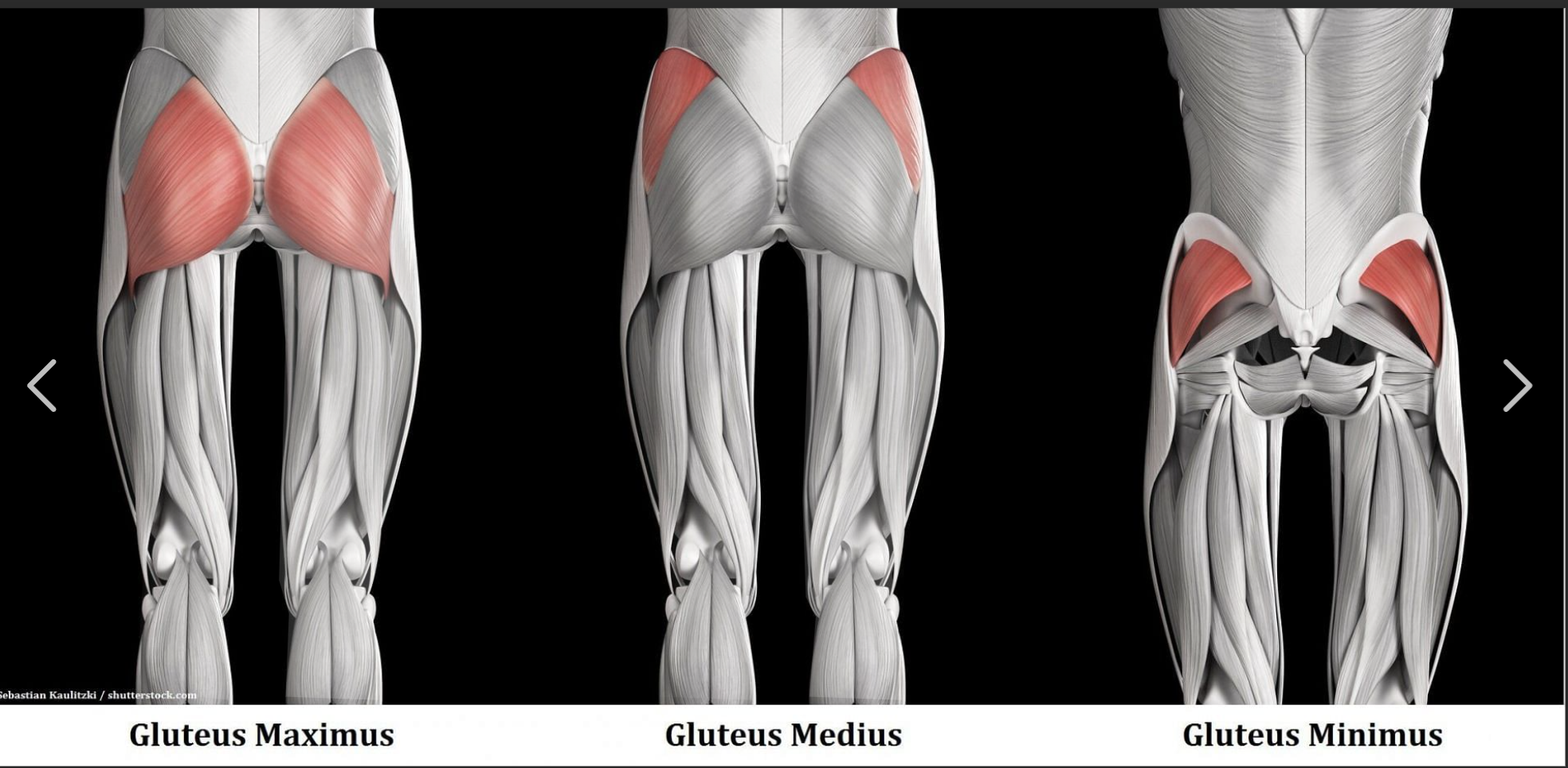
Gluteus Maximus Origin
Posterior ilium, sacrum, coccyx
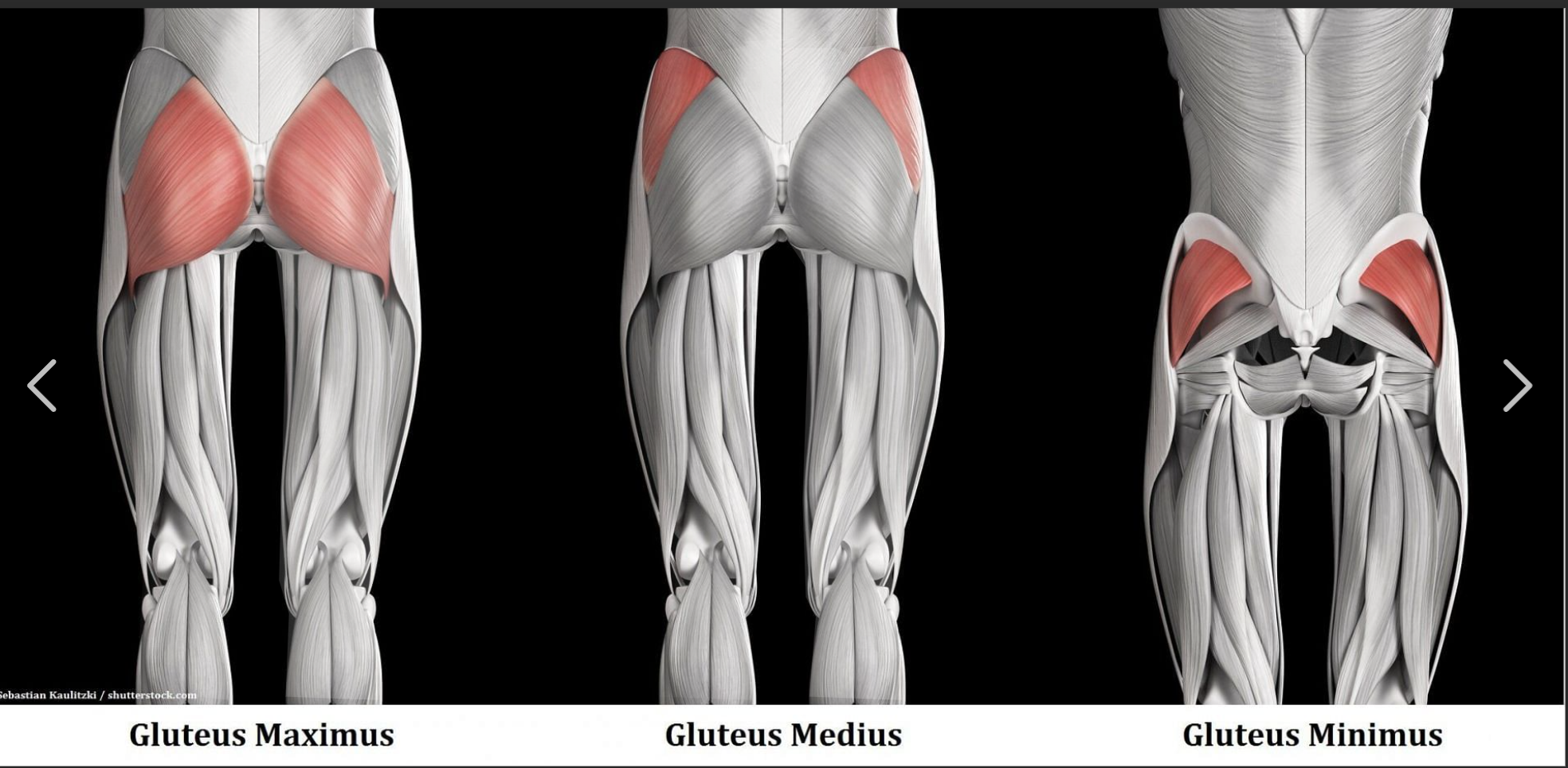
Gluteus Maximus Insertion
Gluteal tuberosity of femur, iliotibial band
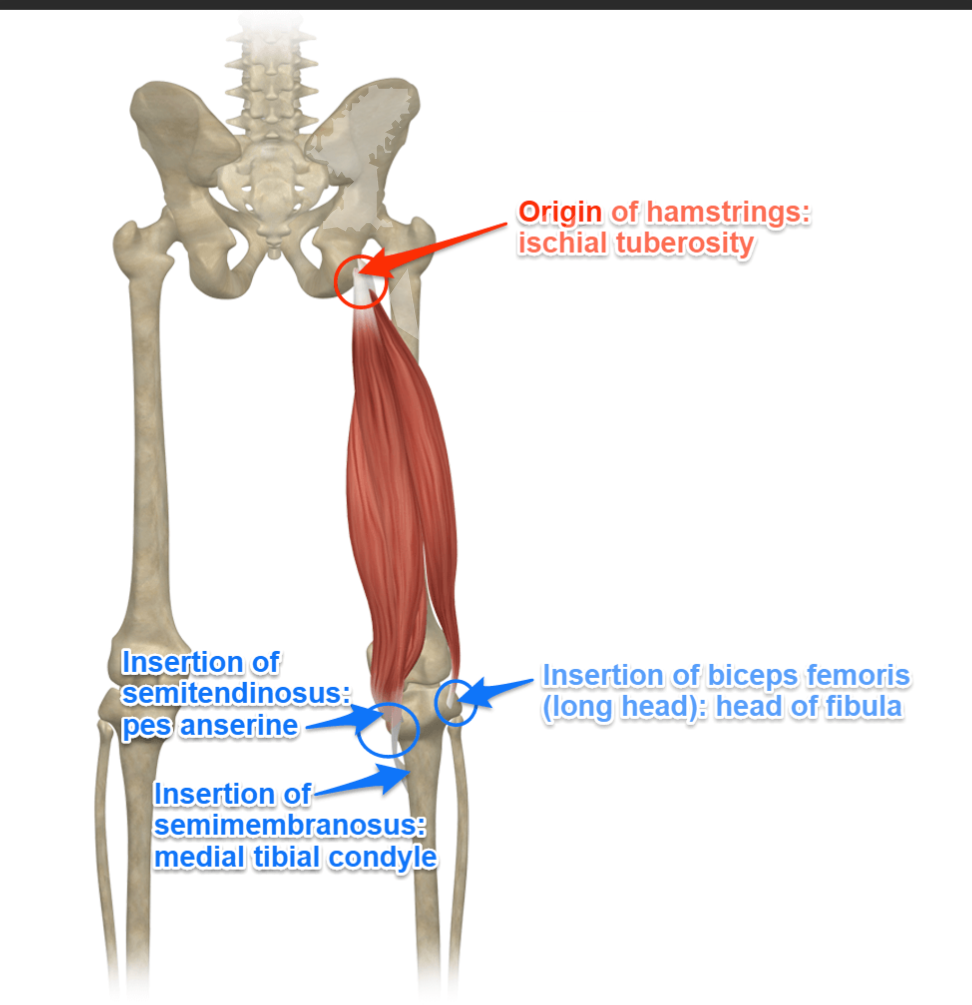
Hamstrings Function
Also extend the hip
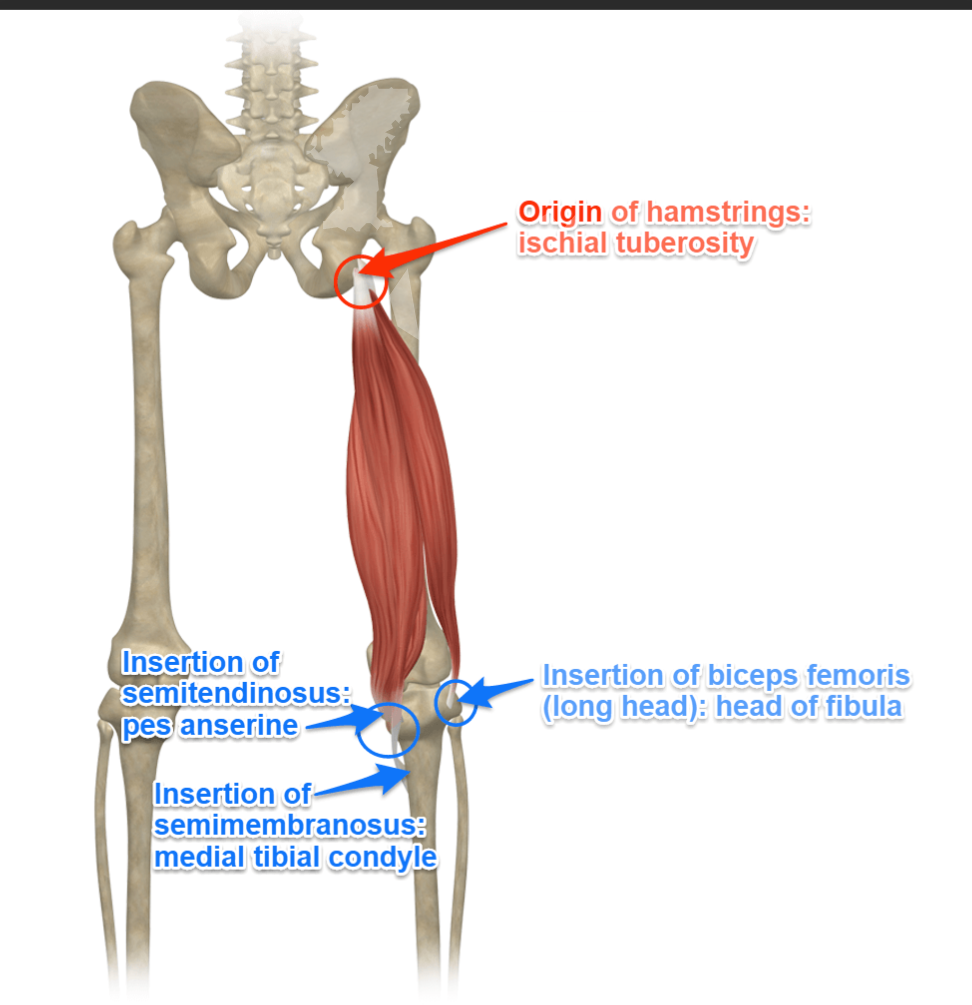
Hamstrings Origin
Ischial tuberosity (long head), femur (short head of biceps femoris)
Tibia
Bone located in the back of the lower leg, associated with the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles.
Fibula
Bone located in the back of the lower leg, associated with the biceps femoris muscle.
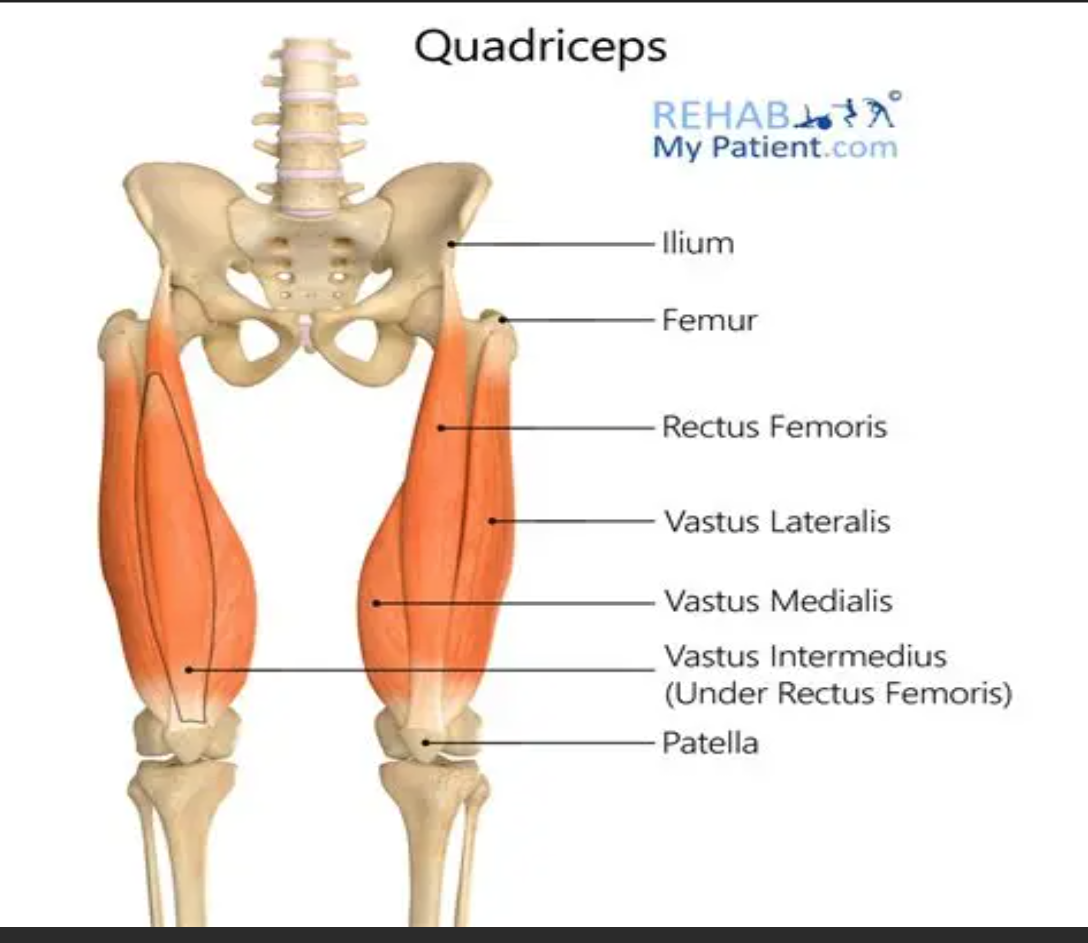
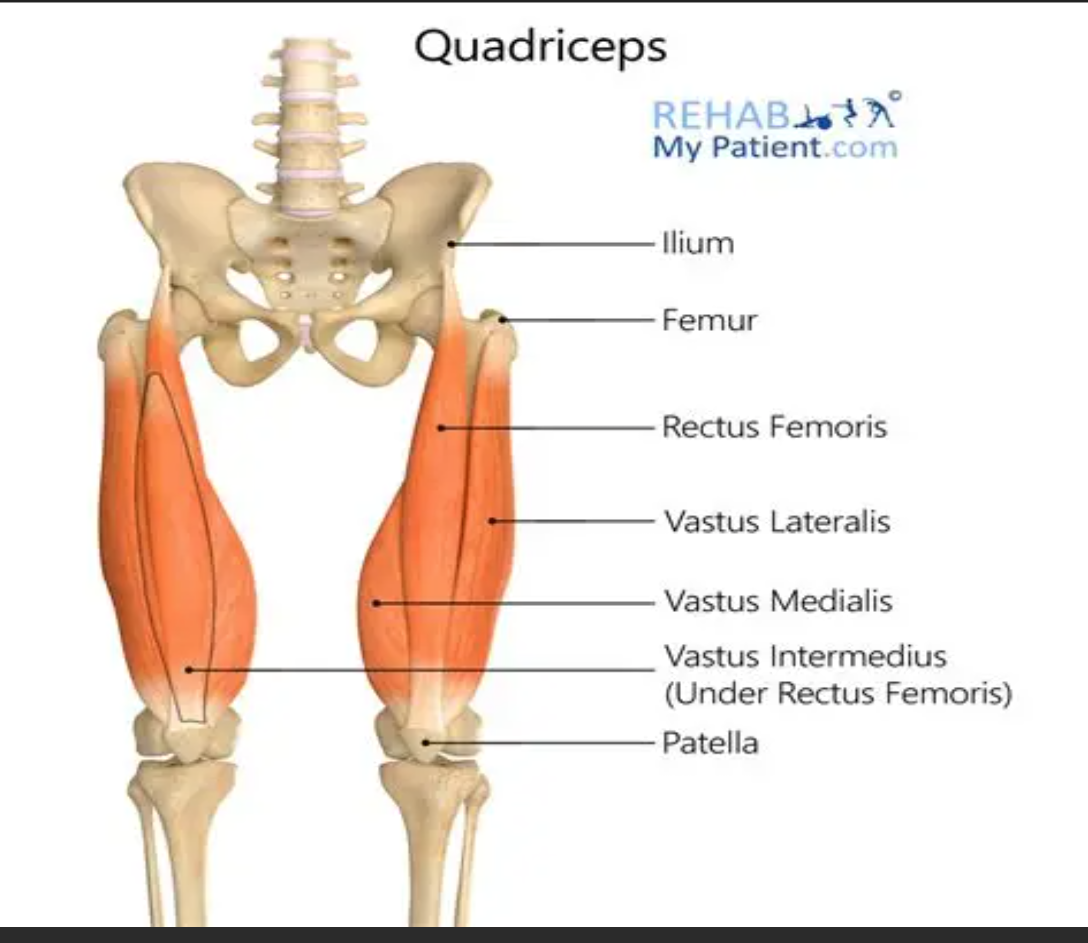
Quadriceps
Muscle group responsible for knee extension, consisting of rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius.
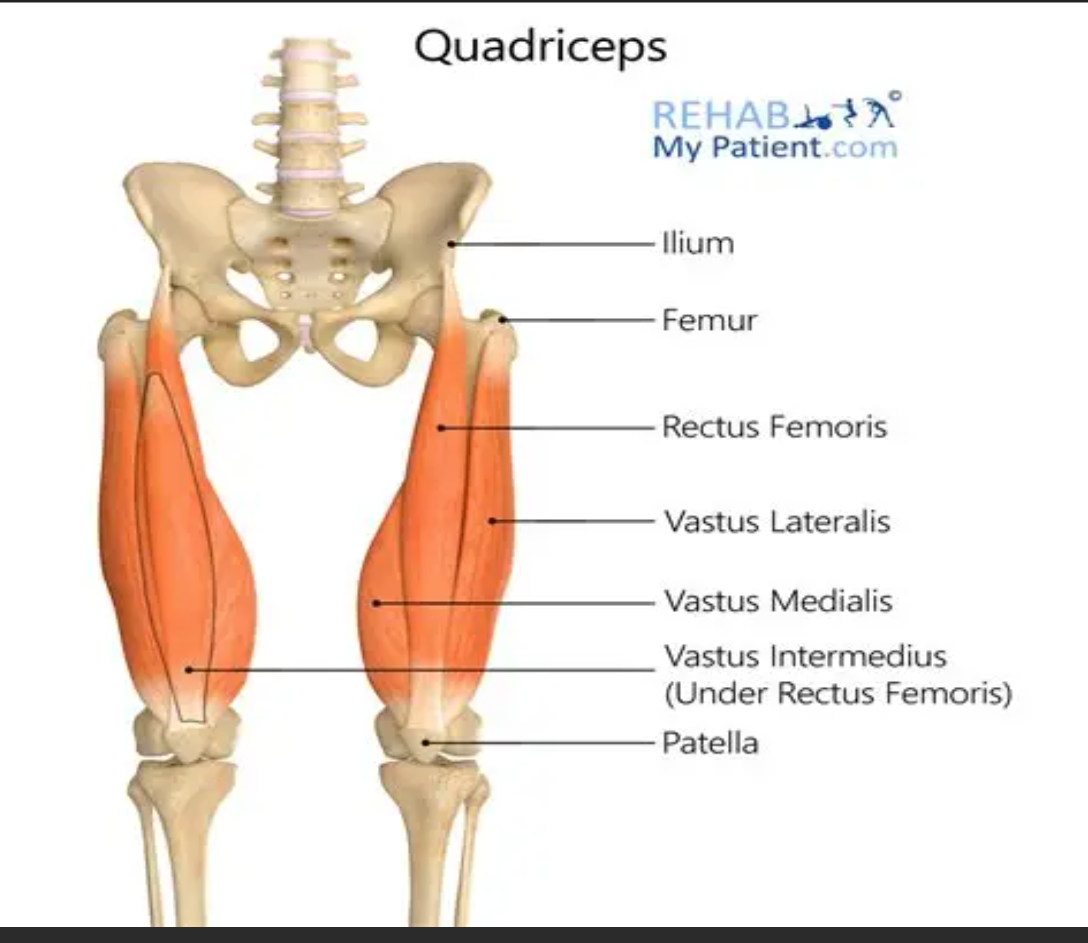
Rectus femoris
Muscle that originates from the anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) and is part of the quadriceps.
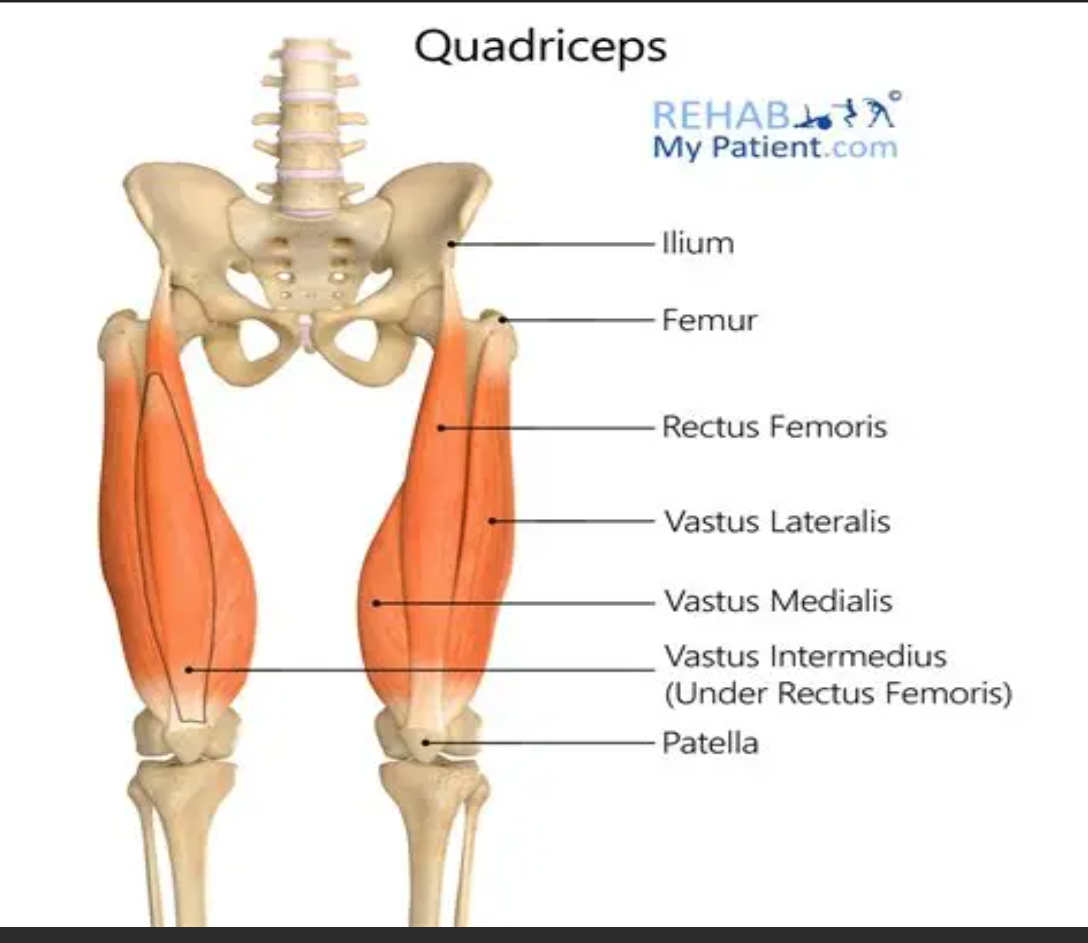
Vasti muscles
Muscles that originate from the femur and are part of the quadriceps.
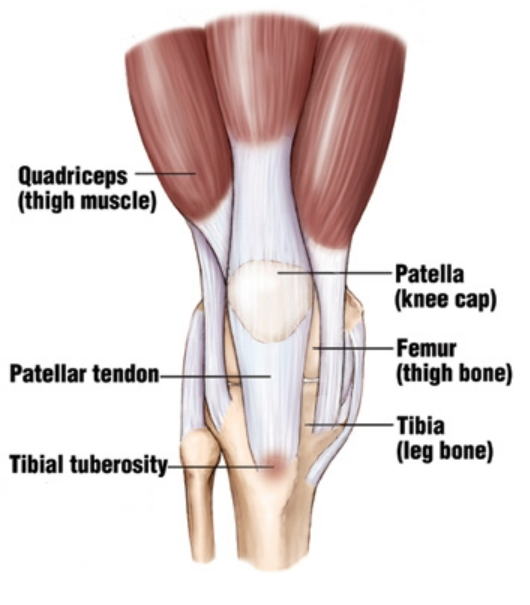
Tibial tuberosity
Insertion point for the quadriceps via the patella tendon, located at the front of the shin.
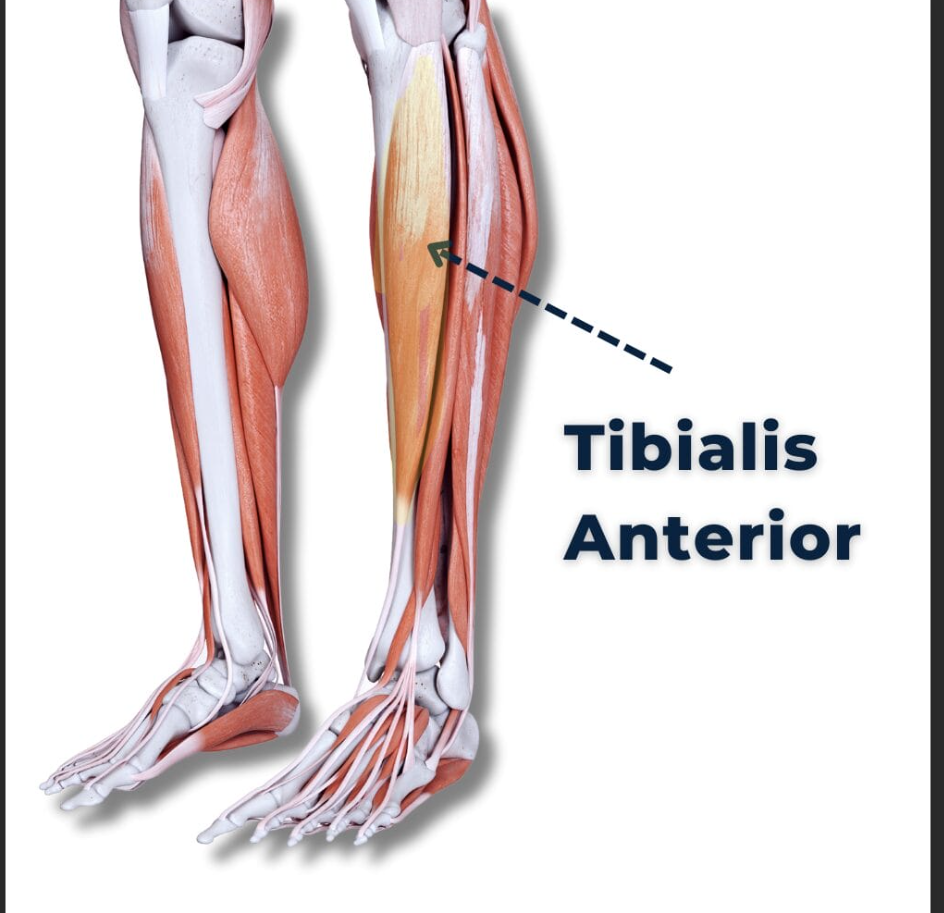
Tibialis anterior
Muscle that dorsiflexes the ankle, originating from the lateral tibia and interosseous membrane.
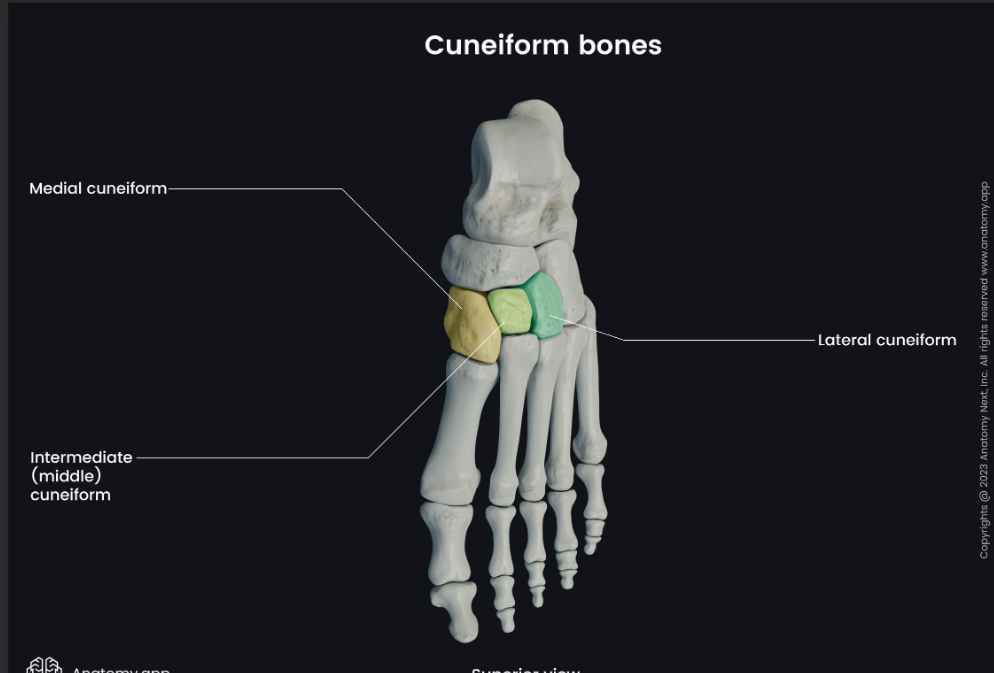
Medial cuneiform
Insertion point for the tibialis anterior, located at the foot.
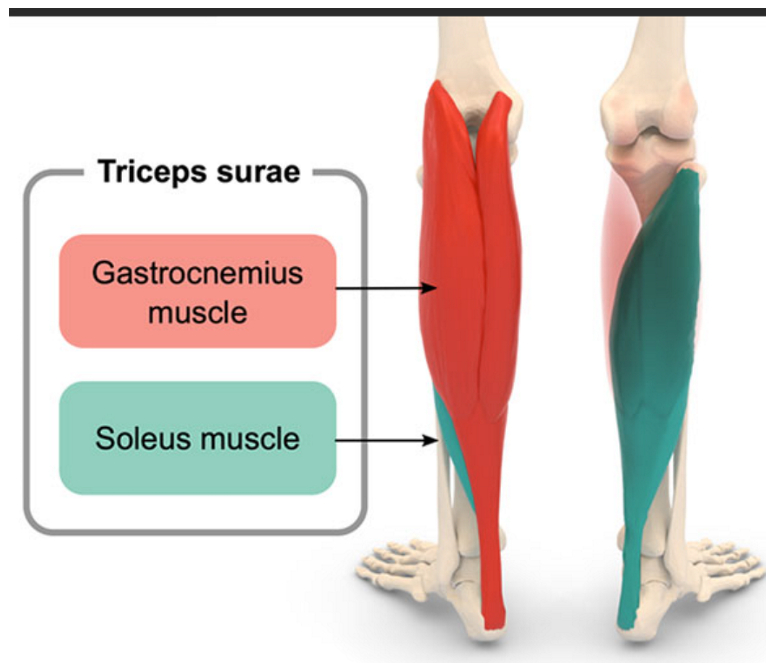
Gastrocnemius
Muscle that plantarflexes the ankle, originating from the medial and lateral femoral condyles.
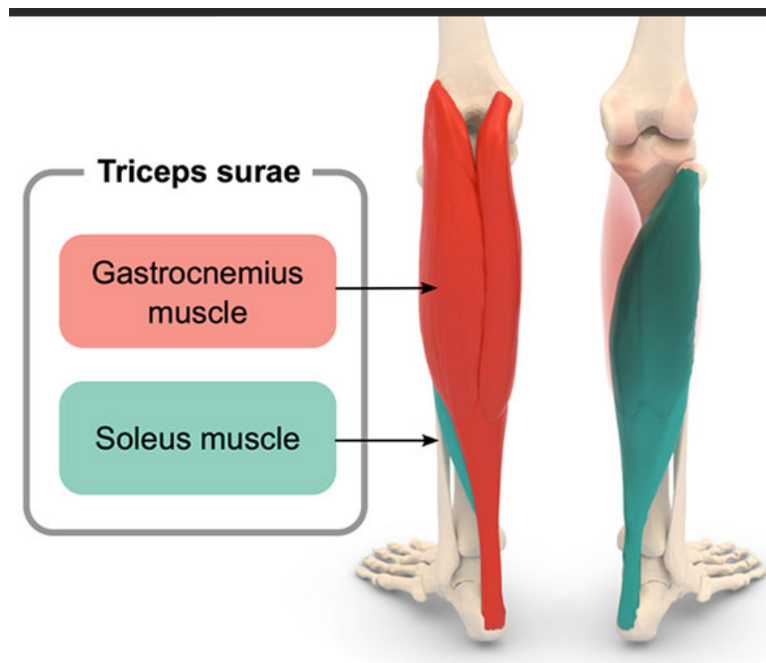
Soleus
Muscle that plantarflexes the ankle, originating from the posterior tibia and fibula.
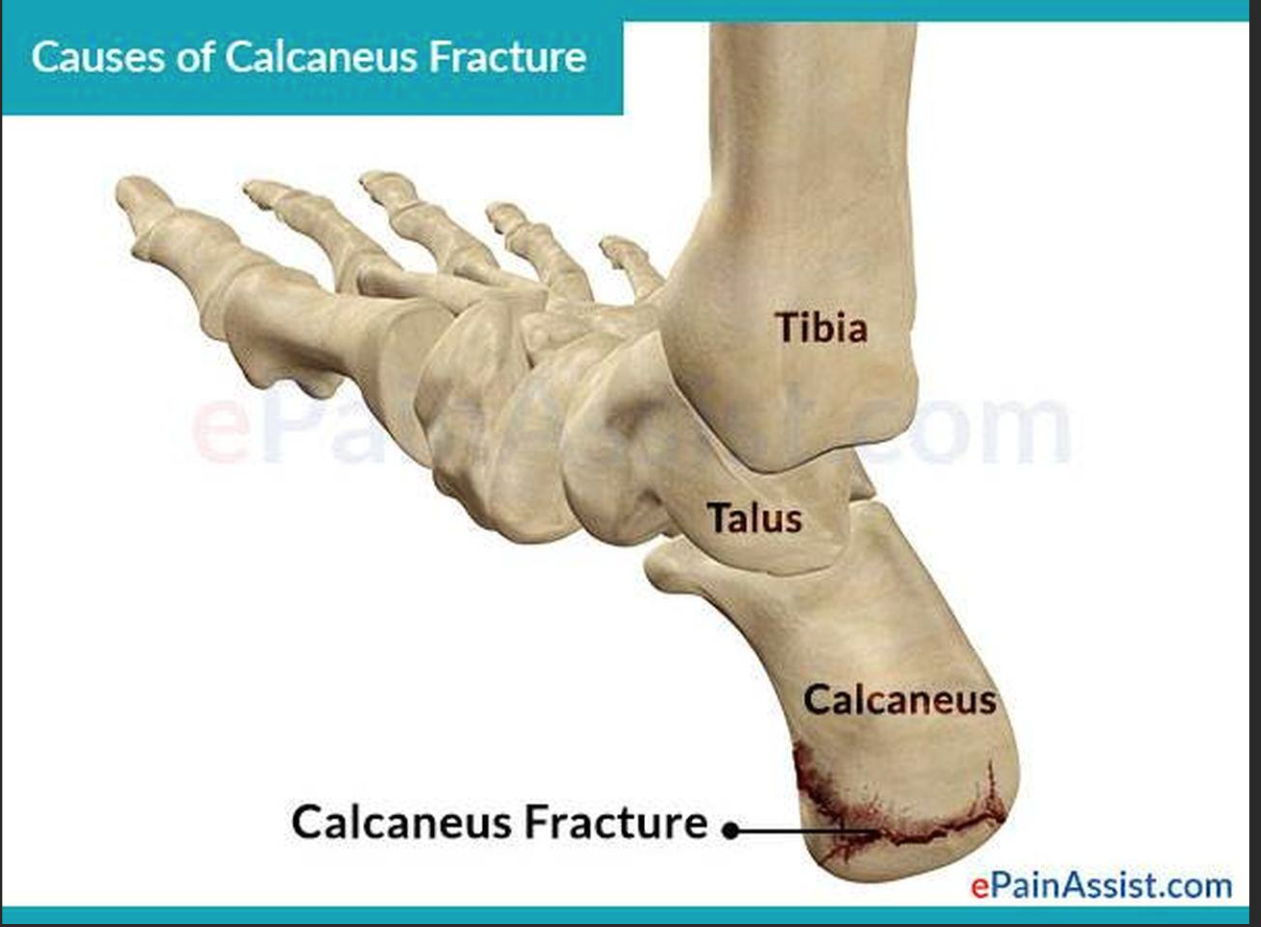
Calcaneus
Insertion point for gastrocnemius and soleus via the Achilles tendon, located at the heel.
Brent's movement factors
Individual factors affecting movement include age, strength, endurance, proprioception, coordination, and fatigue.
Environmental factors
Factors affecting movement include floor surface, child movement, space, distractions, and shoes.
Task factors
Factors affecting movement include repetition, load, attention, and coordination.
Trunk flexion
Movement that occurs at the trunk during Phase 1 (Reaching to Squat).
Hip flexion
Movement that occurs at the left hip during Phase 1, along with slight abduction.
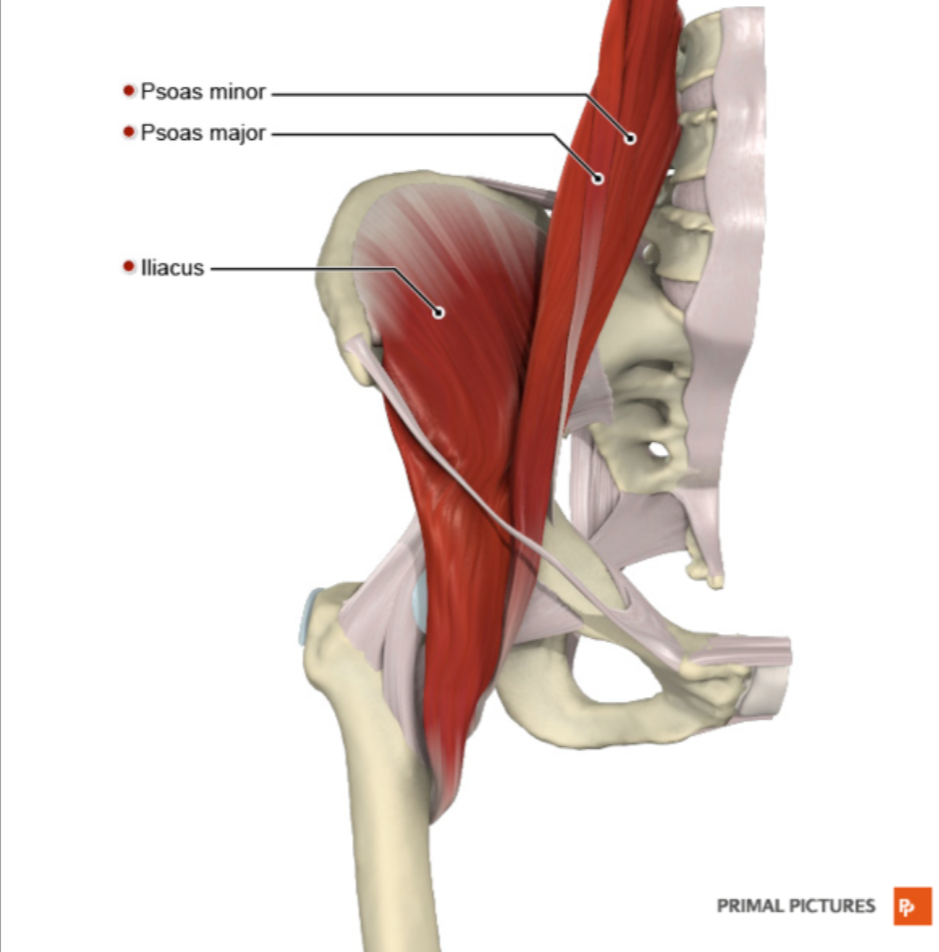
Iliopsoas
Muscle that flexes the left hip in Phase 1.
Knee flexion
Movement that occurs at the left knee during Phase 1.
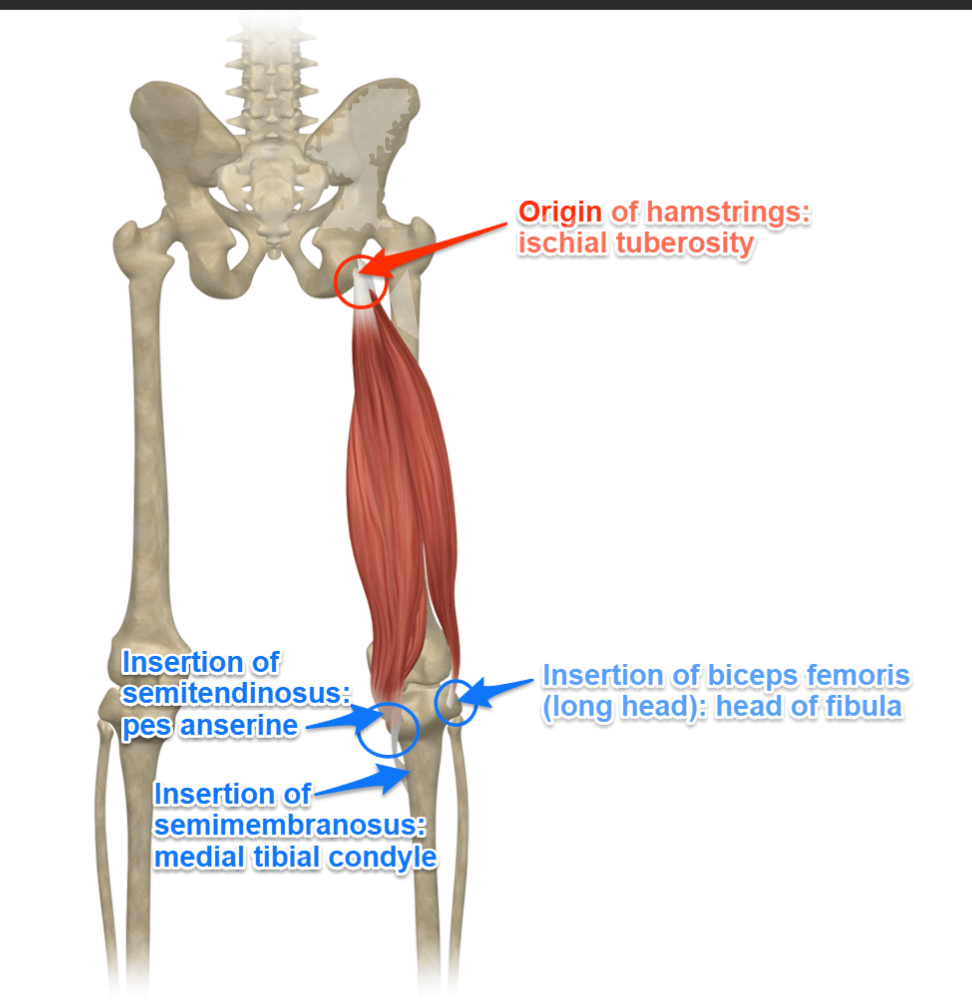
Hamstrings
Muscles that eccentrically control left knee flexion in Phase 1.
Dorsiflexion
Movement that occurs at the left ankle during Phase 1.
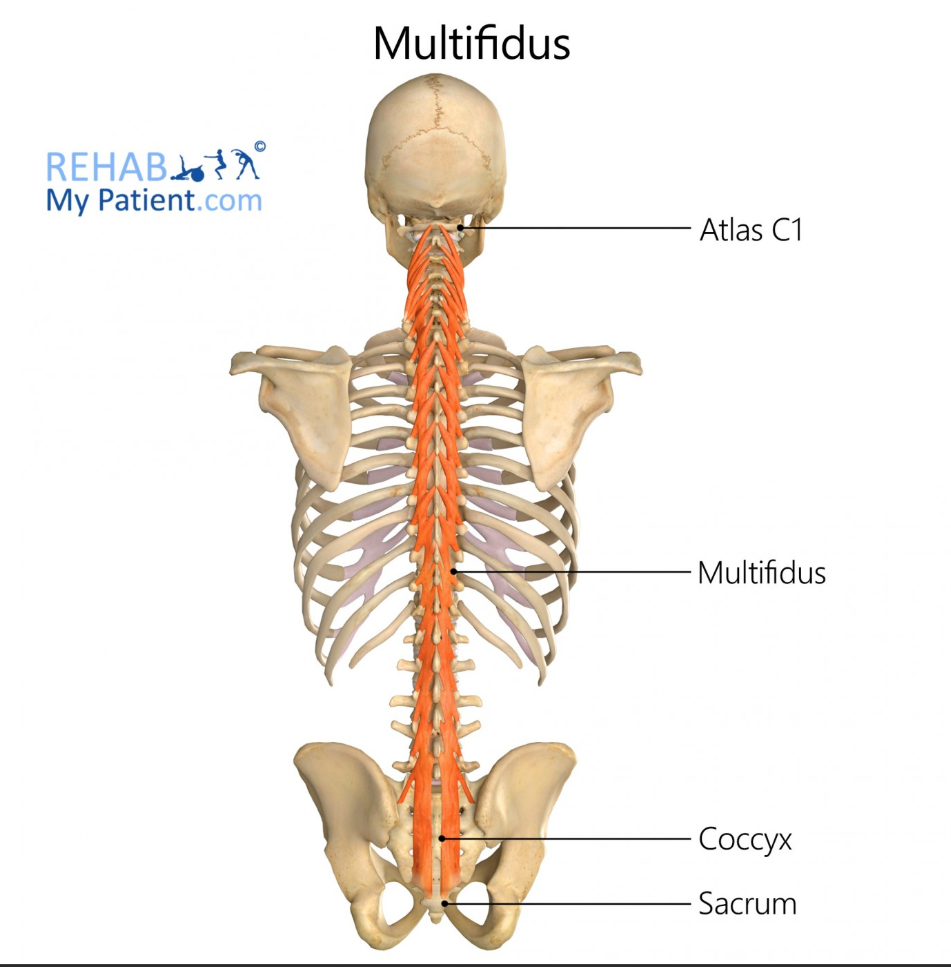
Multifidus
Muscle that stabilizes the trunk during Phase 2.
Shoulder extension
Movement that occurs at the left shoulder during Phase 2, along with slight adduction and internal rotation.
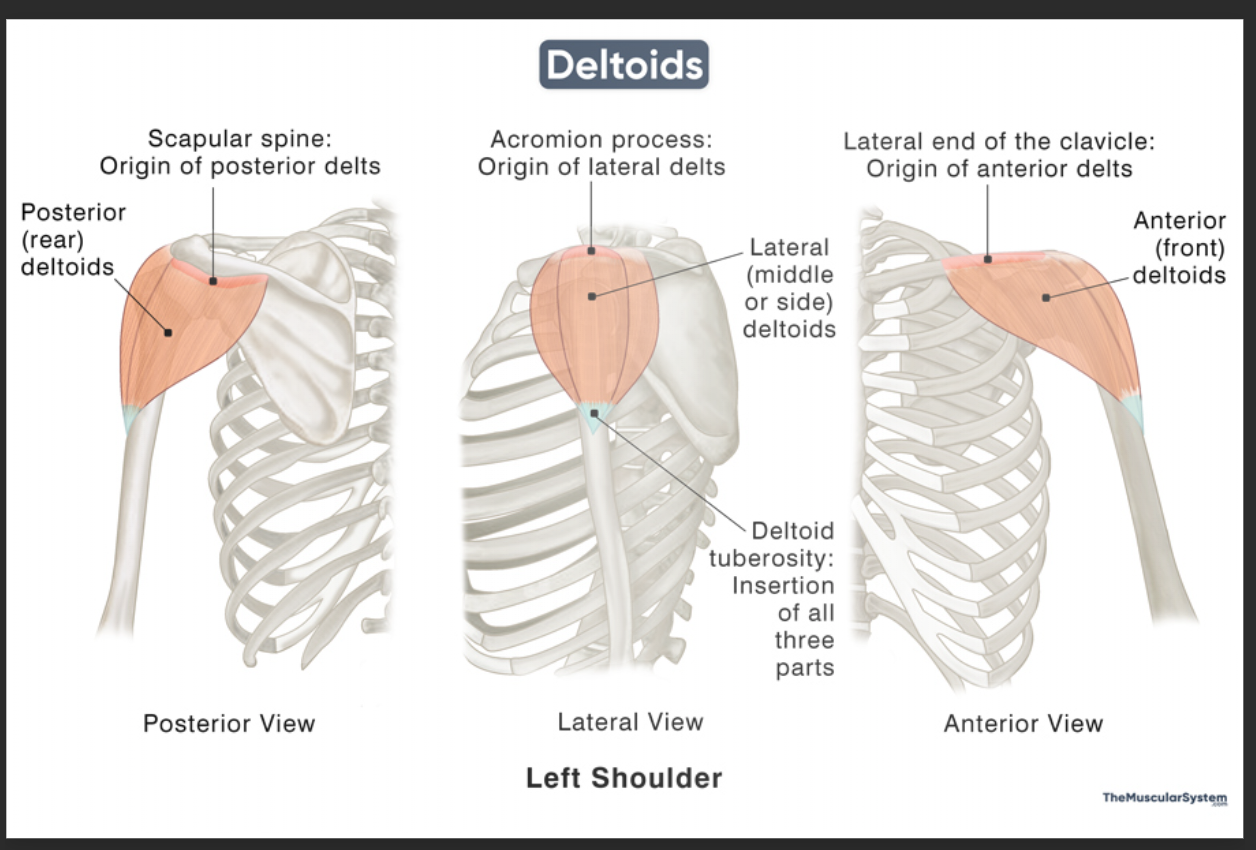
Posterior deltoid
Back of shoulder
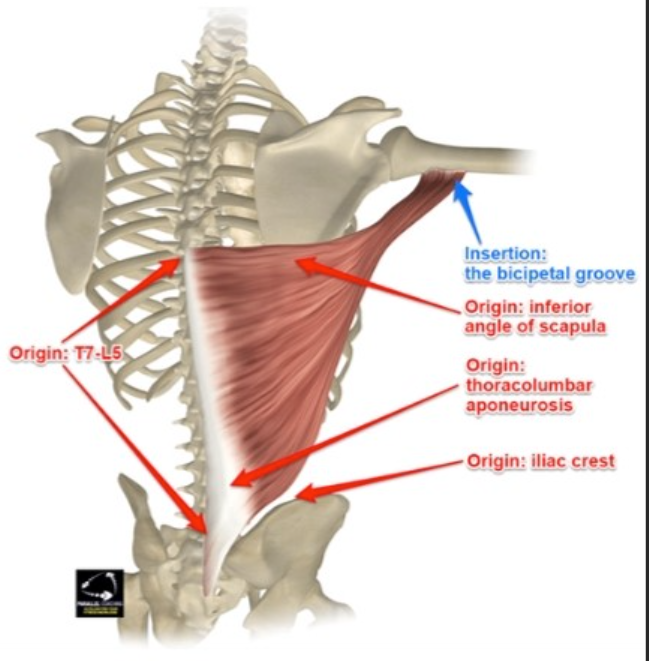
Latissimus dorsi
Mid-back
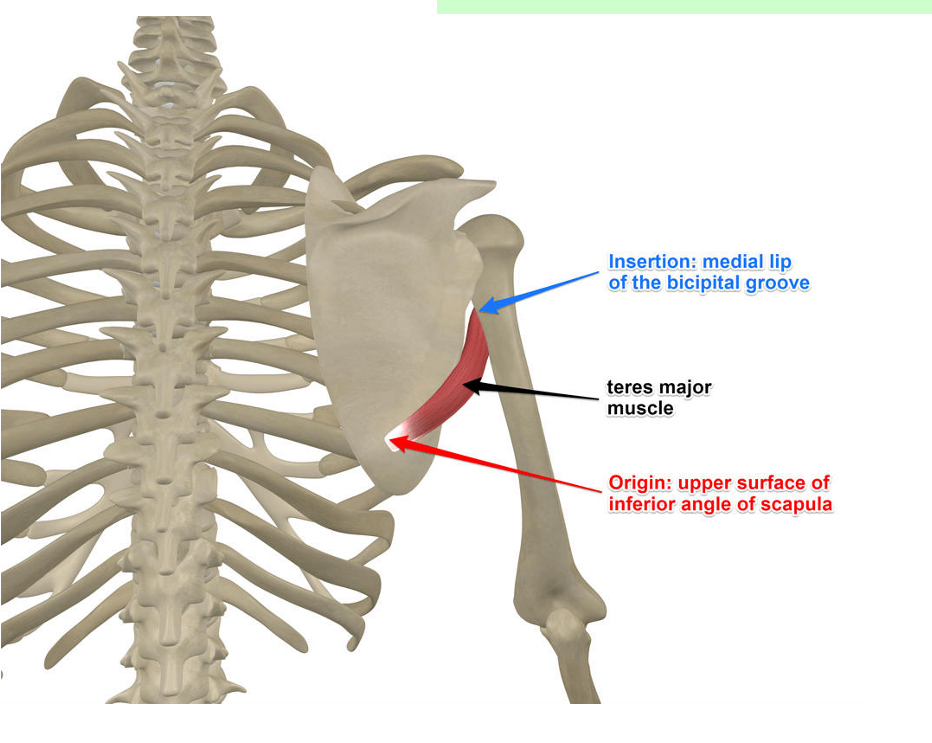
Teres major
Back of shoulder
Elbow flexion
Bending the arm
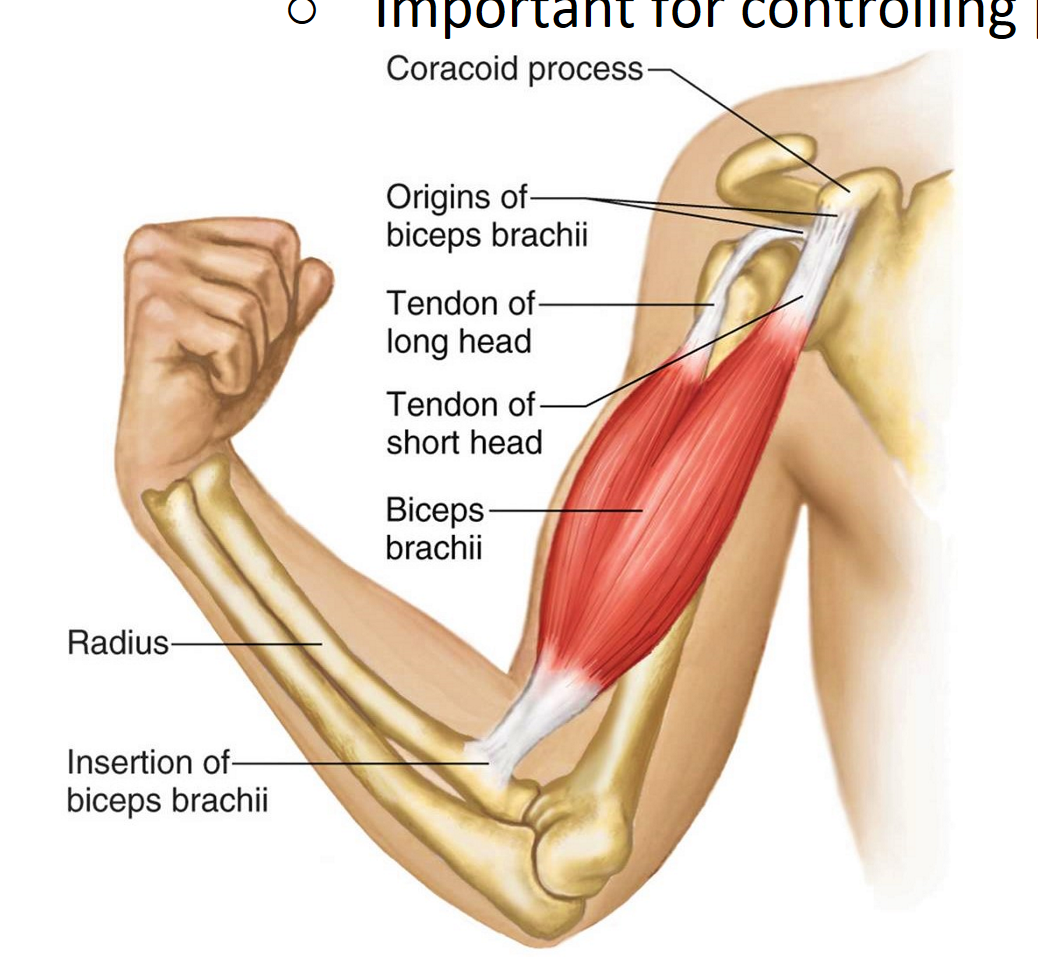
Biceps brachii
Front of upper arm
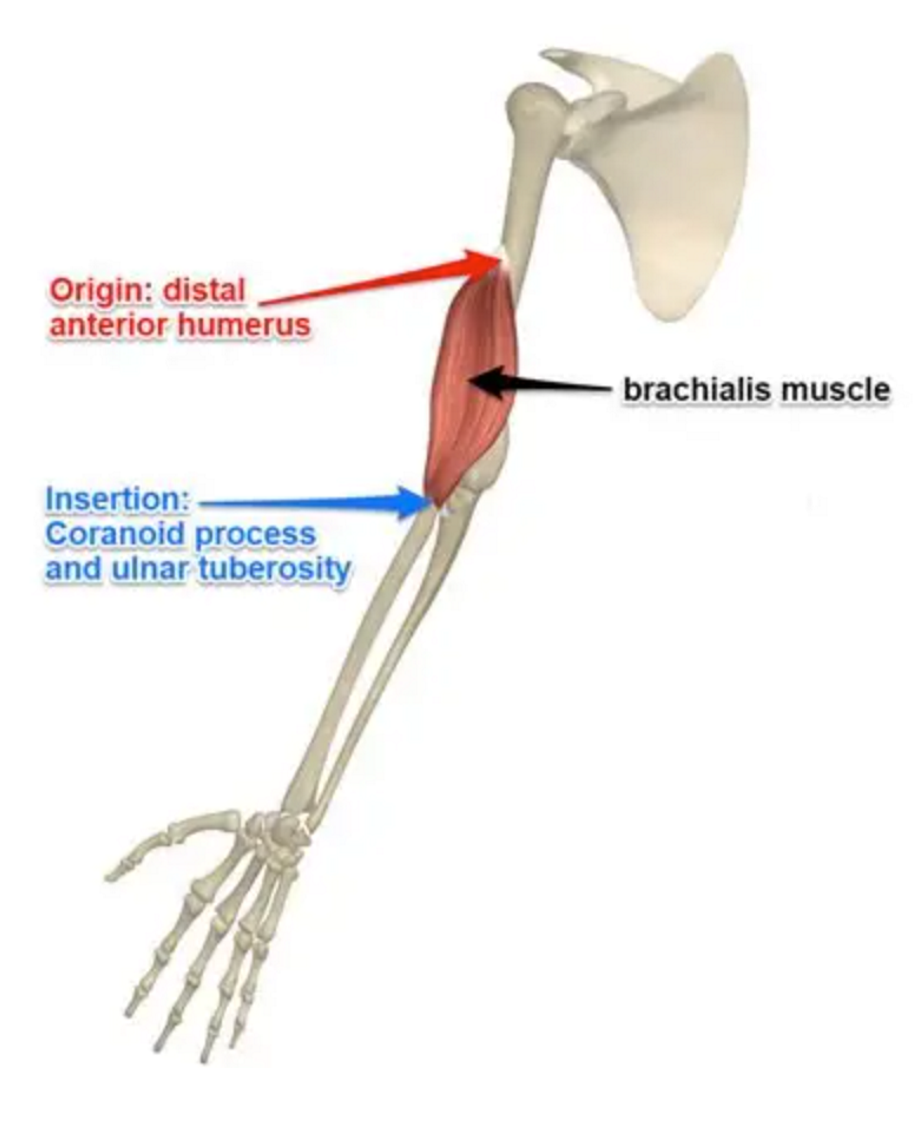
Brachialis
Front of upper arm
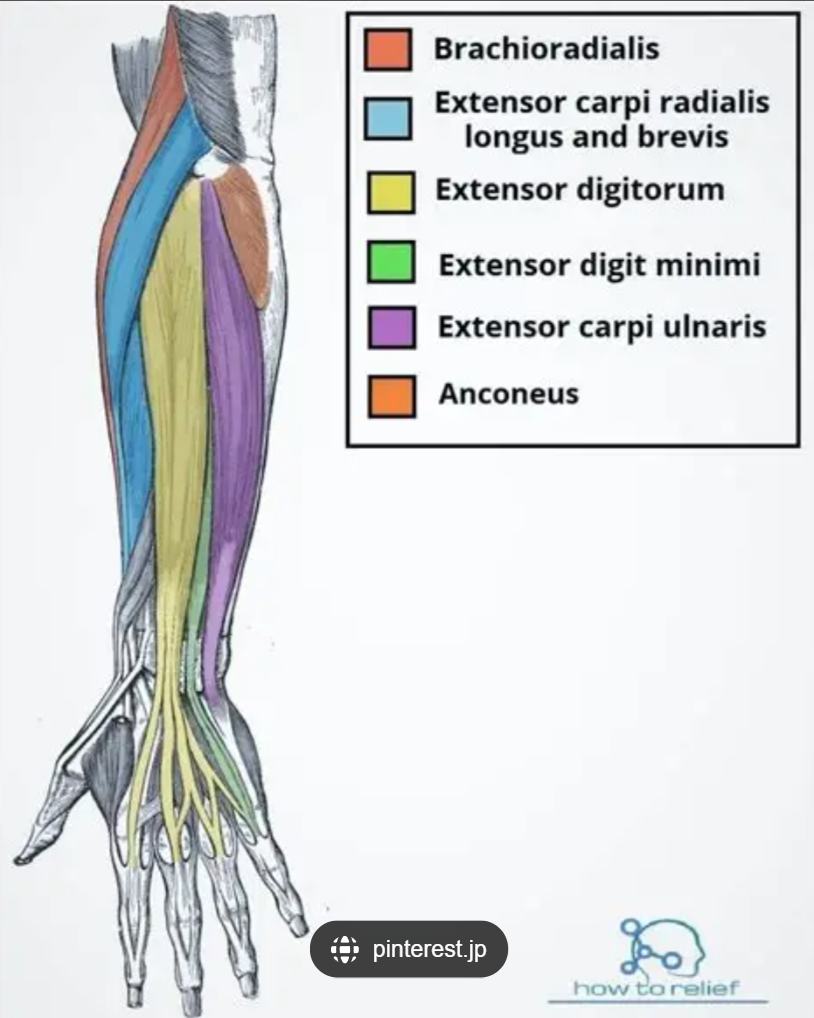
Brachioradialis
Front of upper arm
Neutral or slight flexion
Wrist ready for paddle catch
Trunk extension and rotation toward the paddle
Pulling power from core
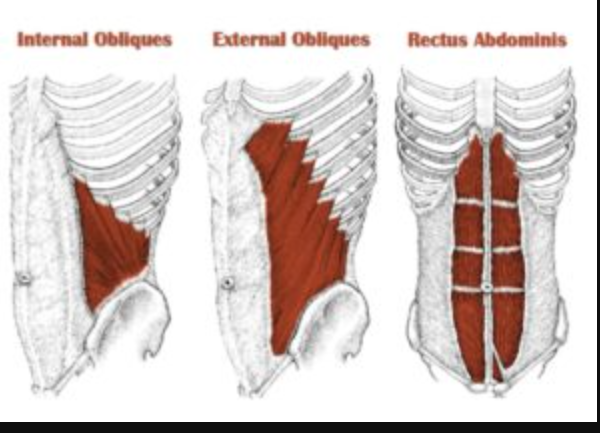
External obliques
Back + oblique twist
Shoulder flexion with slight external rotation
Pulling forward
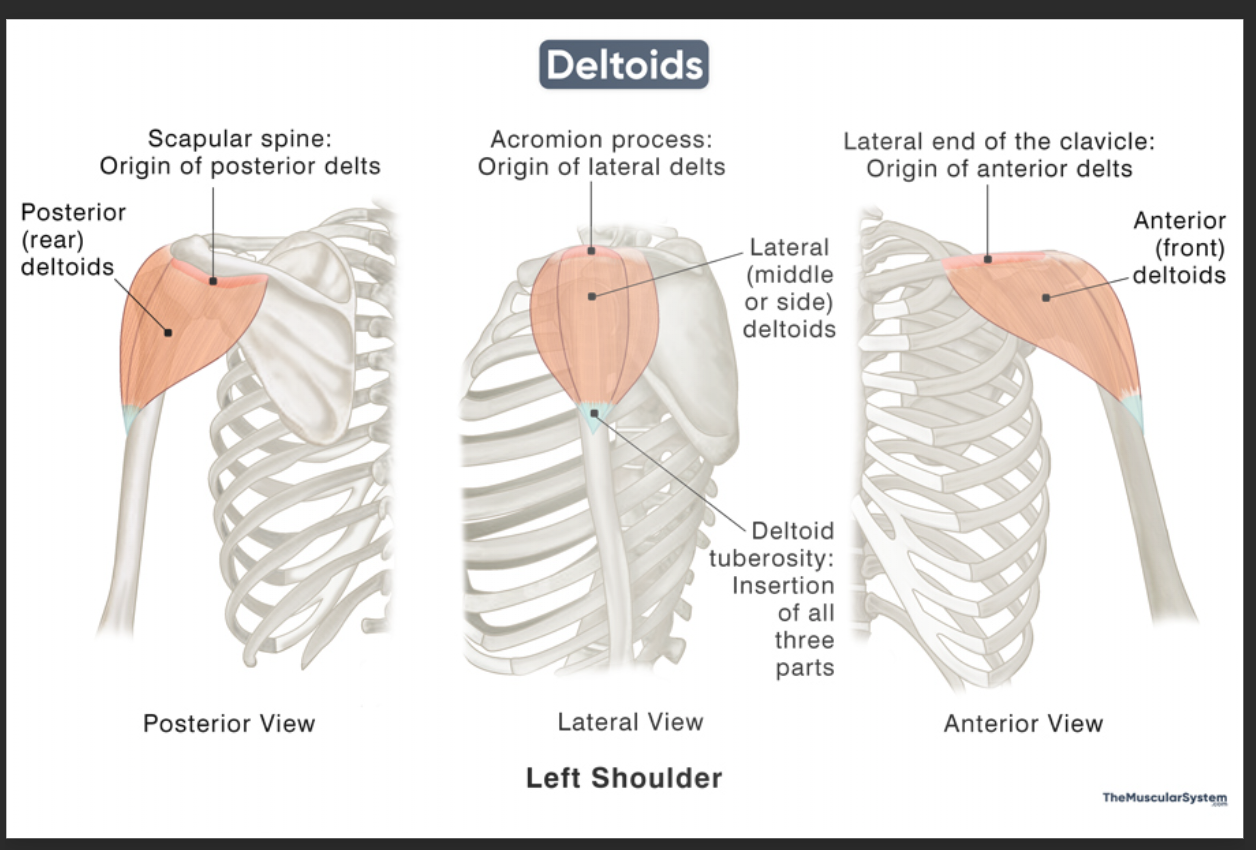
Anterior deltoid
Front of shoulder
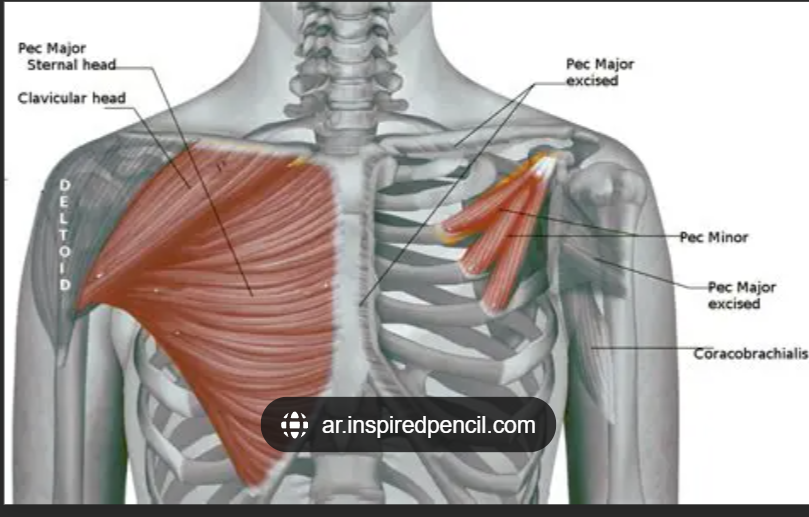
Pectoralis major (clavicular head)
Front of shoulder
Elbow flexion maintained
Pulling arm toward body
Neutral to slight extension
Keep paddle aligned
Trunk flexion/extension to return to neutral
Reset position
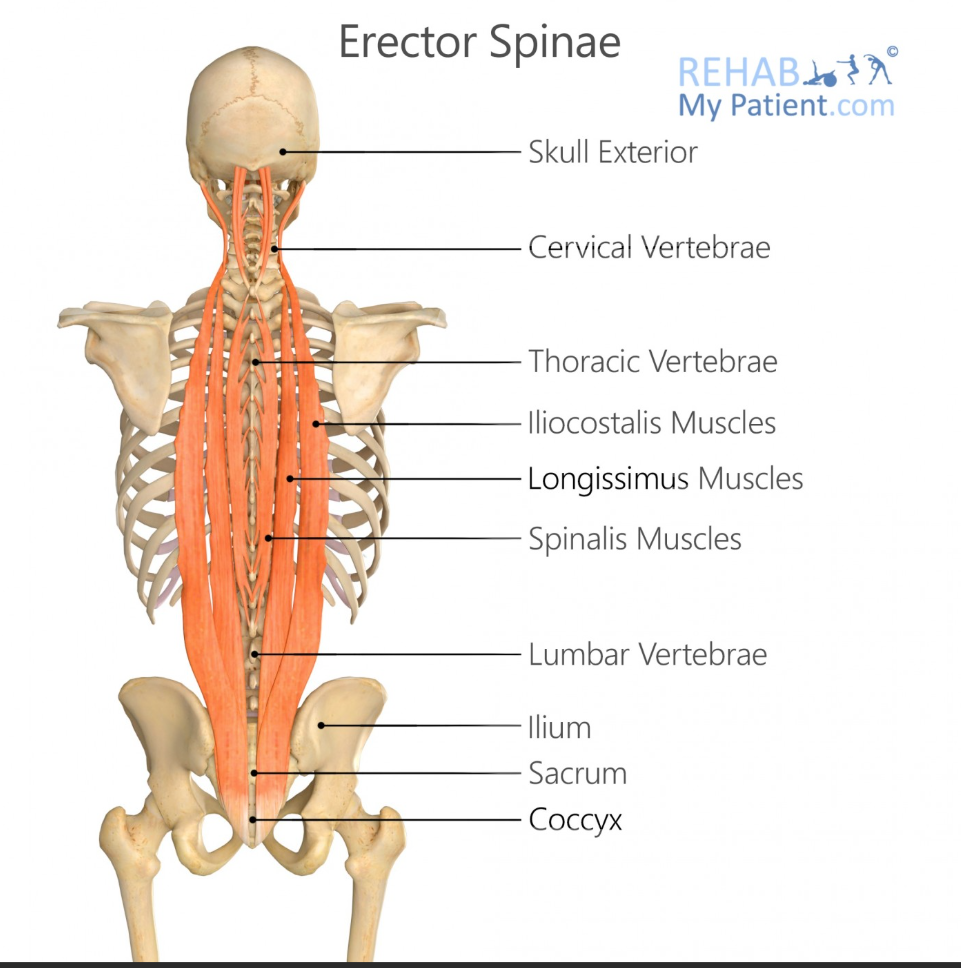
Erector spinae (recovery phase)
Stabilize and control
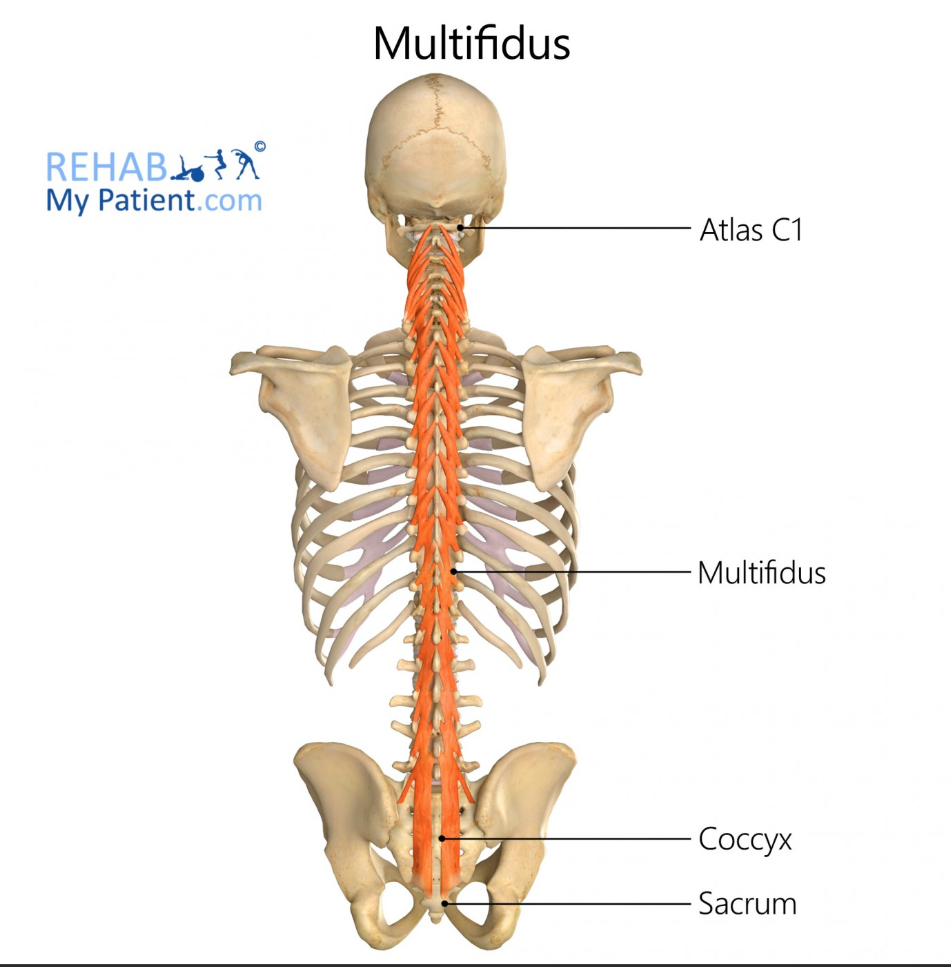
Multifidus (recovery phase)
Stabilize and control
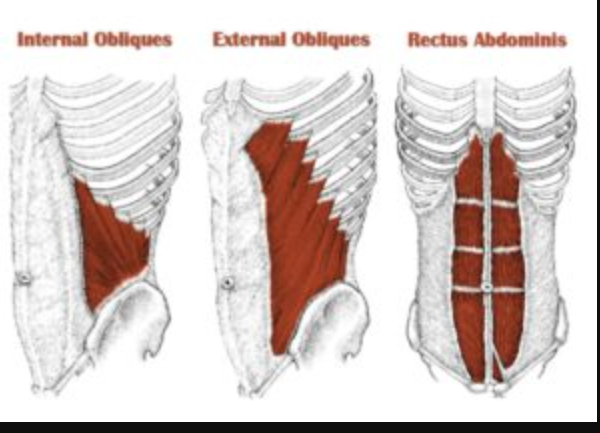
Obliques (recovery phase)
Stabilize and control
Shoulder flexion to return arm forward
Bring arm back to start
Extension to prepare for next catch
Straighten arm
Controlled flexion to neutral
Position for next paddle stroke
Coordination and proprioception
Knowing where limbs are
Fatigue effects on lifting
Reduced strength, slower reaction, higher injury risk
Environmental factors affecting squatting
Floor surface, space, distractions
Task factors affecting squatting efficiency
Repetition, load (child's weight), posture
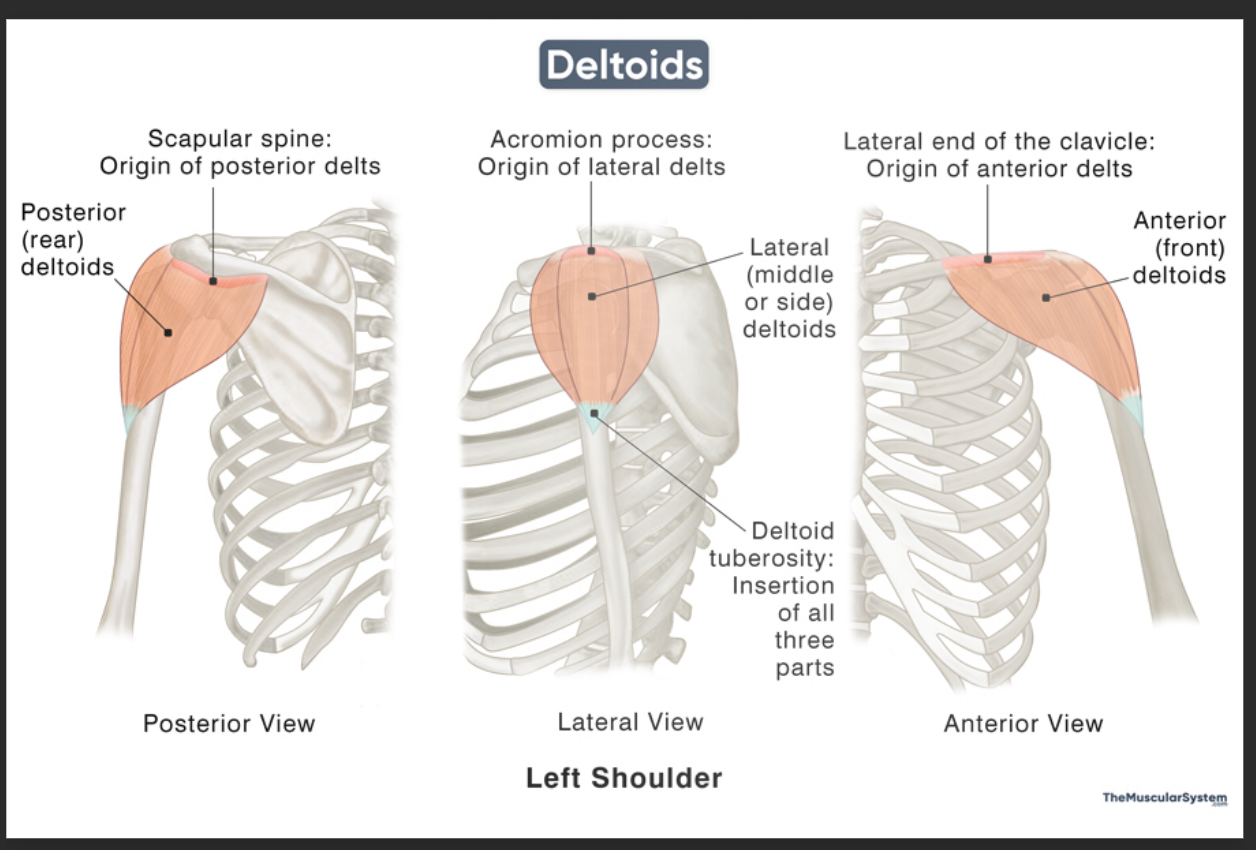
Anterior deltoid origin
Lateral 1/3 of clavicle
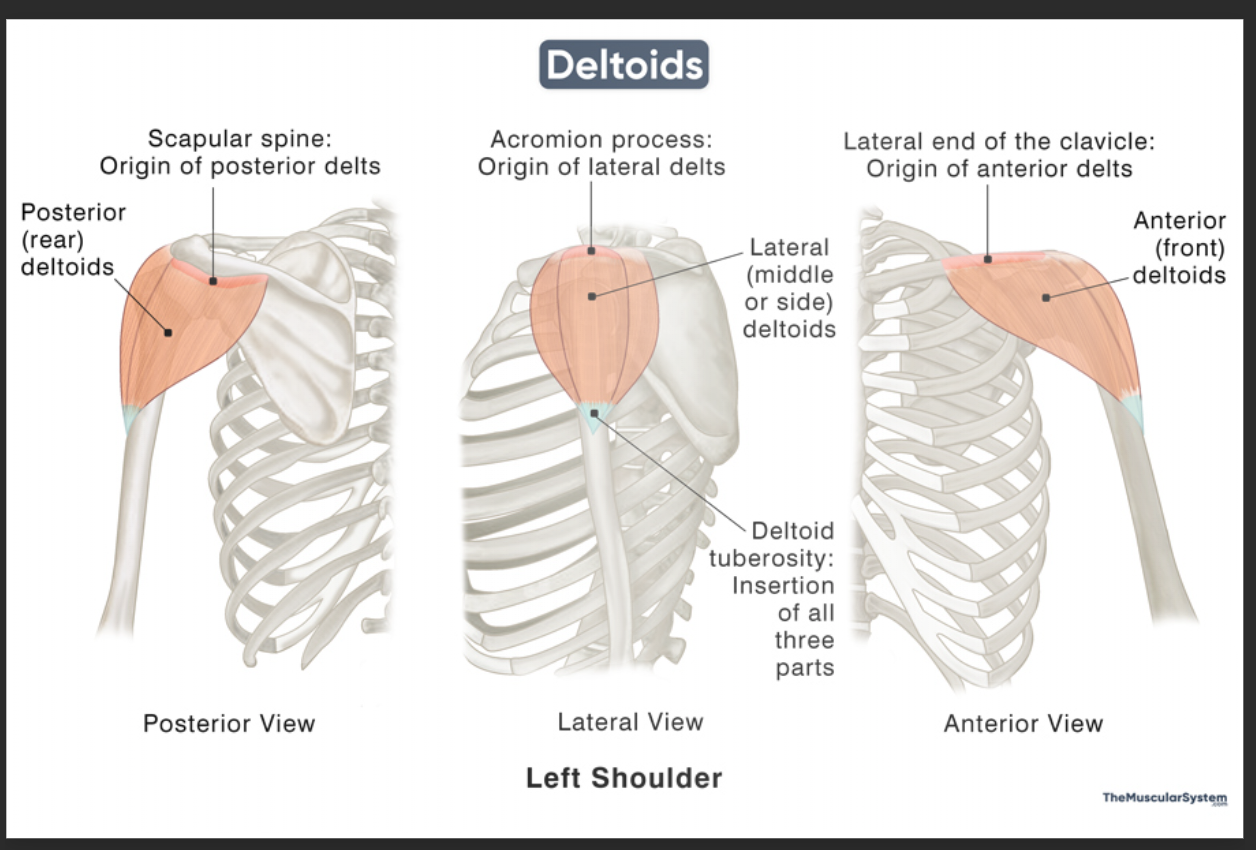
Anterior deltoid insertion
Deltoid tuberosity of humerus
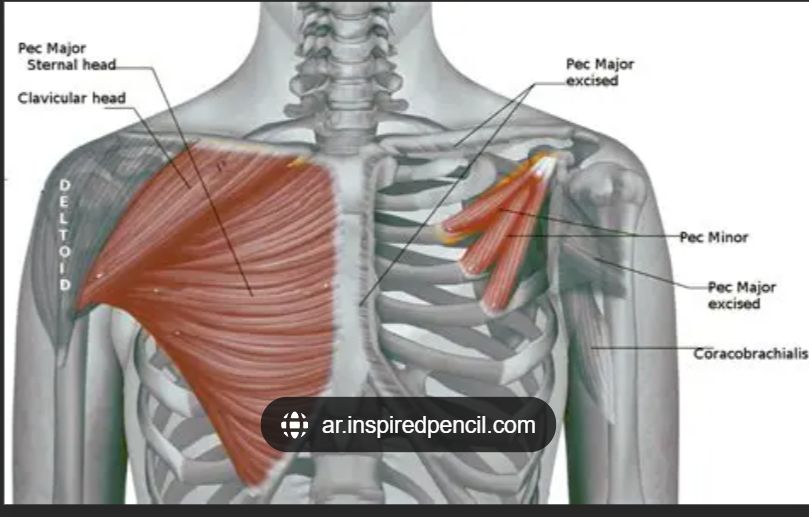
Pectoralis major (clavicular head) origin
Medial 1/2 of clavicle
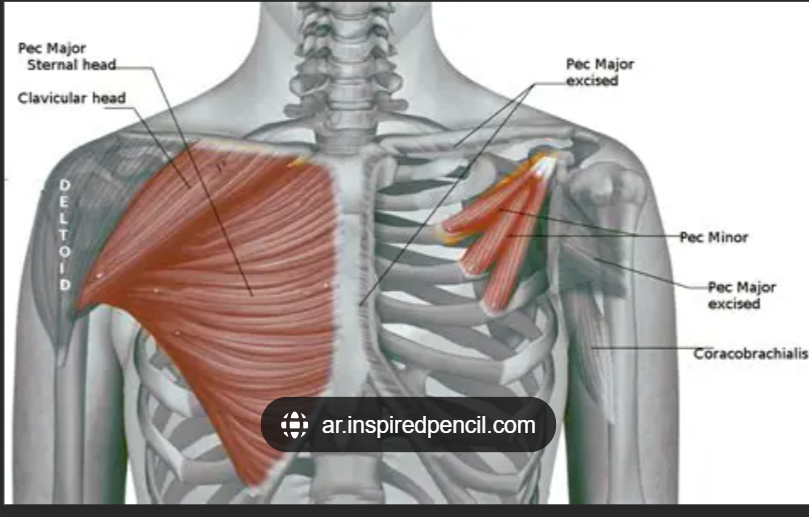
Pectoralis major insertion
Lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus
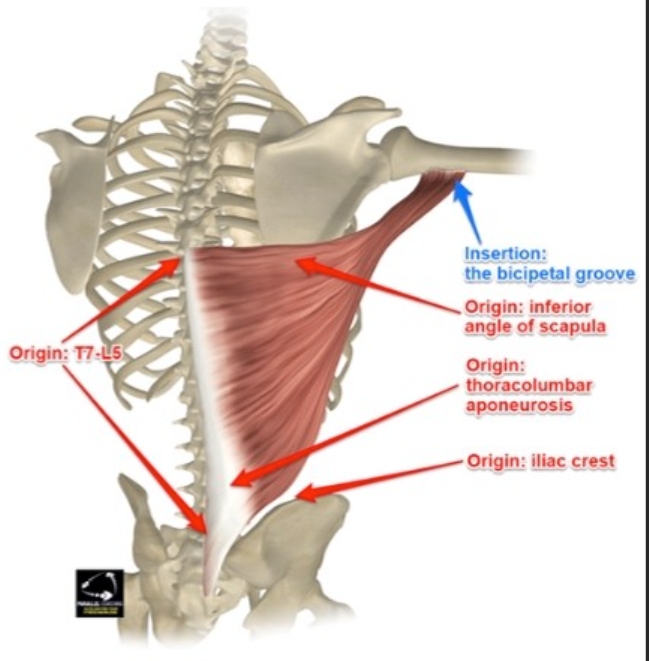
Latissimus dorsi origin
T7-L5 spinous processes, iliac crest, sacrum, lower ribs
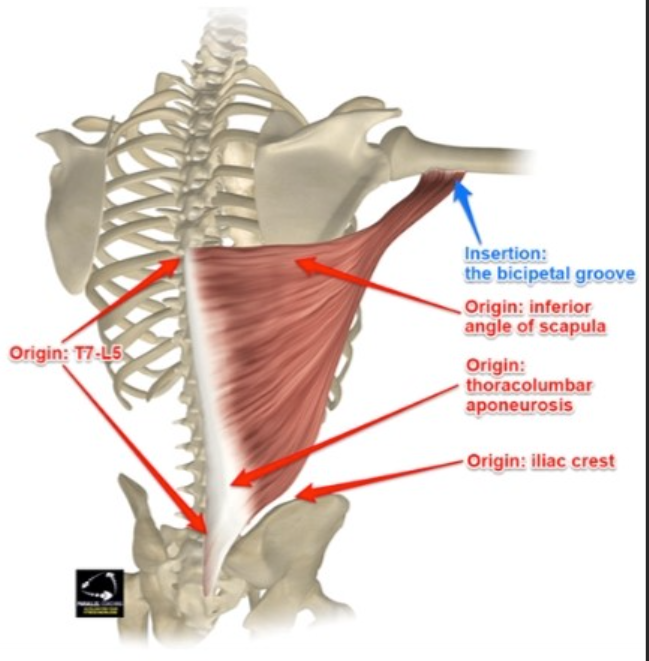
Latissimus dorsi insertion
Floor of bicipital groove of humerus
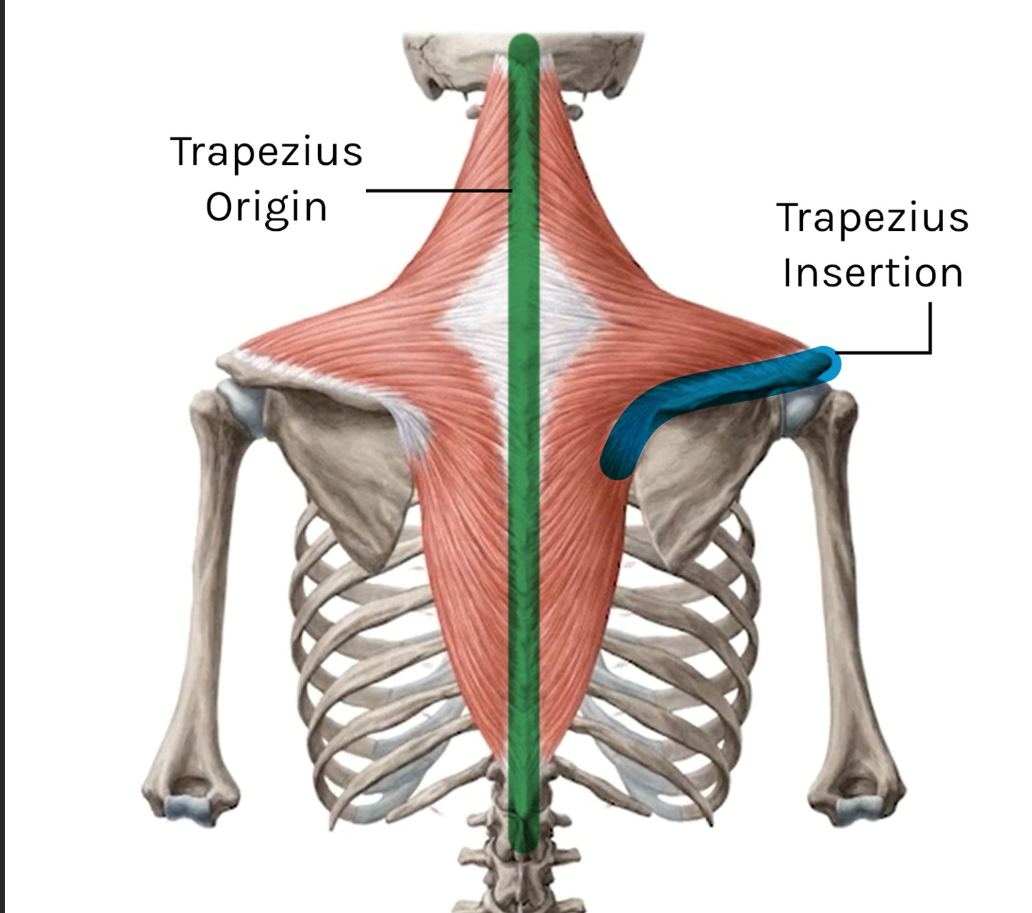
Trapezius (upper fibers) origin
External occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, C7 spinous process
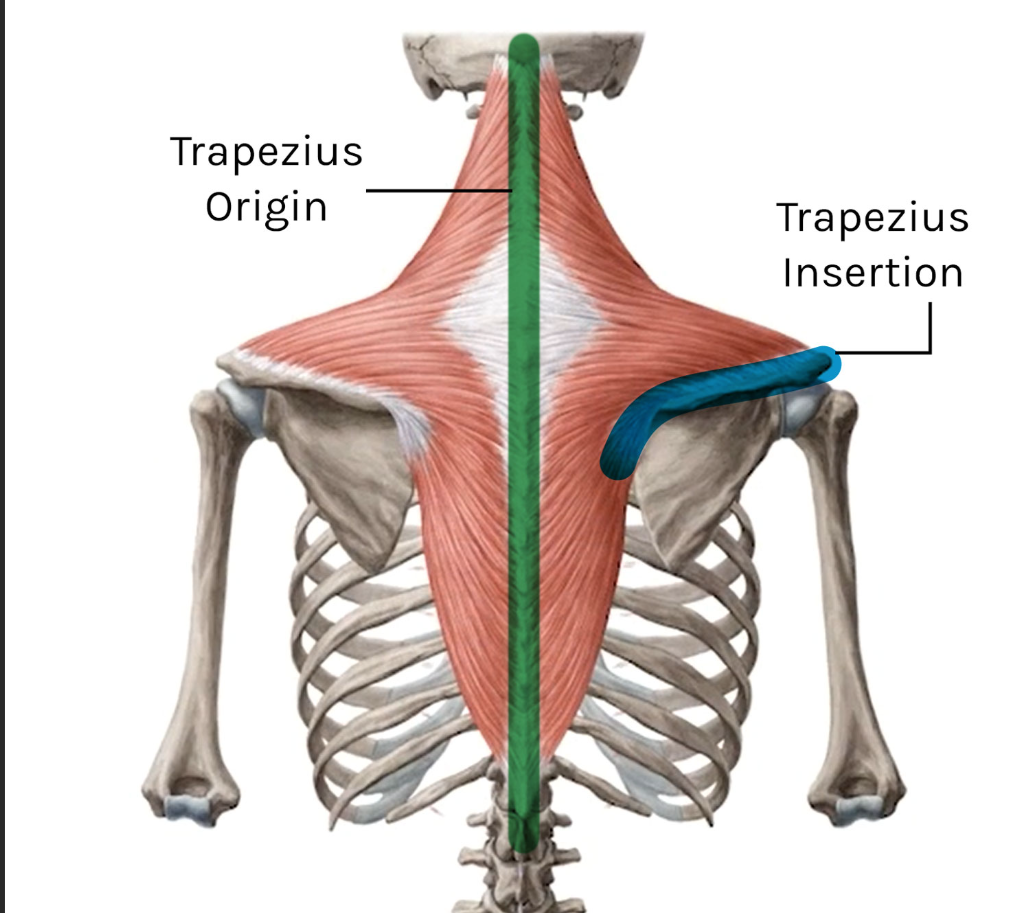
Trapezius insertion
Lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula
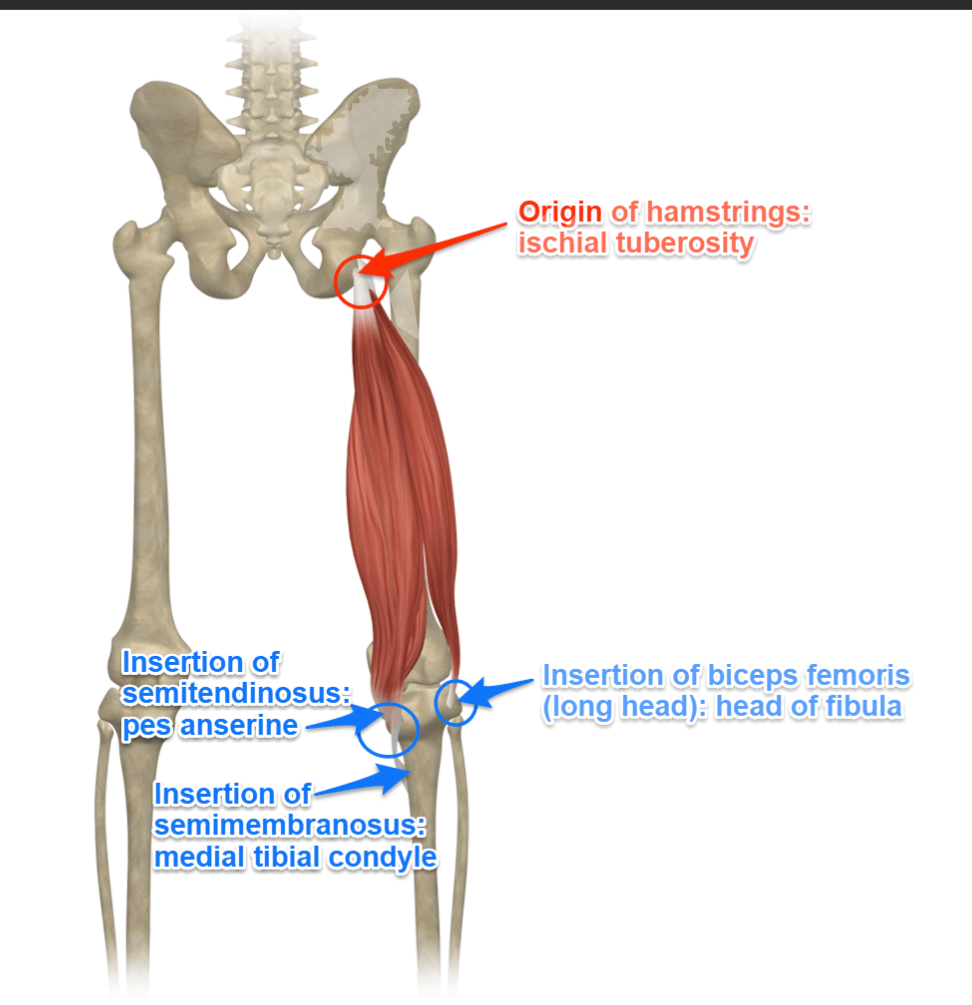
Biceps Femoris (Long Head)
Hamstring muscle
Biceps Femoris (Long Head) origin
Ischial tuberosity (of the pelvis)
Biceps Femoris (Long Head) insertion
Head of fibula
Semitendinosus
Hamstring muscle
Semitendinosus origin
Ischial tuberosity
Semitendinosus insertion
Medial surface of tibia (part of pes anserinus with gracilis + sartorius)
Semimembranosus
Hamstring muscle
Semimembranosus origin
Ischial tuberosity
Semimembranosus insertion
Posterior surface of medial tibial condyle