Physics Electricity GCSE EDEXEL
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what is current
the rate of flow of charge
what is voltage
the energy per unit charge
what is resistance
How hard it is for current to flow through a component
formula for current
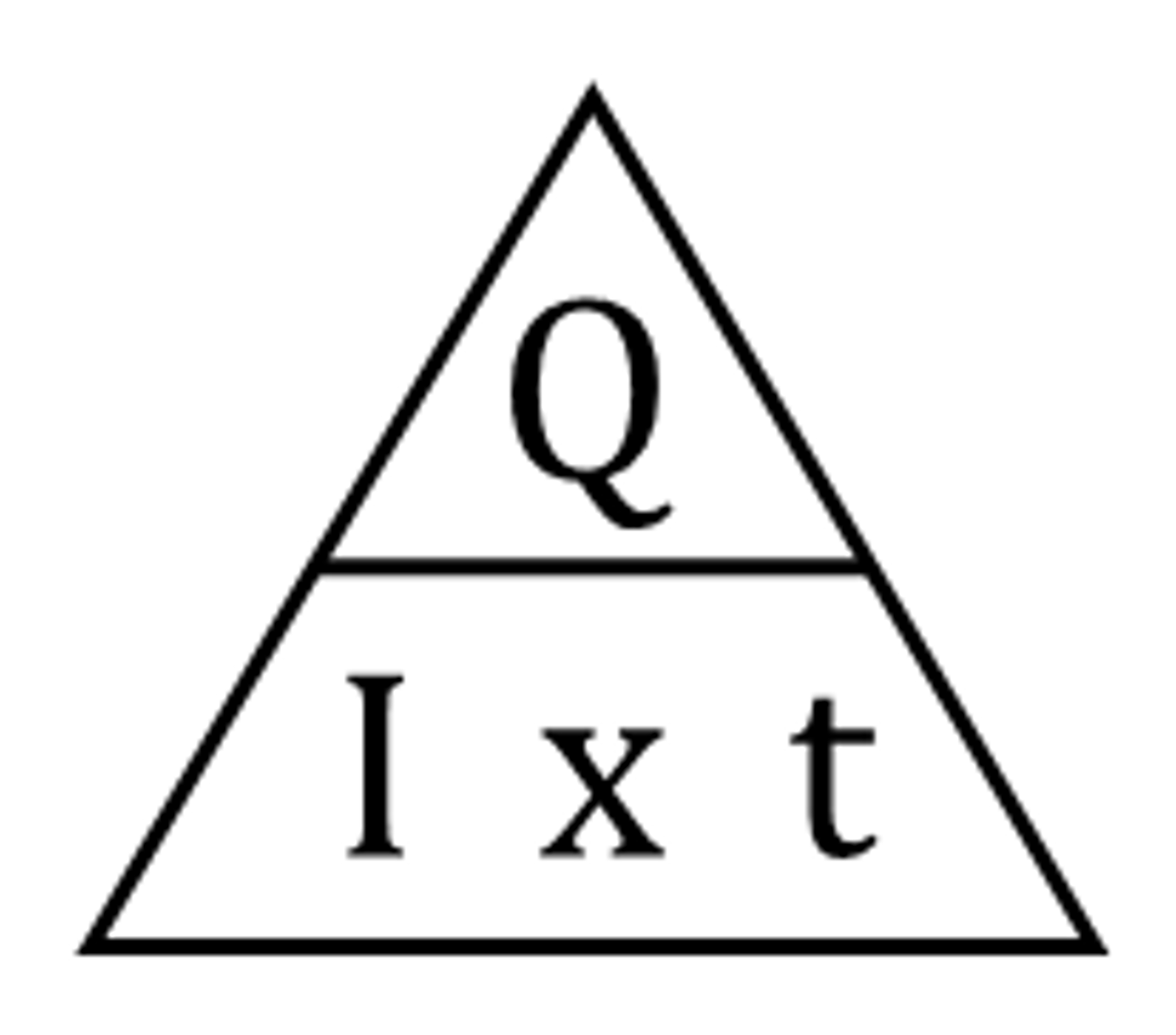
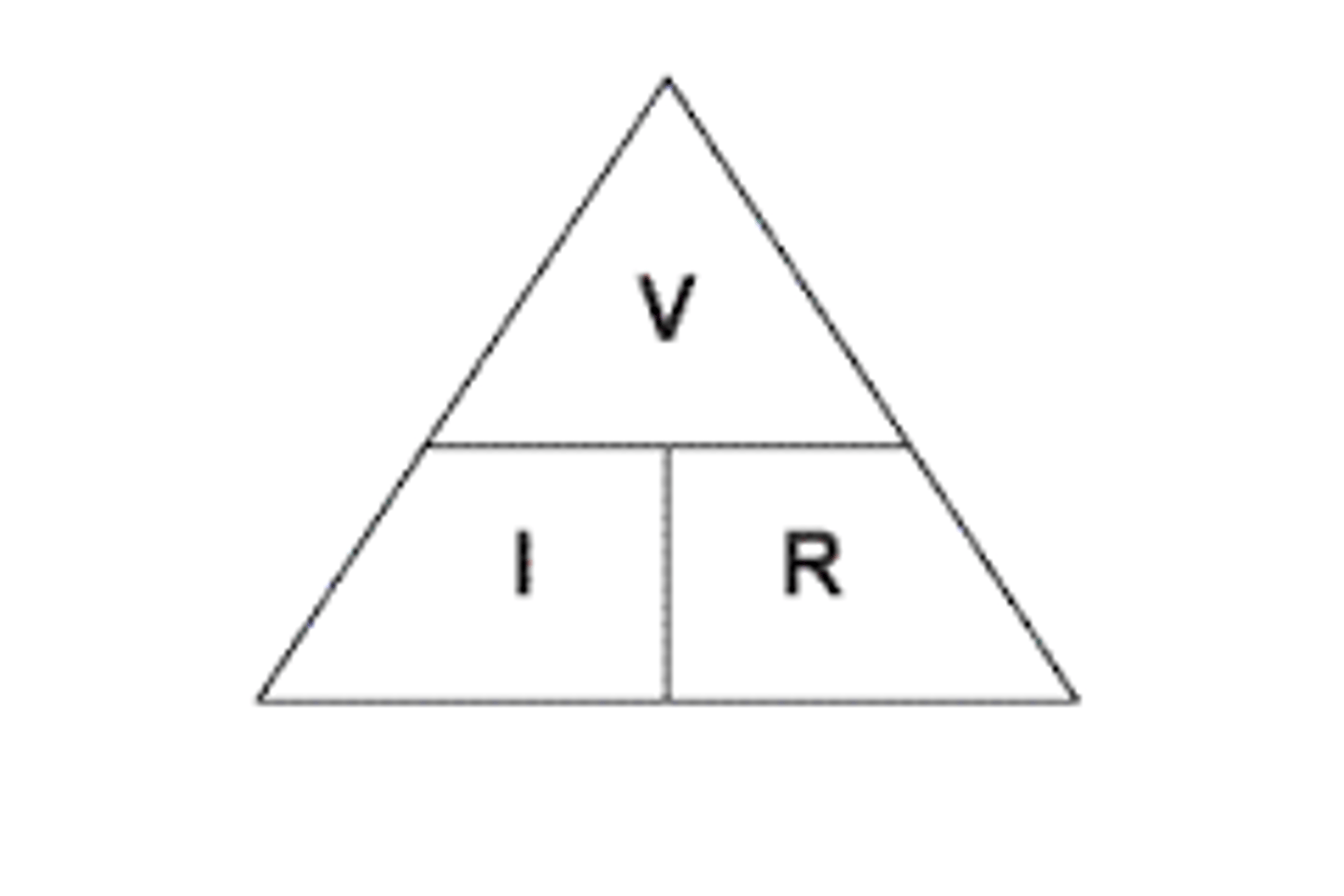
formula for voltage
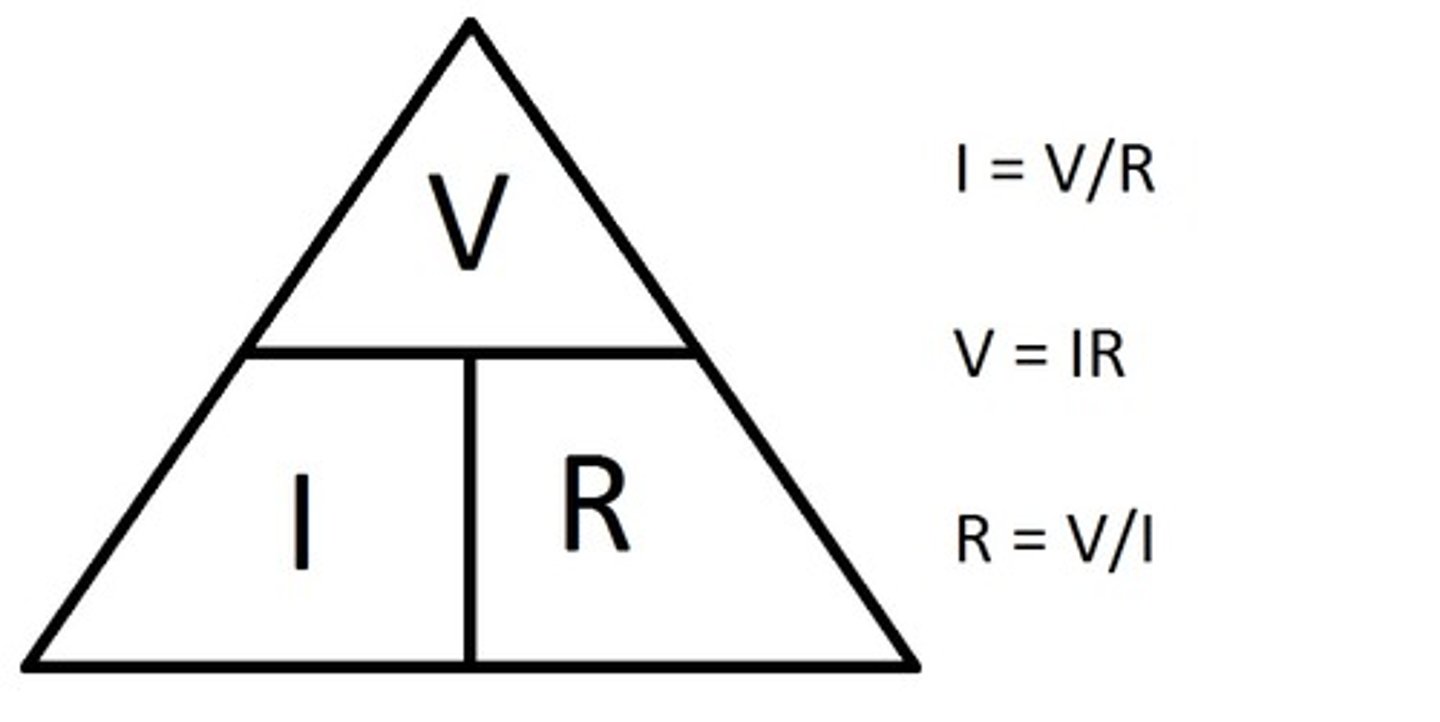
formula for resistance
formula for adding resistance
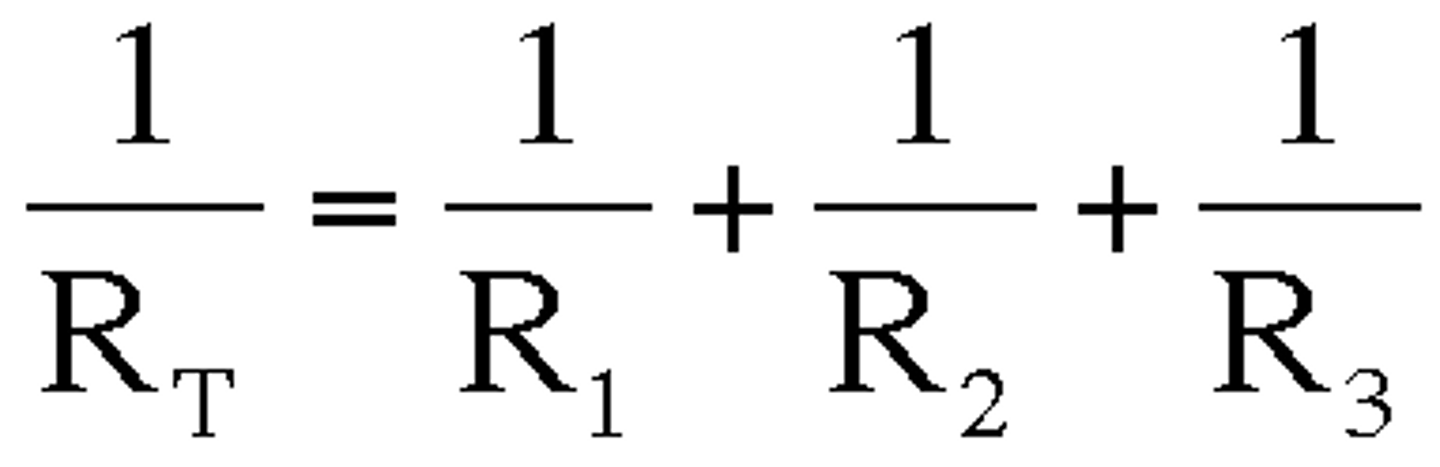
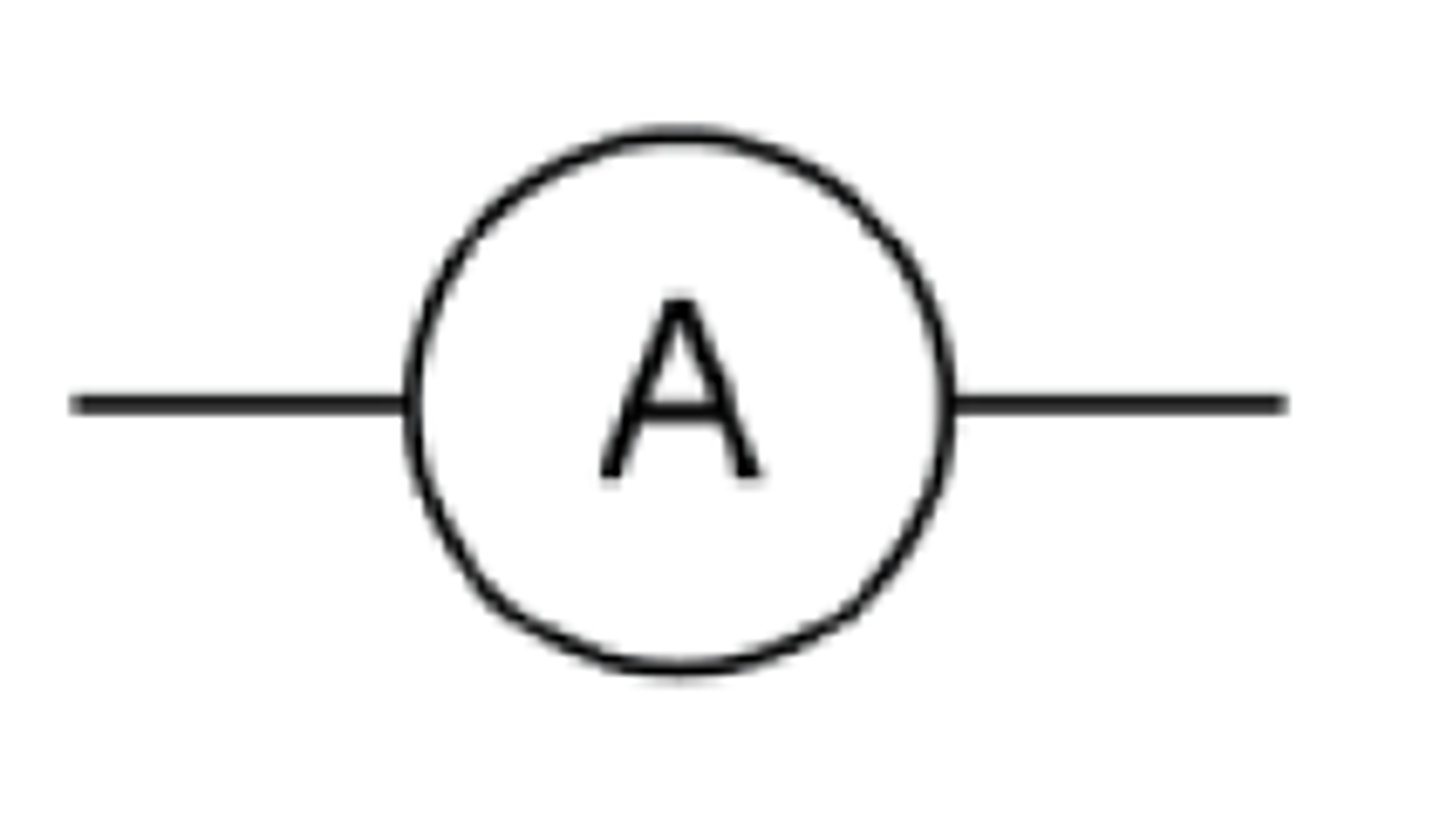
a ammeter
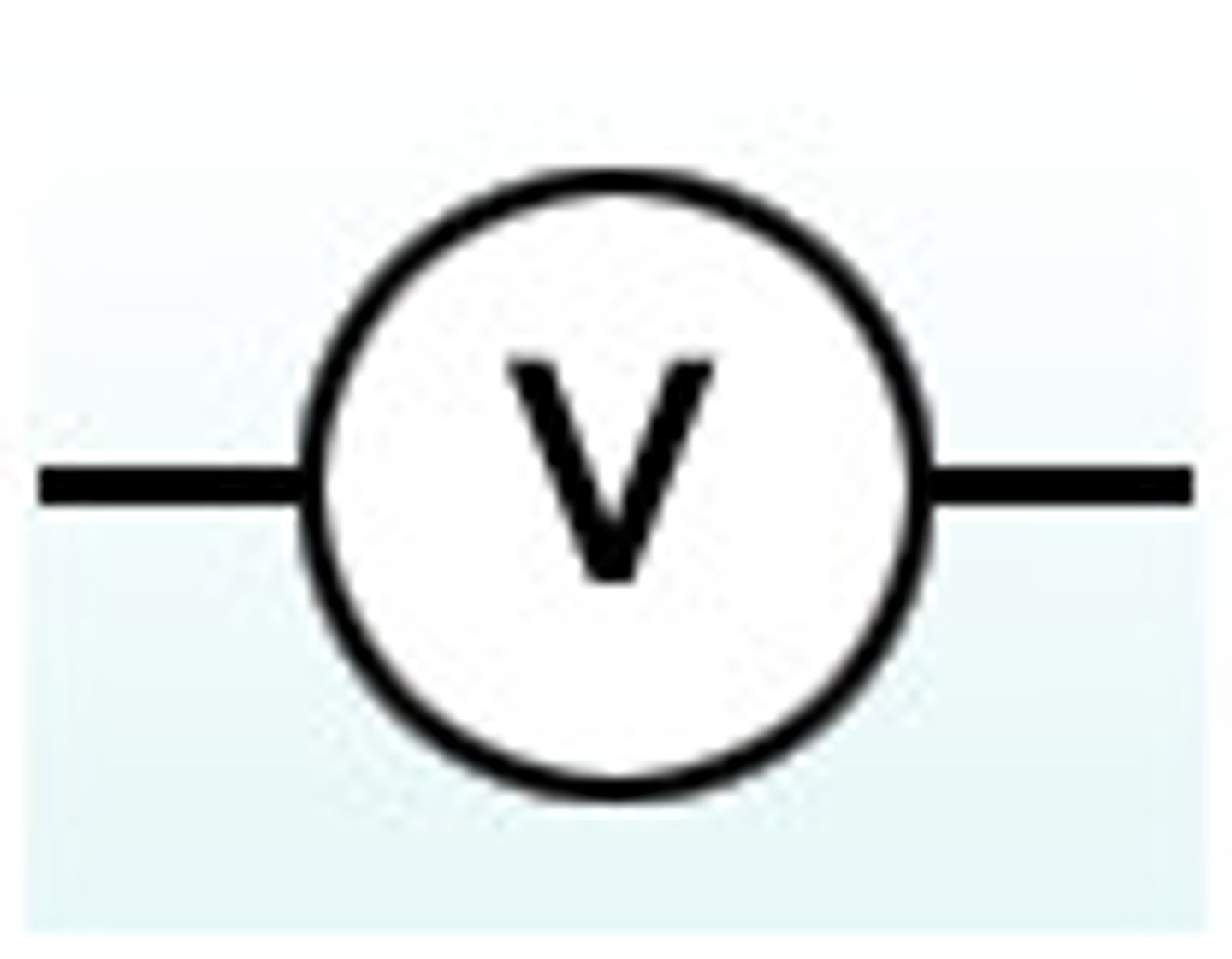
a voltmeter
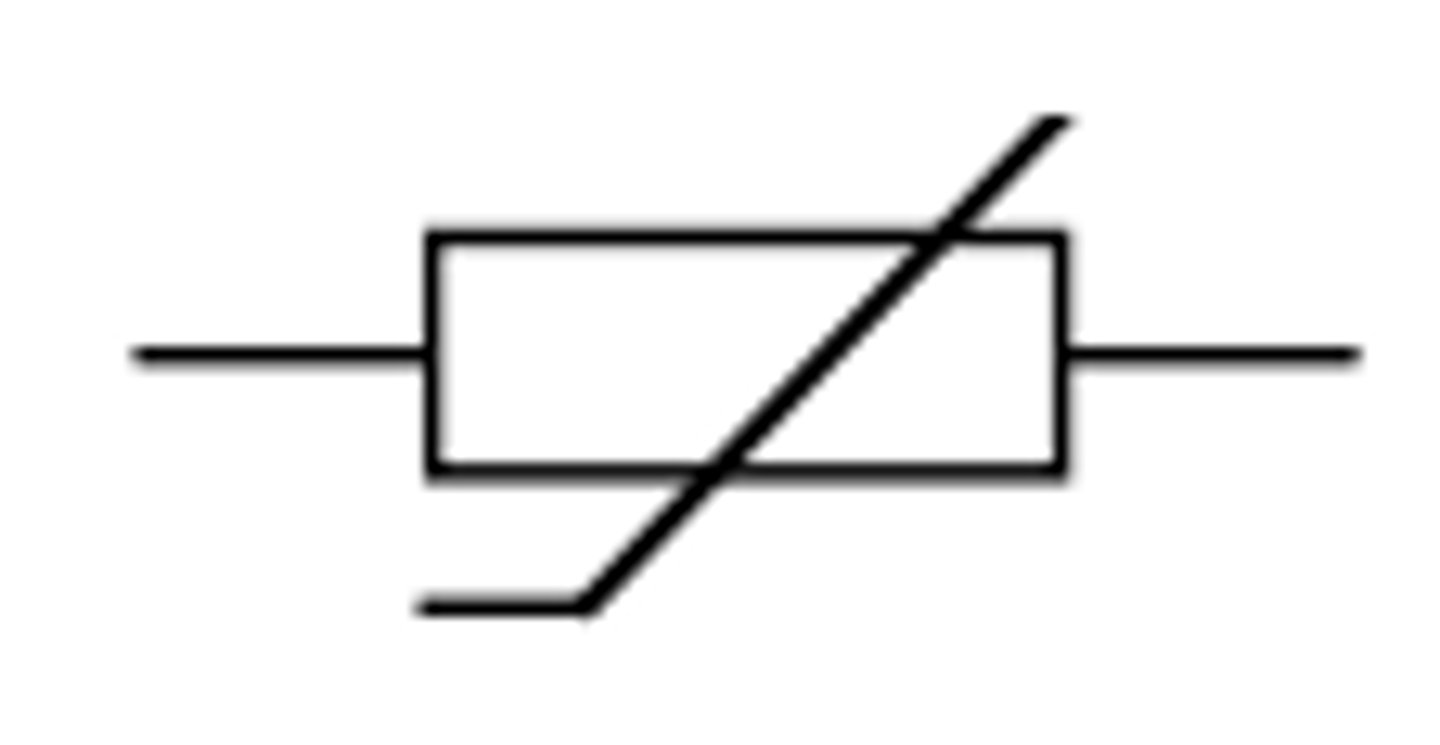
a thermistor
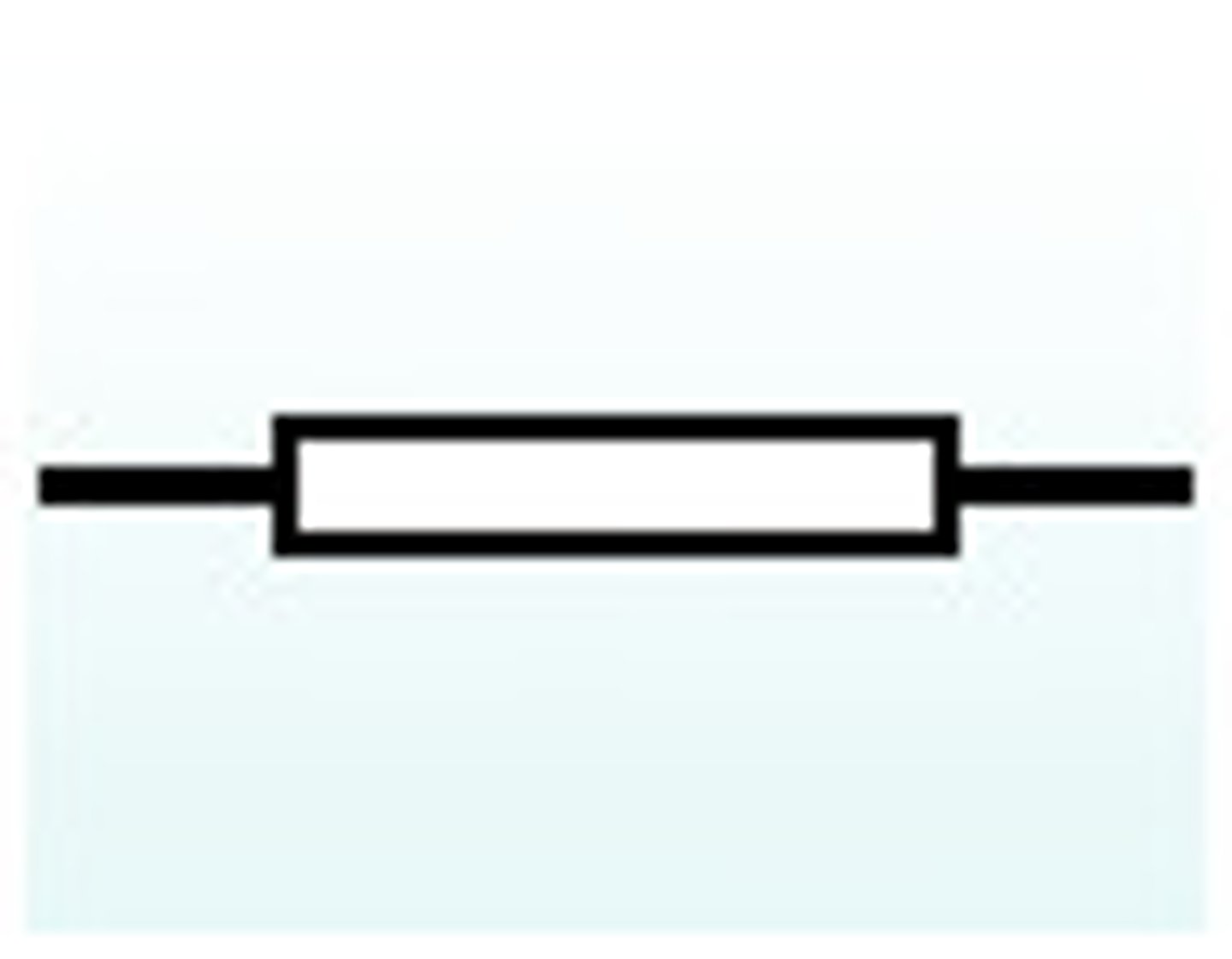
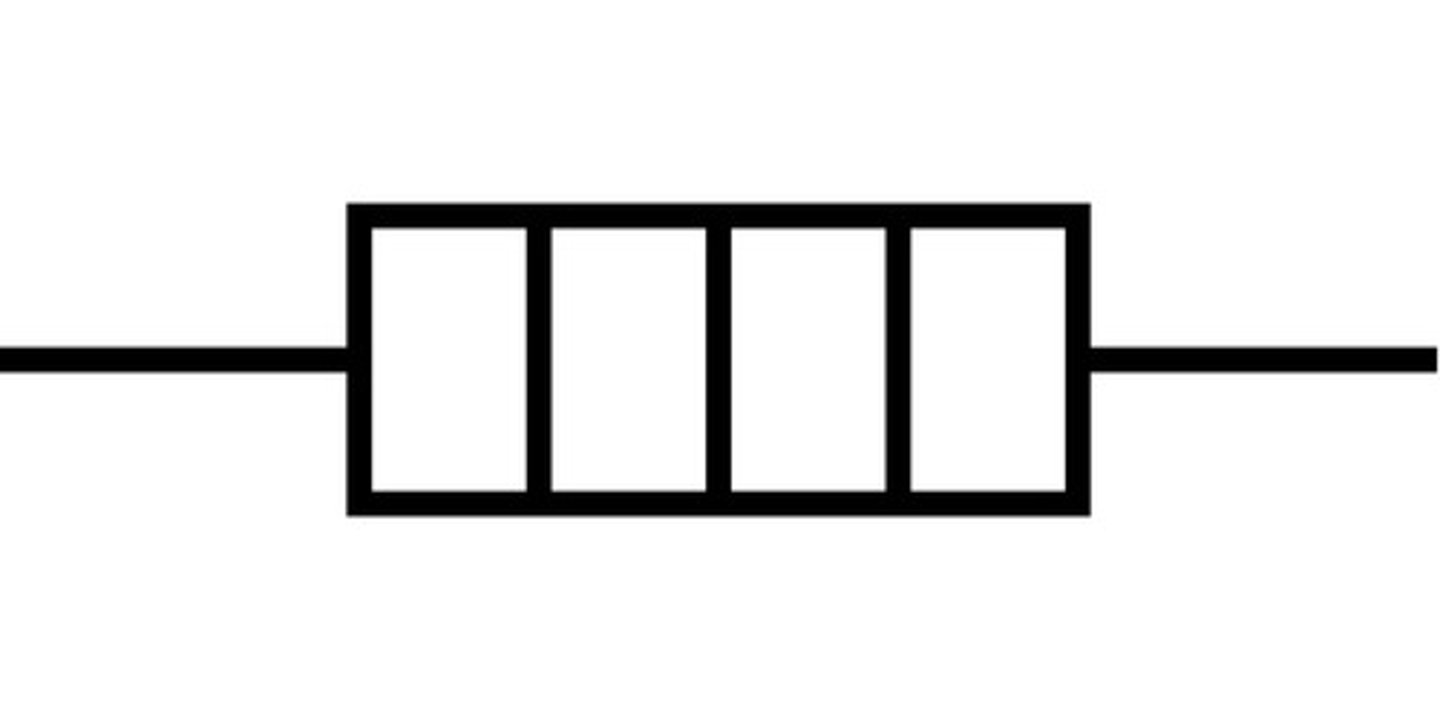
a resistor
a lamp
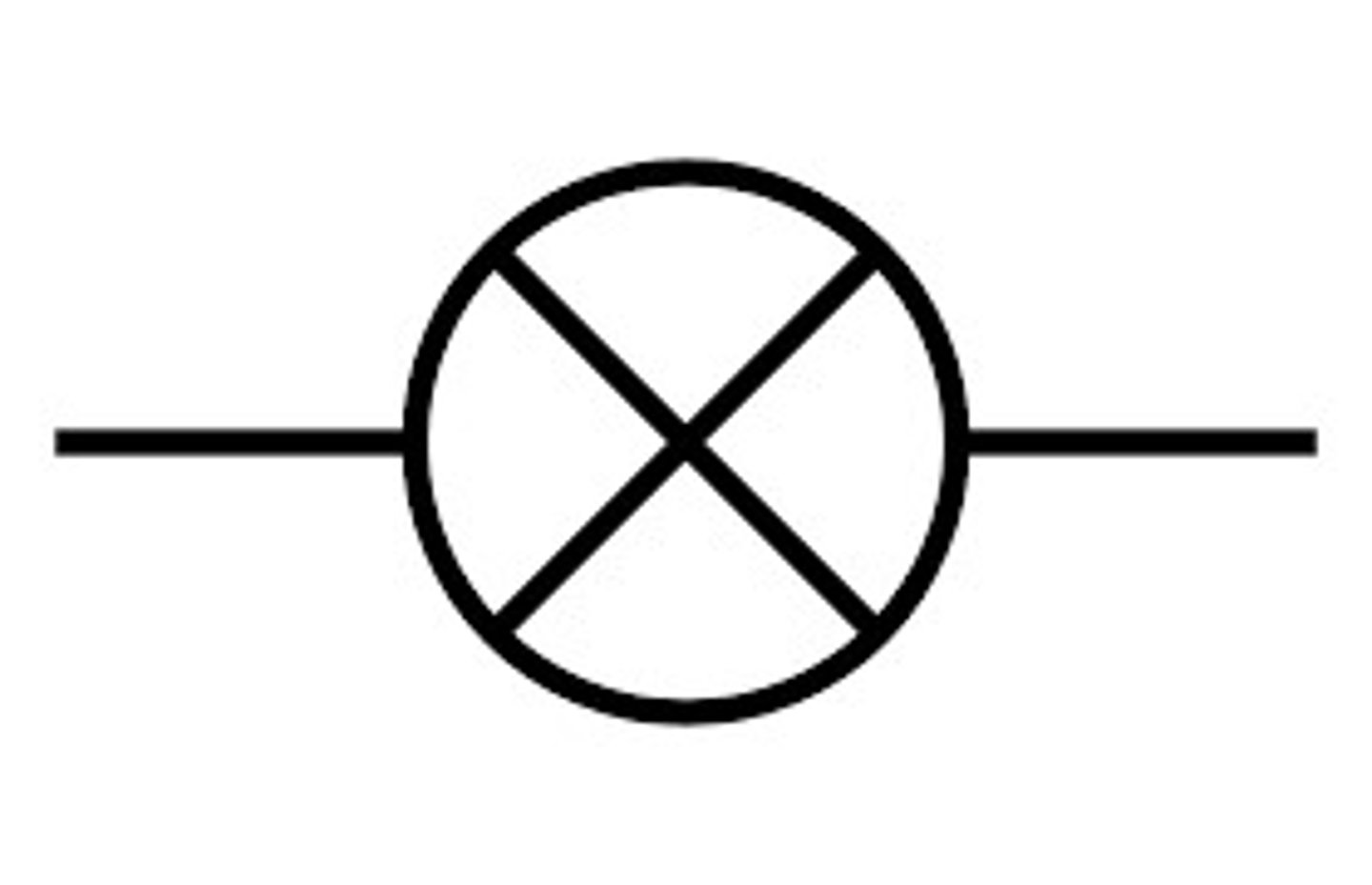
a bulb
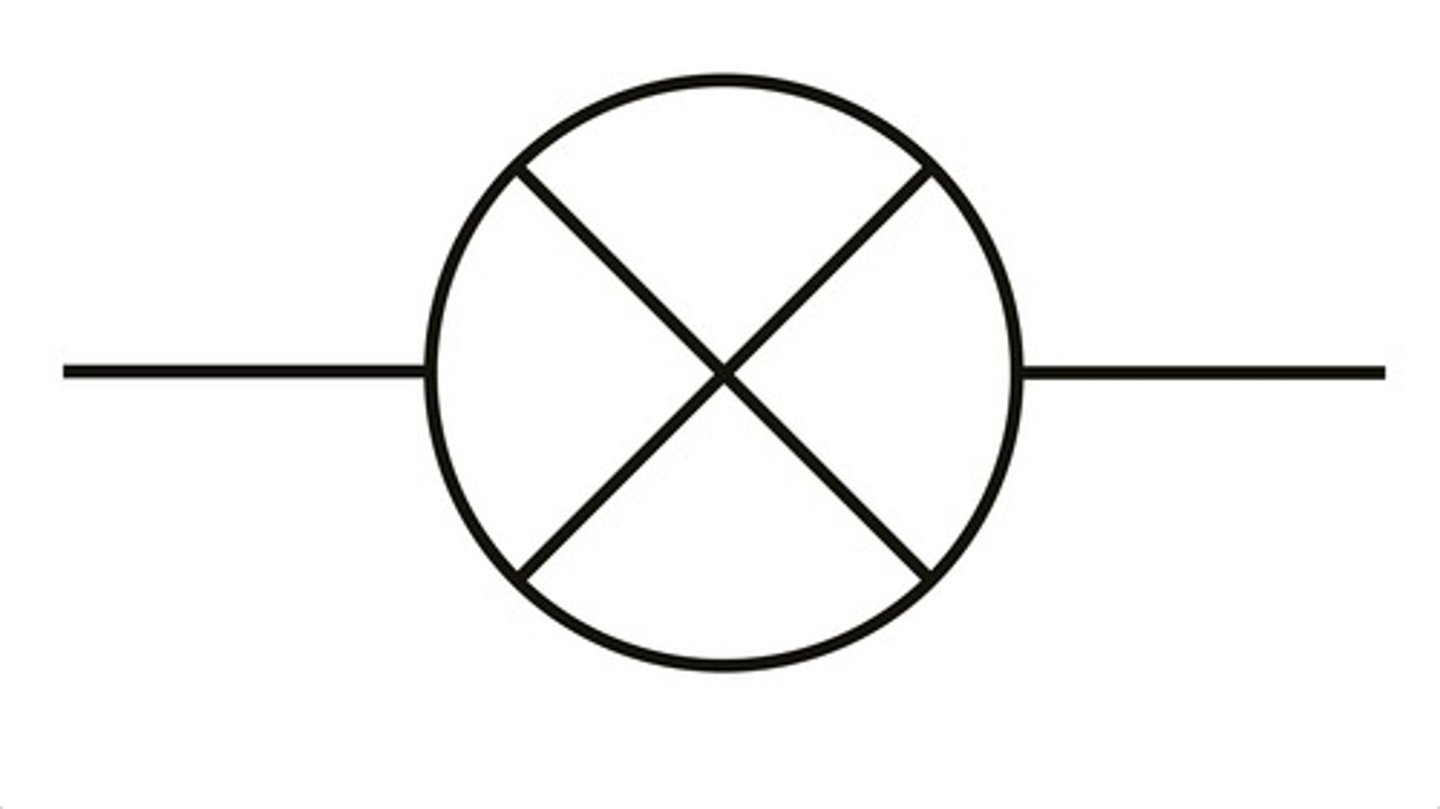
a led
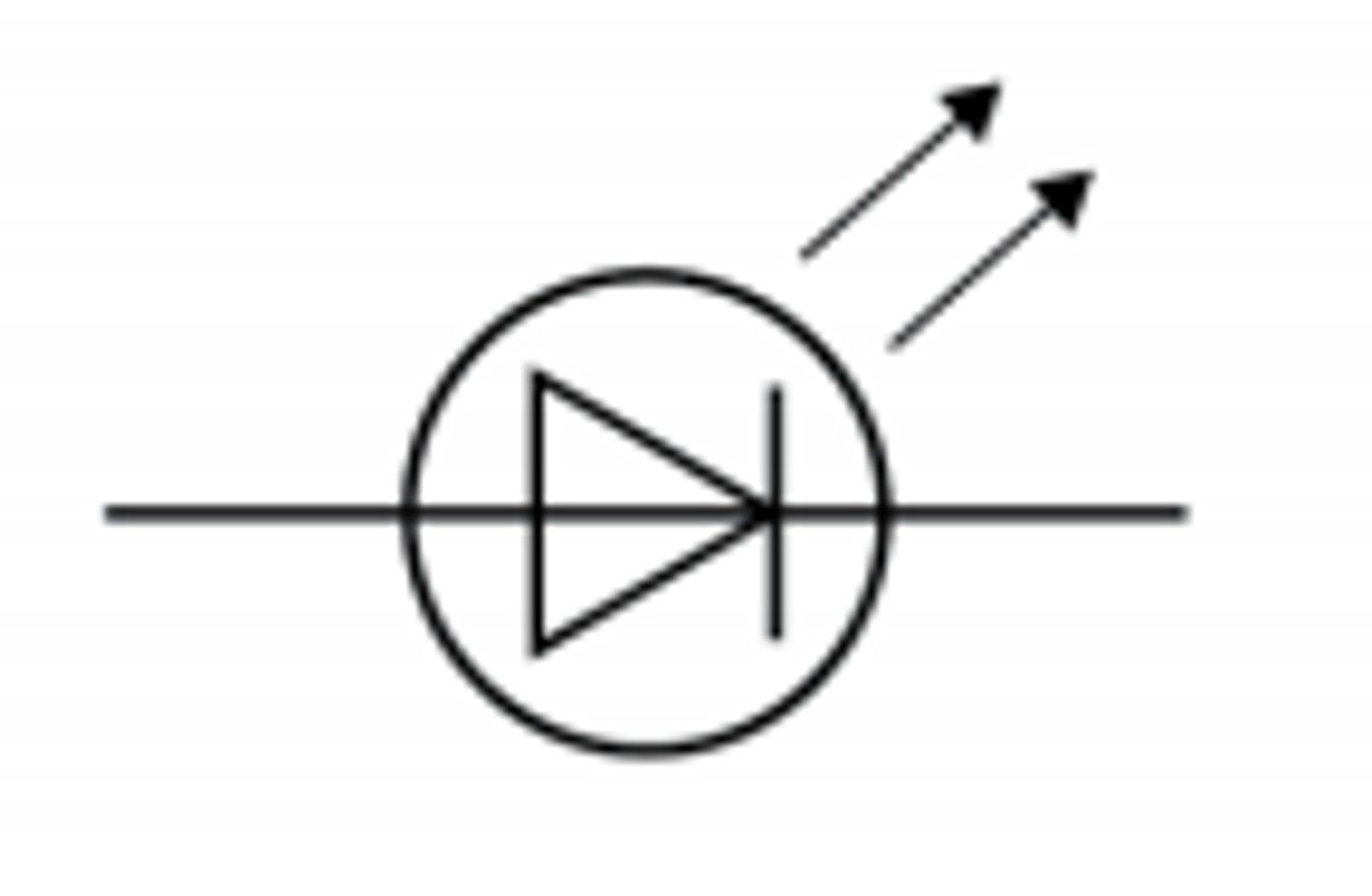
a diode
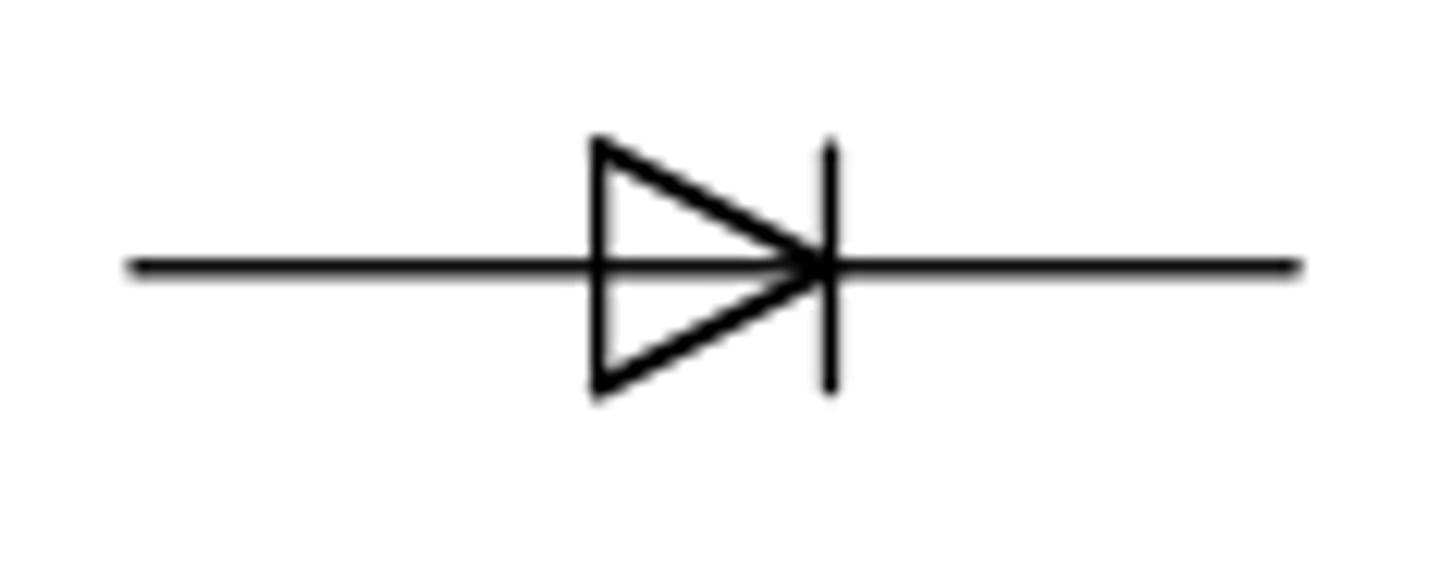
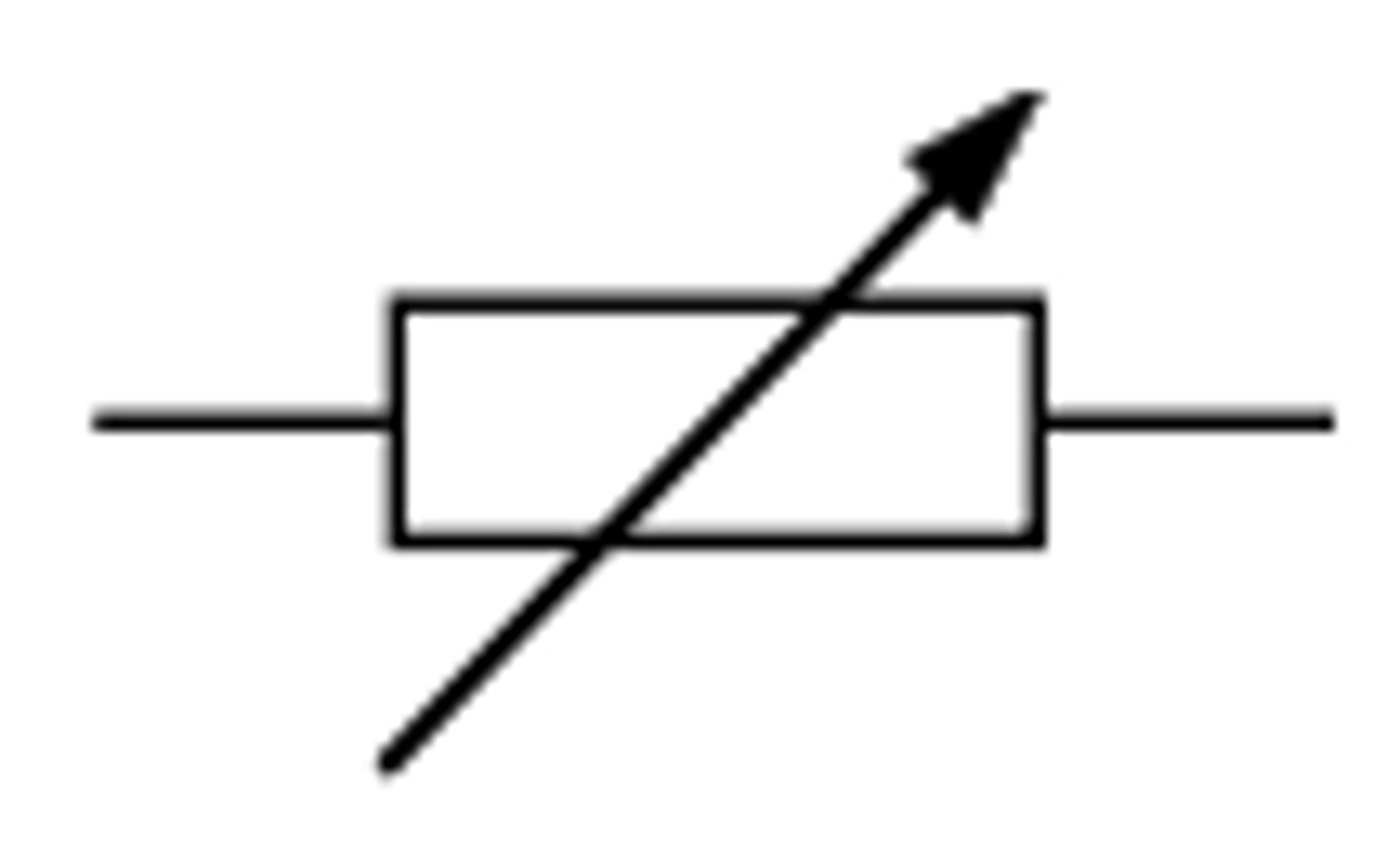
a variable resistor
a battery cell
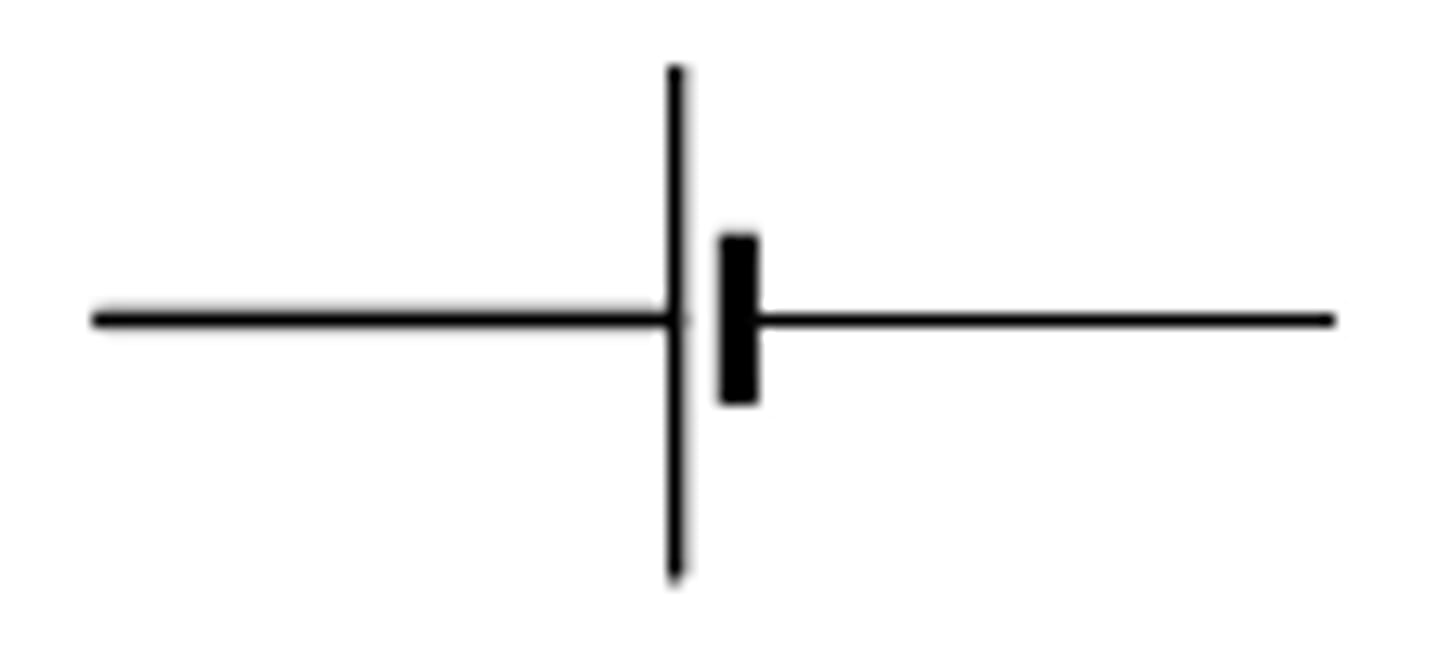
a battery

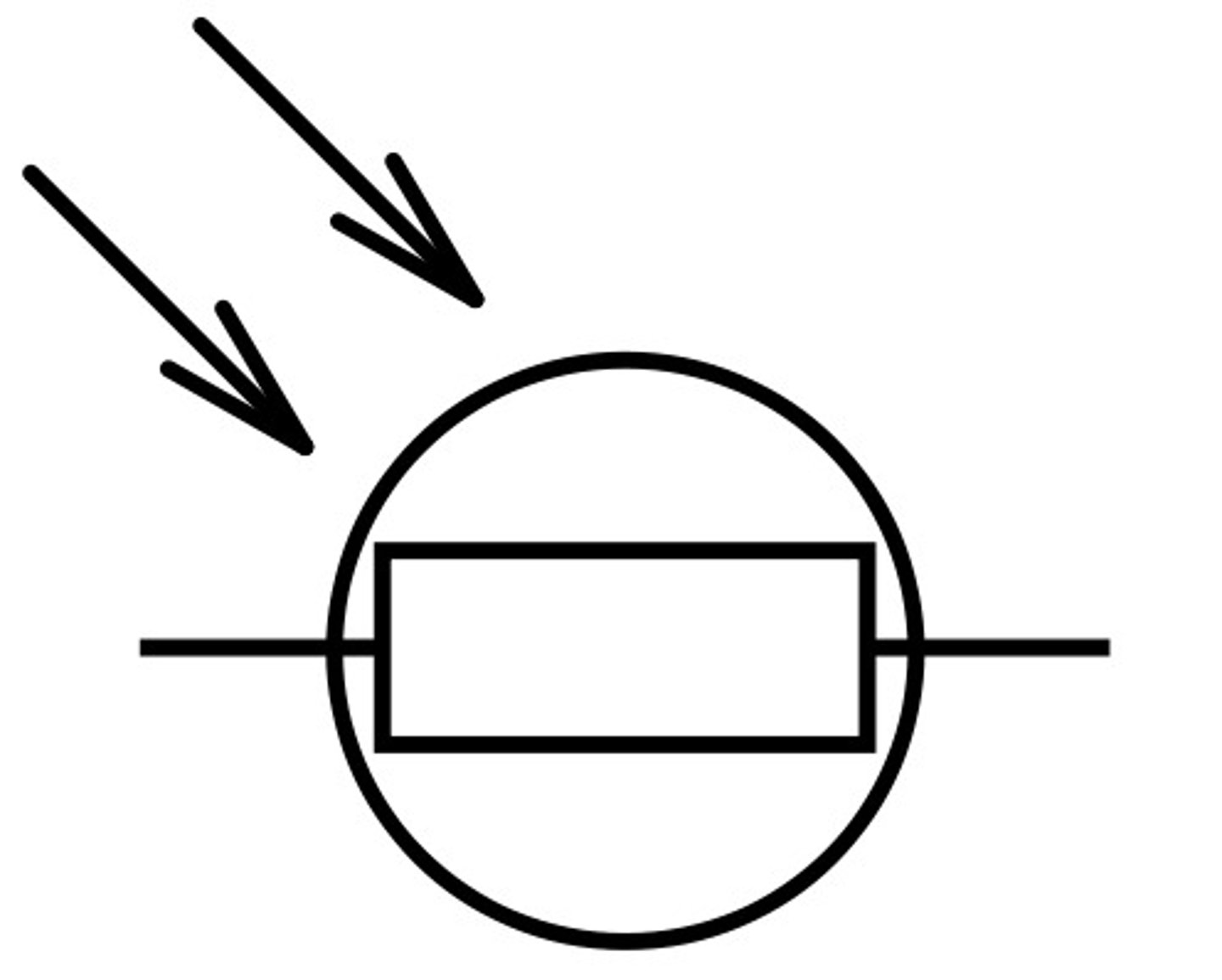
a ldr
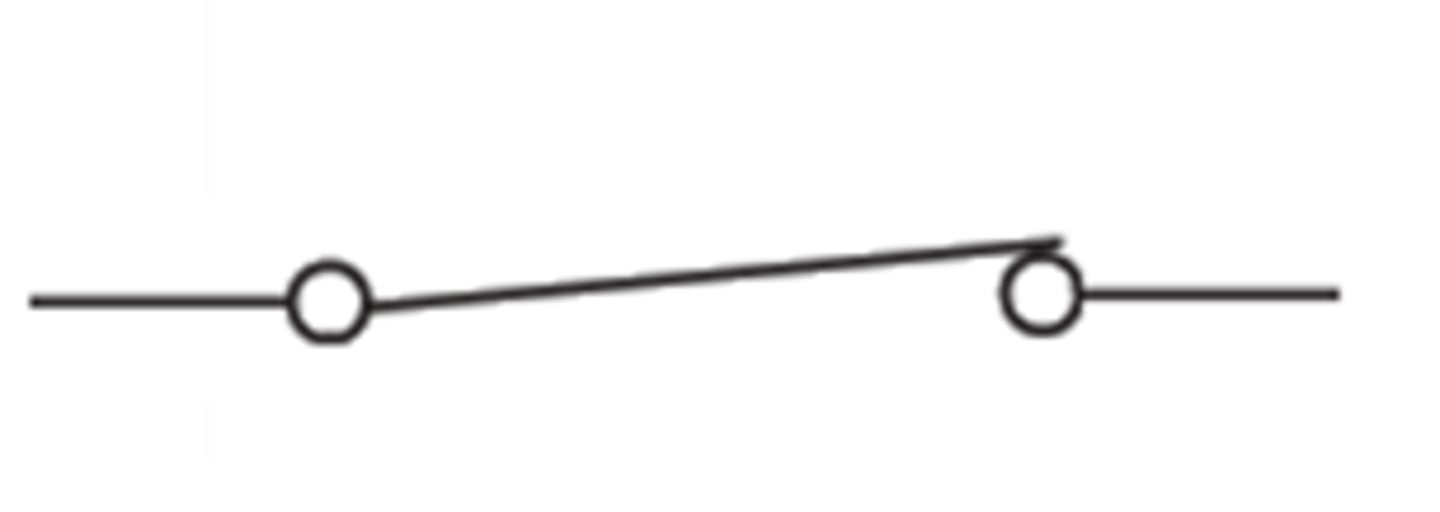
a closed switch

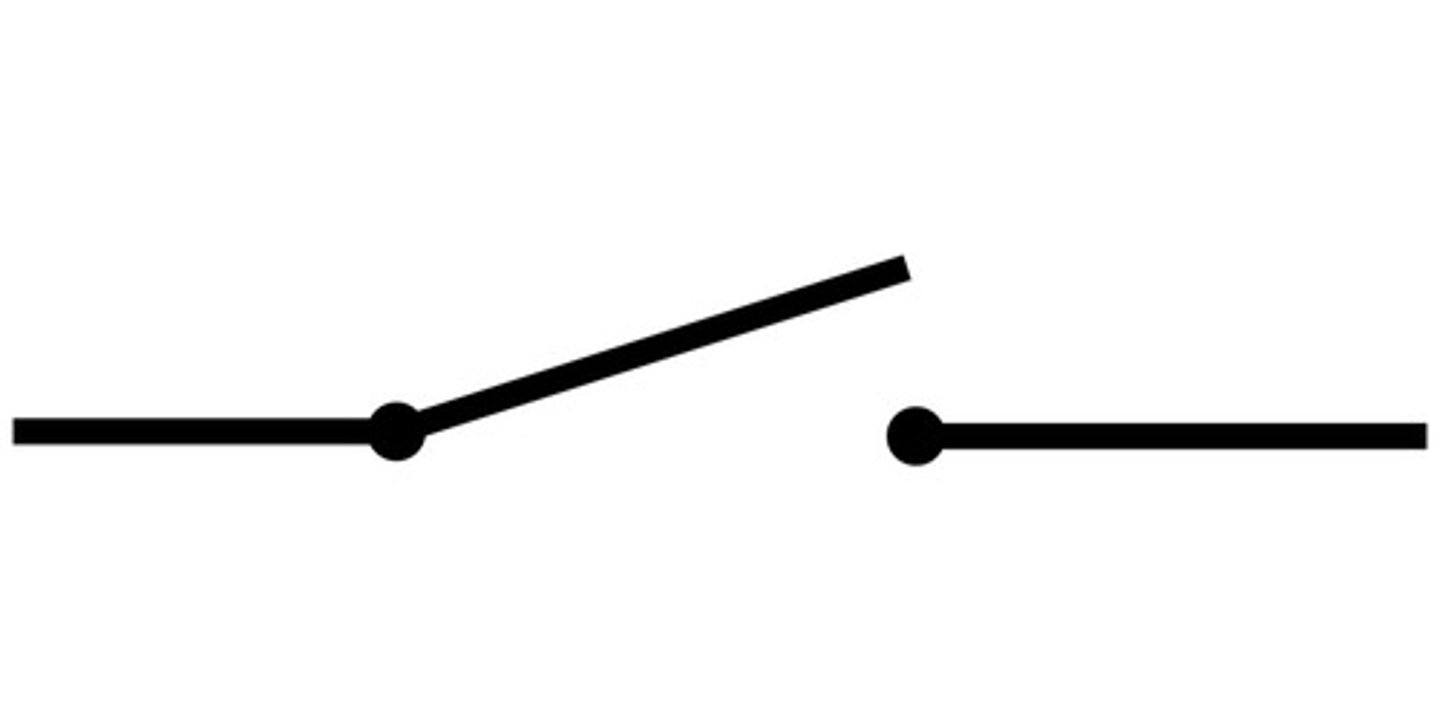
a open switch
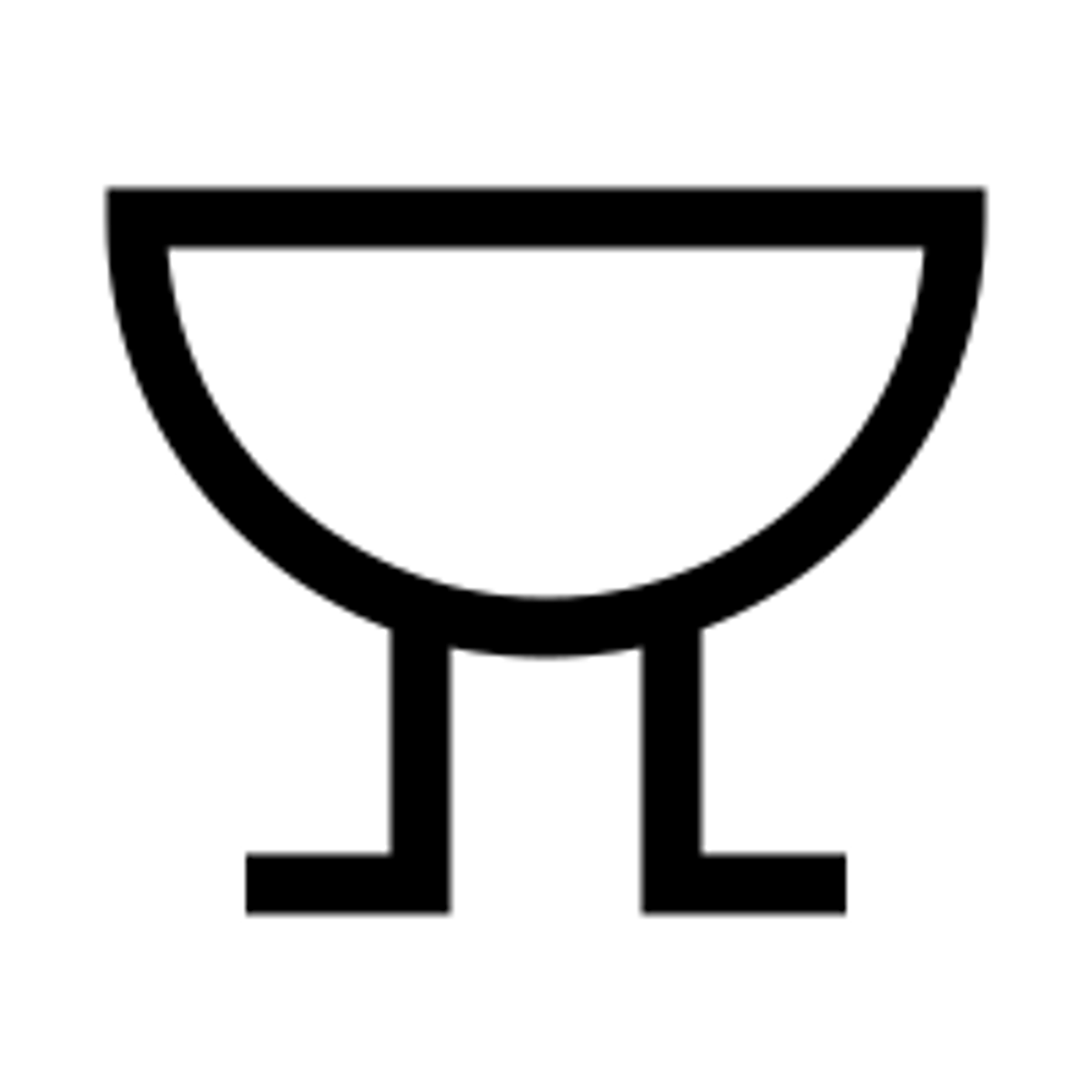
a heater
a buzzer

structure of metals
they have positive ions and delocalised electrons
ohms law
Ohm's law states that the potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current passing through it, provided the temperature remains constant
what is a series circuit
Components are connected in a single loop; if one component breaks, the entire circuit stops working.
what is a parallel circuit
Components are connected in separate branches; the current splits, and components can operate independently.
what happens to the voltage/current in a series circuit
In a series circuit, the current is the same everywhere, while the voltage is shared among the components.
what happens to the voltage/current in a parallel circuit
In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across all branches, while the total current is split among them
coulomb heating
electrical energy is converted to thermal energy as charge flows through a component with resistance, causing the component's temperature to increase.
what is so special about diodes
diodes are polarised, meaning they are one-way round
The resistance is very high in reverse bias
Forward bias results in a lower resistance