Cellular organelles
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cell
The simplest collection of matter that can live, forming the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
Robert Hooke
Scientist who first observed cells in cork using a simple compound microscope in 1665.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
A master microscope maker who discovered bacteria and protozoa, known as one of the fathers of microbiology.
Cell Theory
A fundamental concept in biology stating that all living organisms are composed of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Prokaryotic Cell
A type of cell that is unicellular, less organized, and lacks a membrane-bound nucleus.
Eukaryotic Cell
A type of cell that is multicellular, more organized, and contains internal membranes that compartmentalize functions.
Plasma Membrane
A boundary that separates the living cell from its non-living surroundings, exhibiting selective permeability. Allows nutrients in and allows waste out.
Cytoplasm
the entire region between the cell membrane and the nucleus that houses DNA (cytosol + organelles)
Membrane Structure
Asymmetric phospholipid bilayer. Lipids are scattered between these phospholipid molecules (determine fluidity). Proteins are embedded and otherwise attached. Carbohydrates exist on the outer surface.
Saturated fatty acids
make membranes less fluid
Unsaturated fatty acids
make membranes more fluid
Phospholipid
Amphipathic lipid molecules. Head and Tail conneted by glycerol.
Phospholipid Head
Polar End. Consists of phosphoric acid conjugated to a base (Choline, Serine etc)
Phospholipid Tail
Non-Polar End. Consists of tails of long hydrocarbon chains - fatty acids
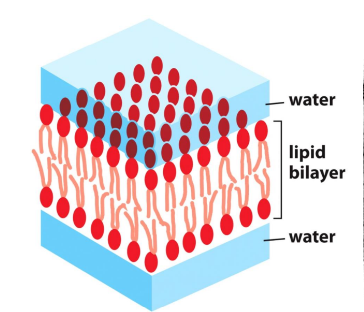
Phospholipid Bilayer
The fundamental structure of biological membranes, consisting of two layers of phospholipids with hydrophobic tails facing inwards and drophilic heads facing outwards.
four major phospholipids
phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol
Organelle
An intracellular compartment that carries out a specific function within the cell.
2 types of organelles
Membraneous organelles and Non-membraneous organelles
Membraneous organelles
nucleus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
mitochondria
Golgi apparatus
lysosomes
peroxisomes
Non-membraneous organelles
ribosomes
cytoskeletal structures
condensed protein structures
Nucleus
The organelle that stores genetic information (DNA) and is involved in gene expression.
Nuclear membrane
Definition: A double-lipid bilayer structure that encases the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. It contains pores for selective transport
Nuclear Lamina: maintains the shape and integrity of the nucleus.
Chromosomes
dynamic assemblies of DNA and proteins, i.e. chromatin
Ribosome
A cellular structure that synthesizes proteins according to the information in genes.
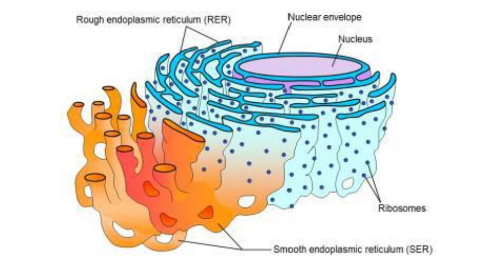
Endoplasmic Reticulum
An interconnected network of membrane-enclosed sacs involved in the synthesis and export of lipids and proteins, consisting of rough (rER) and smooth (sER) types.
Golgi Apparatus
The "post-office" of the cell, responsible for sorting, packaging, and modifying macromolecules.
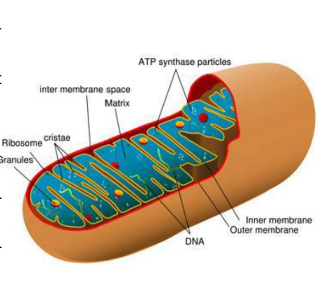
Mitochondria
Organelles known as the power plants of the cell, generating ATP through aerobic respiration.
Mitochondria function
power plants of all eukaryotic cells
generate energy for the cell
combine oxygen with food molecules to produce ATP (aerobic respiration)
calcium storage
regulation of programmed cell death (apoptosis)
Lysosomes
The cell's waste disposal system, containing digestive enzymes that function optimally at low pH.
3 pathways leading to lysosomes
– phagocytosis
– endocytosis
– autophagy
Peroxisomes
Organelles involved in recycling and detoxification, containing oxidative enzymes and self-replicating capabilities.
histones
the major proteins of chromatin
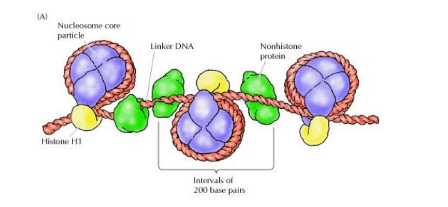
Nucleosome
the basic structural unit of chromatin
Nucleolus
A structure within the nucleus responsible for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene transcription and early ribosome assembly.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins associated with the plasma membrane, classified as integral (penetrating the membrane) or peripheral (not embedded).
Cholesterol
A steroid molecule that stabilizes membrane fluidity, reducing movement at high temperatures and hindering solidification at low temperatures.
Integral proteins
penetrate the hydrophobic core, many are “transmembrane”
Peripheral proteins
are not embedded in the membrane at all, they are often bound to exposed integral proteins or loosely to the surface of the