adult health 1 Final review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
jeopardy and kahoot: Fluid and Electrolytes, Acid Base Balance, COPD, TB, Heme GI, Cardiac Diagnosis, Cardiac Treatment, Heme Misc, ARDS, Asthma, Misc Respiratory
Last updated 4:43 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
What is the normal value for serum potassium?
3.3-5 mEq/L
2
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia?
TIGHT AND CONTRACTED-ST elevation and peaked T waves, arythmias of vfib and cardiac standstill, hypotension, bradycardia, diarrhea, hyperactive BS, paralysis, muscle weakness
3
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hypokalemia?
LOW & SLOW; Flat T waves, ST depression, Promienent U waves, decreased DTR, muscle cramping, parlyzed limbs, decreased GI motility, hypoactive BS, constipation, abd distenstion, parlytic illeus
4
New cards
What is the normal value range of serum sodium?
135-145
5
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hypernatremia?
Big & Bloated; skin is flushed, edema, low grade fever, polydipisia, late- swollen dry tongue, nausea and vomiting, increased muscle tone
6
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hyponatremia?
DEPRESSED & DEFLATED; seizures and coma, tachycardia and weak thready pulses, respiratory arrest
7
New cards
What are normal ranges for serum calcium?
9.0-10.5 (Bones, blood, beats)
8
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia?
CALM & QUIET; heart block, prolonged PR intervals, hypoflexia DTR, Depressed and swallow respiration, hypoactive BS
9
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia?
BUCK WILD; ST depression, T wave inversion, sever- Vfib, Tachycardia; hyporeflexes- increased DTR, abnormal eye movements (nystagmus) diarrhea
10
New cards
What are nursing interventions for hyperkalemia?
increase fluids, use diuretics, hold K+, dialysis, monitor kidney function, monitor EKG and BS.
11
New cards
What are nursing interventions for hypokalemia?
increase foods high in K+ add K+ supplements, recognize s/sx of hypo
12
New cards
what are K+ rich foods?
bananas, dark green leafy vegs, raisins, salt substitutes, bran cereal, potatoes, dried beef
13
New cards
What are nursing interventions for hypernatremia?
Check I&O, weight, admin diuretics, manage sodium intake, increase hydration
14
New cards
What are nursing interventions for hyponatremia?
Check I&O, weights, monitor neuro signs and symptoms, check for edema, manage fluid intake, administer hypertonic saline (NS 0.9%)
15
New cards
what are signs and symptoms of Respiratory Acidosis?
bradycardia, hypotension, agitation, altered mental status, trouble staying awake, retaining CO2, confusion
16
New cards
what causes of Respiratory Acidosis?
Hypoventilation, Respiratory Depression, Asthma, COPD, Pneumonia,Pulmonary Edema
17
New cards
what are sign/Symptoms for Metabolic Acidosis?
Headache, lethargy, Kussmauls's respiration, Nausea, vomiting, confusion, coma
18
New cards
What are causes of Metabolic Acidosis?
Acid increase: Keto Acidosis, starvation, Lactic Acidosis: Shock hypoxemia
Decreased Bicarbonate: severe diarrhea, renal failure
Decreased Bicarbonate: severe diarrhea, renal failure
19
New cards
what are signs and symptoms of Respiratory Alkalosis?
Tachycardia, anxiety, confusions, diaphoresis, dizziness, coma
20
New cards
what are causes of Respiratory Alkalosis?
Hyperventilation, Hypermetabolic states: Fever, anemia, septicemia, Anxiety, pain
21
New cards
What are signs/symptoms for Metabolic Alkalosis?
Weakness muscle cramps, hyperactive reflexes, tetany, confusion, slow shallow respirations to minimize co2 loss(Body needs this to counter alkalotic state), nausea, seizures
22
New cards
What are causes for Metabolic Alkalosis?
Antacids, Hyperaldosteronism; Cushing's disease, steroids, Acid loss by: vomiting, gastric suctioning, Diuretics-K+/NA+ loss
23
New cards
what is the normal value for pH?
7.35-7.45 acid blood level (normal is 7.40)
24
New cards
what is the normal value for PaCO2?
35-45 carbon dioxide (respiratory)
25
New cards
what is the normal value for HCO3?
22-26 base (metabolic)
26
New cards
what is the normal value for PaO2?
80-100 partial pressure of oxygen in bloood
27
New cards
What are the signs, symptoms and lab values for COPD?
- Chronic productive cough 3+ months over 2+ years
- Bronchial walls thicken d/t chronic inflammation, impedes airflow, cannot maintain oxygen levels
- Alveolar walls adjacent to bronchioles become thickened, fibrosed
- Impaired Ventilation: increased mucus, obstruction of small airways, chronic productive cough
- Viral, bacterial respiratory infections common (alveolar macrophages dysfunctional d/t damage)
- Low PaO2- Hypoxemia and High PaCo2-hypercapnic
- Bronchial walls thicken d/t chronic inflammation, impedes airflow, cannot maintain oxygen levels
- Alveolar walls adjacent to bronchioles become thickened, fibrosed
- Impaired Ventilation: increased mucus, obstruction of small airways, chronic productive cough
- Viral, bacterial respiratory infections common (alveolar macrophages dysfunctional d/t damage)
- Low PaO2- Hypoxemia and High PaCo2-hypercapnic
28
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of Emphysema?
- PINK PUFFER- damage to alveloi results in loss of lung elasticity & loss of inflation of lung tissue
- results in loss of lung tissue recoil and air trapping
P: pink skin, pursed lip breathing
I: Increased chest- barrel chest
N: Minimal or NO chronic cough
K: Keep tripoding
- results in loss of lung tissue recoil and air trapping
P: pink skin, pursed lip breathing
I: Increased chest- barrel chest
N: Minimal or NO chronic cough
K: Keep tripoding
29
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of Chronic Bronchitis?
- Inflammation of the bronchi and excessive mucus production resulting in a chronic hacking cough and recurrent infection
B- big and blue skin- cyanosis (hypoxia)
L- long term chronic cough and sputum
U- Unusual lung sounds- crackles and wheezes
E- Edema peripherally due to cor pulmonale
B- big and blue skin- cyanosis (hypoxia)
L- long term chronic cough and sputum
U- Unusual lung sounds- crackles and wheezes
E- Edema peripherally due to cor pulmonale
30
New cards
What are the nursing priorities and interventions for patient with COPD?
- Proper positioning- sit patient upright/high fowler's
- May need BiPAP- to decrease hypercapnea
- Avoid opioids & benzodiazepenes because the decrease breathing which may worsen oxygenation status/respiratory acidosis.
- Anxiety- COPD patients are frequently anxious due to the inability to breathe. Assist with relaxation techniques and pursed lip breathing to prevent air trapping and airway collapse during expiration
- May need BiPAP- to decrease hypercapnea
- Avoid opioids & benzodiazepenes because the decrease breathing which may worsen oxygenation status/respiratory acidosis.
- Anxiety- COPD patients are frequently anxious due to the inability to breathe. Assist with relaxation techniques and pursed lip breathing to prevent air trapping and airway collapse during expiration
31
New cards
What are the important patient teaching for patients with COPD?
- Promote health eating- small frequent meals with rest periods, high calorie and high protien
- Avoid- high carbs, exercise 1 hour before/after meals to conserve energy. Avoid gassy foods
- Increase fluid intake (8 glasses or 2-3L daily) to thin mucous. Avoid drinking fluids with meals
- Report increase in sputum, fever or worsening dyspnea
- Prevention- pneumococcal every 5 years, flu vaccine every year
- Meds- good inhaler technique. Always have albuterol to lessen cough and wheezing
- Bronchitis- guaifensesin and cool mist humidifier to mobilize secretions
- Pursed lip breathing- inhale 2 seconds, exhale 4 seconds
- Hugg coughing technique- sit upright in chair, deep slow inhalation, hold breath for 2-3 seconds and then forcefully exhale
- Avoid- high carbs, exercise 1 hour before/after meals to conserve energy. Avoid gassy foods
- Increase fluid intake (8 glasses or 2-3L daily) to thin mucous. Avoid drinking fluids with meals
- Report increase in sputum, fever or worsening dyspnea
- Prevention- pneumococcal every 5 years, flu vaccine every year
- Meds- good inhaler technique. Always have albuterol to lessen cough and wheezing
- Bronchitis- guaifensesin and cool mist humidifier to mobilize secretions
- Pursed lip breathing- inhale 2 seconds, exhale 4 seconds
- Hugg coughing technique- sit upright in chair, deep slow inhalation, hold breath for 2-3 seconds and then forcefully exhale
32
New cards
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
33
New cards
What type of infection is TB and caused by what bacteria?
Bacterial infection caused by M. Tuberculosis.
34
New cards
how is TB spread?
Spread by airborne route. Inhaled in the lungs and spread to lymph and blood stream
35
New cards
What are the signs and symptoms of TB?
Night sweats, anorexia/ weight loss, cough and hemoptysis- blood tinged sputum, dyspnea and SOB, fever and chills
36
New cards
How is TB diagnoses?
Positive INTRADURMAL Mantoux testing over 15mm duration= positive TST AND Positive Chest x-ray
37
New cards
what are the 3 things that you must have to diagnose TB?
3 sterile positive sputum cultures in 3 consecutive days
38
New cards
What are the 4 TB meds
RIPE:
Rifampin, INH Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol
Rifampin, INH Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol
39
New cards
what is the precautions with administration and monitoring of Rifampin?
RED-FAMPIN- normal to see red, orange in tears urine and sweat. Pts should not wear contacts due to discoloration of tears; oral contraceptives are NOT effective; use back up birth control, monitor for jaundice; heptotoxic!
40
New cards
what is the precautions with administration and monitoring of INH Isoniazid?
interferes with Vit B6 so monitor for peripheral neuropathy- new numbness, tiingling extremities, ataxia. Pts may be on Vit B6 25-50mg daily for supplementation. Hepatotoxic- report jaundice, dark urine, elevated liver enzymes (HOLD MEDS); NO ETOH
41
New cards
what is the precautions with administration and monitoring of Pyrazinamide?
3rd TB drug; hepatotoxic
42
New cards
what is the precautions with administration and monitoring of Ethambutol?
EYE; May cause blurred vision, color changes!
43
New cards
How long is TB medication treatment?
Medication treatment 6-12 months
44
New cards
What kind of mask do you wear when caring for TB?
You must weark N-95 mask with patient care at all times
45
New cards
When is a patient deemed no longer infected with TB? What test results need to happen with TB?
Pt is no longer infected if they have 3 negative cultures on 3 different days
46
New cards
What is characteristic of Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies?
- Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies are characterized by the production of abnormally large erythrocytes called megaloblasts
- Because these cells are abnormal, many are sequestered (trapped) while still in the bone marrow, and their rate of release is decreased
- Some of these cells actually die in the marrow before they can be released into the circulation
- This results in megaloblastic anemia
- Because these cells are abnormal, many are sequestered (trapped) while still in the bone marrow, and their rate of release is decreased
- Some of these cells actually die in the marrow before they can be released into the circulation
- This results in megaloblastic anemia
47
New cards
What are the characteristic signs and symptoms of iron deficiency and anemia?
Iron deficiency in the adult generally indicates blood loss (from bleeding in the GI tract or heavy menstrual flow). Bleeding in the GI tract can be preliminarily identified by testing stool for the presence of blood
48
New cards
Thrombocytopenia is related to what?
can result from a decreased platelet production, increased platelet destruction, or increased consumption of platelets
Impaired platelet communication, antibodies, and autoimmune processes are not typical pathologies
Impaired platelet communication, antibodies, and autoimmune processes are not typical pathologies
49
New cards
What is the first action a nurse should do when suspects a hemolytic blood transfusion reaction?
Stop the blood
The most common causes of acute hemolytic reaction are errors in blood component labeling and patient identification that result in the administration of an ABO-incompatible transfusion
Prophylactic antihistamines are not normally given, and would not prevent acute hemolytic reactions. Similarly, baseline vital signs and slow administration will not prevent this reaction.
The most common causes of acute hemolytic reaction are errors in blood component labeling and patient identification that result in the administration of an ABO-incompatible transfusion
Prophylactic antihistamines are not normally given, and would not prevent acute hemolytic reactions. Similarly, baseline vital signs and slow administration will not prevent this reaction.
50
New cards
What is DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)?
may occur either as a cause or as a complication of shock
widespread clotting and bleeding occur simultaneously. Bruises (ecchymoses) and bleeding (petechiae) may appear in the skin. Coagulation times (e.g., prothrombin time [PT], activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) are prolonged. Clotting factors and platelets are consumed and require replacement therapy to achieve hemostasis.
urinary output of 30 ml/hr is key assessment
widespread clotting and bleeding occur simultaneously. Bruises (ecchymoses) and bleeding (petechiae) may appear in the skin. Coagulation times (e.g., prothrombin time [PT], activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) are prolonged. Clotting factors and platelets are consumed and require replacement therapy to achieve hemostasis.
urinary output of 30 ml/hr is key assessment
51
New cards
how many ml/hr is normal urinary output?
30 ml/hr
52
New cards
What is the most common cause of peptic ulcer?
Most common cause of peptic ulcers is gram-negative bacteria (Helicobacter pylori)
53
New cards
What are some key aspect of duodenal ulcer?
- often awakens between 1 and 2 with pain
- ingestion of food brings relief but experience pain 2 to 3 hours after a meal
- cause hypersecretion of stomach acid
- Vomiting is uncommon
- Hemorrhage is less likely in the client with duodenal ulcer than in the client with gastric ulcer
- may experience weight gain
- black tarry stool (melena)
- ingestion of food brings relief but experience pain 2 to 3 hours after a meal
- cause hypersecretion of stomach acid
- Vomiting is uncommon
- Hemorrhage is less likely in the client with duodenal ulcer than in the client with gastric ulcer
- may experience weight gain
- black tarry stool (melena)
54
New cards
what is a peptic ulcer?
a sore on the lining of your stomach, small intestine or esophagus
55
New cards
esophageal ulcer occurs where?
occurs in the lower part of your esophagus
56
New cards
A duodenal ulcer is a peptic ulcer that develops in the what?
in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum)
57
New cards
A peptic ulcer in the stomach is called what?
Gastric Ulcer
58
New cards
what do patients with a Gastric ulcer experience?
- can vomit blood
- pain increased with food (30-60min)
- weight loss
- pain increased with food (30-60min)
- weight loss
59
New cards
Pt states they have sharp pain resolved with eating, what could this be a sign of?
Peptic Ulcer
60
New cards
why would a Pt with a Peptic Ulcer state they have sharp pain resolved with eating?
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by glands in the stomach in response to the actual or anticipated presence of food
The stomach, which stores and mixes food with secretions, secretes a highly acidic fluid in response to the presence or anticipated ingestion of food
The stomach, which stores and mixes food with secretions, secretes a highly acidic fluid in response to the presence or anticipated ingestion of food
61
New cards
What are some nursing interventions for hiatus hernia?
Eating smaller meals to reduce stomach bulk
Avoiding stimulation of gastric secretions by vomitting, caffeine, and alcohol, which may intensify symptoms
Refraining from smoking, which stimulates gastric acid secretions
Avoiding fatty foods, which promote reflux and delay gastric emptying
Avoiding stimulation of gastric secretions by vomitting, caffeine, and alcohol, which may intensify symptoms
Refraining from smoking, which stimulates gastric acid secretions
Avoiding fatty foods, which promote reflux and delay gastric emptying
62
New cards
What are the steps when finding someone down or just collapsed?
Gently shake and shout “Are you OK?”
Shout for help (“call a code”)
Check for a carotid pulse
Begin chest compressions
Shout for help (“call a code”)
Check for a carotid pulse
Begin chest compressions
63
New cards
What is the normal range of a troponin level?
between 0 and 0.04 ng/ml
64
New cards
How do we interpret an elevated troponin level?
Very high levels of troponin are a sign that a heart attack has occurred
Most patients who have had a heart attack have increased troponin levels within 6 hours.
After 12 hours, almost everyone who has had a heart attack will have raised levels
Troponin levels may remain high for 1 to 2 weeks after a heart attack
Most patients who have had a heart attack have increased troponin levels within 6 hours.
After 12 hours, almost everyone who has had a heart attack will have raised levels
Troponin levels may remain high for 1 to 2 weeks after a heart attack
65
New cards
What is information is important to gather when a patient complains of chest pain?
The nurse must gather information about the patient's symptoms and activities, especially those that precede and precipitate attacks of angina. Scale 0-10, did nitro resolve the pain.
66
New cards
What is cardiac output?
computed by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate
can be affected by changes in either stroke volume or heart rate, such as a heart rate being low or high.
can be affected by changes in either stroke volume or heart rate, such as a heart rate being low or high.
67
New cards
What is pericarditis?
swelling and irritation of the thin, saclike tissue surrounding the heart
68
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of pericarditis?
Sharp, grating, pleuritic chest pain (inspiratory), pleuritic chest pain (inspiratory), and increased WBC, dyspnea (splinting) are all assessment findings related to pericarditis
69
New cards
Why is an MI with ST elevation an emergency?
A heart attack with a completely blocked coronary artery is called a STEMI
STEMI stands for ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction.
STEMI stands for ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction.
70
New cards
What is percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)?
PCI uses a balloon tipped catheter to open blocked coronary vessels
71
New cards
What are the signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock?
a decrease in intravascular volume. Cardiac output is decreased, blood pressure decreases, and pulse is fast, but weak.
72
New cards
What is Neurogenic shock ?
Neurogenic shock can be caused by spinal cord injury.
73
New cards
What are the signs and symptoms of Neurogenic shock?
WARM DRY SKIN is KEY
low blood pressure; bradycardia; and warm, dry skin due to the loss of sympathetic muscle tone and increased parasympathetic stimulation
low blood pressure; bradycardia; and warm, dry skin due to the loss of sympathetic muscle tone and increased parasympathetic stimulation
74
New cards
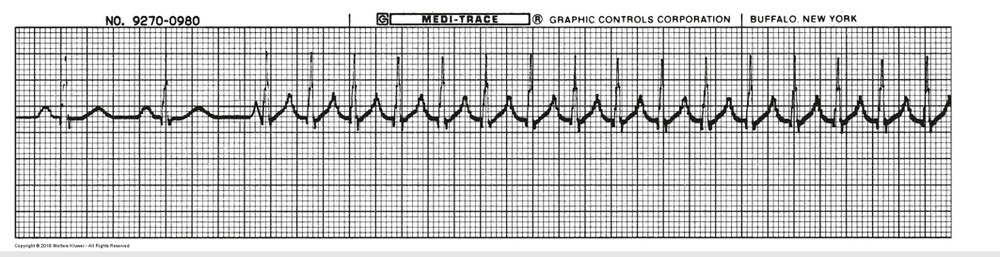
What is this rhythm?
V Tach
75
New cards
What medication is used for V Tach?
SVT Adenosine
76
New cards
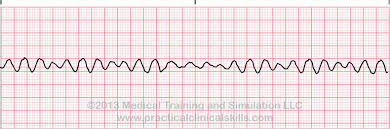
What is this rhythm?
Ventricular fibrillation
77
New cards
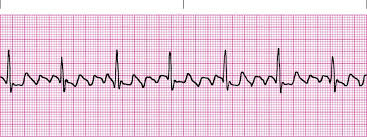
What rhythm is this?
A Flutter
78
New cards
What is Sickle Cell disease?
one of a group of inherited disorders known as sickle cell disease. It affects the shape of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to all parts of the body.
some red blood cells are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These sickle cells also become rigid and sticky, which can slow or block blood flow.
some red blood cells are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These sickle cells also become rigid and sticky, which can slow or block blood flow.
79
New cards
What are nursing interventions for patient care of Sickle Cell disease?
There's no cure for most people with sickle cell anemia. Treatments can relieve pain and help prevent complications associated with the disease.
Hydration is key
Hydration is key
80
New cards
what is the normal hemoglobin value?
12-18
81
New cards
what is the normal HCt value?
36-54%
82
New cards
what is the normal platelet value?
140,000-400,000
83
New cards
what is the normal WBC value?
4500-11,000
84
New cards
What are key nursing interventions for neutropenia?
- Avoid all fresh fruits and vegetables, including all fresh garnishes
- Avoid raw or rare-cooked meat, fish, and eggs
- Avoid salad bars, fruit bars, and deli counters
- Avoid raw nuts
- Make sure all of the dairy products you eat are pasteurized
- Avoid yogurt and yogurt products with live and active cultures
- Monitor for temperatures. if fever then culture
- Avoid raw or rare-cooked meat, fish, and eggs
- Avoid salad bars, fruit bars, and deli counters
- Avoid raw nuts
- Make sure all of the dairy products you eat are pasteurized
- Avoid yogurt and yogurt products with live and active cultures
- Monitor for temperatures. if fever then culture
85
New cards
When caring for postoperative patient's what are the key nursing assessments?
ABC:
Airway
Breathing
Circulation-hemorrhage
Airway
Breathing
Circulation-hemorrhage
86
New cards
What places patient at risk for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)?
The client with advanced age is at risk for developing MODS due to the lack of physiological reserve. The client with malnutrition metabolic compromise and the client with multiple comorbidities is at risk for developing MODS due to decreased organ function.
87
New cards
What happens in the body during Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
Diffuse inflammatory damage to alveolar capillary membranes, inflammatory exudate builds up in alveoli and causes collapse.
- Shunting of blood
- decreased perfusion
- increased capillary pressure
- hypoxiema
- Shunting of blood
- decreased perfusion
- increased capillary pressure
- hypoxiema
88
New cards
What causes ARDS?
Imparied gas exchange leads to multisystem organ failure. It is a secondary disorder cause by something such as sepis, trauma or shock.
89
New cards
What is Acute Respiratory Failure (ARF)?
Hypoxemic failure (Low O2 and High Co2)
90
New cards
What is the medical management for ARDS?
Identify primary disorder. Agressive respiratory support including PEEP (improve alveoli function). increase FiO2 to keep PaO2>60 mm Hg; Spo2>90%
Balance fluid resuscitation. treat shock.
Balance fluid resuscitation. treat shock.
91
New cards
What is the priority complication of ARDS?
MORTALITY RATE- 35-60%
92
New cards
How is ARDS treated?
Balance fluid resuscitation. treat shock.
93
New cards
What are 4 priority assessments and s/s of ARDS?
- recognize early
- May mimic pulm edema
- First sign of hypoxemia- Agitation, restlessness, confusion
- Increasing anxiety, SOB, tachypnea, dyspnea
- Decreased breath sounds with crackles. Retractions
- Hypoxemia despite high FiO2. Hypotension, Tachycardia. shock. pulmonary hypertension.
- May mimic pulm edema
- First sign of hypoxemia- Agitation, restlessness, confusion
- Increasing anxiety, SOB, tachypnea, dyspnea
- Decreased breath sounds with crackles. Retractions
- Hypoxemia despite high FiO2. Hypotension, Tachycardia. shock. pulmonary hypertension.
94
New cards
What is 1 of the priority nursing diagnosis for ARDS?
Impaired Breathing Pattern- Impaired Respiratory Function, inflammatory response and pain
95
New cards
What are the nursing interventions for ARDS?
H-O-L-Y
High fowler's, oxygen and suctioning, listen to lung sounds, yell for help (notify HCP)
Monitor respiratory status. Positioning to optimize inhalation and chest expansion.
Freq turning to improve ventilation and perfusion
Promote comfort
Monitor for complications- pneumothorax, PE/blood clots
High fowler's, oxygen and suctioning, listen to lung sounds, yell for help (notify HCP)
Monitor respiratory status. Positioning to optimize inhalation and chest expansion.
Freq turning to improve ventilation and perfusion
Promote comfort
Monitor for complications- pneumothorax, PE/blood clots
96
New cards
What is the proper positioning for a patient with ARDS?
Prone positioning may be utilized to max oxygenation
97
New cards
What are signs and symptoms of asthma?
A-S-T-H-M-A
A- accessory muscle use
S- shortness of breath and dyspnea
T- tight chest and tachypnea
H- high pitched wheezing
M- minimal diminished breath sounds
A- Absent breath sounds (silent chest) PRIORITY, acidosis, air trapping (prolonged expiration)
MAY LEAD TO RESPIRATORY FAILURE= High CO2, hypercapnic; Respiratory acidosis- PaO2< 80 Hypoxic
A- accessory muscle use
S- shortness of breath and dyspnea
T- tight chest and tachypnea
H- high pitched wheezing
M- minimal diminished breath sounds
A- Absent breath sounds (silent chest) PRIORITY, acidosis, air trapping (prolonged expiration)
MAY LEAD TO RESPIRATORY FAILURE= High CO2, hypercapnic; Respiratory acidosis- PaO2< 80 Hypoxic
98
New cards
What is the first sign and symptom of an asthma exacerbation?
Night time non-prod cough
99
New cards
What are danger signs of an asthma exacerbation?
1st sign of hypoxia- mental status change
2. agitation
3. restlessness
4. drowsiness
*Status asthmaticus- may require endotracheal intubation
2. agitation
3. restlessness
4. drowsiness
*Status asthmaticus- may require endotracheal intubation
100
New cards
what is the first sign of hypoxia?
mental status change