Clostridium botulinum
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
gram + or -
gram positive
shape
rod
growth temp
optimum temperature for toxin production (Topt)
is 25-40°C
type of organism
sporeformer, meaning it produces resistant structures known as spores
Obligate anaerobe- does not tolerate 02 and dies in its presence
motile sporeforming rod
survival
Its spores are highly resistant structures
disease
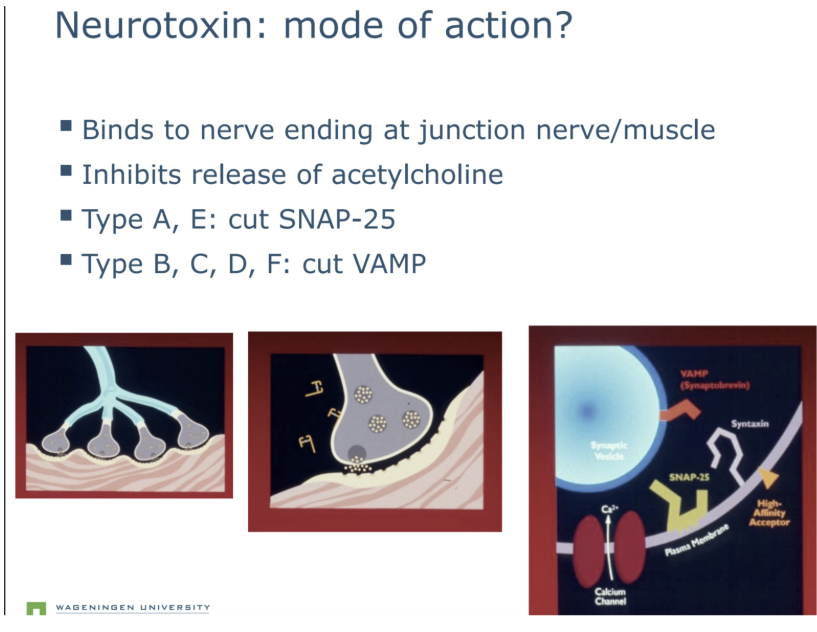
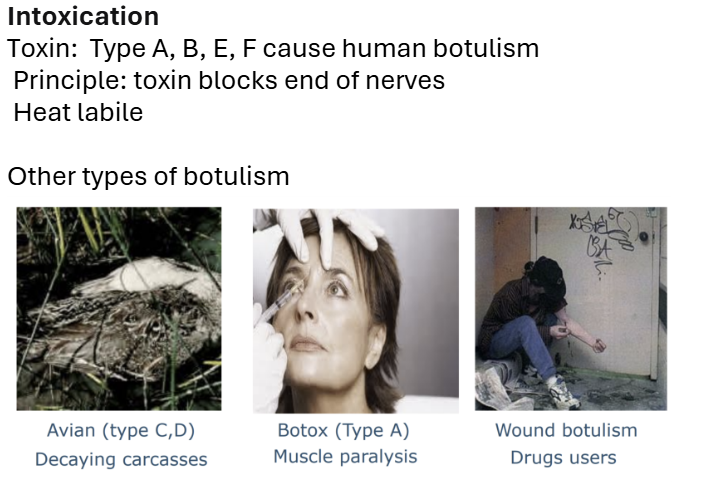
Botulism- Causes botulism through the production of a potent toxin. Lethal neurotoxin.
characteristic of the botulinum toxin :It can be activated in the gut of humans.
main symptons
Vomiting, nausea, muscular pain, double vision
Infant botulism: spores in food which colonize and produce toxin in the intestinal tract of infants. Infant botulism differs from the classical syndrome in that it results from colonization of the infant's gut with Clostridium botulinum and production of toxin in situ.
incubation time
12-48h
duration ilness
1-8 days
transmission and sources
Ubiquitous in soil and manure
prevention and control
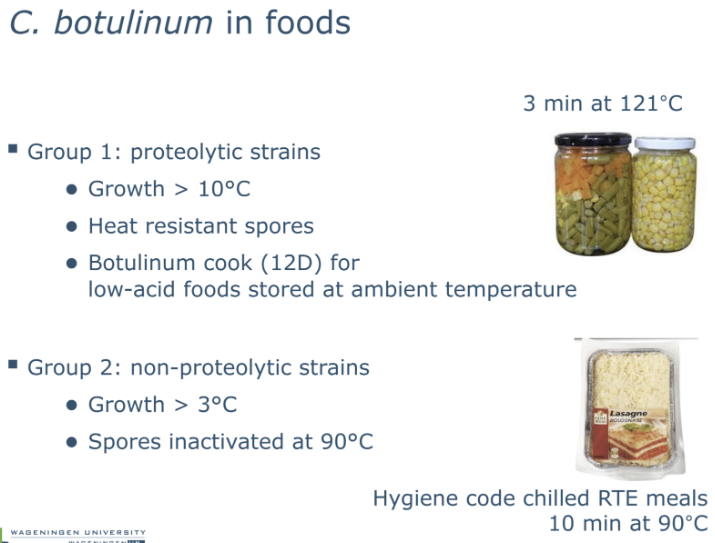
A "Botulinum cook" is a specific heat treatment required for low-acid canned foods (pH > 4.5) to ensure a 12-log (12D) reduction in the level of Clostridium botulinum.
At ph<4.5 Clostridium botulinum does not grow anymore below this pH
Do not feed honey to baby during your first year-intestinal flora not fully developed.
◦ To achieve this 12D reduction (with D121 = 0.2 min), 2.4 minutes of heating at 121°C is needed, often referenced as an F0 or F121 value of 3 minutes.
◦ It is important to note that a "Botulinum cook" does not achieve full sterilization, meaning other spoilage organisms may still survive
Nitrite above 100 mg/kg inhibits Clostridium botulinum, which might survive the heating process applied to many cured meats.
d value
The D-value for Clostridium botulinum spores is 0.1-0.2 minutes at a reference temperature of 121°C
z value
The z-value for spores is typically around 10°C, indicating that their heat resistance is less temperature-dependent than that of vegetative cells
mortality rate
10% of cases lethal---- High mortality rate
mode of action