UNIT 2 EXAM ANIMAL SCIENCE
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
How is horse height measured?
-measured in hands
-front hoof to withers
What are the three horse classifications?
-light horse
-draft horse
-pony
What are the four types of light horses?
-gaited
-sport
-stock
-baroque
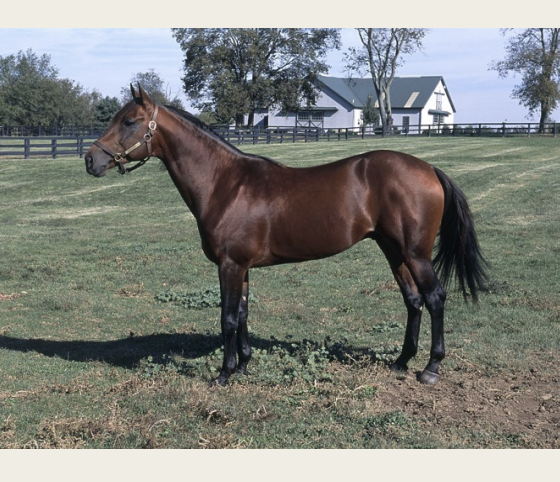

American Saddlebred
-origin: US
-Classification: light
-type: gaited
-color: any solid color, mostly chestnut
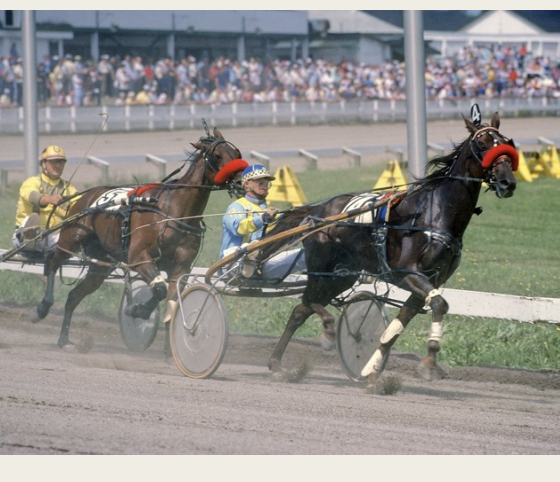

American Standardbred
-Origin: Us
-Classification: Light
-Type: Gaited
-Color: any solid color, mostly brown, bay, black, chestnut
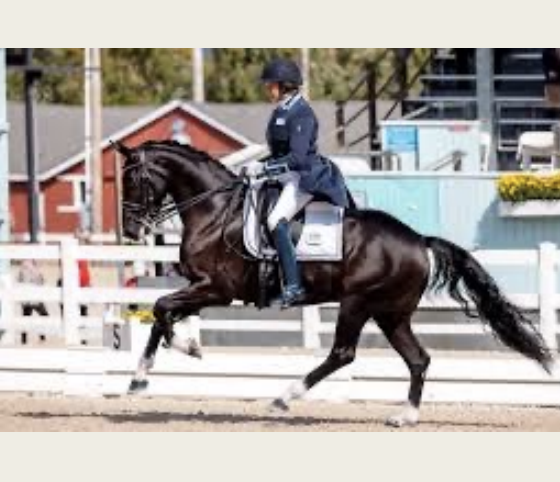

American Warmblood
-Origin: US
-Classification: Light
-Type: Gaited
-Color: any color
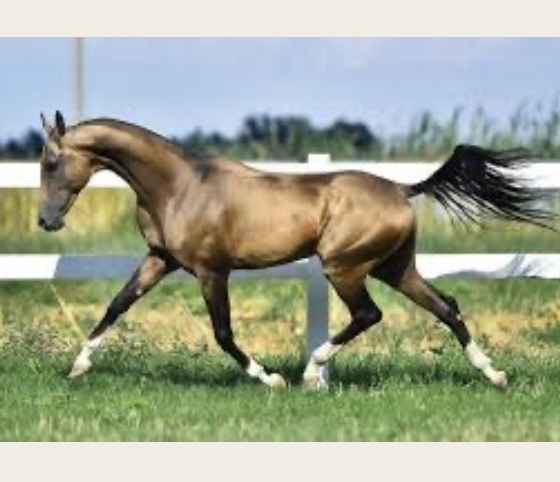

Akhal Teke
-Origin: Turkmenistan
-Classification: Light
-Type: Sport
-Color: Gold with metallic sheen; also, bay, cream, chestnut
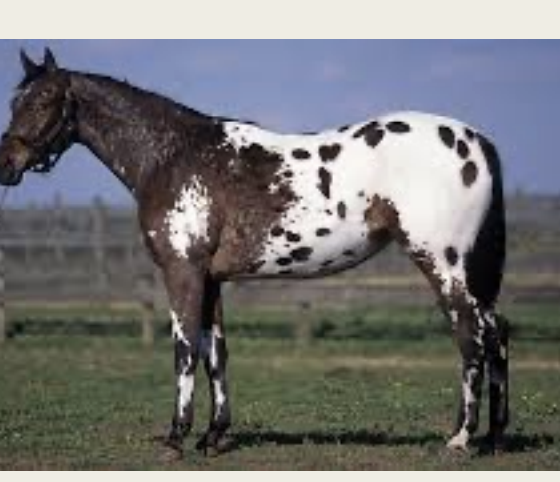

Appaloosa
-Origin: Spain, US
-Classification: Light
-Type: Stock
-Color: variety of colors, coat pattern
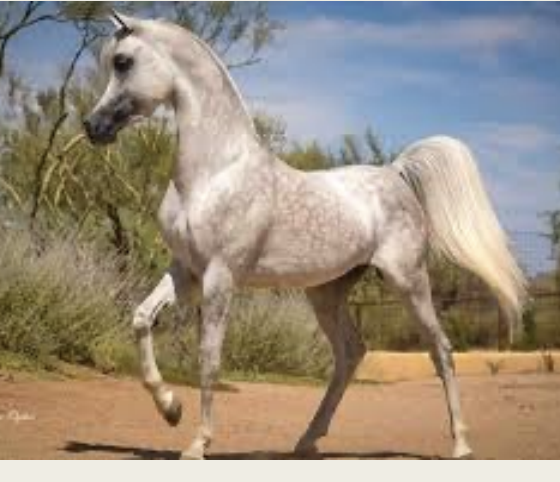

Arabian
-Origin: Arabia
-Classification: Light
-Type: Sport
-color: Bay, brown, chestnut, gray, black
-considered the common ancestor for most light horse breeds
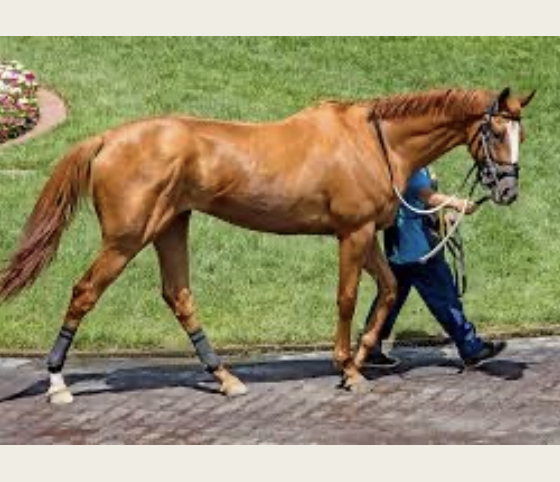
Thoroughbred
-Origin: England
-Classification: Light
-Type: Sport
-Color: any solid color, white markings allowed
-Must be bred natural mating to be registered for racing
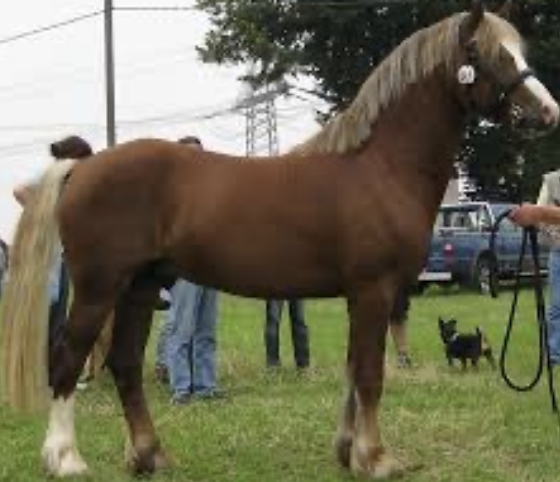

Welsh
-Origin: Wales
-Classification: Pony
-Color: any solid color
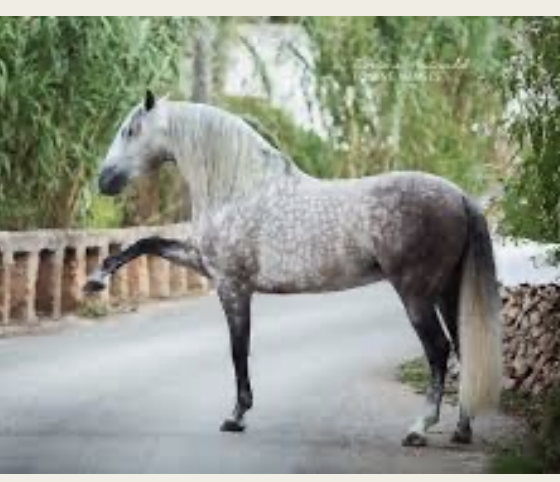

Andalusian
-Origin: Spain
-Classification: Light
-Type: Baroque
-Color: Gray, born dark and become lighter over the years
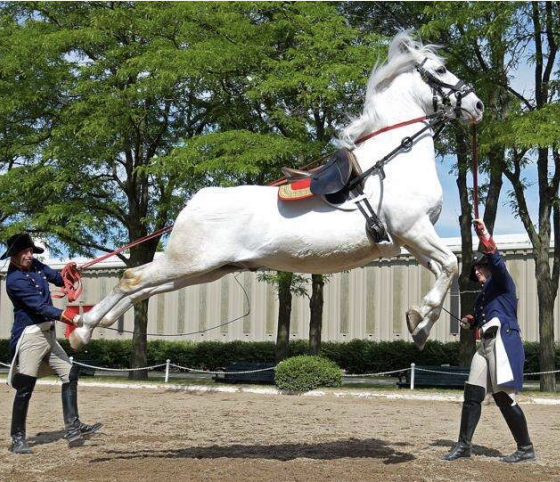

Lipizzaner
-Origin: Austria
-Classification: Light
-Type: Baroque
-Color: mostly gray
-Famous dancing horses
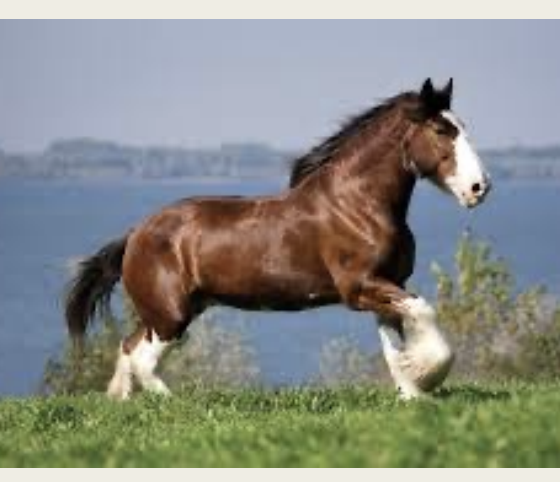

Clydesdale
-origin: Scotland
-classification: Draft
-color: bay, brown, black, roan; much white on face and legs, sometimes on body
-budweiser horse
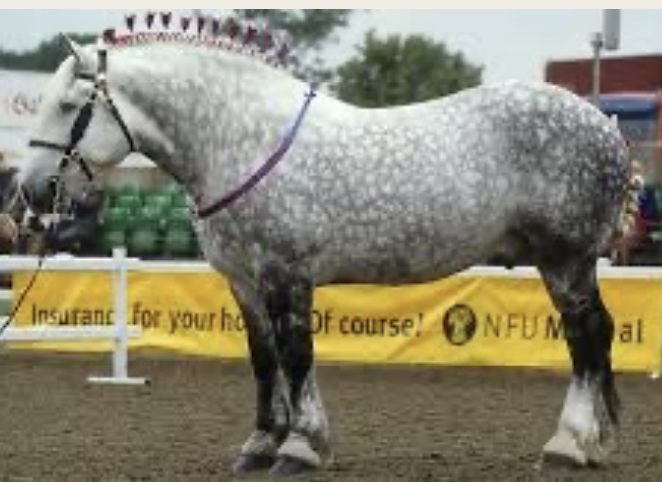

Percheron
-Origin: France
-Classification: Draft
-color: gray, black
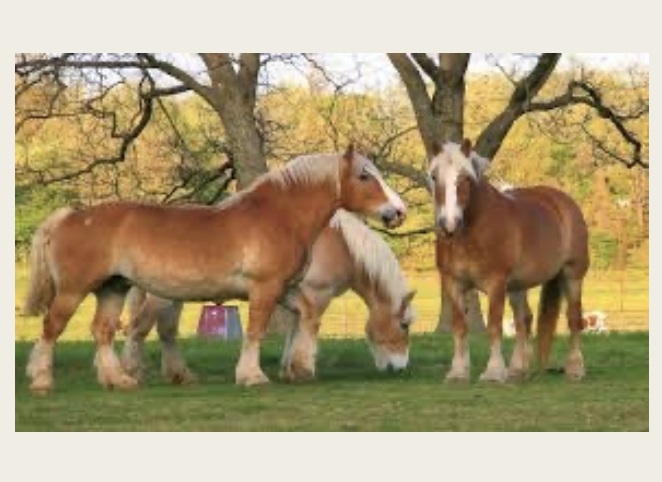

Belgian
Origin: Belgium
-Classification: Draft
-colors: mostly roans with black points, chestnut, sometimes bay, brown, dun, gray
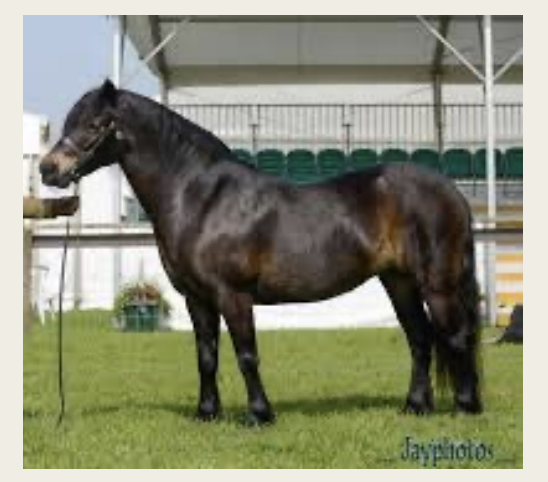

Dartmoor
-Origin: British Isles
-Classification: Pony
-Color: mostly black
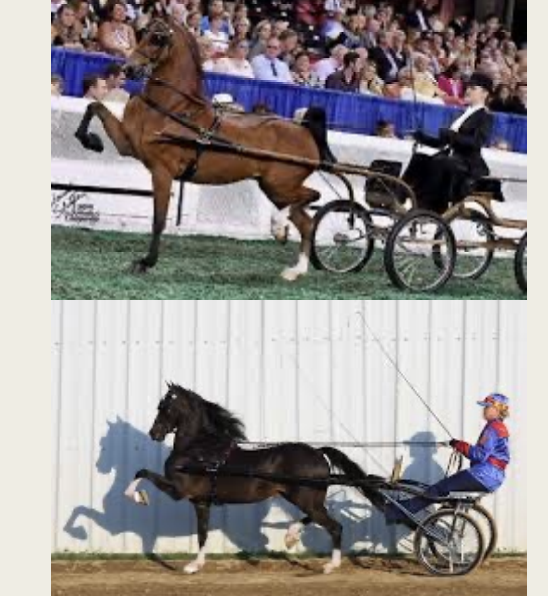

Hackney
-Origin: england
-classification: pony or light horse
-type: gaited horse
-color: dark brown, bay, black, chestnut
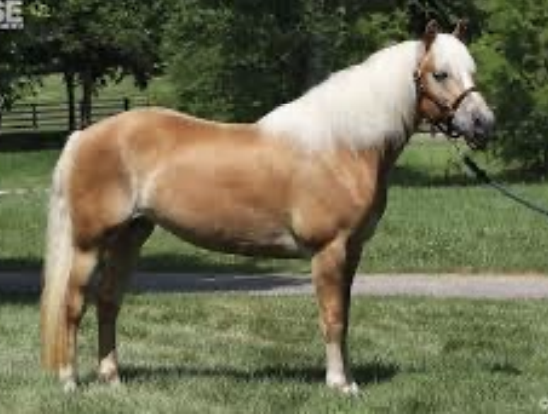

Haflinger
-Origin: Austria
-Classification: Pony
-Color: chestnut, white mane, and tail
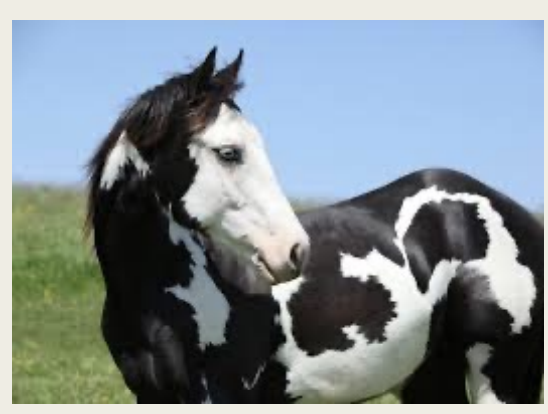

American Paint Horse
-Origin: austria
-classification: light
-type: stock
-color: black and white or red and white in bold patches all over body
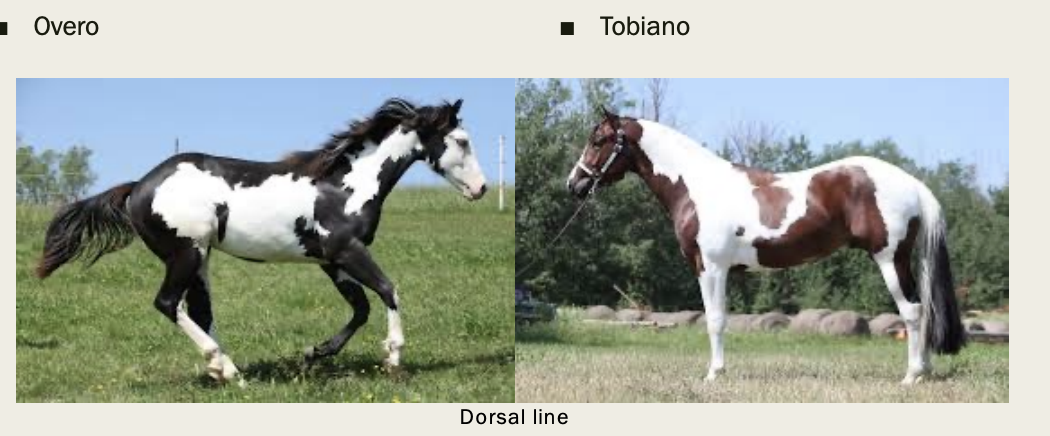

Overo is mostly what and the tobiano is mostly what?
Overo is mostly colored with some white
Tobiano is mostly white and any color
Horse Digestive System
-monogastric
-hind-gut fermentor-specialized for digesting fibrous plant material
Horse reproductive cycle
-produces 1 offspring
-twin, rare
-gestation length: 330-345 days
-long day seasonal breeders
Sow
female pig that has given birth to at least one littler of piglets
Boar
Male pig that has reached puberty and remains intact
Gilt
Female pig that has not yet given birth to a litter of piglets
Barrow
Castrated male pig
Farrowing
Process of giving birth to piglets
Gestation
3 month, 3 weeks, 3 days
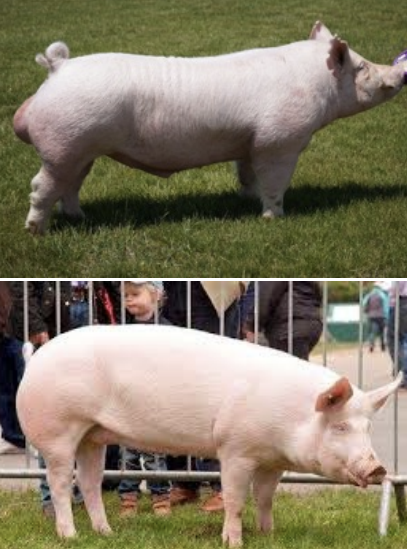

Yorkshire
-Most recorded breed in the US
-Erect ears
-Heavy muscling
-High proportion of lean meat
-Lot of backfat
-Structural soundness and durability
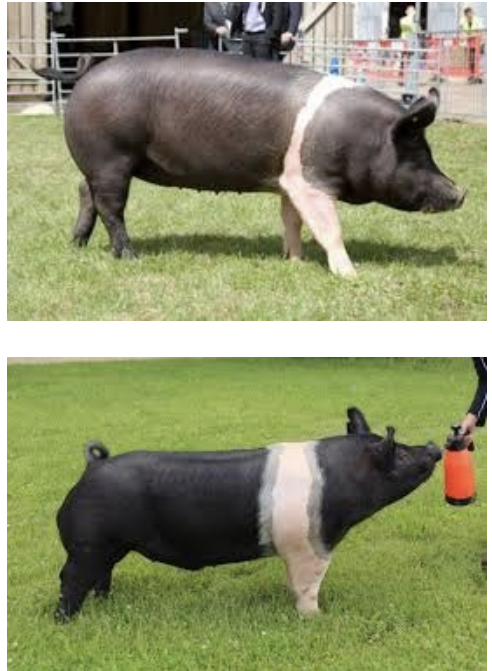

Hampshire
-belt
-4th most recorded breed in the US
-high lean muscle production
-high carcass quality
-minimal backfat
-large loin eye
-good mothering abilities
-good longeviity
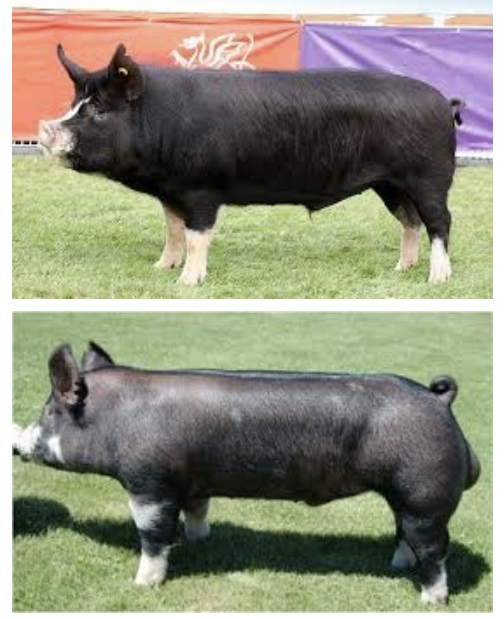

Berkshire
-3rd most recorded breed in the US
-fast and efficient growth
-reproductive efficiency
-excellent meat flavor and value
-oldest swine registry in the US
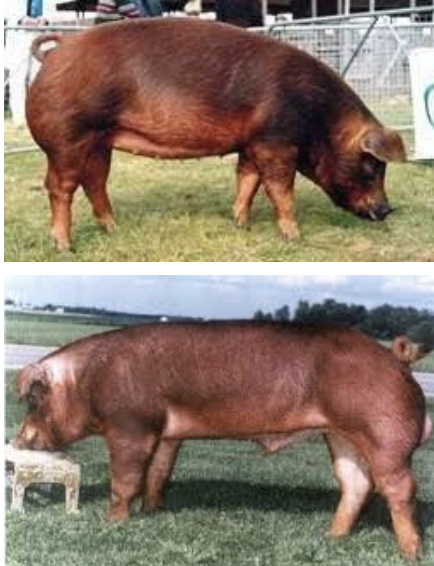

Duroc
-2nd most recorded breed in the US
-red pig with drooping ears
-Excelled product quality
-good carcass yield
-fast growth
-excellent lean-gain efficiency
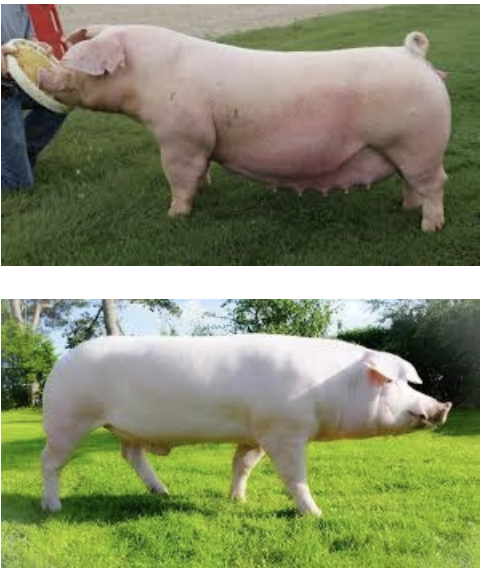
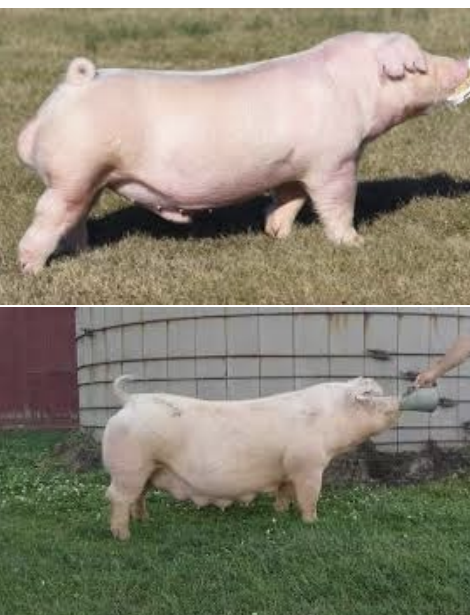
Landrace
-Excellent mothering abilities
-Heavy milkers
-Often crossed with other breeds
-High lengths of body
-High percent of carcass weight in loin/ham

Chester White
-Originated in Chester County, PA
-Droopy medium sized ears
-Good mothering abilities
-Durable
-Structural soundness
-Good muscle quality
How long is the gestation length for swine?
114 days (3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days)
How long is the estrous cycle for swine
18-24 days
How does AI work for swine?
-Breeding rod: corkscrew (screws into the cervix)
-Deposits semen into the cervix (allows sow to pull semen in instead of push)
What are the four type of farrowing systems for swine?
Crate, hybrid, group, and pasture
What does piglet processing entaill?
-clipping needle teeth (not common practice anymore)
-Treating umbilical cord
-Iron
-Tail docking
-Identification
-Sours prevention and treatment
-Castration
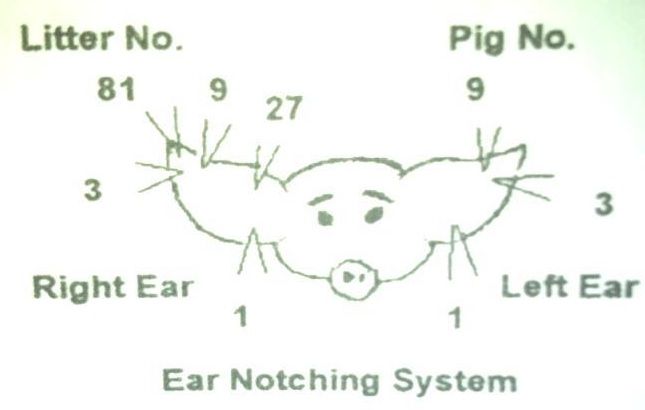
What is ear notching?
Right ear is litter number and left ear is individual number.
read litter number - individual number
What do nursery facilities look like?
-Specialized care for the weaned pigs
-Sanitary
-Environmental control
-Critical for early weaned pigs
-Warm, draft free environment needed
-Intense management
-Frequent observation and feeding
What do finishing facilities look like?
-Wide variation in type
-Group size is larger (25 to 500 pigs/pen)
-Mechanical/natural ventilation
-Labor intense/labor minimal
-Variation in feeder type
-Wean-finish has become new option for many systems
-Pigs go direct to finishing barn at weaning - eliminate nursery phase
What is a breed?
-a group of animals having similar characteristics.
-characteristics may include color, wool and/or wool characteristics, breeding, and reproductive characteristics
-breeds are something typically found in domesticated species where we can control selection and mating for specific targets
What are the methods of sheep breed classification for primary function?
ram (terminal) and ewe (maternal)
-Dual-purpose, dairy, heritage, etc
What are the methods of sheep classification for wool type?
Fine, medium, coarse, hair,
What are the methods of sheep breed classification for face color?
Black, White, Red, Gray, and Brockled
What are the methods of sheep breed classification for origin of breed?
England (U.K.) , U.S, Spain, South Africa

Katahdin
-Mature body weight: ram (180-250 lb) ewe (120-160 lb)
-Developed in Maine
-St. Croix X Suffolk X Wiltshire Horn
-Easy care sheep, survivors
-Hair coat of any color or pattern
-Largest of hair breeds
-Lean carcasses, ligher muscled
-Parasite resistance

Merino
-Spain for centuries bred sheep with the finest wool and forbade the trading of sheep with other countries
-napoleon’s war with all of europe weakened spain’s ability to control export
-col. humphery illegally brought back 100 merinos in 1802 (tremendous genetic pool improvement)
-Consul Jarvis imported another 3,850

Border Leicester
-Mature body weight (<200 lb ews)
-Developed in England
-Leicester X Cheviot crosses
-U.S - high rainfall, good pasture areas
-Medium to large frame
-Good milker/mothers
-Long-stapled, lustrous coarse wool for hand spinning
-Featured on the movies babe

Cottswold
-Mature body weight (>200-300 lbs)
-Gentle giants
-Cotes (enclosures), wolds (hills)
-Historic breed (pre-1400s)
-Over ¾ million in US ca 1914
-Under 400 in 1990s
-Removed from rare list
-Foundational breed for many others

Rambouillet
-Mature body weight (~200 lbs)
-Largest fine wool breed
-Developed from the Spanish Merino
-In France and Germany
-Backbone of Western U.S. sheep industry
-Adaptable to dry, arid conditions
-High-quality fine wool fleece

Lincoln
-Mature body weight (250-300 lbs)
-Developed in England
-Leicester X “Lincolnshire” crosses
-Large, deep-bodied, polled
-course, lustrous, heavy fleece
-Dual-purpose sheep breed
What does the colors face black tell you about sheep?
terminal breed, muscle, and meat production
What does the face color white tell you about sheep?
primarily wool or mothering breeds

Tunis
-Heat tolerant, out-of-season breeders
-Dual-purpose, moderate and wool
-Originally from North Africa imported to the US in 1799
-Devastation of the American Civil War nearly eliminated the breed in 1865

Scottish Blackface
-Mature body weight: Ram (150-175 lbs) and Ewe (115-130 lbs)
-Developed in the border area of Scotland and England
-One of the most important sheep breeds in the UK
-Used to improve pastures
-Excellent mothers
-Thrive well on brushy hillsides and withstand harsh winter conditions.

Shropshire
-Mature body size: 200-250 lbs
-Developed in England
-Introduced into U.S. in 1855
-Native sheep and southdown, leicester, cotswold crosses
-Flock favorite for many years
-Good mothers but sed as terminal sire
-One of most popular breeds of sheep through 1950s and 60s are once again gaining in popularity (youth projects)

Hampshire
-Most influential carcass sheep East of the Mississippi (adapt well to different geography)
-larger breed, roughly 250-300 lbs
-fast growth, muscular, statured
-imported in 1840s gone by 1870
-re imported in the 1880s

Suffolk
-Developed in England imported US in 1888
-Largest US breed (up to 400 lbs) fastest growing carcass quality
-Highest number of registration among all breeds in the US
-spider lamb and scrapie carriers
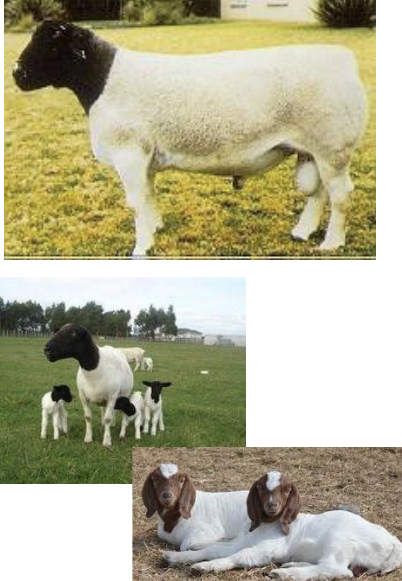

Dorper
-Mature body weight (~200 lbs)
-Developed in South Africa
-Blackheaded Persian X Horned Dorset
-Mixture of hair and wool does not require shearing
-Non-selective razers
-Rapid growth, quality carcasses
-Growing popularity

Corriedale
-Mature body weight (175-200 lbs)
-Developed in New Zealand - 1860s (breed officially established in 1924)
-Merino X English Lincoln Longwool
-Heavy yielding fleeces
-Moderately framed, decent carcasses
-Mothering ability adapt well
-Black nose and hooves

Southdown
-high cutability carcass
-only lost national carcass show 3 times between 1906 and 1956
-moderately sized, roughly 200 lbs
-dual-purpose medium wool
-heritage breed (arrived with the colonists)

Horned Dorset
-Originated in Southern England was original foundation for the Polled Dorset breed
-introduced into US in 1885
-horned characteristic is sex-influenced both rams and ewes have horns
-Rams possess a heavy masculine hron, ewes possess a fine, feminine horn
-out-of-season breeders
-excellent milkers
-known for mothering ability

Polled Dorset
-out of season breeders
-mature body weight (200-250 lbs)
-developed in southern england
-dorset horn to U.S. in 1885
-Mutation at NCSU in 1948 created Polled strain
-Excellent milkers
-Excellent commercial ewe base

Cheviot
-mature body weight: Ram (160-200 lbs) and Ewe (120-160 lbs)
-developed in hill country between scotland and england
-small frame size
-highly adaptable
-excellent lamb vigor
-produce valuable small carcasses

Texel
-mature body weight (~200 lbs)
-developed in Netherlands
-introduced into the US in 1990s
-hardy, adaptable, medium sized
-high muscled-bone (lean-fat) ratios
-extreme muscling
-excellent carcass cutability

columbia (durans fav)
-mature body weight (250+ lbs)
-first breed developed in the US (1912)
-dubois research station
-Lincoln X rambouillet
-Large frame heavy sheep
-increased use as terminal sires to increase the frame size in commercial blends
-Heavy medium fleece
-pink nose white hooves

Targhee
-Moderate wool cross (225 lbs)
-US breed developed in 1926
-Association in 1952, Mont St. Univ.
-Named after the forest near Dubois
-Designed ¾ fine fleece, ¼ long wool

Montadale
-Mature body weight Ram (200-275 lbs) Ewe (160-180lbs)
-Developed in US
-Cheviot X Columbia crosses
-Found in many midwest farm flock states
-white head and legs white wool
-black nostrils and hooves
-produce excellent lean carcasses
-good maternal traits

Polypay
-dream breed from US exp. station (1960s, registration 1980s)
-combo of: finn for prolificacy, rambouillet for wool fineness, dorset for long breeding season, carcass, targhee for frame size
-Wool quality, mothering, growth
Club Lamb Industry
-influenced by suffolk, hampshire, dorset, and southdown
-lucrative industry
-expensive: some rams can sell for $100,000
-follow a trend
-terminal production
terminal production
emphasis: growth, feed efficiency, carcass, lamb livability
reproduction
emphasis: prolificacy, weaning weight, milk production, out-of-season lambing.
environment
rangeland, wet grassland, southern heat
fleece production
fleece micron (smaller, the higher quality)
what is the annular cycle for sheep?
lambing (target 60 days), weaning/feeding (target 60 days and Ewes 120+), flush/breed (flush 6 weeks and Ram same), and pregnancy (150 days)
Rumen developement
-fully functional at 6-8 weeks
-before: hay is less nutritional value (provides scratch factor to initiate rumen developement)
-Lambs learn from dam to eat
-Hay is effective to the creep
-Rumen development starts as soon as lambs begin eating
Weaning
-remove ewes and leave lambs (ideally out of sight and hearing)
-Do not change ration at weaning
-Maintain same grouping (I.E. keep siblings together)
-Minimum interruptions
Body condition scoring
-pick the highs and lows in groups
-gives you idea of overall herd
-or score
-When feeding get a handle on the spine and feel the processes
-Make feeding adjustments slowly (remember the weather changes intake needs as well)
Seasonal cyclicty
-seasonally polyestrous
-fall breeders typically
-decreases in day length = increase in melatonin synthesis
-typically august through march (peak: oct. through dec.)
-can be manipulated for out of season breeding
Ram management
-breeding soundness exam (evaluates the rams ability to breed females)
Components of exam:
-BCS, feet/legs/mouth/teeth, scrotum/testicles/epididymis, sheath/prepuce/penis, semen evaluation, and libido test
-utilize a marking harness to track mountings.
What are the common internal parasites?
tapeworm, roundworm, haemonchus, coccidia, and flukes
What are the common external parasites?
lice, keds, ticks, flies, and mites
What are internal parasite management?
-deworming most common practice
-anthelmintic
-ivermectin
-cydectin
-valbazen
What is fly strike
-common problem in the sheep industry
-due to soiled wool and flies
-more prevalent in hot climates (texas, california but can happen anywhere)
-Treatment: remove maggots and struck wool, apply dressing to affected area OR apply specific spray for screw worms
What are the three classifications for goats?
Dairy, meat, and fiber
What are the dairy breeds?
Alpine, Lamancha, Nigerian Dwarf, Nubian, Saanen, Toggenburg
What are the meat breeds?
Boer, Kiko, Pygmy, Spanish, TexMaster,
What are the fiber breeds?
Angora, Cashmere, and Pygora
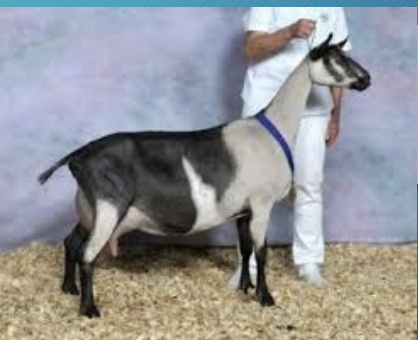
Alpine
-originated in the Alps
-generally short haired (no distinct color established and 7+ color variations)
-Moderate size: 135-170 lbs
-Heavy milkers
-Emphasis on milk production and udder placement

Lamancha
-Developed in Oregon, USA
-Excellent dairy temperament
-Two types of ears: gopher ear: max. 1” in length with little to no cartilage OR elf ear: max. 2” in length
-high component milk
-high fat

Nigerian Dwarf
-west african origination
-miniature goat: ideal weight 75 lbs
-high prolificacy: up to 5 kids, new brons 2 lbs, with early onset puberty
-smaller udder/teats than other breeds

Nubian
-Developed in England ]
-Anglo-Nubian
-Pendulous ears
-Good udder quality
-Large frame: >250 lbs
-All purpose breed
-Moderate milk production with high avg. butter fat

Saanen
-Originated in Switzerland
-Heavy milk production (3-4% milk fat)
-Color: white or light cream
-Performs best in cooler conditions

Toggenburg
-Originated in Switzerland
-Oldest known dairy goat breed
-Medium sized: does - 125 lbs
-Excellent udder development
-high milk production: avg. 3.7% fat
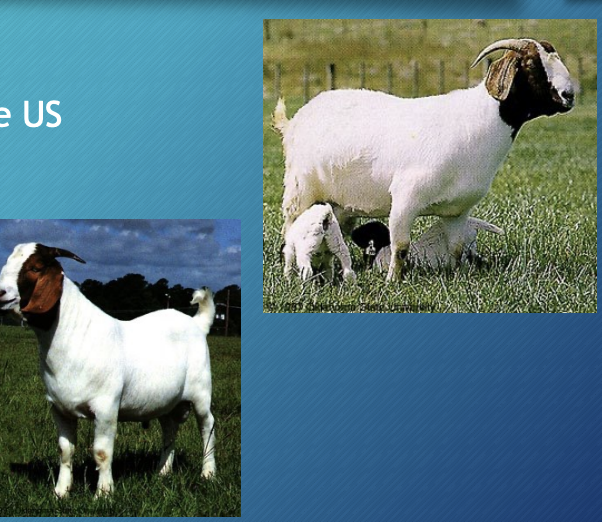

Boer
-Large meat breed: >200 lbs
-Imported from South Africa into the US
-Fast growing breed within Us
-Excellent carcasses
-150% kidding rate

Kiko
-Originated in New Zealand
-Crossbreeding feral does (w/ nubian, toggenburg, and saanen)
-moderate frame: 100+ lbs
-imported to US in 1990s
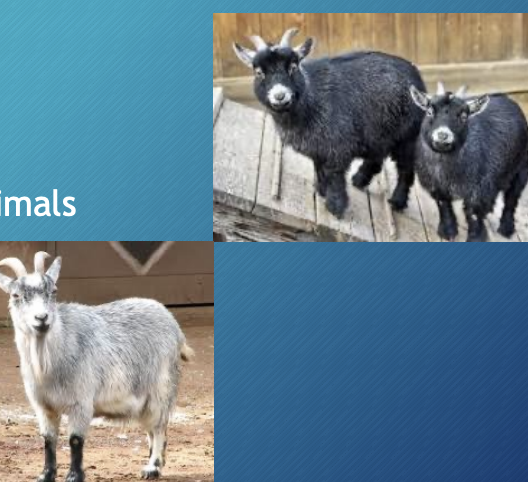

Pygmy
-West African origination
-small frame: 15-20” tall and 30-60lbs on avg.
-Now utilized more as a companion animals