speed of reaction
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
collision theory
the higher the frequency of successful collisions, the faster the reaction
catalysts
substance that increases the rate of a reaction
itself remains unchanged chemically and in its mass at the end of the reaction
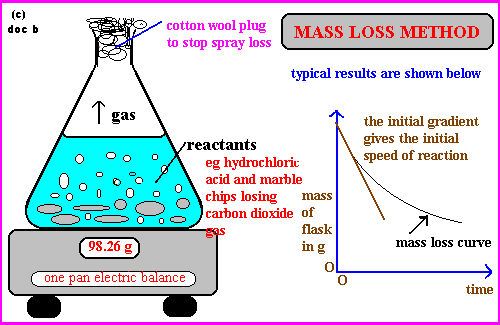
measuring speed of reaction methods — mass loss method
measuring the amount of reactant used up per unit time
marble chips — CaCO3
why stopper not used?
stopper prevents mass loss, thus cotton wool is used to allow carbon dioxide to escape
cotton wool — prevent acid spray due to vigorous reaction
eqn: speed of reaction = amount of reactant used up/time taken
normally used for CO2 production
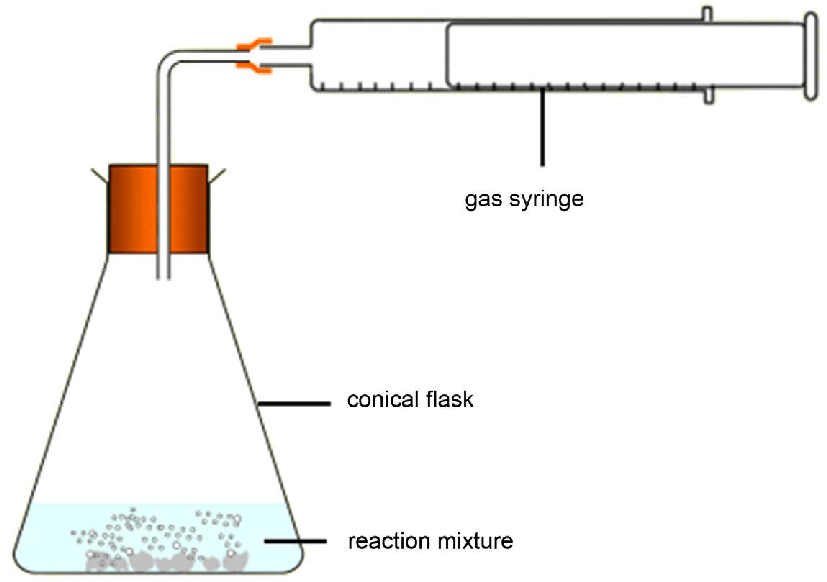
measuring speed of reaction methods — measuring the amount of product formed per unit time
eqn: amount of product formed/time taken
measuring speed of reaction
change in mass of reacting mixture
colour changes
formation of precipitate
pH changes
temp changes
titration to monitor change in conc.
collision theory core concept
for reaction to occur, reactant particles need to collide
however collisions with too little energy will not produce a reaction
all colliding particles need a minimum amount of energy — activation energy
collision theory states for a reaction to occur between 2 particles —
reacting particles must collide with each other
must collide with minimum energy — activation energy
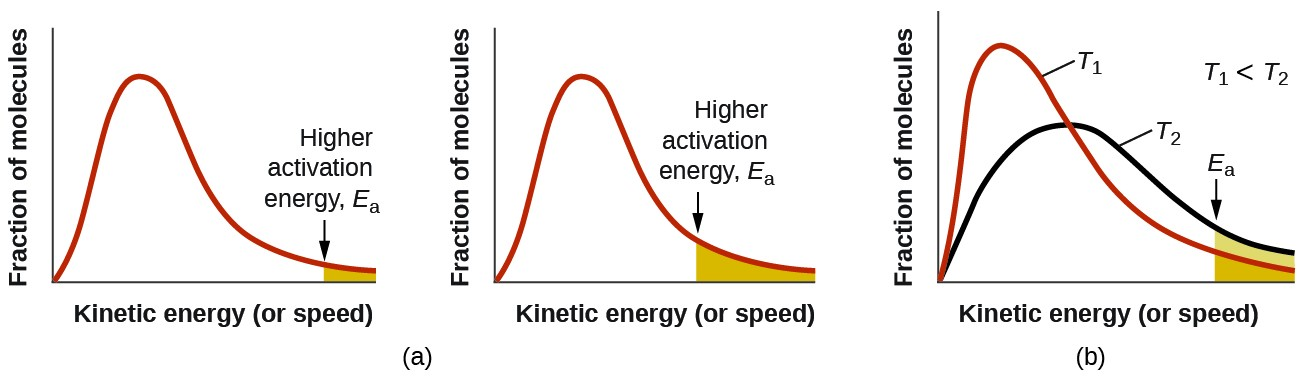
temperature
at low temp —
particles have lower kinetic energy
they possess energy lower than activation energy
move slower ⇒ lower frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
slower rate of reaction
at high temp —
particles have higher kinetic energy
they possess a higher energy than the activation energy
move faster ⇒ higher frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
faster rate of reaction
note: rate of reaction approx. doubles for every 10.0°C increase
total surface area
large lump —
smaller surface area exposed to reactant particles
lower frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction decreases
smaller lumps —
increased surface area exposed to reactant particles
higher frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction increases
concentration of reactant
dilute solution —
fewer reactant particles per unit volume
lower frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction decreases
concentrated solution —
more reactant particles per unit volume
higher frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction increases
pressure (significant for gaseous reactant)
lower pressure —
fewer reactant particles per unit volume
lower frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction decreases
higher pressure —
more reactant particles per unit volume
higher frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles
rate of reaction increases
catalysts
physical appearance may change at end of reaction but not its chemical properties
not consumed during the reaction so the mass remains the same
it increases the speed of reaction but not yield of reaction
only small amount is required to catalyse a reaction
most catalysts — transition metals or compounds of transitions metals
how does catalysts increase rate of reaction
increases rate of reaction —
providing alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy
more reactant particles will have energy greater than equal to the activation energy to undergo successful collisions for a reaction to take place
answering tech:
[CATALYST] speed up the reaction by providing alternative pathway of lower activation energy for the reaction to proceed
more [REACTANT] particles have energy greater than or equal to the activation energy
higher frequency of successful collisions to take place
faster reaction rate
why are there high risk of explosion in coal mines
fine coal dust burns more rapidly than large pieces of coal
as the exposed surface are of coal dust is much greater
when coal is extracted, a lot of dust is produced
greater exposed surface area of coal dust when mixed with combustible gas
result in higher frequency of successful collisions with oxygen molecules in the air
spark can easily ignite the coal dust causing an explosion