504 Exam 1 Review – Spring 2025
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards summarizing foundational theories, clinical concepts, vision/hearing changes, fall prevention, dementia care, and key policies relevant to OT practice and the 504 Exam 1 review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Free Radical Theory
Aging results from cumulative oxidative damage to cells and tissues caused by free radicals.
Shawn has been having trouble hearing. Upon inspection his
doctor says it is due to a impacted earwax. What type of hearing
loss is this?
Conductive hearing loss
True/False: Accelerated aging includes income, education,
neighborhood disadvantage, and discrimination .
True
Reminder: Accumulated Risk Theory= Life-course model showing how exposures (e.g., low SES, war, job changes) add up to affect health such as CVD.
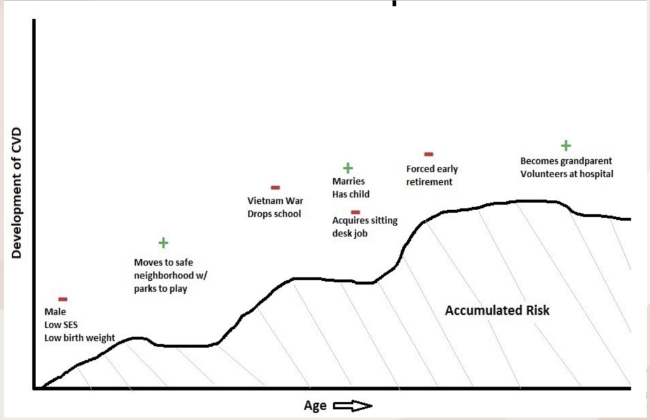
What theory does this graph represent?
Life Course Perspective- A theoretical framework that emphasizes the importance of the timing of life events and social experiences on health outcomes throughout a person's life.
Who can attend a PACE Program? (Eligibility)
Age 55+, live in program’s service area, need nursing-home level care, and can live safely with PACE services.
Accelerated Aging Factors
Income, education, neighborhood disadvantage, and discrimination contribute to faster biological aging.
What is NOT a fundamental mechanism of Selective Optimization with Compensation?
1. Selection
2. Optimization
3. Augmentation
4. Compensation
Selective Optimization With Compensation (SOC) = Adaptive aging model with three mechanisms: Selection, Optimization, and Compensation (not Augmentation).
What are the Care Services provided at a CCRC (Continuing-Care Retirement Community)?
Provides independent living, assisted living, memory care (Alzheimer’s care), nursing home services, and hospice care.
What level of complexity would you rate a patient with 4 performance deficits?
Moderate Complexity (OT Eval)
True/False Changes in cognition that negatively impact function are NOT a part of health aging
True
Negative functional cognitive changes are NOT considered part of healthy aging.
Which theory states older people will primarily engage in activities and interactions that are emotionally meaningful compared to young people?
Socioemotional Selectivity Theory= Older adults prioritize emotionally meaningful activities and relationships over information-seeking ones.
What are at least 3 consequences of changes in the cardiovascular system?
Hypertension, fatigue, shortness of breath (SOB), dyspnea, postural/orthostatic hypotension, stroke, heart attack, aneurysm, peripheral vascular disease (PVD), thrombus.
How does taste change as we age?
Fewer taste buds and less saliva; reduced salt and sugar taste intensity.
What are the criteria for Fried’s Frailty Phenotype (PEW3)?
Low physical activity, Exhaustion, unintentional Weight loss, Weak grip, and slow Walking speed.
_______ is defined as finding strategies or techniques that work
around limitations.
Compensation (SOC) = Finding strategies/techniques that work around limitations.
Adaptation
Modifying the setting or task demands to facilitate performance.
Which Act required hospitals to notify family caregivers when a patient is to be discharged?
Caregiving Advise, Record, and Enable (CARE) Act
What are the eligibility requirements of Medicare?
65+, or under 65 with disability/end-stage renal disease (ESRD)/ALS; must qualify for SS benefits and be a U.S. resident ≥5 years.
True/False: You can NOT be covered by Medicare and Medicaid
False
Dual Eligible= Individual who is covered by both Medicare and Medicaid.
4Ms of Age-Friendly Health Systems
What Matters, Medication, Mentation, Mobility.
Is mild cognitive impairment (MCI) considered dementia?
No, cognitive decline that is not severe enough to be classified as dementia.
The nurse only talks to Edith's daughter about her care even when Edith can be included in the conversation. What type of ageist communication is this?
Ignoring Talk = Ageist communication where the older adult is excluded from conversations about their care.
“Hi sweetie how about we get you dressed you would look so cute in this cardigan” is an example of what kind of ageist communication.
Elderspeak = Patronizing baby-talk style speech directed toward older adults (e.g., “Hi sweetie”).
What sets the communication enhancement model apart from the communication predicament model?
Instead of stereotyped expectations modifying communication, the individual is taken into account first for cues, modified communication, and individual assessment. Leading to enhanced empowerment, well-being, effectiveness, and communication.
What major neurocognitive disorder impacts IADLS and ADLs?
Major (Moderate/Severe) Neurocognitive Disorder (Major-Moderate NCD)
Describe how the netherlands and switzerland approach dementia care.
Dutch/Swiss dementia villages (‘Dementiaville’ Model) emphasizing independence, meaningful activity, and minimal medication.
Functional Cognition
How a person uses thinking and processing skills to complete everyday activities in real contexts.
Delirium Symptoms
Fluctuating attention, altered awareness, waxing/waning cognition, agitation, psychosis.
Medicare Parts
Part A–inpatient; Part B–outpatient; Part C–Medicare Advantage; Part D–prescription drugs.
True/False: presbyopia creates
difficulty with near vision
True
Presbyopia= Age-related difficulty with near vision due to loss of lens elasticity.
Common Dementia Subtypes
Alzheimer disease, Vascular dementia, and Lewy Body dementia.
What approach is characterized by the Positive Approach to Positive Approach to Care (PAC) skills?
Teepa Snow’s dementia care method emphasizing retained abilities and positive interaction. (Snow Approach)
What dementia is categorized by visual hallucinations?
Dementia With Lewy Bodies= Dementia subtype notable for recurrent visual hallucinations and parkinsonism.
Jackson was diagnosed with Alzheimer's Disease and no long responds to his name and is dependent on help for his daily activities. What stage of Alzheimer’s is he in?
Severe Alzheimer’s Disease (Stage 3)= Loss of name recognition, full dependence in ADLs, severe cognitive decline.
You are an OT seeing a client diagnosed with mild dementia. What interventions and approaches will you apply?
Education, predictable routines, compensatory strategies, future planning, resource linkage, and impact on occupation.
What stage of dementia specifically mentioned maintaining QOL and dignity as a intervention?
Late-Stage Dementia/Severe Dementia Interventions= Emphasize quality of life, dignity, comfort, and meaningful sensory engagement.
What are the visual changes associated with cataracts?
Cataract Vision Changes= cloudiness, blurry vision, faded colors, halos around lights.
True/False: generally Accessibility of U.S. Housing is accessible
False
Generally not accessible for older adults and those with disabilities.
WeHSA (Westmead Home Safety Assessment)
Gold-standard comprehensive home-safety assessment tool.
Lewis is complaining about issues seeing in his peripheral and feels like he is looking through a tunnel. What visual condition might he be experiencing?
Glaucoma= Optic nerve damage causing peripheral vision loss (‘tunnel vision’).
True/False: Kelly stumbles on the edge of a rug and lands on
her bed. This is not considered a fall.
False, a fall is considered any unexpected/unintentional event in which the person comes to rest on the ground/floor or lower level.
Which of the following is NOT a CDC recommendation for fall prevention
1. Remove clutter and tripping hazard
2. Get an eye exam as needed
3. Speak up to your healthcare provider and review medications
4. Incorporate exercises to address strength and balance
‘Get an eye exam as needed’ is NOT an official CDC recommendation; exams should be yearly.
Closed captioning, auditory liquid level indicator, and a vibrating alarm are all examples of___ type of AE?
ALTERNATIVE Assistive Technology= Devices that replace a lost sense/function (e.g., closed captioning, vibrating alarm).
What visual condition would using an Amsler Grid be appropriate for?
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Self-monitoring tool for detecting central vision distortion in age-related macular degeneration.
Describe Project CAPABLE and its impact on clients.
- An interprofessional program for urban older adults that provides an occupational therapist, nurse, and handy worker to address self-identified functional goals.
-Six times return on investment. Roughly $3,000 in program costs per participant yielded more than $30,000 in savings in medical costs
OT-nurse-handy worker program helping urban older adults meet functional goals; 6:1 ROI.
When Carrie is standing she is unable to stand still without swaying or holding onto something. What type of balance does Carrie has trouble with?
Static Balance= Ability to maintain upright posture without movement; difficulty indicates increased fall risk.
What groups/populations are states required to provide coverage for under Medicaid?
Children, pregnant women, adults with dependent children, individuals with disabilities, older adults.
What is the recommended frequency for balance training? And how can the difficulty be increased?
Practice 1–7×/week; increase difficulty by narrowing BOS, unstable surfaces, reduced vision, dual-tasking.
Which of the following is NOT an age-related change that
affects balance?
- Loss of proprioception and vibration sense
- Hyperkyphosis
- Slowed reaction times
- Increased vestibular information
Increased vestibular information is NOT an age-related change (actually vestibular input declines).
What are at least 3 fall risk factors studies have identified?
Muscle weakness, previous falls, gait deficits, assistive device use, impaired ADLs.
Jim had a fall a few months ago in his home. He now walks very slowly, holds onto furniture when walking, and tries not to go out much. What is Jim demonstrating? What are the consequences?
Fear of Falling= Post-fall anxiety causing activity restriction, deconditioning, depression, and lower QoL.
How does the visual field change with age?
Visual field narrows with age, reducing side vision.
Phil asks himself “Has life been worth living?”. What theme of meaning in late life does this represent?
Existential Meaning in Late Life= Thoughts on whether life has been worthwhile; part of meaning-making themes.
What is the difference in appearance of wet vs dry age-related macular degeneration? And how does it impact function?
Dry: thinning, white/yellow fatty protein deposits ; Wet: abnormal growth of blood vessels; Functional Impact: both impair central detailed vision (so impacts reading, driving, identifying faces, worlds, and letters, also safety and falls)
What changes in vision are associated with diabetic retinopathy?
Reduced near/distance acuity and scotomas (dark spots) in vision.
What is the difference between age-related hearing loss (AHRL/Presbycusis) and noise-induced hearing loss?
Presbycusis: stereocilia die naturally as a person ages and results in symmetric high-frequency loss from aging; NIHL: stereocilia damaged and asymmetric damage from >85 dB prolonged exposure.
Jackie has a home in Florida she travels to every winter from NY.
What term best describes this behavior.
Snowbird= Person who migrates seasonally from colder to warmer climates (e.g., NY to Florida).
What does the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) identify?
Standardized tool for identifying delirium in clinical settings.
Different assessments are used compared to mild/major NCD due those with delirium being unable to attend to long assessments.
Sally has been diagnosed with a Mild NCD (MCI), she currently uses a small notebook to jot down notes and writes reminders on her bathroom mirror. What kind of aid is she engaging in?
External Memory Aids= Tools outside the body (notebooks, calendars, mirror notes) used to support cognition.
What are some internal aids that may be beneficial?
Mental rehearsal, visualization, chunking, mnemonics, and association strategies.
True/False occupational therapists can help with life transitions such as retirement and widowhood.
True, occupational therapists assist individuals in adapting to significant life changes by developing strategies and facilitating engagement in meaningful activities.