1.2 System Design Basics
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Computer Hardware
Physical, tangible elements of a computer system (e.g CPU, HDD)
Computer Software
Set of instructions for the CPU to preform specific operations, comprised of both programs and data
Peripheral Device
Auxiliary device that can connect to, communicate and work with the computer (e.g input/output devices, printers, etc.)
Copmuter Network
Set of computer systems that are interconnected and share resources as well as data
Human Resources
People who are used or could be used in organization, business, or economy.
Dumb Terminal Role
A device that usually consists of a keyboard, a monitor, and a network card that is connected to a server or a powerful computer. Dumb terminals depend entirely on the computer to which they are connected for computations, data processing, and data management
Thin Client Role
Relatively low performance terminal, which heavily but not entirely, depends on the server to which it is connected
Client Role
Receiving data via the network, whereas the server has saved data on it and offers this to clients. It accesses services made available by server, by sending requests to the server
Server
Program/host computer that fulfills requests from client programs or computers across network and shares info to clients
Email Server
Message transfer agent that transfers electronic messages from one computer to another in a network
Domain Name Server (DNS)
Server that translates web addresses written in letters (more memorable for humans) to the numeric IP (internet protocol) address
Router
Connects networks together to forward data packets between networks, deciding where to send information from its destination address and routing policy
Domain Name System Server
Attributes names to network addresses and therefore allows users to input string names instead of numerical IP address
Firewall
Controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, determining what data packets should be allowed through, based on a rule set. Needed to protect the integrity of client computer
Client-server
Software network architecture system where clients request information and servers perform tasks in order to provide the information. At least one server machine is required as a prerequisite for the client-server architecture. The main difference between server and clients is that servers share their resources whereas clients do not
Reliability (Social and Ethical Issues)
Refers to how well an IT system functions. Computer failures cause data loss, time loss, money loss, injury, or even death. The reliability of IT systems determines confidence in their value
Integrity (Social and Ethical Issues)
Refers to protecting the completeness and accuracy of data. Data lacks integrity if it is incomplete, out of date, or has been purposely or unintentionally altered
Inconsistency (Social and Ethical Issues)
Problems may also arise if information is duplicated in a database and only one copy is updated, causing inconsistency (e.g. telephone field)
Security (Social and Ethical Issues)
Refers to the protection of hardware, software, peripherals, and computer networks from unauthorized access. Biometrics, proprietary tokens, passwords, firewalls, and locks are some of the most common security systems placed to restrict access to IT systems.
Authenticity (Social and Ethical Issues)
Involves a person proving their identity to gain access to a computer system beyond reasonable doubt. it is important to mention that requiring more than one independent factor increases the difficulty of providing false credentials
Privacy (Social and Ethical Issues)
The ability to control how and to what extent data is used and disseminated to others. It includes issues such as: how long data is stored, who was access to the data, and how the data is used.
Anonymity (Social and Ethical Issues)
Privacy becomes anonymity when, for instance, an individual uses an IT system to conceal his/her true identity in order to cyberbully another person, commit illegal actions or crimes, hack computers, or commit terrorism, etc.
Intellectual property (Social and Ethical Issues)
Refers to ideas, discoveries, scientific endeavors, photographs, films, essays, and art works. Copyright laws are designed to protect intellectual property from unauthorized and illegal reproduction. Modern “copy and paste” and file-sharing practices and devices make it easy to break copyright laws.
The Digital Divide and Equality of Access (Social and Ethical Issues)
The growth and the use of IT systems have not developed at the same rate for everybody in all parts of the world, or in all areas of the same country. Even within advanced countries there are people who lack access to IT infrastructures, and online services. Economic costs, financial costs, lack of literacy, lack of language skills, and lack of basic resources such as electricity are the main reasons that sustain the digital divide
Surveillance (Social and Ethical Issues)
Using IT to monitor individuals or groups of people either with or without (also a privacy issues) their knowledge or permission. Governments, law enforcement, private groups, employers, traffic control, etc. may perform surveillance.
Globalization and Cultural Diversity (Social and Ethical Issues)
IT helps to diminish the importance of geographical, political, economic, and cultural boundaries while speeding up the global, financial, sport, and cultural news. Traditional cultures and values may diminish gradually over time.
May diminish traditional cultures
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
An authentication technique used to control computer access. Use must exhibit at least two out of three categories.
What are the authentication factors used in MFA?
Knowledge factors: “things only the user knows”, passwords
Possession factors: “things only the user has” , ATM Card
Inherence factors: “things only the user is”, biometrics
IT Policies (Social and Ethical Issues)
Enforceable procedures and measures that promote the appropriate use of computers, networks, information systems and technologies. Governments, public authorities, local authorities, businesses, private groups or individuals are developers of various IT policies. The fast pace of information technology progression means policies often quickly made obsolete.
Standards and Protocols (Social and Ethical Issues)
Predefined technical rules and conventions that developers of hardware and software should follow. Standards and protocols allow for compatibility, facilitate communication and interoperability. They are needed to ensure different systems are compatible with each other
People and Machines (Social and Ethical Issues)
Internet addiction is a social impact. The use of AI in military or law-enforcement situations is also an issue of social concern. This subject analyzes all aspects of the interaction between IT and humans
Stakeholders
Individuals, teams, groups, or organizations that have an interest in the realization of a project or might be affected by the outcome. Any person who has interests in an existing or proposed information system can be described as a stakeholder of the system
End-User
The person who is going to use the product. A relevant stakeholder can also be a frequent user of the current system. He/She will be able to identify flaws and errors of the current system or inconveniences that he/she has spotted. They will be able to propose some improvements that will be crucial to the update of the system.
Reasons for Employees Working From Home
Saving in fuel cost and commuting time
An opportunity to work at your own pace (more comfortable, therefore increased productivity). Also able to work in an undisturbed environment, choose their own work hours
Convenience of not having to travel
Reasons Against Employees Working From Home
Employees can clam the employees are part time consultants or the like to avoid paying benefits like insurance, medical plans, taxes
Stain on families that result when a family member works from home
At-home employees miss interaction with co-workers at the office
At-home employees think they work too much, employers think they do not work enough
Employees cannot monitor employees, expensive of setting up a VPN
Reliability (Issues to Consider when Networking)
How consistently a computer system functions according to its specifications with minimal system failure. Failures result in data, time, or revenue loss
Data Integrity and Consistency (Issues to Consider when Networking)
Maintenance of accuracy and consistency of data. Must be complete, up-to-date and unaltered. Inconsistent if theres data duplication/redundancy
Standards and Protocols
Rules followed in development of systems, including proprietary standards (e.g. computers compatible with Microsoft operating systems), industry standards, and ‘de facto’ standards
Interviews (Method to Obtain and Evaluate Requirements)
Face-to-face with verbal responses. Can be structured with the same questions and manner for every stakeholder, or unstructured with more flexibility
Reasons for Interviews
Talk directly to users/members of the organization and can observe non-verbal behavior, meaning data can be considered more reliable and valid
Unstructured interviews can reveal more questions that otherwise wouldn’t have been addressed, meaning more detailed reports.
Reasons Against Interviews
Data from unstructured interviews is hard to summarize, evaluate, and analyze clearly
Level of detail depends on the type of interview - structured interviews can less detailed responses
Time-consuming to gather detailed results
Questionnaires (Method to Obtain and Evaluate Requirements)
Can be closed/restricted (box checking, yes/no form) or open/unrestricted (free-open questions)
Survey methodology
Domain of applied statistics that focuses on taking samples from a population as well as improving on the carious data collection techniques
Reasons for Questionnaires
Time-saving and cost-efficient: can acquire information from a large group people easily and cheaply
Closed/restricted questions makes data easier to compare
Open questions means more detailed reported can be created
Reasons Against Questionnaires
Level of detail depends on type of questions: closed questions don’t allow for clarifications or extra detail
Stakeholder could interpret the meaning of the question incorrectly and therefore invalidate their answere
Direct Observation of Current Procedures (Method to Obtain and Evaluate Requirements)
On-site observation of different departments to see where things can be more different
Reasons for Direct Observation of Current Procedures
Quick realistic information on procedures in the current system
Highlight aspects not detected in questionnaires/interviews, meaning more detailed reports can be introduced
May be more reliable than interviews, can see what stakeholders actually do, instead of what they report to do
Help to understand positive and negative features of the current system, which can be used when specifying the requirements of the new system
Reasons Against Direct Observation of Current Procedures
Time-consuming and expensive, an entire business or system cycle make be observed which could take significant time and administration costs
People act differently when they are being observed/scrutinized, making some observations unreliable
Observations may be made by only one person, and thus may be biased
Examining Current Systems
Process that involves the detailed examination of the current system, analysis of its functions and procedures, studying the business and the system documents such as order documents, logistics documents, and computer systems procedures and reports used by operations and senior managers
Literature Review
The identification, retrieval and management of various sources in order to find information on a topic, areas that might be interesting for further studies, derive conclusions, as well as develop guidelines for practices
Competing Products
The analysis of competitive factors, their benefits, vulnerabilities, successful characteristics, the breakthroughs that they introduce, their design features as well as the users’ and stakeholders’ acceptance
What should a modern information system be planned to?
Increase client trust
Preserve brand strength
Preserve organization reputation
Maintain corporate resiliency
Enhance organizational piece
Requirements Specification Document
A document that specifies system requirements. This document defines the specific customer requirements of a customer system. It is included within the system analysis and may be later used to test the system, after implementation, in order to evaluate it
Types of Processing
Online processing (interactive)
Data processing preformed by a single processor through the use of equipment that it controls.
Real-time processing
Data processing performed on-the-fly in which the generated data influences the actual process taking place
Batch Processing
Data processing performed on data that have been composed and processed as a single unit
System Flowchart
The description of a data processing system, including the flow of data through any individual programs involved, but excluding the details of such programs. Constructed during analysis activities and represent various computer programs, files, databases, associated manual processes,etc

What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Action or Process

What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Input or Output Device
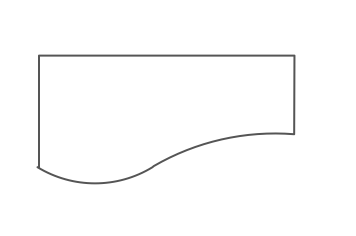
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Document
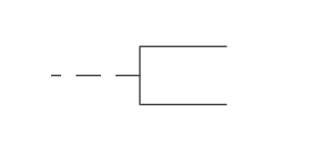
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Annotation
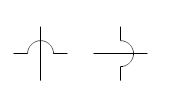
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Lines Crossing
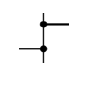
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Lines Joining
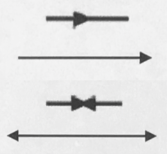
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Data Flow
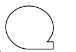
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Tape
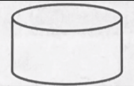
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Disk
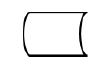
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Online Storage
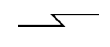
What does this symbol represent in system flowcharts?
Communication Link (Two Way unless Indicated)
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Used to describe the problem to be solved. Shows how the data moves through a system and the data stores that the system uses. Does not specify the type of the data storage and the type of data.
What does this symbol represent in DFD?
Process. A operation performed on the date
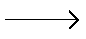
What does this symbol represent in DFD?
Data Flow. Direction of data flow.

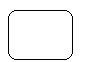
What does this symbol represent in DFD?
Data Store. File held on disk or a batch of documents.
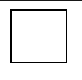
What does this symbol represent in DFD?
External Entity
Structure Chart
Describes functions and sub-functions of a system, as well as the relationships between modules of a computer program. The organization of a structure chart is straightforward, allowing the analyst to split a large problem into smaller ones.
Modular Design
The process of a designing system modules individually and then combining the modules to form a solution to an overall problem.
Top-Down Design or “Stepwise Refinement”
A software design and problem solving technique that involves the partition of a problem into smaller sub-problems
Pseudocode
An artificial language that is not directly related to any particular hardware and is used to describe algorithms.
Module
Complete and independent part of a program or an algorithm
Modular Programming or “Modularity”
Method of partitioning a computer program into separate sub-programs. The main advantage is that each sub-program can be easily modified and maintained without the necessity to alter other subprograms of the program
Modular Language
Language that supports modular programming
Prototype
An early version or model of a system
Functionalities of a protoype
Attracts the attention of the client, since it encourages them to use it and “get a feel for it”
Provides just enough of the concept for the investors to decide if they want to fund the full production or not
Encourages active participation between users and developers
Gives an idea of the final product
Helps in the identification of problems with the efficiency or the desiItegn
Increases system development speed.
Iteration (Design)
The repetition of a set of instructions for a specific number of times or until the operations yield a desired results.
With each iteration, additional features may be added until there is a fully functional software
What are consequences of not having end-user participation?
Software not suitable for its intended use because of a lack of feedback
Adverse effects on user productivity, efficiency, and so on.
What are some social and ethical issues associated with the introduction of new IT systems?
Robots are replacing humans in many tasks, can be interpreted as just the job changing. Would create social disturbance similar to that during the Industrial Revolution
Should this uncontrollable development continue?
Continuous development of computerized systems may absorb people and cause them to drift apart from the physical world and become enclosed in virtual environments.
Accessibility
The potential of a service, product, device, or environment to serve and meet the needs of as many individuals as possible.
Usability
The potential of a product, application, or website to accomplish user goals
Ergonomics or human engineering
the design of safe and comfortable products, systems or process, specifically for people.
8 Quality Components of Usability
Complexity/Simplicity: Amount of effort to find a solution or get a result
Effectiveness: Comparison of user performance against a predefined level
Efficiency: Task completion time after the initial adjusting period
Error: Numbers of errors, type of errors and the time needed to recover from errors
Learnability: time used to accomplish tasks on the first use
Memorability: time, number of button clicks, pages, and steps used by users when they return to the device after a period of not using it
Readability/comprehensibility: Reading speed
Satisfaction: Attitude of users toward applications after using them; i.e. if users like it.
GPS Usability Problems
Small Screen
Low-quality speakers
Antenna with poor performance that makes it difficult to receive a satellite signal
Inaccurate geographical data
Outdated street data
Inefficient routing software
Tablets Usability Problems
Accidental touches leads to undsired selections
Difficult to learn different gesture features of various manufacturers
Bad or poor scaling and zoom control
Difficult-to-use control features
Small side buttons
Poorly written instructions
Game Consoles Usability Problems
Some portable game consoles have relatively small screens
Buttons may be too small
Difficult to use outdoors (insufficient brightness)
Short battery life
PCs
Excessive keyboard use may lead to RSI (repetitive strain injury) syndrome
Excessive use of a large, bright screen may cause eyesight problems or tire the eyes
Poor room lighting conditions may lead to distracting reflections on the screen
The mouse of a PC is a designed for right-handed people, making its use difficult for left-handed people.
Digital Cameras
Incorrect calibration of touch screen menus
The need to hold the camera vertically, does not allow convenient navigation through the touch-screens. An auto rotate screen option would increase usability
If a camera does not have a flash capability or it is equipped with an inadequate flash then the user has to purchase and carry an extra hardware component
The buttons are too small, making it difficult to push them
Some cameras requires specific software to connect them with a computer and store or transfer files (no drag and drop files option)
Mobile Phones
The keyboard of a mobile phone is very small and as a result many novice users elderly people or users with bad eyesight struggle to use it
Some users don’t really need all the special feature; they just need a basic device for calls and SMS messaging
MP3
Tiny buttons
Insufficient memory
Fragile
Lack of a screen in “micro” or “shuffle” devices
Overall usability can be improved by use of NLP (natural language processing) and making the overall interface more intuitive, so that even people not familiar with technology can use them
Use of acceleration sensors or gesture control to enhance functionality
Solutions for Visual Impairment (blindness to color vision deficiency)
Input Devices/Methods
Larger Screen;
Braille input devices,
Output Devices/Methods
Color or contrast changes
Access to hotkey
Functionality;
Text-to-speech;
Screen Magnification
Speech Recognition
Solutions for Hearing and Speech
Subtitles
Visual Effects
Voice Recognition
Solutions for Cognitive Problems (learning disabilities)
Word processing to correct dyslexia
Special software with strong interaction
Use of touch screen and bright colors
Solutions for Mobility Issues (limited hand mobility and Parkinson disease)
Input methods/devices:
Specialized disks
Pointing device to press keys and control a personal computer
Left-handed and right-handed keyboards
Track balls and specialized input devices
Expanded keyboards
Scanning and Morse code
Special Knobs
Sip-and-Puff (SNP)
Natural Language processing, voice recognition, and speech-recognition
Word Prediction
What it happens if user interface is bad?
Users will leave. If an interface is not appealing then it will not attract users.
Difference between morals and ethics
They both refer to “right and wrong”. Religion, society, profession, and family set the ethic framework. One’s own principles set morals.