Osmosis - Biology Double Award
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Osmosis:
Osmosis is the diffusion (movement) of water from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution through a selectively permeable membrane
What is the difference between Osmosis and Active Transport?
Active Transport requires energy
How does Osmosis work?
When a solute dissolves in water it does so because the water molecules are attracted to the solute and cluster around it. This reduces the freedom of movement of the water molecules.
How does water move in pure water?
Freely moving and exerting pressure. This is called water potential.
What happens when you add sucrose and salt to pure water?
This reduces the freedom of movement of water molecules, so adding some solute lowers the water potential
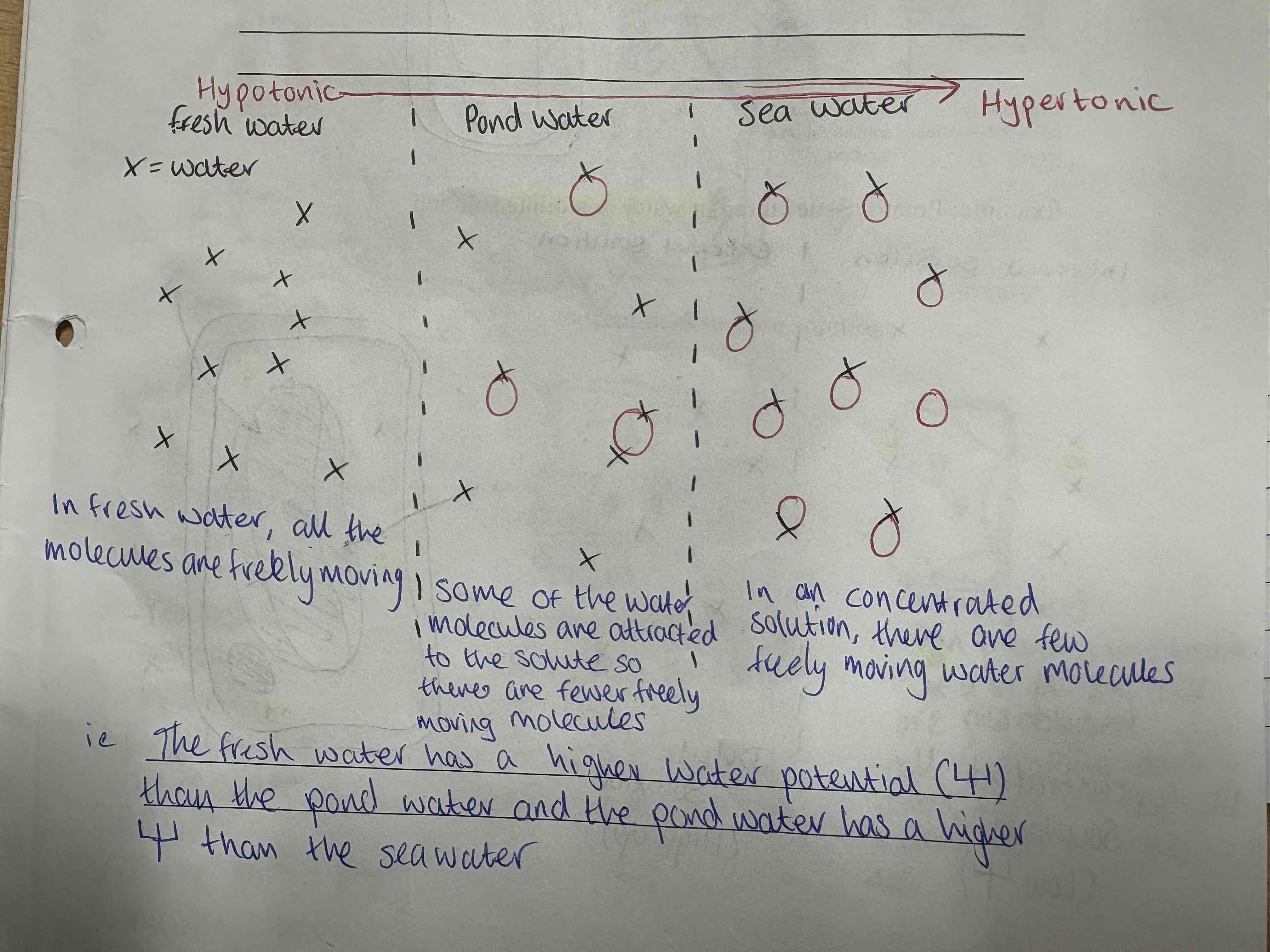
Look at this image:
Hypotonic = freely moving molecules
Hypertonic = very few freely moving molecules
Describe the effect of Osmosis in plant cells:
When plant cells are in contact with dilute solutions (which have a higher water potential) they gain water by Osmosis
The vacuole fills up with water and swells eventually the cell gains so much water that the cell wall pushes back on the contents of the cell
The cell wall prevents excessive water uptake and so prevents the cell from bursting
Describe Turgid, Flaccid, Plasmolysed:
Turgid -
Reached max water intake
Cell membrane pushes against the cell wall
Sign of healthy plant
Vacuole expands
Flaccid -
When plant is droopy it is a sign the cells are turning flaccid
Vacuole is smaller
Less sturdy
Plasmolysed -
When plant is unsalvable it is a sign the cells are Plasmolysed
Cell membrane tears away from the cell wall
Shrivelled vacuole
The space between the cell wall and the cell membrane is filled with the external sugar solution because the cell wall is fully permeable
Describe the effect of Osmosis in animal cells:
If the Animal Cell is placed in a solution with higher water potential the Animal Cell will continue to swell as it doesn’t have a cell wall to prevent excessive water uptake. If the RBC absorbs to much water it bursts (lysis)
If the Animal Cell is placed in a solution with lower water potential the Animal Cell will lose water by Osmosis and become shrivelled (Crenation)
Isotonic solutions are solutions with the same water potential as the Animal Cell
Why do plants need water?
Support -
Plants don’t have a skeleton so they rely on the turgidity of the cells to keep them upright
Transport -
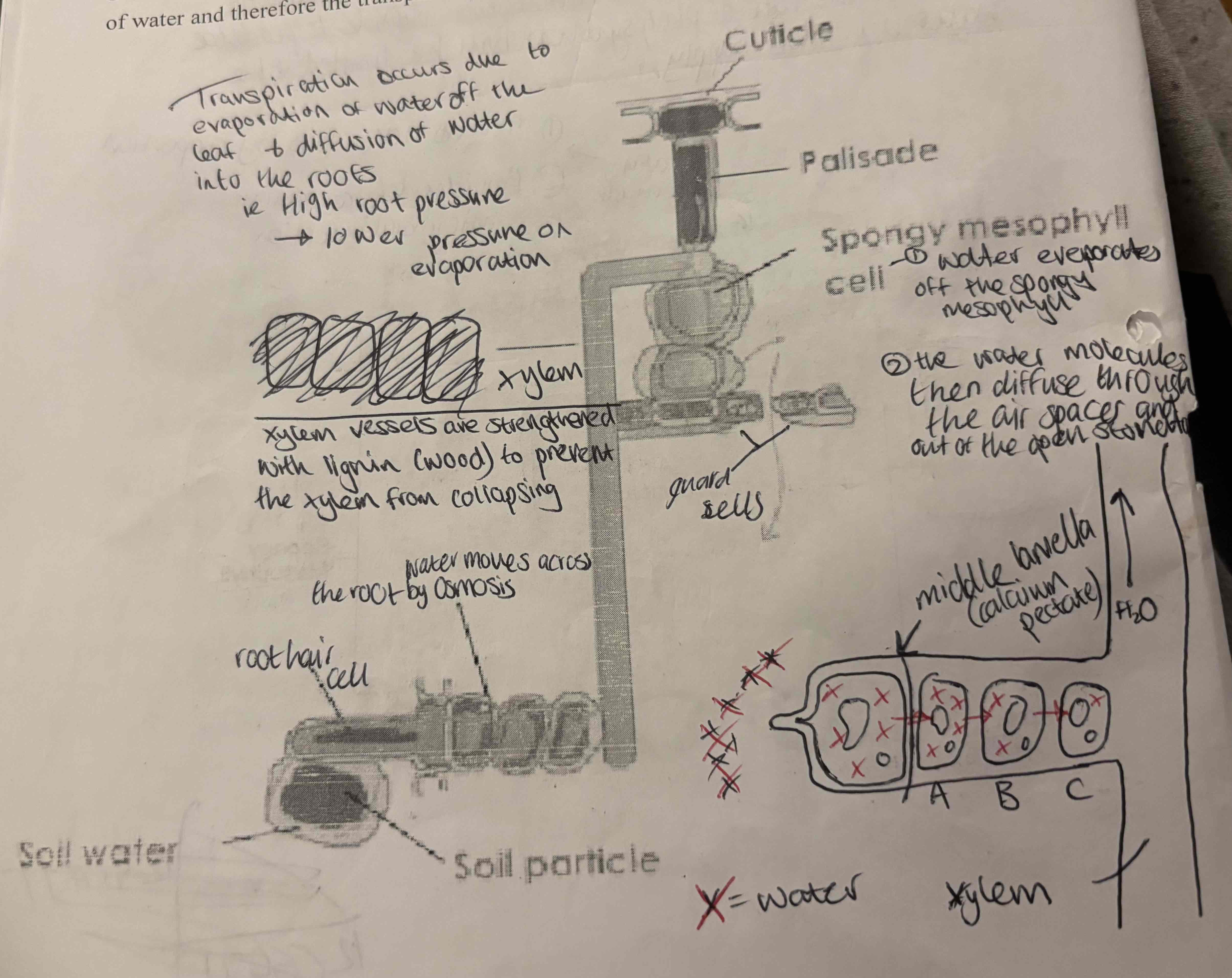
Mineral ions dissolve in water in the soil and are transported throughout the plant within the xylem
Photosynthesis -
Water is a reactant in the process of photosynthesis; it combines with CO2 to produce glucose. The rate of photosynthesis will be limited if the water is in short supply.
What does the waxy cuticle do for water in plants?
Prevents water loss by evaporation
Provides defence against microbial infection
Transpiration:
The evaporation of water off the spongy mesophyll surfaces surfaces followed by diffusion through the air spaces and out of the stomata
Explain the stages of Transpiration:
Water evaporates off the spongy mesopyll
The water molecules then diffuse through the air spaces and out of the open stomata
What is the transpiration rate?
The amount of water lost from a leaf or a plant in a set period of time
Name the factors that affect the Transpiration Rate:
Temperature
Increasing the temp increases the rate of evaporation of water from the surface of the spongy mesophyll cells
Humidity
In humid air, there is a lot of moisture. This reduces the diffusion gradient, decreasing transpiration
Wind Speed
In windy conditions, moisture filled air can’t accumulate on the underside of the leaf. This increases the diffusion gradient, increasing transpiration
Surface Area
Increasing leaf surface, increases the number of stomata therefore increasing transpiration. Most stomata are on the lower leaf surface, Vaseline can be used to block stomata in transpiration experiments
Light
Stomata close in the dark (as CO2 isn’t needed for photosynthesis) Therefore, transpiration stops at night
What items can you use to affect Transpiration Rate?
Heater - Temp Increases
Fan - Wind Speed
Plastic bag over shoot - Humidity
Removal of leaves - Decrease SA
Cut shoot at angle - Increase SA
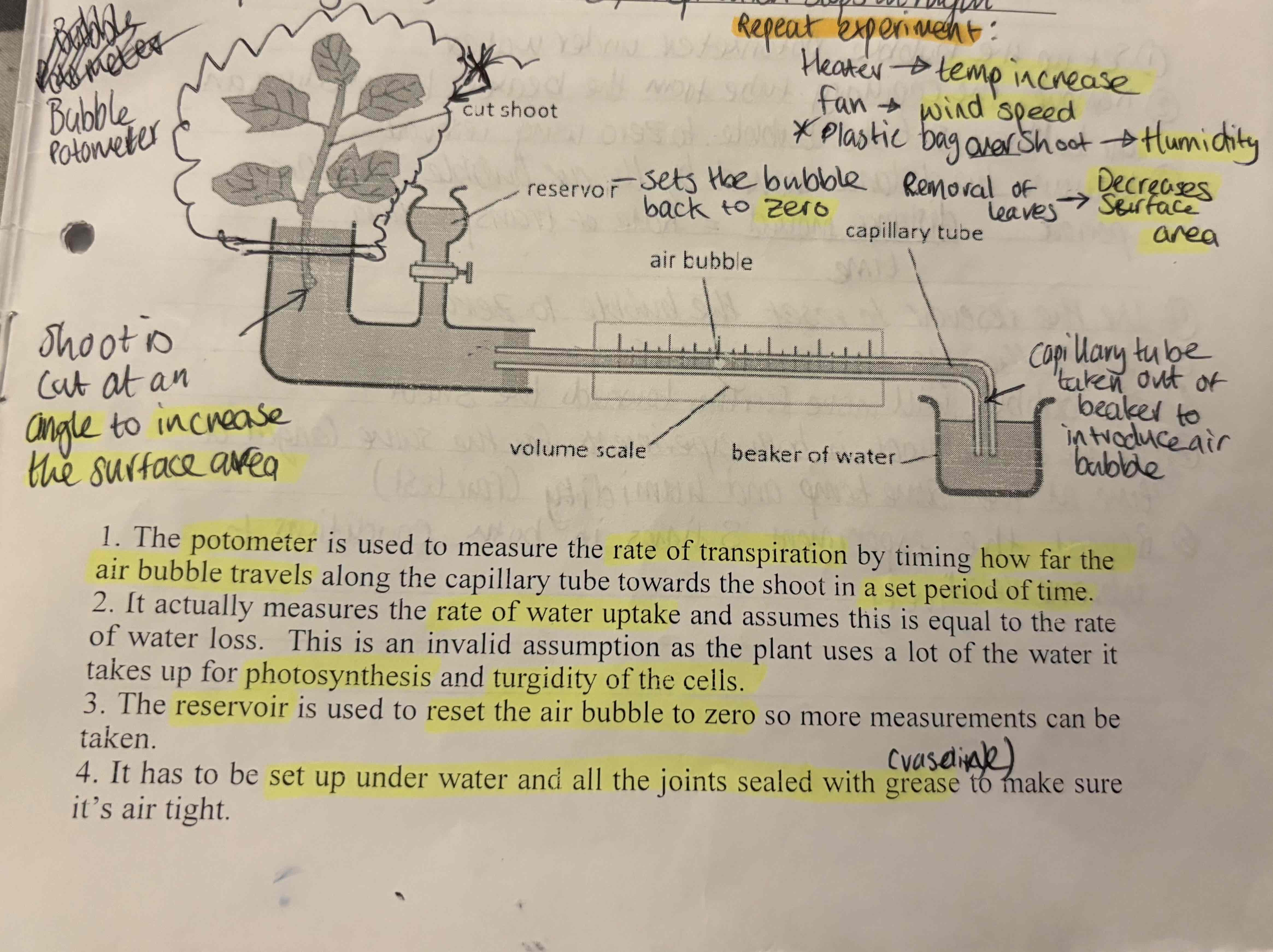
Explain the apparatus of the bubble potometer:
The potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration by timing how far the air bubble travels along the capillary tube towards the shoot in a set period of time
It actually measures the rate of water uptake and assumes this is equal to the rate of water loss. This is an invalid assumption as the plant uses a lot of the water it takes up for the photosynthesis and turgidity of the cells
The reservoir is used to reset the air bubble to zero so more measurements can be taken
It has to be set up under water and all the joints sealed with grease (Vaseline) to make sure its air tight
Explain the weight potometer experiment:
Weigh plant and pot at start of the experiment
Leave for 24hrs
Reweigh
Repeat using heat, fan, or plastic bag to mimic temp, wind or humidity
Work out the rate of transpiration which is:
Amount of water lost/24hours

Explain the bubble potometer experiment:
Set up the bubble potometer under water
Remove the capillary tube from the beaker to introduce an air bubble. Set the bubble to zero using reservoir
Measure the distance moved by the air bubble in a 30min period
Distance moved/time
Use the reservoir to reset the bubble to zero
Repeat the experiment using a fan
The bubble will move further towards the shoot
Use the same shoot in both experiments, for the same length of time at the same temp and humidity (fair test)
Repeat the experiment 3 times in both conditions to improve reliability