Intrapartum (class 7,8,9,10)
5.0(2)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:05 AM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Process of moving the fetus, placenta and membranes out of the birth canal
Labor
2
New cards
First stage of labor
onset of regular contractions to full dilation of cervix
3
New cards
second stage of labor
full dilation to delivery of baby
4
New cards
third stage of labor
delivery of baby to delivery of placenta
5
New cards
fourth stage of labpr
delivery of placenta to first 4 hours after birth
6
New cards
**Impending signs of approaching labour involve a variety of physiological and psychological signs. Like:**
**Lightening (fetal engagement)** \n **Braxton Hicks contractions** \n **Bloody Show** \n **Backache** \n **Spontaneous Rupture of membranes (SROM)**
**Diarrhea** \n **Spurt of energy (nesting)** \n **Weight loss**
**Diarrhea** \n **Spurt of energy (nesting)** \n **Weight loss**
7
New cards
True or False labor: Contractions are regular and close together
true
8
New cards
true or false labor: contractions are irregular and not occurring closer together
false
9
New cards
How would change in activity affect true labor vs false labor
True labor: Contractions continue no matter if comfort measures.
False labor: Contractions may stop or slow down with comfort measures
False labor: Contractions may stop or slow down with comfort measures
10
New cards
cervical changes in true vs false labor:
true labor: Progressive dilatation & effacement.
false labor: Cervix may be soft but no sign in change in effacement or dilation and no show
false labor: Cervix may be soft but no sign in change in effacement or dilation and no show
11
New cards
True or false labor:Contraction discomfort is Usually felt in the front of the abdomen. May be felt in the back
false
12
New cards
true or false labor: contraction discomfort Starts in the back and radiates towards the front of the abdomen
true
13
New cards
contraction strength of true labor
becomes stronger with time; vaginal pressure is felt
14
New cards
contraction strength of false labor
freq weak; not getting stronger with time
15
New cards
what are the P’s of labor
Power
Passageway
passenger
position
Psychological response
Passageway
passenger
position
Psychological response
16
New cards
Powers
**Primary** – Involuntary uterine contractions that result in Effacement and Dilatation of the cervix
**Secondary** – Involuntary urge to push
**Secondary** – Involuntary urge to push
17
New cards
average primiparous woman dilates __ cm / hr
1
18
New cards
average multiparous woman dilates __ cm / hr
1\.5
19
New cards
Passageway
**Refers to Maternal Pelvis**
\-**Structures,**
**-Types (shape),**
**-Diameter,** -
**and Soft tissues**
\
**-“Give” of joints –effect of hormones**
\-**Structures,**
**-Types (shape),**
**-Diameter,** -
**and Soft tissues**
\
**-“Give” of joints –effect of hormones**
20
New cards
Effacement
the cervix stretches and gets thinner
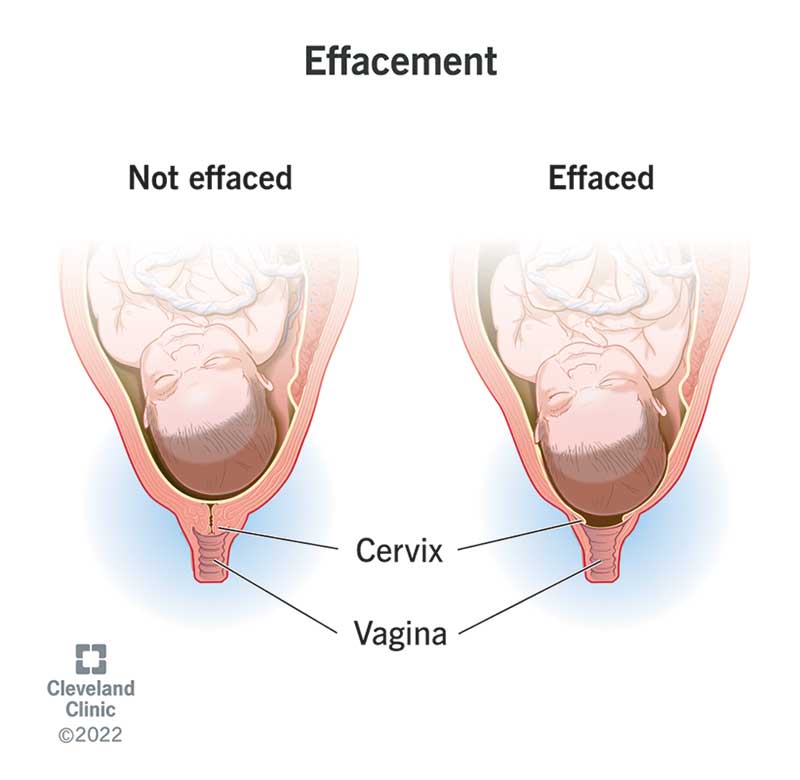
21
New cards
dilation
Dilatation means that the cervix opens
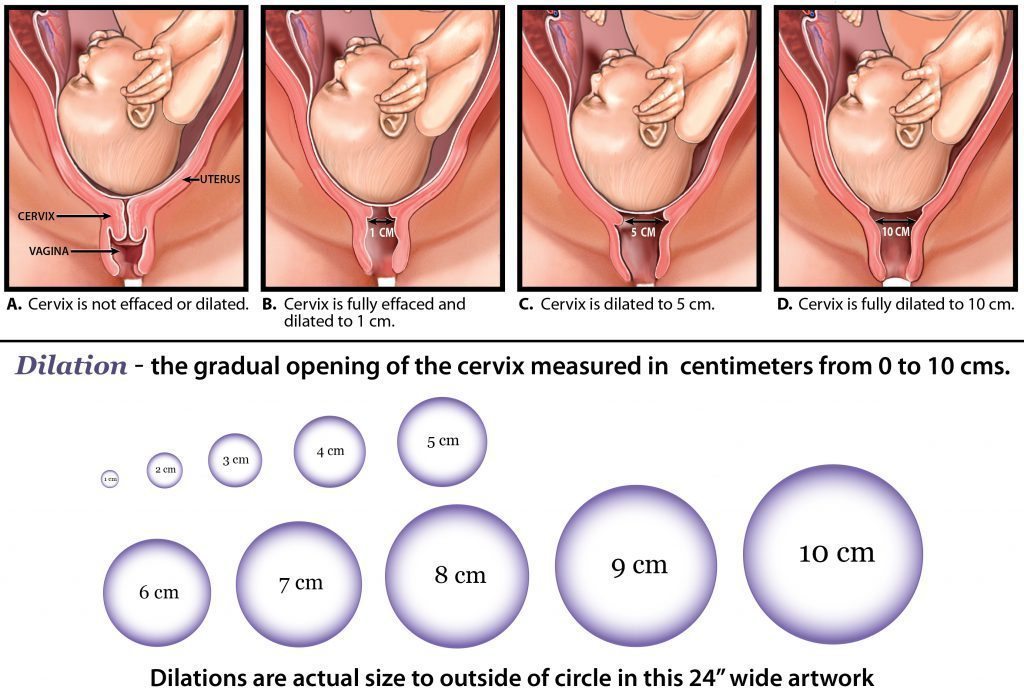
22
New cards
passenger
**Fetal head – dimensions**
**Cranial Vault (Bones)**
**Sutures (sagittal/lambdoidal/coronal)**
**Fontanelles** \n **Biparietal diameter**
\
\*Fontanelles/ \n sutures and fetal head positioning are important mechanisms to aid in passing through the maternal pelvis
**Cranial Vault (Bones)**
**Sutures (sagittal/lambdoidal/coronal)**
**Fontanelles** \n **Biparietal diameter**
\
\*Fontanelles/ \n sutures and fetal head positioning are important mechanisms to aid in passing through the maternal pelvis
23
New cards
fetal lie
Fetal lie refers to the relationship between the longitudinal axis of the baby with respect to the longitudinal axis of the mother (longitudinal lie, transverse lie, oblique lie)
24
New cards
fetal presentation
Fetal presentation refers to the part of the baby that is overlying the maternal pelvis.
25
New cards
fetal presenting part
the presenting part is the part of the baby that leads the way through the birth canal. Most often, it is the baby's head, but it can be a shoulder, the buttocks, or the feet.
26
New cards
fetal station
Station is the relationship of the presenting fetal part to an imaginary line drawn between the maternal ischial spines and is a measure of the degree of descent of the presenting part of the fetus through the birth canal.
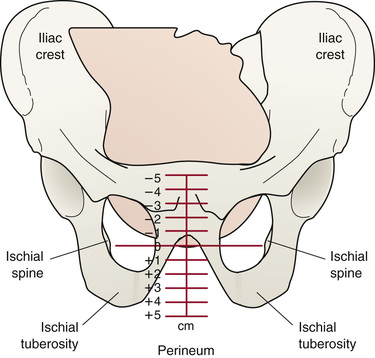
27
New cards
Engagement
Engagement is the term used to indicate that the largest transverse diameter of the presenting part (usually the biparietal diameter) has passed through the maternal pelvic brim or 405inlet into the true pelvis and usually corresponds to station 0. Engagement often occurs in the weeks just before labour begins in nulliparas and may occur before or during labour in multiparas. Engagement can be determined by abdominal or vaginal examination.
28
New cards
friedman’s curve
Relationship between cervical E&D and fetal descent in relation to time and progression of labour
29
New cards
lateral position improves
circulation
30
New cards
hands and knees position makes
fetus rotate
31
New cards
squatting position does what
opens the pelvis
32
New cards
what stage is labor: is the process of effacement (%) and dilation (cm) of the cervix
first
33
New cards
what are the 3 phases of the first stage of labor
latent, active, transition
34
New cards
latent phase of first stage takes how long?
7-8 hours
35
New cards
how much dilated are they in latent stage
0-3cm
36
New cards
how long are contractions in the latent phase of phase 1
30-45 seconds
37
New cards
how long is the active phase in the first stage of labor
3-5 hours
38
New cards
how far dilated are they in the active stage
4-7cm
\
\
39
New cards
what % effaced in the active stage
40-80%
40
New cards
how long are contractions in the active stage of the first stage
40-60 seconds in length
41
New cards
how many cm dilated in the transition stage
8-10cm
42
New cards
how long is the transition stage
30 min - 2 hrs
43
New cards
what % effaced in the transition phase
80-100%
44
New cards
how long are contractions in the transition phase
60-90 seconds
45
New cards
first stage physical assessment
\-Vaginal examination- to determine the progress of labour (cervical effacement and dilation)
- Uterine activity- Contractions pattern and strength
\- Bloody show
\- Amniotic fluid
\- Comfort level
\-Vital signs
\- Fetal assessment – fetal heart rate patterns
\- Leopolds manoeuvres
\-Hydration status
\- Bowel, bladder status
- Uterine activity- Contractions pattern and strength
\- Bloody show
\- Amniotic fluid
\- Comfort level
\-Vital signs
\- Fetal assessment – fetal heart rate patterns
\- Leopolds manoeuvres
\-Hydration status
\- Bowel, bladder status
46
New cards
rupture of membranes there will be a presence of ______ in amniotic fluid
sodium chloride
47
New cards
what if rupture of membranes is green amniotic fluid
\-meconium stained amniotic fluid.
\-Meconium in the amniotic fluid increases the risk for meconium aspiration syndrome.
\
* Endotracheal intubation and suctioning in infants who
are not vigorous at birth should occur prior to drying and stimulation to remove any meconium from the trachea.
\-Meconium in the amniotic fluid increases the risk for meconium aspiration syndrome.
\
* Endotracheal intubation and suctioning in infants who
are not vigorous at birth should occur prior to drying and stimulation to remove any meconium from the trachea.
48
New cards
stage 1 latent phase nursing interventions :
* Contractions – Q 30 -45 sec duration, mild to mod, 5 – 20 min apart
* Encourage mobility, change positions frequently
* Encourage voiding q2h
* Maintain adequate hydration/ diet
* Support/ comfort measures
* Monitoring of labour progress and fetal adaptation to labour stress
* Maternal positioning that facilitates descent of the fetus and comfort for the labouring person
* Encourage mobility, change positions frequently
* Encourage voiding q2h
* Maintain adequate hydration/ diet
* Support/ comfort measures
* Monitoring of labour progress and fetal adaptation to labour stress
* Maternal positioning that facilitates descent of the fetus and comfort for the labouring person
49
New cards
what part of the first stage of labor is this:
\
Contractions- Q 2- 4 min apart, moderate to strong, 60 seconds duration.
Progression of emotional display as labour progresses
\
Contractions- Q 2- 4 min apart, moderate to strong, 60 seconds duration.
Progression of emotional display as labour progresses
active phase
50
New cards
active phase of labor nursing interventions
\-Continue with latent phase interventions (mobility, positioning, voiding, hydration, etc... )
\-Monitor comfort/pain management – pain becomes more intense during this phase
\-Fetal monitoring and assessment – important to note how fetus is responding to labour progress
\-Monitor comfort/pain management – pain becomes more intense during this phase
\-Fetal monitoring and assessment – important to note how fetus is responding to labour progress
51
New cards
Op position during labor is a lot of
back pain
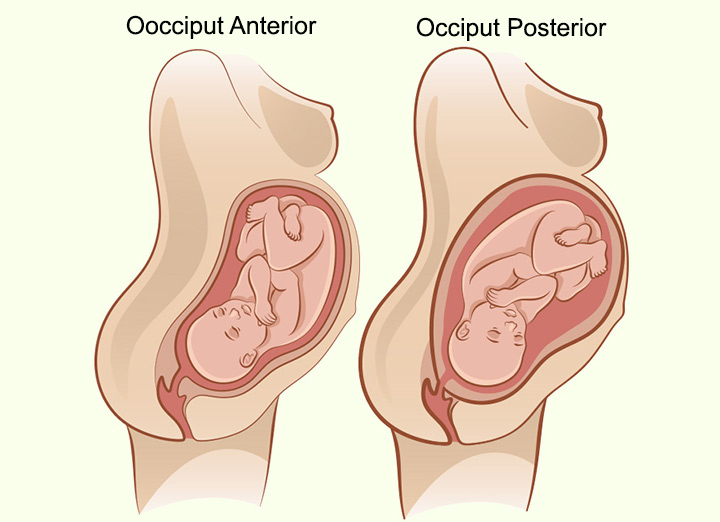
52
New cards
OP vs OA position
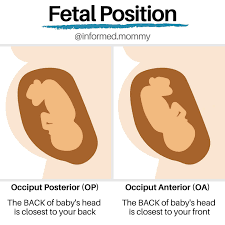
53
New cards
effleurage
(non pharm pain management)
a form of massage involving a circular __stroking__ movement made with the palm of the hand.
a form of massage involving a circular __stroking__ movement made with the palm of the hand.
54
New cards
transition stage contractions
70-90 secs in duration.
strong.
30-60 seconds apart
strong.
30-60 seconds apart
55
New cards
transition phase nursing care
\-Emotional support +++/positive reinforcement. May need frequent focus and direction
\- Help control breathing through contractions \n -Begin to get for delivery
\- Prepare bed and positioning for pushing
childbirth \n - Pharmacologic Pain control may be too late at
this point (respiratory effects on neonate)
\- Help control breathing through contractions \n -Begin to get for delivery
\- Prepare bed and positioning for pushing
childbirth \n - Pharmacologic Pain control may be too late at
this point (respiratory effects on neonate)
56
New cards
induction of labor is a common intervention during the ____ stage of labor
first
57
New cards
what is induction of labor
artificial initiation of labor
58
New cards
important considerations prior to induction of labour
Bishop Score System -Measures cervical readiness for induction by scoring 5 characteristics of the cervix
5 characteristics include:
1\. Dilation (**5 cm or more)
2. Effacement (80% or more)
3. Station (**+1 or more )
4\. Cervical consistency (firm, medium, soft)
5\. Cervical Position (Posterior, midposition, anterior\*\*)
5 characteristics include:
1\. Dilation (**5 cm or more)
2. Effacement (80% or more)
3. Station (**+1 or more )
4\. Cervical consistency (firm, medium, soft)
5\. Cervical Position (Posterior, midposition, anterior\*\*)
59
New cards
why would induction of labour be required
* Post term infant
* Diagnosed issue of intrauterine environment
ie.) perfusion of fetus
* Fetal distress (if not severe) or risk for fetal
distress identified.
* Diagnosed issue of intrauterine environment
ie.) perfusion of fetus
* Fetal distress (if not severe) or risk for fetal
distress identified.
60
New cards
augmentation
labor has started but it needs help
61
New cards
why would augmentation of labour be reuired
\-Supplementation of a naturally occurring labour with synthetic oxytocin. \n • Purpose would be to increase the strength/
pattern or duration of contractions to improve the labour process.
pattern or duration of contractions to improve the labour process.
62
New cards
post term pregnancy continues past the end of the ____ completed weeks of gestation
41
63
New cards
risks of post term labor on mother
\-tears/lacerations
\-Labour dystocia
\-Increased risk of infection and hemorrhage
\-Labour dystocia
\-Increased risk of infection and hemorrhage
64
New cards
risk of post term labor on infant
* Meconium aspiration
* Infant injury from birthing process
* Mortality rate increases after 40 weeks
* Infant injury from birthing process
* Mortality rate increases after 40 weeks
65
New cards
methods of cervical ripening
__Natural endogenous oxytocin release:__
• Sexual intercourse
\
__Mechanical methods:__ \n • Amniotomy \n • Stripping or sweeping of membranes
\
__Pharmacologic methods:__
• Prostaglandins \n • Oxytocin
• Sexual intercourse
\
__Mechanical methods:__ \n • Amniotomy \n • Stripping or sweeping of membranes
\
__Pharmacologic methods:__
• Prostaglandins \n • Oxytocin
66
New cards
synthetic prostaglandins (PGE2)
* Frequently used to ripen the cervix.
* Cervix has to be ripened for labour to be initiated. If bishop score is less than 6, a cervical ripening agent such as prostaglandins must be used before labour induction.
* If cervix is not ripened, augmentation or induction with oxytocin will not be successful
* Cervix has to be ripened for labour to be initiated. If bishop score is less than 6, a cervical ripening agent such as prostaglandins must be used before labour induction.
* If cervix is not ripened, augmentation or induction with oxytocin will not be successful
67
New cards
synthetic oxytocin
• Synthetic form of the naturally occurring hormone
• Used to facilitate uterine contractions \n • Can be used to induce labour or augment labour
• Piggybacked into main IV infusion line
and titrated until regular contraction pattern is established
• Used to facilitate uterine contractions \n • Can be used to induce labour or augment labour
• Piggybacked into main IV infusion line
and titrated until regular contraction pattern is established
68
New cards
nursing care for oxytocin induction
• V/S q30mins (BP &P) and on increase of drip
• Record FHR & contractions q15mins \n • Monitor contractions closely
\
• If fetal distress- \n -d/c oxytocin, increase main line \n -turn on left side \n -administer oxygen \n -reevaluate contractions and fetal response -notify doctor \n -document
• Record FHR & contractions q15mins \n • Monitor contractions closely
\
• If fetal distress- \n -d/c oxytocin, increase main line \n -turn on left side \n -administer oxygen \n -reevaluate contractions and fetal response -notify doctor \n -document
69
New cards
second stage of labor Phases:
\-initial latent phase
\-descent (cardinal ,ovements)
\-active expulsion phase (pushing and crowning)
\-descent (cardinal ,ovements)
\-active expulsion phase (pushing and crowning)
70
New cards
how long is the second stage of labor
lasts up to 1 hour
71
New cards
from complete dilation (10 cm) to birth of the newborn
second stage of labor
72
New cards
physiological s/s of full dilation (2nd stage of labor)
Sudden appearance of sweat on upper lip
Vomiting episode \n Increase in bloody show
Increased restlessness/agitation ;
verbalization – “I cant go on”
Involuntary bearing down efforts
Bulging perineum, labia
Vomiting episode \n Increase in bloody show
Increased restlessness/agitation ;
verbalization – “I cant go on”
Involuntary bearing down efforts
Bulging perineum, labia
73
New cards
7 cardinal movements
\-Descent \n -Flexion \n - Internal Rotation
\- Extension
\- Restitution \n - External Rotation
\- Expulsion
\- Extension
\- Restitution \n - External Rotation
\- Expulsion
74
New cards
when is apgar scoring done
1 min after birth and 5 mins
75
New cards
what degree tear? involves fourchette, perineal skin, vaginal mucous membrane without involving any muscles.
first
76
New cards
what degree tear? muscles of perineum
second
77
New cards
what degree tear? also extends to rectal sphincter
third
78
New cards
what degree tear?also extends into rectum
fourth
79
New cards
third stage of labor is the separation and delivery of the placenta. usually takes ? mins after birth of baby
5-30
80
New cards
signs of separation of placenta in the 3rd stage of labor
\-Firmly contracting uterus
\- Change in shape of uterus from discoid
to globular
\- Lengthening of cord \n - Sudden gush of blood \n -Vaginal fullness or membranes at the
introitus
\- Change in shape of uterus from discoid
to globular
\- Lengthening of cord \n - Sudden gush of blood \n -Vaginal fullness or membranes at the
introitus
81
New cards
what is the baby side of the placenta
shiny schultz
82
New cards
maternal side of placenta
dirty duncan
83
New cards
when is the placenta considered retained?
30 mins after delivery… not good if its still there
84
New cards
fourth stage of labor
1- 4 hr after birth of the newborn; period of maternal physiological adjustment.
\-Restoration of physiology \n -Myometrial contractions and retractions & vessel thrombosis \n -BLEEDING MAIN CONCERN \n -Formation of mother-newborn relationship
\-Consolidation of family unit
\-Restoration of physiology \n -Myometrial contractions and retractions & vessel thrombosis \n -BLEEDING MAIN CONCERN \n -Formation of mother-newborn relationship
\-Consolidation of family unit
85
New cards
the golden hour
undisturbed first hour after birth spent skin to skin on mother’s (or father’s) chest, unclothed
* Many benefit for infant as well as mother’s transition to postpartum period
* Facilitates bonding and attachment
* Promotes regulation of newborns physiological
transitions to extra uterine life (Eases transition period)
* Allows mother to adjust to puerperium stage physically and emotionally
* Many benefit for infant as well as mother’s transition to postpartum period
* Facilitates bonding and attachment
* Promotes regulation of newborns physiological
transitions to extra uterine life (Eases transition period)
* Allows mother to adjust to puerperium stage physically and emotionally
86
New cards
Preterm labour is true labour that begins before __ completed weeks of gestation
37
87
New cards
premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
* rupture or membranes prior to onset of labour regardless of gestational age
\
* Preterm PROM (pPROM) – rupture of membranes before 37 weeks gestation
* Predisposing factors- maternal nutritional deficiencies, substance use, placental abruption, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancy, prior preterm birth or PPROM, infections \*\*primarily chorioamnionitis or trauma
* Once membranes rupture - risk of infection- chorioamnionitis. Usually caused by normal flora e.g. E coli
\
* Preterm PROM (pPROM) – rupture of membranes before 37 weeks gestation
* Predisposing factors- maternal nutritional deficiencies, substance use, placental abruption, polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancy, prior preterm birth or PPROM, infections \*\*primarily chorioamnionitis or trauma
* Once membranes rupture - risk of infection- chorioamnionitis. Usually caused by normal flora e.g. E coli
88
New cards
care for PROM
* Restrict activity with ongoing assessment.
* Ie) Temp at least Q2hr together with WBC and CBC
monitoring daily. Admin of broad spectrum antibiotics
• Try to prevent infection- no pv exams, frequent changing of pads, observe amniotic fluid for signs of infection, tachycardia in baby, adequate hydration
* Ie) Temp at least Q2hr together with WBC and CBC
monitoring daily. Admin of broad spectrum antibiotics
• Try to prevent infection- no pv exams, frequent changing of pads, observe amniotic fluid for signs of infection, tachycardia in baby, adequate hydration
89
New cards
most women will go into labor within 24hr of PROM. but if not, ______ is necessary if they are over 37 weeks (not preterm)
induction
90
New cards
Prom.
if fetal distress or infection..
if fetal distress or infection..
induce right away
91
New cards
cervical insufficiency
\-Generally painless cervical dilation \n -Often associated with pPROM and preterm birth
\-Risk Factors: Excessive cervical dilation for curettage or biopsy, history of previous cervical lacerations during childbirth, cervical and uterine anomalies, a hx of short labours and/or losses at early gestations
\-TX: Cerclage, Restricted Activity (potentially bedrest)
\-Placed at 13 – 14 weeks and removed at 37 weeks gestation
\-Risk Factors: Excessive cervical dilation for curettage or biopsy, history of previous cervical lacerations during childbirth, cervical and uterine anomalies, a hx of short labours and/or losses at early gestations
\-TX: Cerclage, Restricted Activity (potentially bedrest)
\-Placed at 13 – 14 weeks and removed at 37 weeks gestation
92
New cards
suppressing premature labor
* Bedrest – left lateral
* incraesed hydration so increased plasma volume
* Avoid unnecessary pv exams
* Tocolytics
* Corticosteroids- betamethasone/dexamethasone•
* Continuous monitoring of FHR and contractions
* Needs lots of psychological support
* \
* incraesed hydration so increased plasma volume
* Avoid unnecessary pv exams
* Tocolytics
* Corticosteroids- betamethasone/dexamethasone•
* Continuous monitoring of FHR and contractions
* Needs lots of psychological support
* \
93
New cards
dystocia
long, difficult, or abnormal labor
94
New cards
criteria for dystocia
> 4 hours of < 0.5 cm/hr dilation (active first
phase)
\n OR
1 hr with no descent while pushing (second stage)
phase)
\n OR
1 hr with no descent while pushing (second stage)
95
New cards
failure to progress
(dystocia)
(dystocia)
cervix does not dilate despite normal uterine contraction and no CPD
96
New cards
hypotonic labor
\-Unable to dilate cervix normally \n -Uterus is easily indented at peak of contraction \n -Usually occurs in active phase of First Stage \n -Possible causes: Uterine overdistention, fetal malposition, analgesics, regional anaesthesia
\
\
97
New cards
management of hypotonic labor
If membranes intact and presenting part is engaged – amninotomy and/or oxytocin augmentation
98
New cards
hypertonic labor
Possible cause may be synthetic oxytocin ,hyperstimulation, or placental abruption
\
Usually occurs in latent phase in the first stage of labor
\
Management:
* Rest
* Fluids
* Sedation/ analgesia
* No oxytocin (Stop infusion -Short half life)
\
Usually occurs in latent phase in the first stage of labor
\
Management:
* Rest
* Fluids
* Sedation/ analgesia
* No oxytocin (Stop infusion -Short half life)
99
New cards
Occurs when the uterus never fully relaxes between contractions.
\
Contractions are erratic and poorly co-ordinated
\
Cervix doesn’t dilate as normal (labour prolonged)
\
Placental Perfusion is compromised; Fetal oxygenation is reduced
\
Contractions are erratic and poorly co-ordinated
\
Cervix doesn’t dilate as normal (labour prolonged)
\
Placental Perfusion is compromised; Fetal oxygenation is reduced
hypertonic labor
100
New cards
FDI
frequency, duration, intensity
(of contractions)
(of contractions)