Chapter 4: Computer Systems and Networks
The Internet
- Internet: is a network of networks.
- The word Internet came from “interconnection of computer networks.”
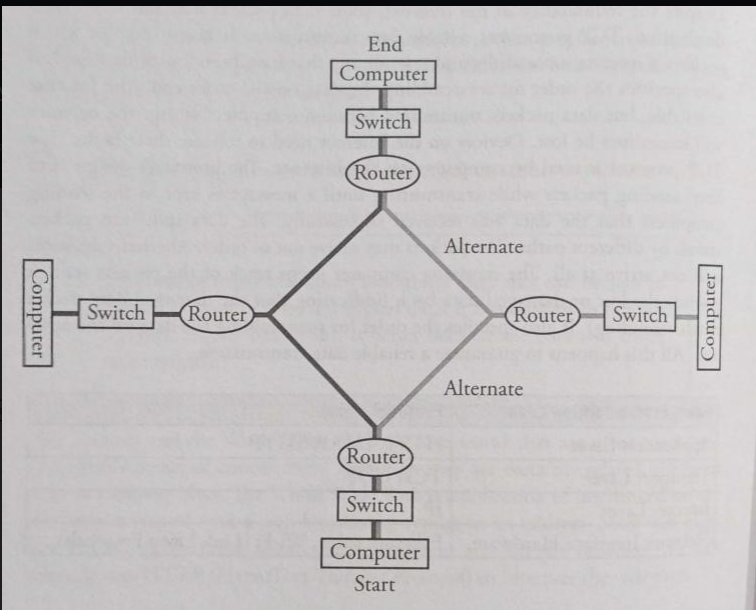
- The Internet is very hardware driven with wires, cables, and devices such as routers and servers.
- Routers are computing devices along a path that send the information along to the next stop on the path.
- Routing: is the process of finding a path from sender to receiver
- Bandwidth: is a measure of the maximum amount of data that can be transferred through a channel or network connection.
- It's measured in bits per second, and it determines how quickly you can download and upload files from the internet.
- Internet protocol (IP): is responsible for addressing and routing your online requests.
- Transmission control protocol (TCP): is a protocol that defines how computers send packets of data to each other.
- User datagram protocol (UDP): is a protocol that allows computer applications to send messages without checking for missing packets to save on time needed to retransmit missing packets.
Scalability
- Scalability: is the ability for a system, network or process to handle a growing amount of work in an efficient manner.
- It can also be defined as the capacity to increase services and products quickly with minimal interruption and cost.
- This is especially important in software engineering, where scalability is crucial when developing applications that are expected to handle large amounts of traffic or data.
FAULT TOLERANCE
Hardware Failure
- Hardware failure: is when a hardware device, such as a computer or printer, stops working properly due to an issue with the physical components.
- The cause of the failure can be anything from electrical wiring issues to incorrect installation and configuration of hardware components.
- In any case, diagnosing and repairing hardware failures can be difficult without proper tools and experience in dealing with this type of issue.
Operational Failures
- Operational failures: are any issues or breakdowns in the operation of a business, machine, system, process, etc.
- They can range from unexpected downtime to incorrect results due to faulty programming.
- Operational failures can have significant impacts on profitability and reputation if not addressed swiftly and appropriately.
Weather
- The internet has cables and wires spanning the world that connect computers.
- Natural disasters: could cause the hardware to be destroyed, bringing the network activity to a halt.
- Solar Flare: is an intense radiation that is released from the sun.
- This happens because of the released from the sun.
Cyberattacks
- Cyberattacks: are malicious attempts to damage or disrupt computer systems, networks, and data.
- They can be carried out by individuals, groups, or organizations with malicious intent.
- Cyberattacks typically involve the use of malware such as viruses and ransomware that allow attackers to gain access to a system for a variety of nefarious purposes including stealing data and financial information or launching denial-of-service attacks.
- Some cyberattack methods used today include phishing campaigns; social engineering attacks; website defacement; distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks; SQL injection exploits; man-in-the middle (MITM) attack vectors etc.
Parallel and Distributed Computing
Parallel Computing
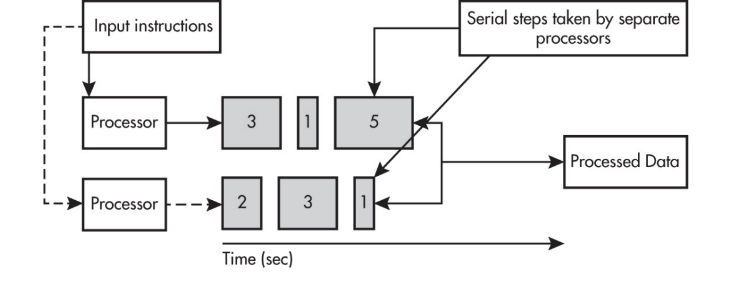
- Parallel computing solution takes as long as the longest of the tasks done in parallel.
- A parallel computing solution takes as long as its sequential tasks plus the longest of its parallel tasks.
- Parallel computing can consist of a parallel portion and a sequential portion.
Why Is Parallel Computing Used?
Parallel computing is needed for real-world simulations and modeling.
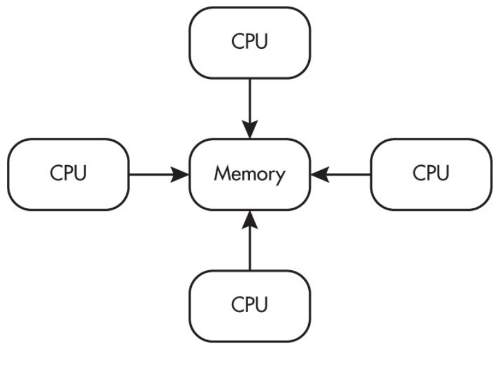
Multiple processors can operate independently but share the same memory resources.
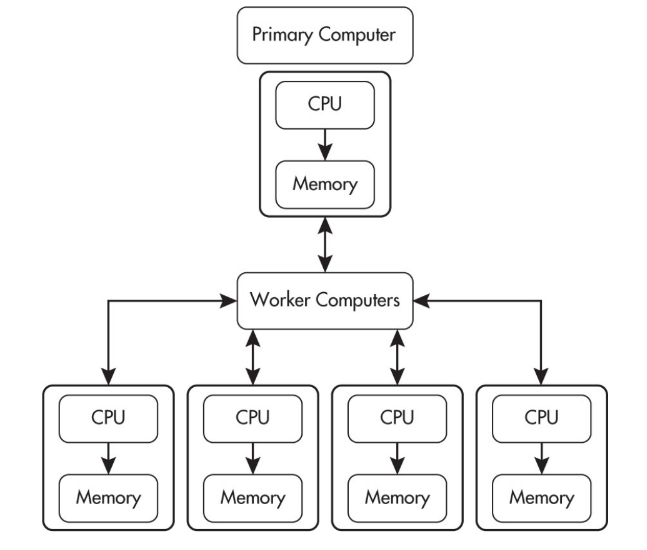
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer because of either the processing time or storage needs involved.
Parallel computing uses a single computer with multiple processors.
Distributed computing uses multiple computing devices to process those tasks.