Autoimmune and Hypersensitivity Disorders
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
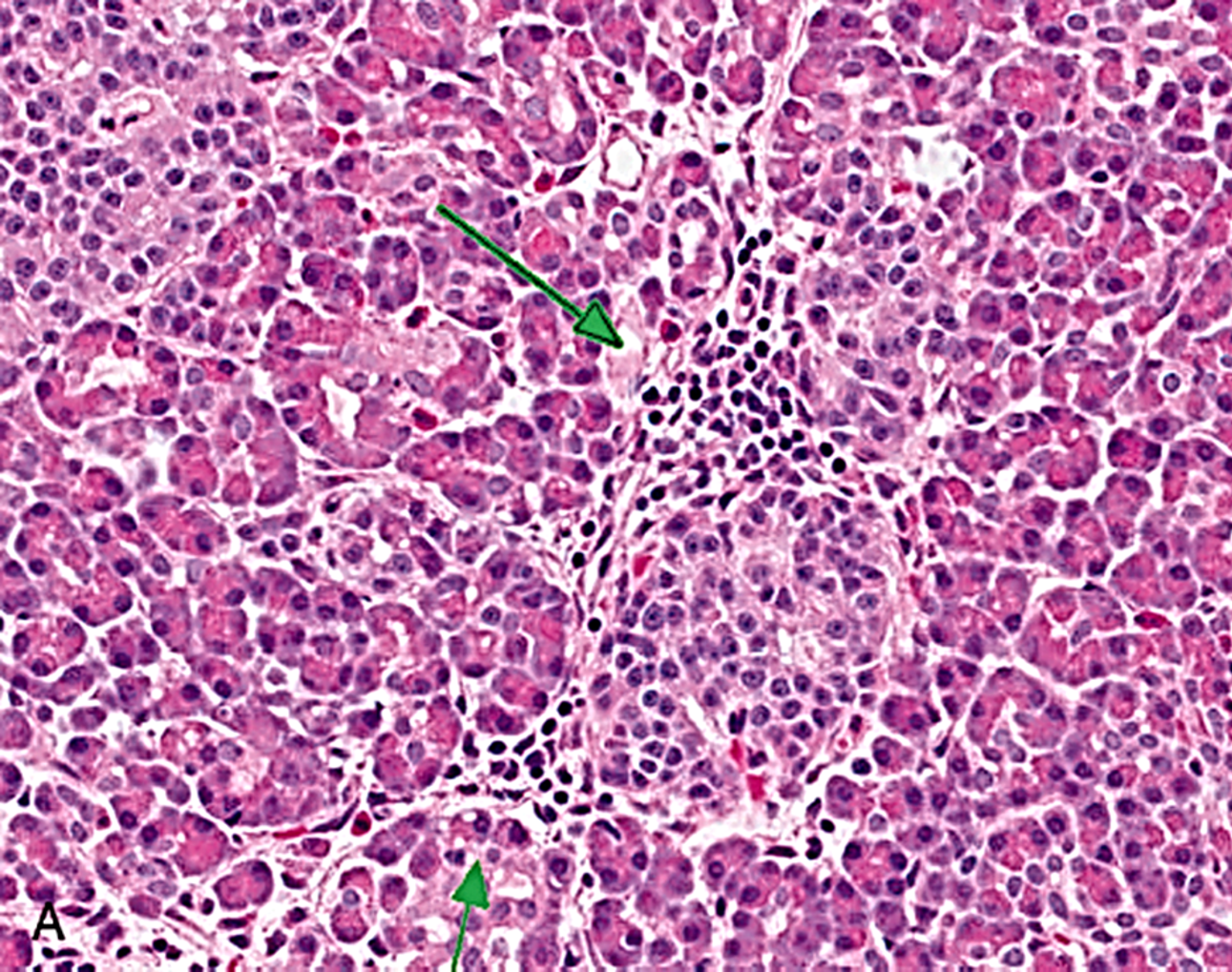
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Targets the CNS, antigens are myelin proteins (MBP, MOG, PLP, MAG, lipids) and the antibodies target the proteins
Multiple Sclerosis
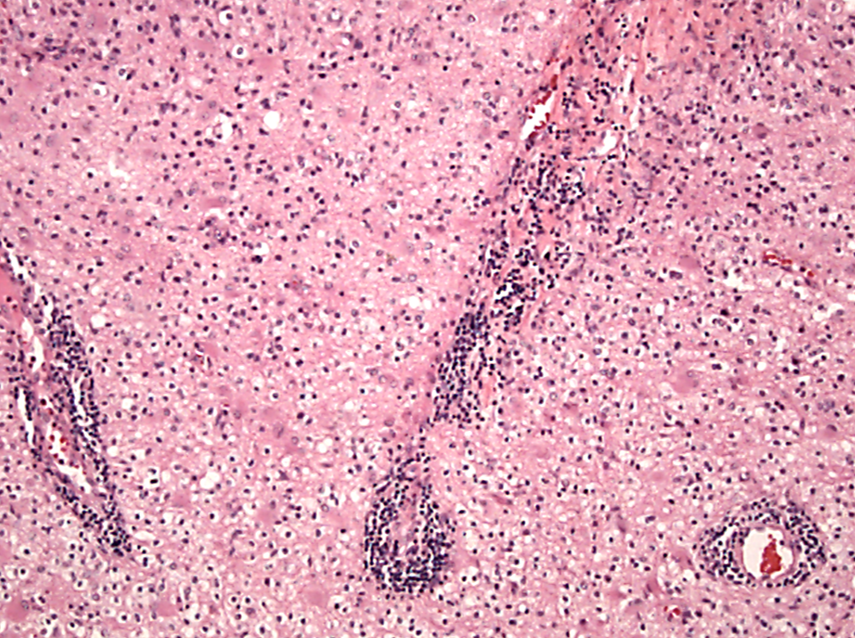
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Targets pancreatic beta-islets for the glutamate decarboxylase receptor, insulin receptor and insulin; infiltrates make their way into the islets.
Type 1 Diabetes
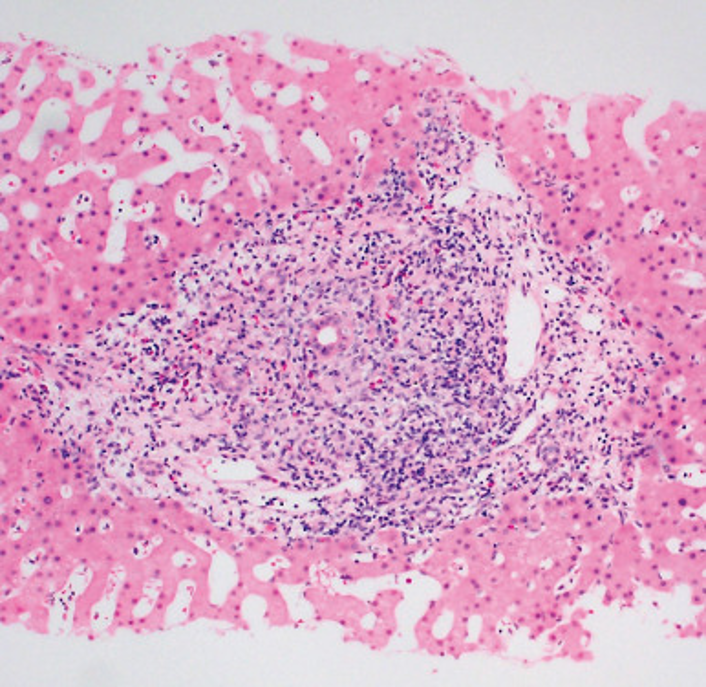
Targets the small and medium sized intrahepatic bile ducts for the mitochondrial antigens; produces AMAutoantibodies
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
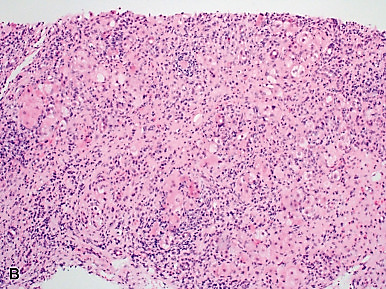
targets the liver; chromatin, ribonucleoproteins, asialoglycoprotein receptor, F-actin and CYP2D6 antigens
Autoimmune Hepatitis
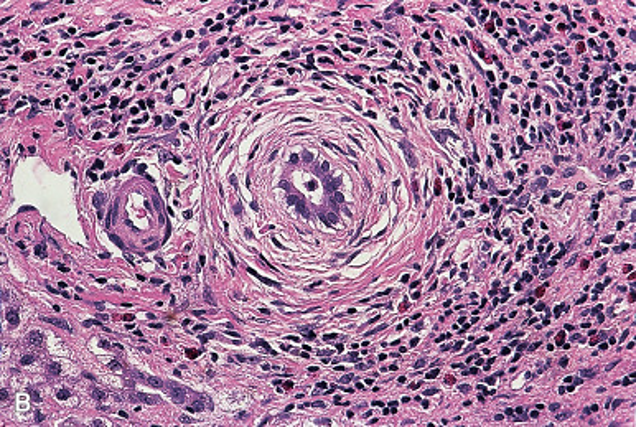
Targets the bile ducts; Tubulin beta-5 antigens, antineutrophil, antiendothelial cell antibody; “onion-skin” lesions
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
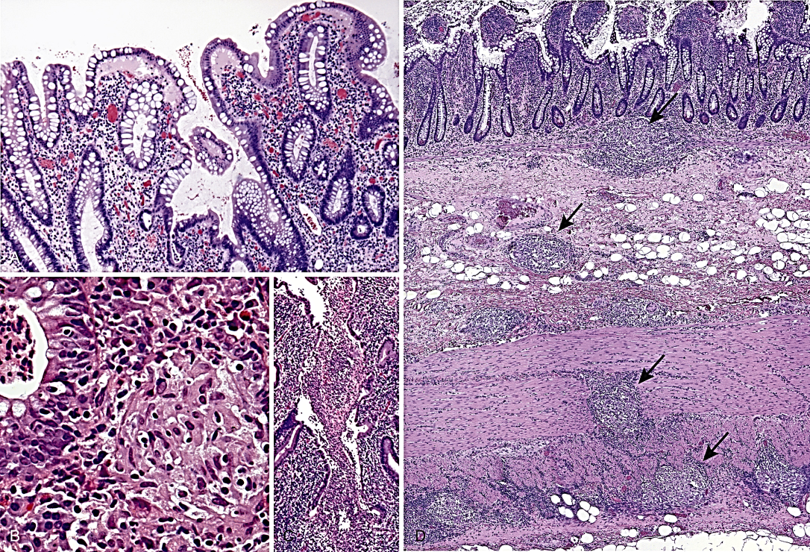
Targets the GI tract; antigens are Tubulin beta-5 and desmin
Crohn’s Disease
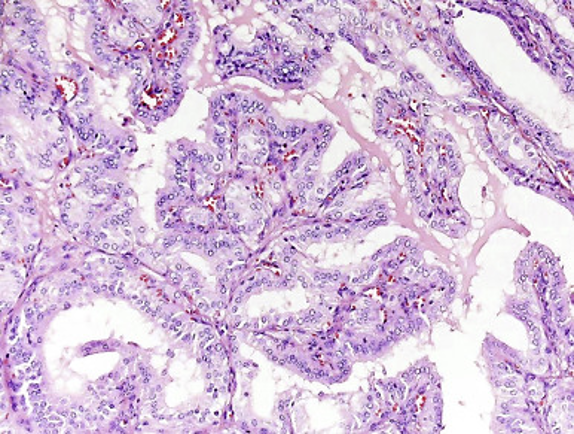
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Targets the thyroid receptors with anti-thyroid receptor antibodies
Grave’s Disease
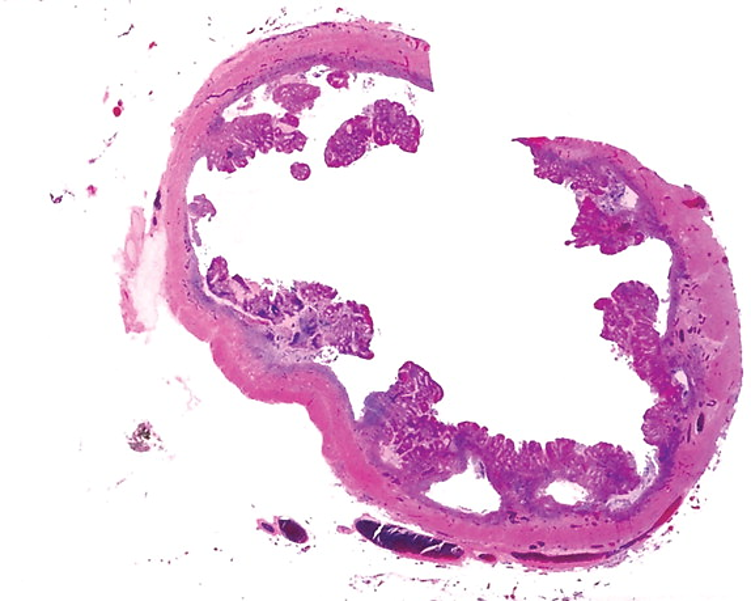
Targets the colon by attacking desmin and Tubulin beta-5
Ulcerative Colitis
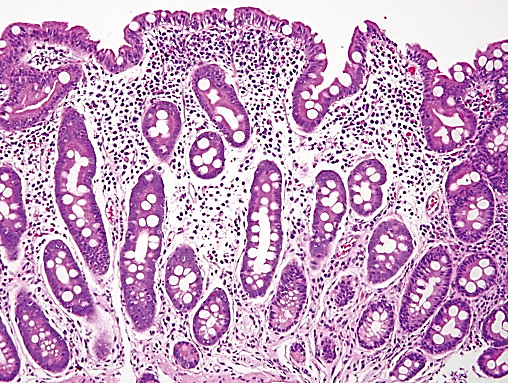
Targets the small intestine via tissue transglutaminase antigen; marked by IgA infiltrates
Celiac Disease
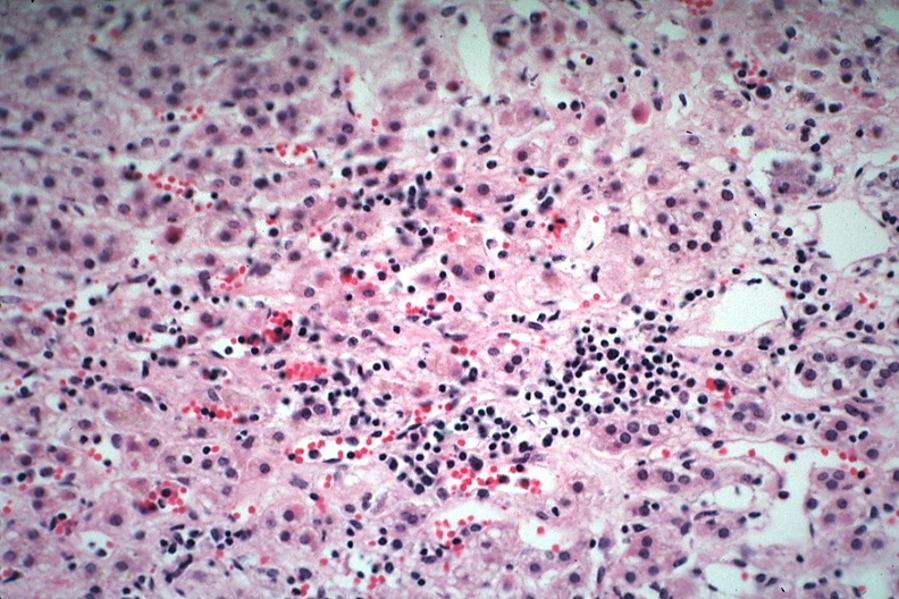
Targets the adrenal glands via 21-hydroxylase (CYP21)
Addison’s Disease
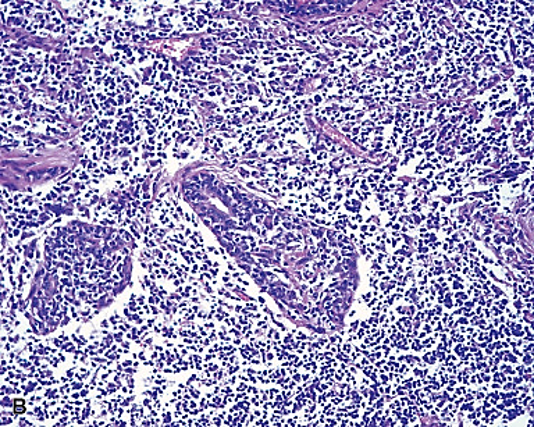
Targets several organs: lungs liver kidneys CNS but mainly salivary/lacrimal glands via La phosphoprotein
Sjogren’s Disease
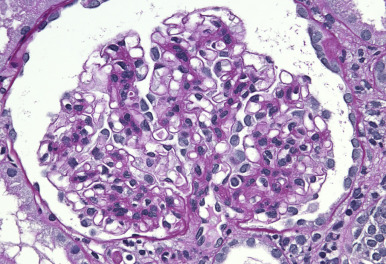
TYPE 3 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Targets many organs via nucleic proteins with antinuclear antibodies. Picture is nephritis caused by this
SLE
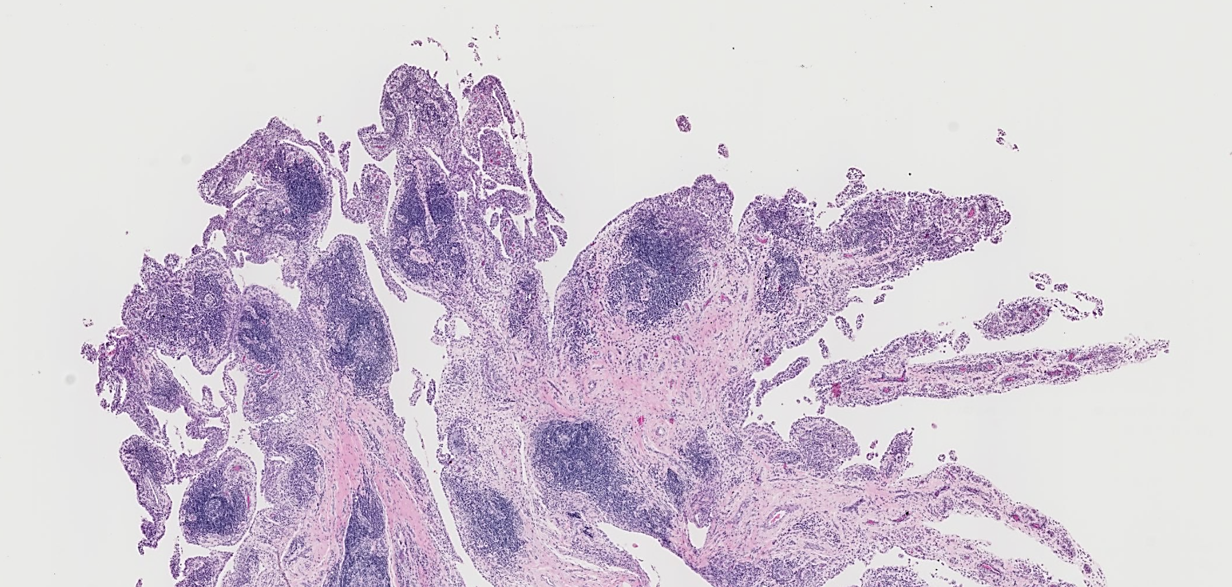
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Targets the synovium of joints via antigens such as collagen, ccp, fibronectin, keratin
Rheumatoid Arthritis
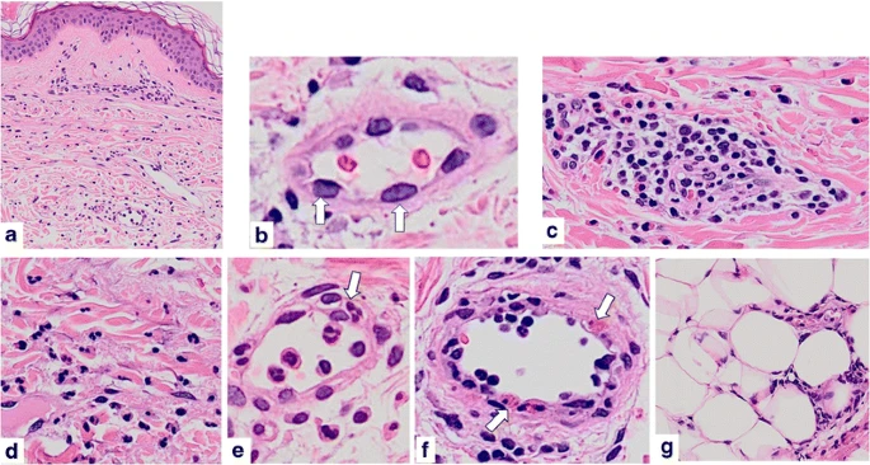
TYPE 1 HYPERSENSITIVITY
a Dermal edema and perivascular and interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration with minimal epidermal change
b Dilatation of small vessel and swelling of endothelium (arrows)
c Perivascular mixed cell infiltrate with lymphocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils.
d Interstitial infiltration. Neutrophils are scattered among the collagen bundles
e Neutrophils are present inside the dilated small vessel. A neutrophil migrates into the vessel wall (arrow)
f Some eosinophils are attached to and emigrated from the vessel wall (arrow)
g Subcutaneous cellular infiltration
Urticaria
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
targets RBC membrane proteins (Rh, I antigen)
opsonizes and phagocytizes RBC’s
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
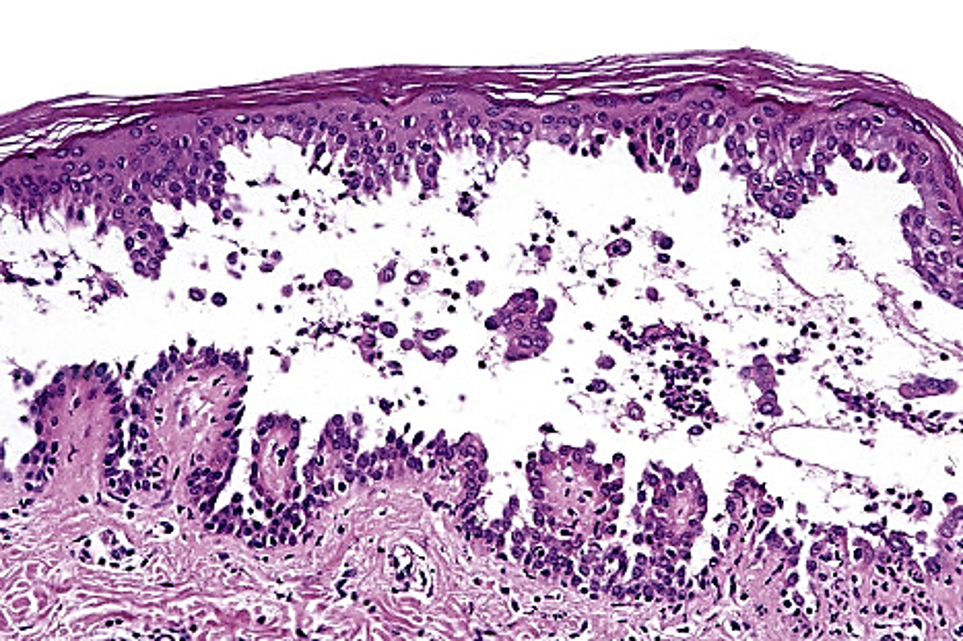
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
antigens are desmogliens between epidermal cells; causes skin vesicles
Pemphigus Vulgaris
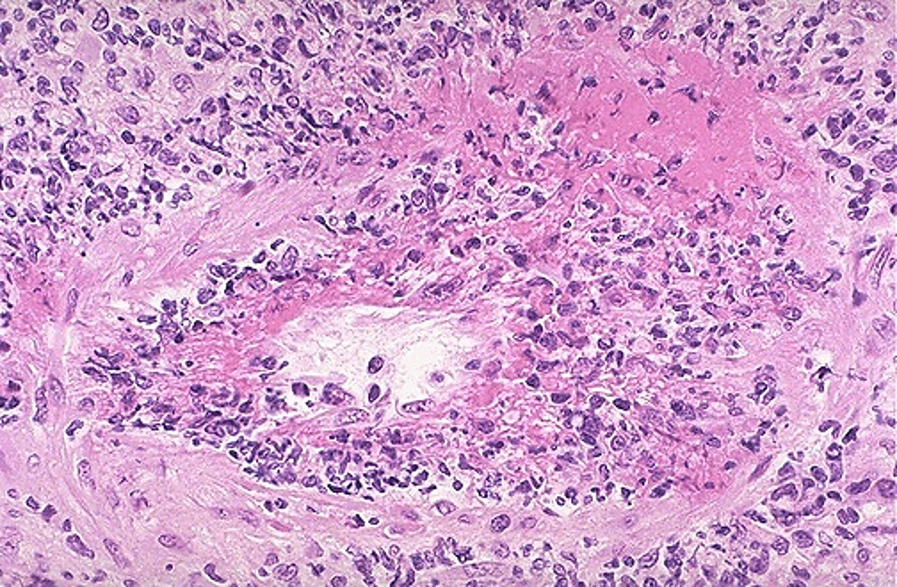
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
reaction caused by neutrophil degranulation
ANCA vasculitis
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
targets basement membranes of the kidneys and the lungs
complement and Fc-receptor mediated inflammation; nephritis and lung hemorrhage
Good Pasture Syndrome
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
streptococcal cell wall antigen will cross react with myocardial antigen, leading to myocarditis
Acute Rheumatic Fever
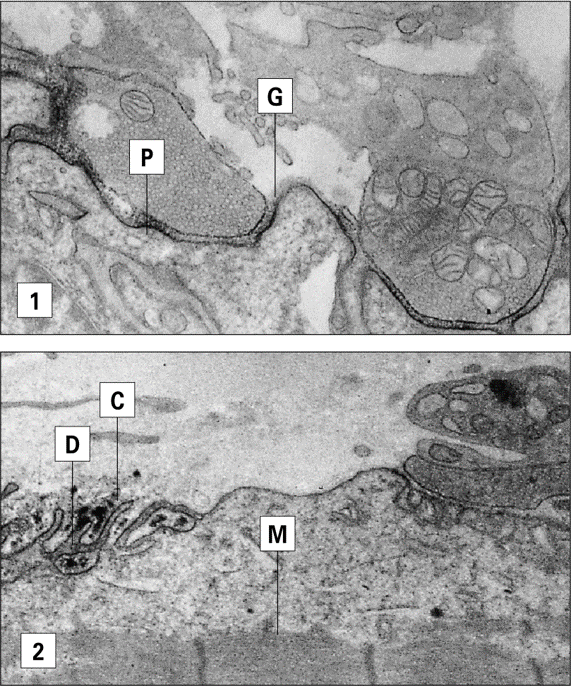
TYPE 2 HYPERSENSITIVITY
target the acetylcholine receptor and inhibits binding, causing paralysis and muscle weakness
Myasthenia Gravis
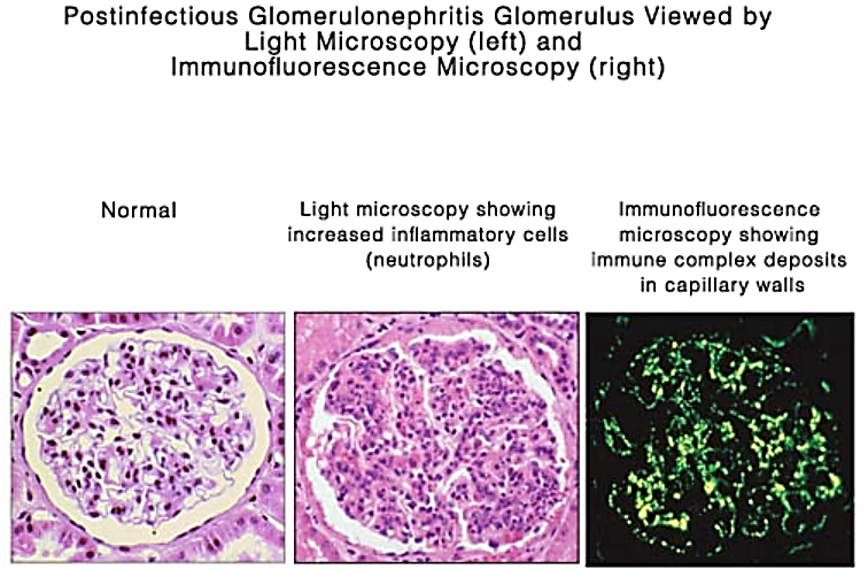
TYPE 3 HYPERSENSITIVITY
streptococcal cell wall antigen may plant itself into glomerular membrane
Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis
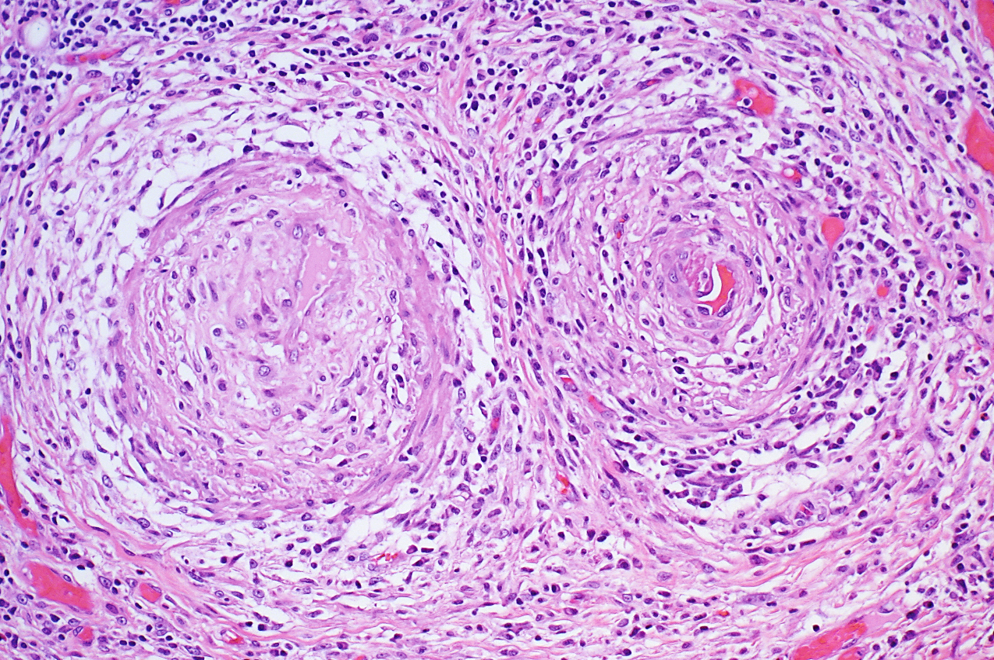
TYPE 3 HYERSENSITIVITY
causes systemic vasculitis, sometimes by hepB antigens
Polyarteritis Nodosa
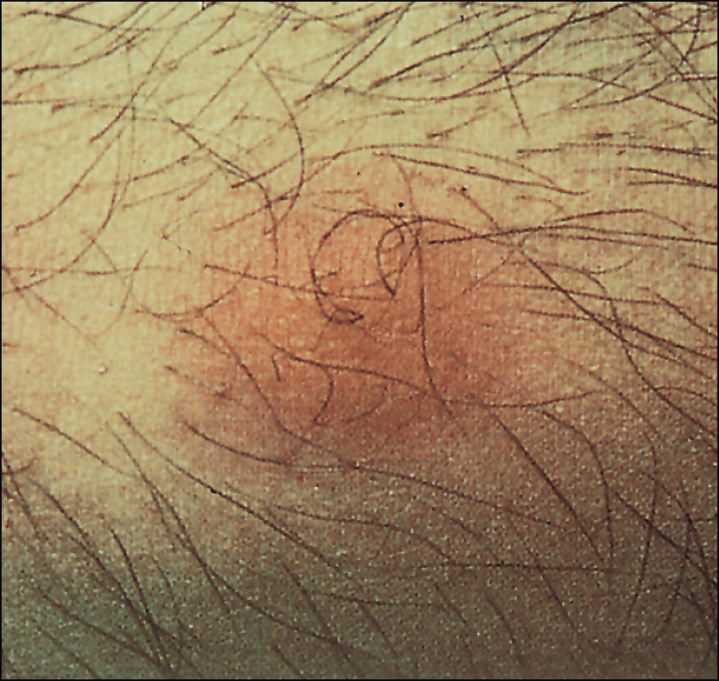
TYPE 3 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Causes cutaneous vasculitis from various foreign antigens
Arthus Reaction
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
Inflammation of the intestines by TH1 and TH17 cytokines
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
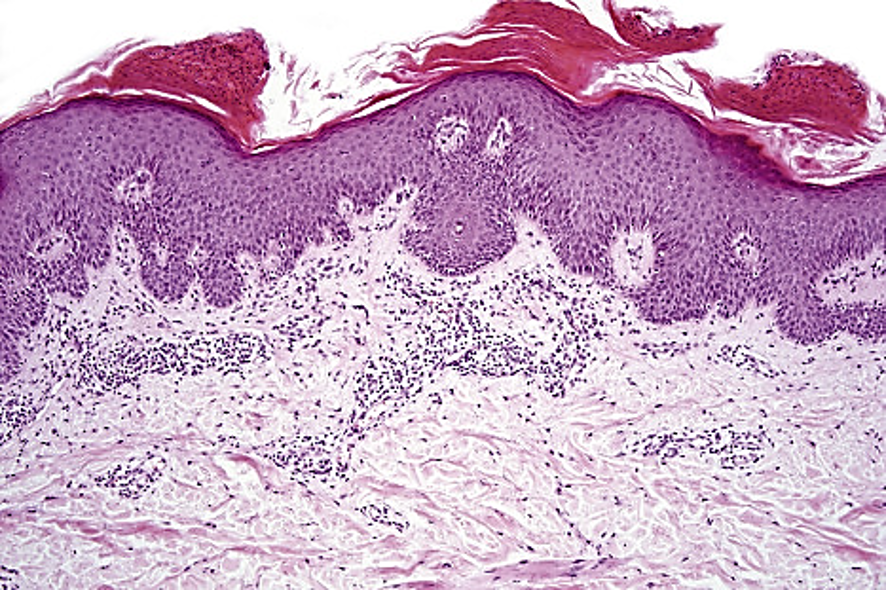
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
inflammation is mediated by TH17 cytokines - causes destructive skin plaques
Psoriasis
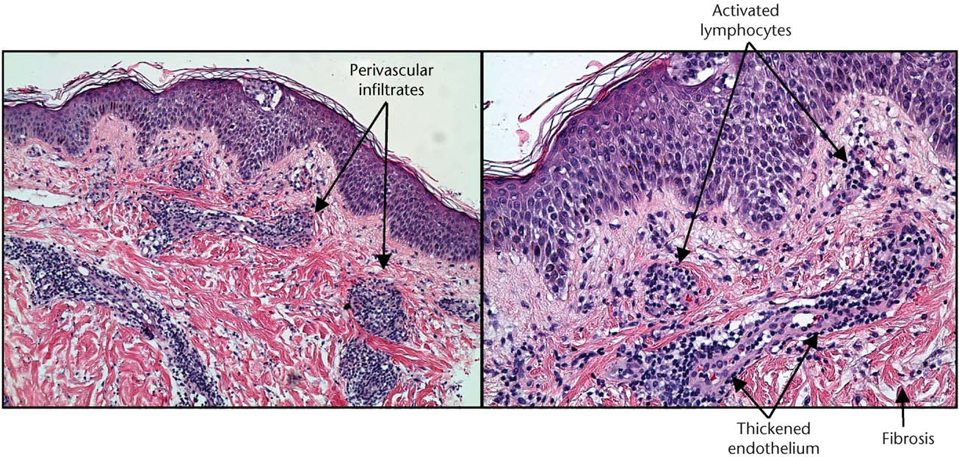
TYPE 4 HYPERSENSITIVITY
causes epidermal necrosis and dermal inflammation by TH1 and potentially TH17 cytokines (think poison ivy)
Contact Sensitivity