transition metals colours
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
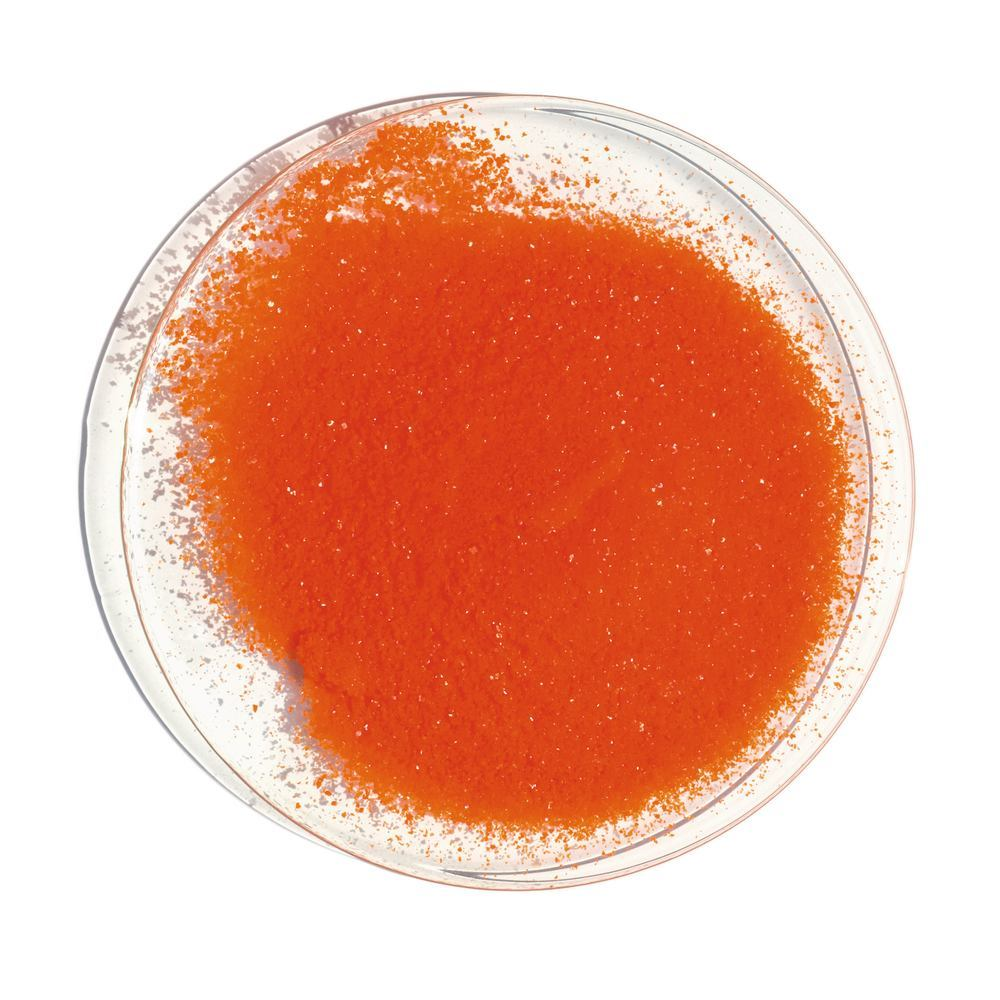
K₂Cr₂O₇ potassium dichromate (VI)
bright orange

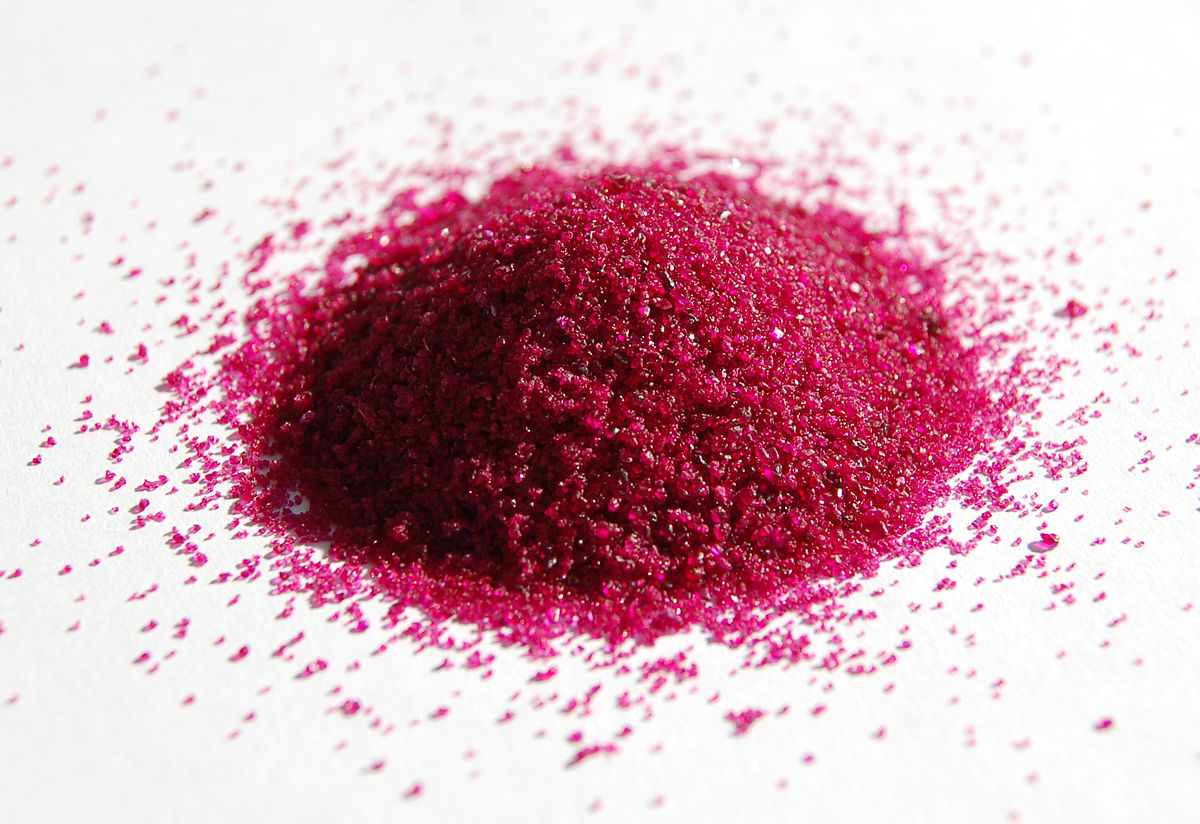
CoCl ₂ cobalt (II) chloride
pink-purple

NiSO₄ nickel (II) sulfate
green

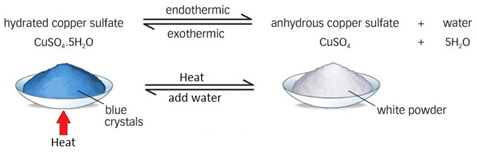
CuSO4·5H2O hydrated copper (II) sulfate
blue
iron (II) and iron (III) in solution
+2: pale green
+3: yellow

Cr (III) and Cr (VI)
+3: green
+6: yellow or orange

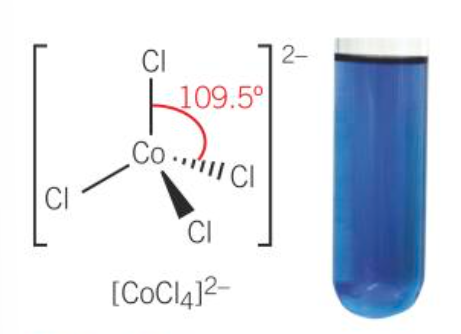
[CoCl4)2-
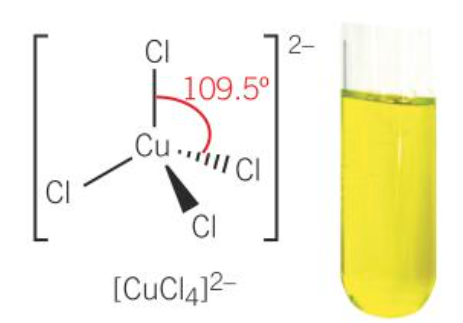
[CuCl4]2-
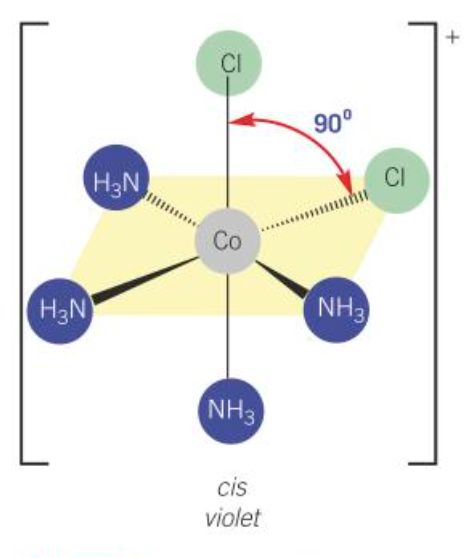
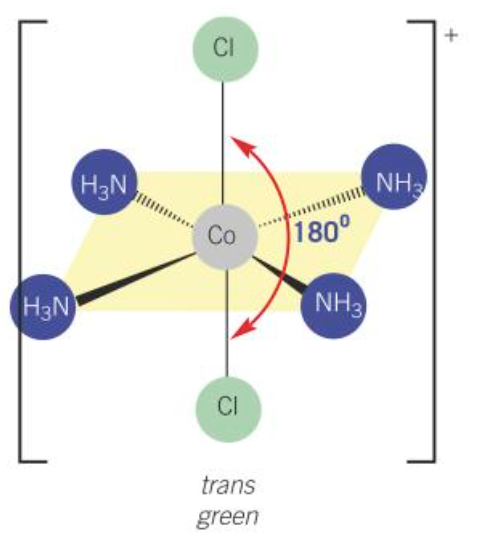
cis [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
violet
trans [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
green
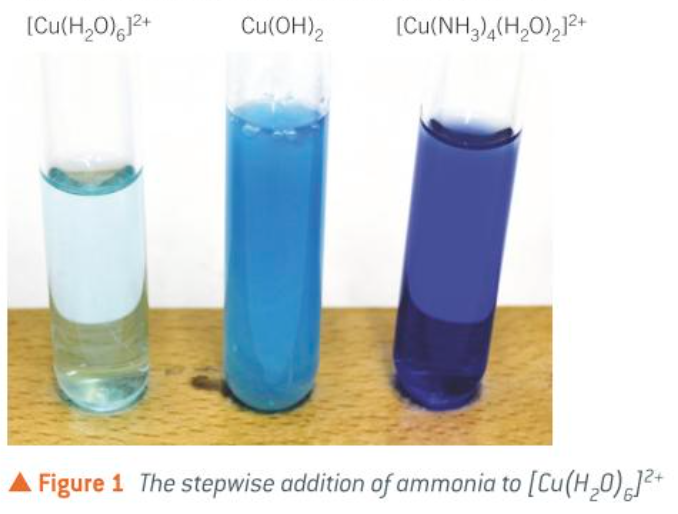
[Cu(H2O)6]2+
pale blue
what happens when XS NH3(aq) is added dropwise to a solution containing [Cu(H2O)6]2+
a pale blue ppt of Cu(OH)2 forming in the first stage of the rxn
the Cu(OH)2 ppt dissolving in XS NH3 to form a dark blue solution

what happens when an XS of conc HCl is added to a solution containing [Cu(H2O)6]2+
pale blue solution changes to form a yellow solution
if water is added to the yellow solution, a blue solution will be formed, although more dilute and paler in colour than the original blue solution
if you take care making observations, you will see an intermediate green solution (the result of the two solutions mixing)

what happens when KCr(SO4)2 • 12(H2O) (aka chrome alum) is dissolved in water
the complex ion [Cr(H2O)6]3+ (a pale purple solution) is formed
![<p>the complex ion [Cr(H2O)6]3+ (a pale purple solution) is formed</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8dac35fb-7402-489b-b4d7-b3190d7ec9a4.png)
what happens when you add XS NH3(aq) dropwise to [Cr(H2O)6]3+
initially a grey-green ppt of Cr(OH)3 is formed
the Cr(OH)3 ppt dissolves in XS NH3 to form the complex ion [Cr(NH3)6]3+
[Cr(H2O)6]3+(aq) (violet) + 6NH3(aq) → [Cr(NH3)6]3+(aq) (purple) + 6H2O(l)
![<ol><li><p>initially a grey-green ppt of Cr(OH)3 is formed</p></li><li><p>the Cr(OH)3 ppt dissolves in XS NH3 to form the complex ion [Cr(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+</sup></p></li></ol><p></p><p>[Cr(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+</sup>(aq) (violet) + 6NH<sub>3</sub>(aq) <span>→ [Cr(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+</sup>(aq) (purple) + 6H<sub>2</sub>O(l)</span></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8e0333d2-b761-4c3f-a3fa-e7d2bcdfabff.png)
colours of Cu2+(aq), Fe2+(aq), Fe3+(aq), and Mn2+(aq)
Cu2+(aq): blue solution
Fe2+(aq): pale green solution
Fe3+(aq): yellow/light brown (or purple in some cases)
Mn2+(aq): [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is pale pink
![<p>Cu2+(aq): blue solution</p><p>Fe2+(aq): pale green solution</p><p>Fe3+(aq): yellow/light brown (or purple in some cases)</p><p>Mn2+(aq): [Mn(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> is pale pink</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9c984412-12da-40bd-8f2f-4c6f507ef7f4.png)
colours of Cu2+(aq), Fe2+(aq), Fe3+(aq), and Mn2+(aq) when + NaOH(aq)
Cu2+(aq): pale blue ppt
Fe2+(aq): green ppt
Fe3+(aq): orange-brown ppt
Mn2+(aq): pale brown ppt
table for rxns of the aqueous transition metals w NaOH(aq)
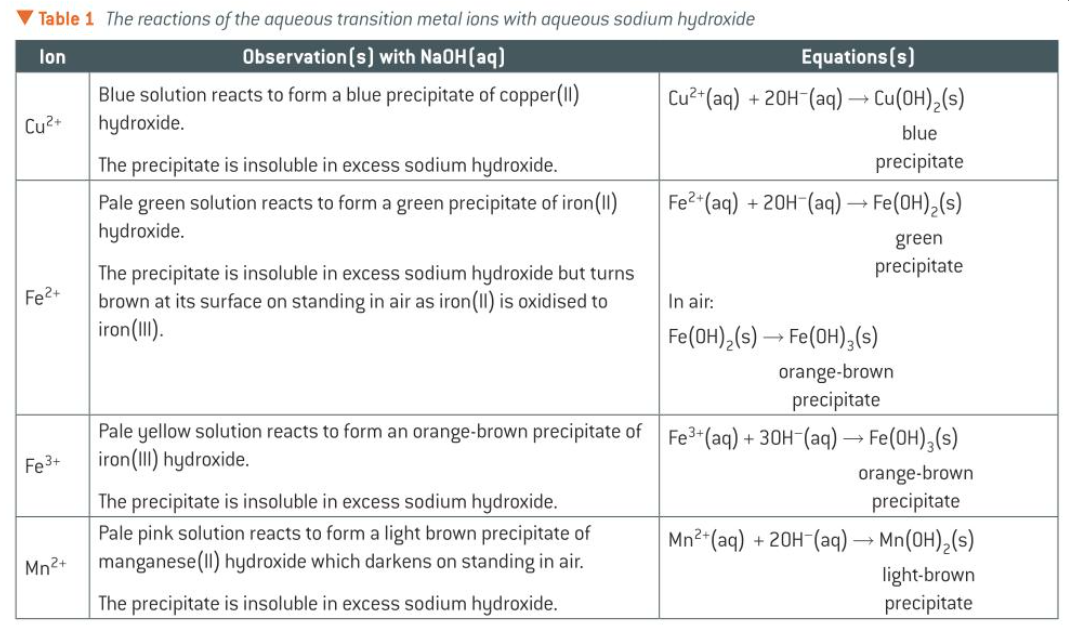
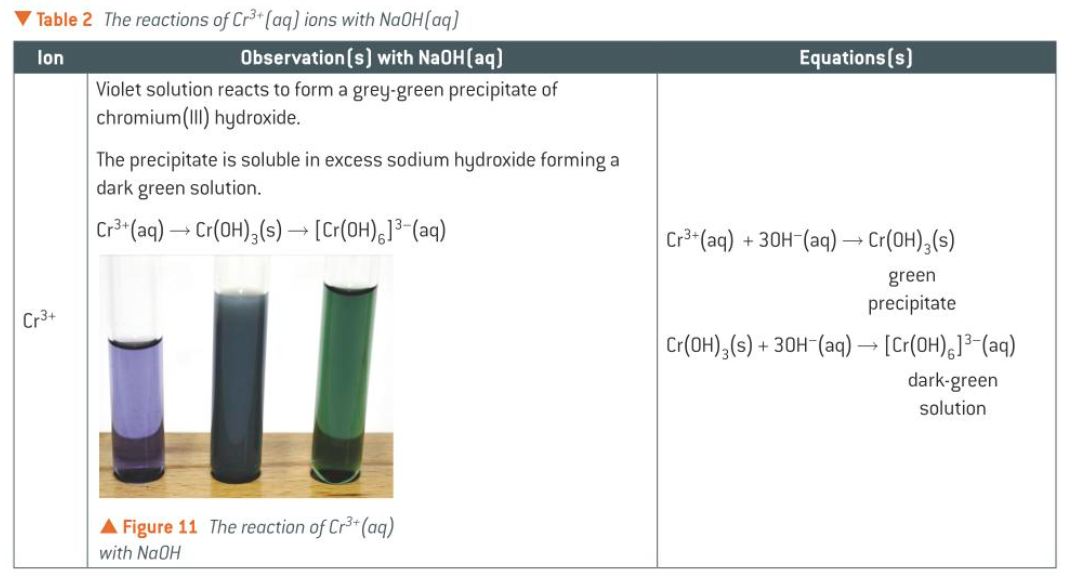
table for rxns of Cr3+(aq) ions w NaOH(aq)
Cu(OH)2(s)
blue ppt which dissolves in XS NH3 to form a deep blue solution [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+(aq)
Cr(OH)3(s)
green ppt which dissolves in XS NH3 to form a purple solution [Cr(NH3)6]3+
how do Fe2+, Fe3+, and Mn2+ react w XS NH3(aq)
in the same way they react w NaOH(aq)
form ppt of Fe(OH)2(s), Fe(OH)3(s), and Mn(OH)2(s)
there is no further rxn w NH3(aq) to these ppts don’t dissolve
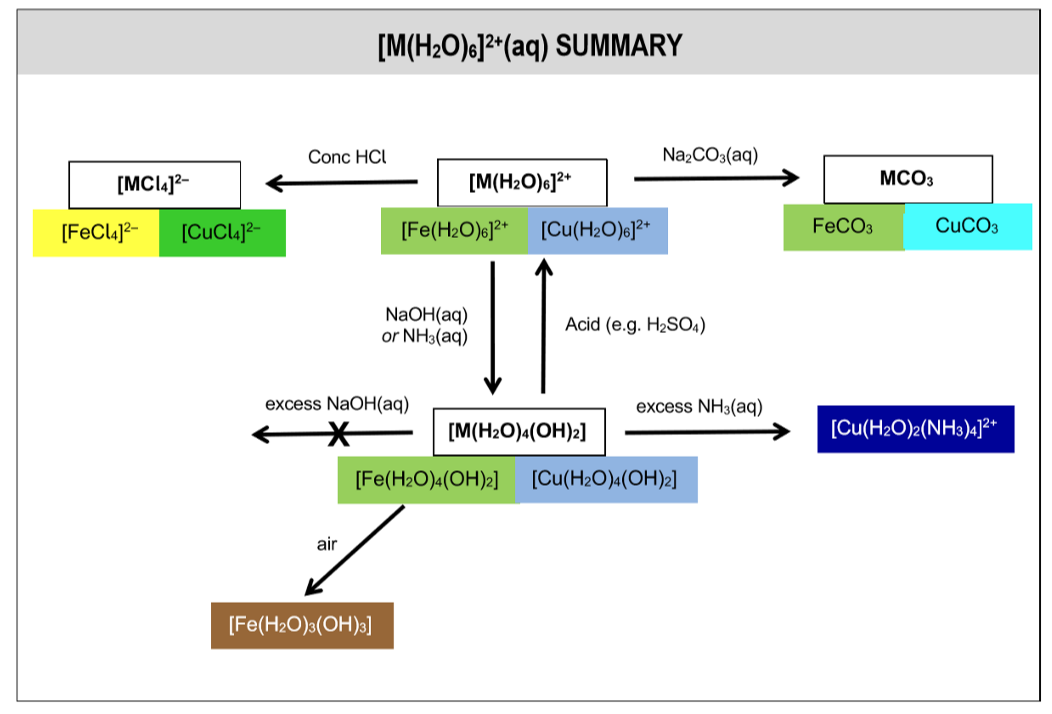
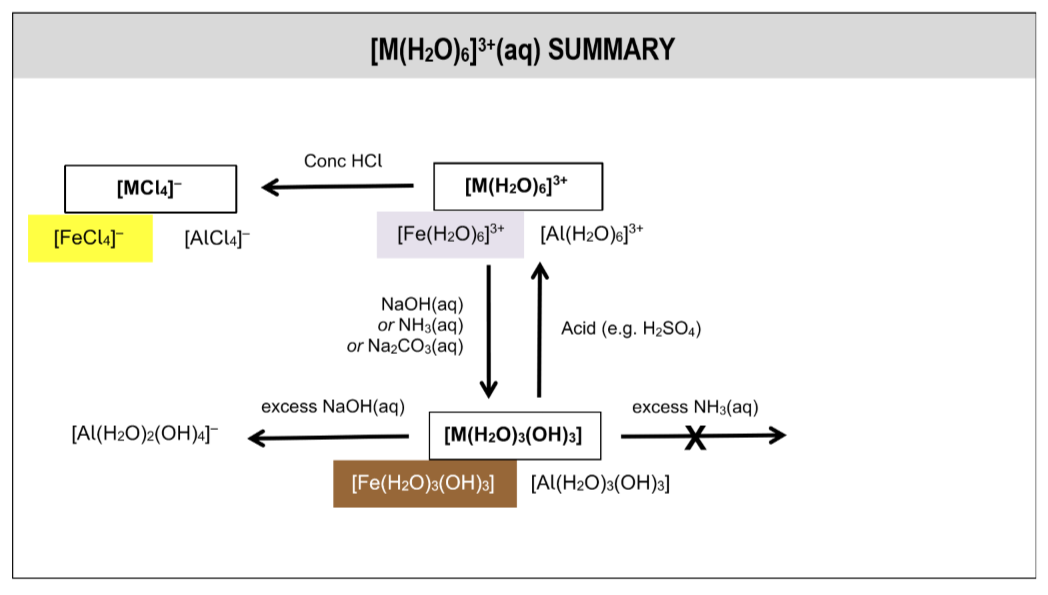
summary of rxns of aqua ions
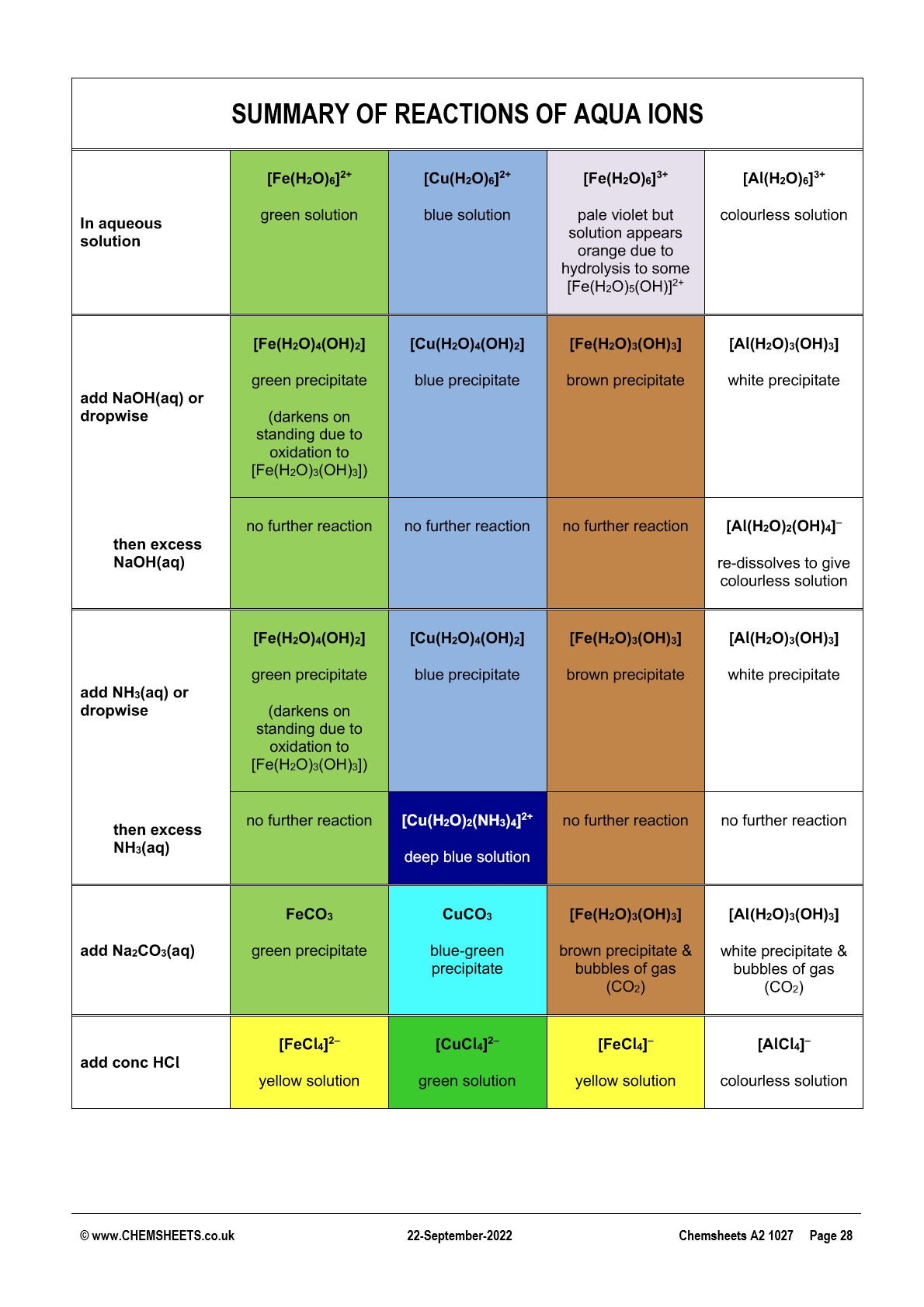
[M(H2O)6]2+(aq) summary
[M(H2O)6]3+(aq) summary
colour of MnO4- and Mn2+
purple to colourless

redox rxn between Fe2+(aq) and MnO4- (manganate VII ions)
Fe2+ is oxidised to Fe3+
MnO4- is reduced to Mn2+
the solution containing MnO4- ions is purple and is decolourised by Fe2+(aq) to form a colourless solution containing Mn2+(aq)

reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ by I-(aq)
orange-brown Fe3+(aq) are reduced to pale green Fe2+(aq)
but this is obscured by the oxidation of the I- to form I2(aq) which has a brown colour
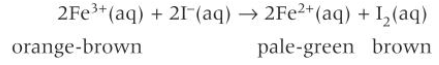
colours of Cr2O72-, Cr3+, and Cr2+
Cr2O72- orange
Cr3+ green
Cr2+ pale blue
