Energy production and oxygen consumption
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what does O2 cascade show
how PO2 decreases as air moves through respiratory system and into cells
partial pressure gradient for O2 between air and mitochondria
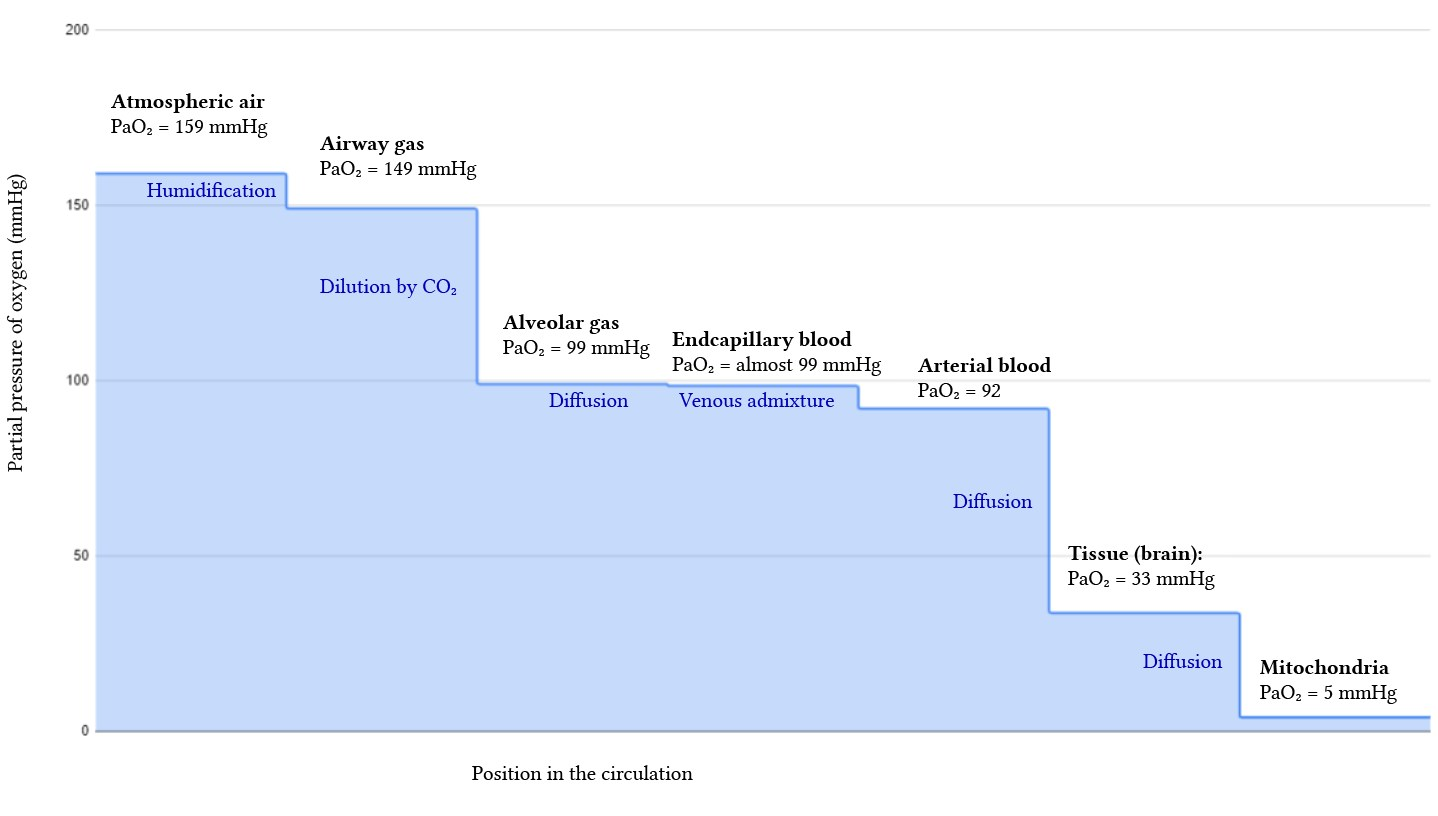
steps in the oxygen cascade
humidification
alveolar gas
alveolar-capillary diffusion
ventilation-perfusion mismatch and shunt
tissue diffusion
diffusion within cell
atmospheric PO2
21kPa
inspired PO2
19.9kPa
alveolar PO2
14.9kPa
pulmonary capillary PO2
14.9 kPa
arterial PO2
13.6kPa
mean tissue PO2
5kPa
mitochondrial PO2
>0.15kPa
pasteur’s point→ PO2 in mitochondria used in cellular respiration
oxygen delivery (ḊO2)
amount of oxygen leaving the heart in one minute
calculating oxygen delivery
amount of oxygen in blood x amount of blood leaving the heart
normal amount of O2 in blood for healthy person at rest
19 ml/dL
normal resting cardiac output
5.25 L/min
normal ḊO2 in health resting individual
1000ml/min
oxygen consumption (VO2)
amount of oxygen used by the body in one minute
basal metabolic rate
body’s resting rate of energy expenditure
oxygen consumption for healthy, resting individual
200ml/min
measurement of V̇O2
direct calorimetry
indirect calorimetry:
arterio-venous CO2 difference
Inspired-expired O2 volume difference
factors V̇O2
age→ peak at 0-2yrs, falls for rest of life
temperature→ metabolic rate doubles with every 10C
exercise
physiological responses to anaemia
increased 2,3-DPG shifts O2-Hb curve to right
reduced blood flow to non-essential organs (e.g. skin, bowel)
increased oxygen extraction from blood
increase in cardiac output
respiratory exchange ratio
ratio of carbon dioxide production (V̇CO2) to oxygen consumption (V̇O2)
respiratory quotient=RER at rest
RER for different molecules
carbohydrates→ 1.0
fatty acids→ 0.7
protein→ 0.8
cardio-pulmonary exercise training
V̇CO2 plotted against V̇O2 while subject exercises
testing used to assess RER pre-surgery→ assesses whether patient can cope with oxygen stress during surgery
cardio-pulmonary exercise test graphs
V̇O2 on x-axis
V̇CO2 found on y axis
anaerobic threshold→ hockey-stick bend
glyocolysis
occurs in cytoplasm
glucose→ pyruvate or lactate
no oxygen required
2 STP molecules per glucose
TCA cycle
occurs in mitochondria
Acetyl CoA from glycolysis to CO2
38 ATP molecules made per glucose
O2 required
oxidative phosphorylation
occurs in mitochondria
NADH provides H+
H+ combines with O2 to produce water
ATP produced
causes of cellular hypoxia
anoxic→ lack of O2:
leads to respiratory failure
stagnant→ lack of blood supply:
leads to angina
anaemic→ lack of haemoglobin