CH 10 Genetic Analysis and Genetic Engineering
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is applied science?
using applications from basic research science
Examples of applied science
Utilizing DNA to identify a suspect in a crime
Fixing the underlying genetic mutation to treat disease
Utilizing RNA regulatory molecules to permanently “fix” diseases
Properties of DNA (3)
Can be unwound by helicase
Strands separate when exposed to temperatures below boiling
Strands will regain their double-stranded form when the DNA is cooled
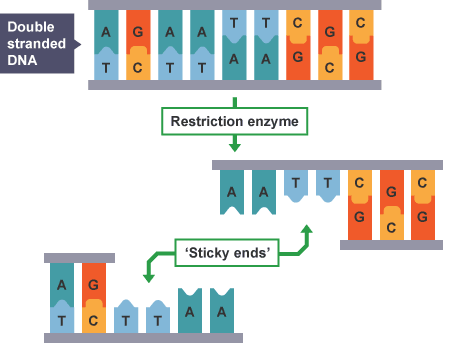
What are restriction endonucleases
AKA restriction enzymes
are responsible for cleaving DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites (restriction sites)
Properties of Restriction Endonucleases (6)
are enzymes
clip DNA crosswise at selected positions
recognizes foreign DNA
capable of breaking phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
protects bacteria and archaea from bacteriophage or plasmids
recognizes a sequence of 4 to 10 base pairs
What are palindromes
sequences of DNA that are identical when read from the 5’ to 3’ direction on one strand and the 5’ to 3’ direction on the other strand
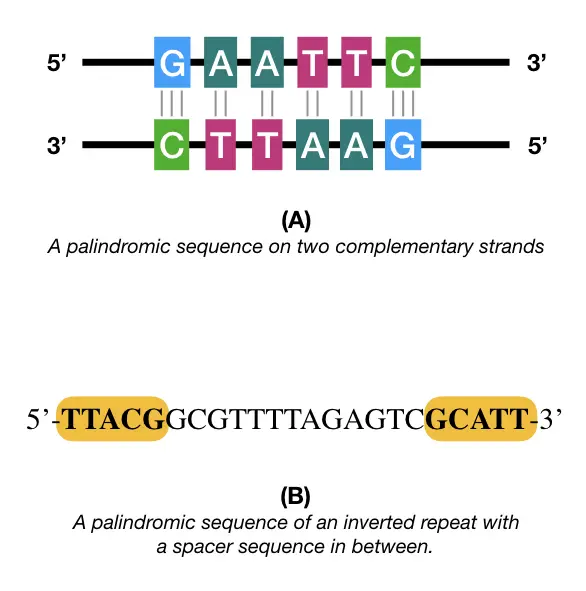
What are sticky ends
are staggered symmetrical cuts (done by restrictive enzymes) that leave short tails
4 to 5 bases on each strand
T/F: Restriction enzymes recognizes and cleaves DNA at the palindrome sequence
True
Restriction enzymes recognizes and cleaves DNA at the palindrome sequence. How? List the steps
A restriction enzyme recognizes and cleaves DNA at the site of a specific palindromic sequence
Cleavage can produce sticky ends that accept complementary tails for gene splicing
Sticky ends can be used to join DNA from different organisms by cutting it with the same restriction enzyme
What are restriction fragments?
pieces of DNA produced by restrictive enzymes
What are restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)?
the differences in the cutting pattern of specific restrictive enzymes causes restrictive patterns of different lengths
T/F: RFLPs allows for direct comparison of DNA of two different organisms at a specific site
true
What is ligase
an enzyme
necessary to seal sticky ends together
What is the main application of ligase
final splicing of genes into plasmids and chromosomes
What is reverse transcriptase
an enzyme responsible for converting RNA into DNA
can replicate HIV and other retroviruses
What is cDNA and its function
Complementary DNA
synthesizes eukaryotic genes from mRNA transcripts
What is cDNA made from
messenger RNA
transfer RNA
ribosomal RNA
other forms of RNA
What are the steps of making cDNA from eukaryotic mRNA?
Transcription of eukaryotic DNA makes precursor mRNA
Splicing removes introns from precursor mRNA, making final mRNA for translation
mRNA is extracted from cells
Reverse transcriptase synthesizes DNA from mRNA
DNA polymerase completes cDNA (no introns)
What is the function of CRISPR
enzymes recognize and cuts out foreign DNA left behind by invading bacteriophages or plasmids
How do scientists use CRISPR
they exploit the system to cut DNA in just about any organism exactly where they want to
Applications of CRISPR
DNA Editing (find and replace function)
cell is transfected with an enzyme-complex containing: guide molecule, healthy DNA copy, and DNA-cutting enzyme
guide molecule finds target DNA strand
DNA-cutting enzyme cuts off target DNA strand
defective DNA strand is replaced with a healthy copy
What is the purpose of gel electrophoresis
to produce a readable pattern of DNA fragments
Process of using gel electrophoresis
Samples of DNA are placed in compartments in a soft agar gel and subjected to an electrical current
The negative charge on the phosphate groups cause the DNA to move toward the positive pole on the gel
The rate of movement of DNA through the gel is based on the size of the fragments
Positions of DNA fragments are determined by staining the DNA fragments in the gel
What are the benefits of distinctive electrophoresis patterns?
Useful in characterizing DNA fragments
Allow for comparison of genetic similarities among samples as in a genetic fingerprint
What is the function of PCR?
Rapidly increases the amount of DNA in a sample without the need for making cultures or carrying out complex purification techniques
What are the abilities of PCR?
can replicate a target DNA from a few copies to billions of copies in a few hours
can detect cancer from a single cell
can diagnose an infection from a single gene copy
T/F: PCR uses the same events of DNA replication.
True
What are the events of PCR?
Opening of the double helix
Using the exposed strands as templates
Addition of primers
Action of DNA a polymerase
What are the specialized ingredients used in PCR
primers and DNA polymerases
What are primers
oligonucleotides that indicate where DNA amplification should begin
What are DNA polymerases
enzymes responsible for the replication of DNA
each version of DNA polymerase completes a unique portion of the replication process
Why are DNA polymerases that are isolated from thermophilic bacteria used in PCR?
Because of the high temperatures used
What are the three steps of PCR technique
denaturation
priming
extension
Denaturation
heat target DNA to 94 C to separate strands
Cool target DNA between 50-65 C
Strands stay separated
Priming
Add primers that bind to the complementary strand of DNA
Extension
Increase temp to 72 C
Add DNA polymerase and nucleotides
2 complete strands of DNA are produced
What is the purpose of real-time PCR
to detect products during the reaction instead of at the end
What are the essential roles of PCR?
gene mapping
studying genetic defects and cancer
forensics
diagnosing infectious diseases
taxonomy studies
What is recombinant DNA technology used for
To deliberately remove genetic material from one organism and combining it with that of a different organism
forms genetic clones
Example of recombinant DNA Technology
Production of drug alpha-2a interferon (Roferon-A):
Used to treat hairy cell leukemia and Kaposi’s sarcomas
What is cloning
the removal of a selected gene from an animal, plant or microorganism
Process of cloning
Gene is inserted into a vector
Vector is inserted into a cloning host
Gene is translated into the protein product for which it codes
What is a vector
a plasmid or virus
Plasmid vectors
Small, well characterized, easy to manipulate
Can be transferred into appropriate host cells through transformation
Carry genetic markers for resistance to antibiotics
Virus (bacteriophage) Vectors
Have the natural ability to inject DNA into bacterial hosts through transduction
What are the three important features of cloning vectors
an origin of replication (ORI)
needed to be replicated by DNA polymerase of cloning host
must accept DNA of the desired size
contains a gene that gives/maintains drug resistance
What is a cloning host
bacteria or yeast
What are some desirable features in cloning host (7)
Rapid turnover; fast growth rate
Can be grown in large quantities using ordinary culture methods
Nonpathogenic
Genome that is well mapped
Capable of accepting plasmid or bacteriophage vectors
Maintains foreign genes through multiple generations
Will secrete a high yield of proteins from expressed foreign genes
What are the ingredients needed for gene cloning
the target gene and cloning vector
Steps in gene cloning
Prepare the isolated gene for splicing into plasmid
Digest gene and plasmid with same restriction enzyme
Results in complementary sicky ends
Ligase seals gene and plasmid together
Introduce plasmid to cloning host via transformation
Search for recombinant clones
What are some uses of recombinant DNA technology
Recombinant organisms
Sources of protein products
Nucleotide sequences
Medications that cannot be manufactured by other means
Large-scale manufacture of hormones and enzymes:
Insulin
Human growth hormone
Interferons
peptides used to treat some types of cancer, multiple sclerosis, and viral infections such as hepatitis and genital warts
Interleukins
types of cytokines that regulate the immune function of white blood cells, used in cancer treatment
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
used to treat cancer
Erthyropoietin (EPO)
a peptide that stimulates bone marrow; used to treat some forms of anemia
Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
stimulates growth in children with dwarfism; prevents wasting syndrome
Transgenic Organisms
AKA GMOs
Recombinant organisms produced through the introduction of foreign genes
Uses of recombinant microbes
Prevent ice crystals from forming
Destroy invading insects
Make plants more resistant to insect pests
What is the controversy surrounding the release of genetically engineered plants
Concern that transgenic plants will share their genes for herbicide, pesticide, and virus resistance with natural plants leading to “superweeds”
What can an analysis of DNA do?
reveal genetic abnormalities, ancestry, etc
determine if one sample of DNA is the same as another sample
What is DNA profiling used for?
used to differentiate between organisms that might be causing a disease outbreak
used in criminal investigations to match a suspect to the DNA left at a crime scene