Ch 8
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
managers are “_____” of shareholders,
agents
method of valuing common stock (2)
free cash flow model
dividend growth model
what is free cash flow
cash flow available for investors
what is wacc
rate of return required by investors
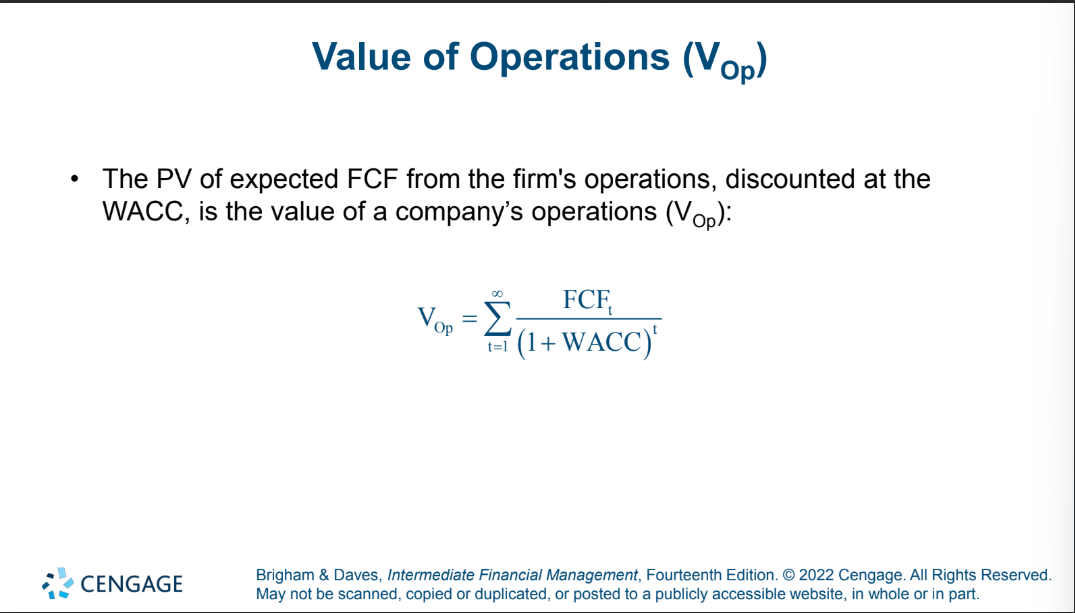
PV of expected cash flow
sources of value (2)
value of operations
nonoperating assets
order of claim
bondholders
preferred stockholders
common stockholders
value of operations = PV of FCF Discounted at WACC
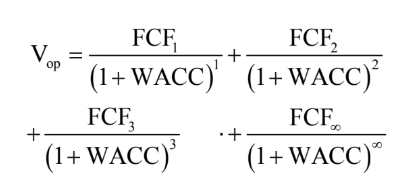
constant growth formula
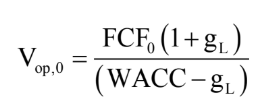
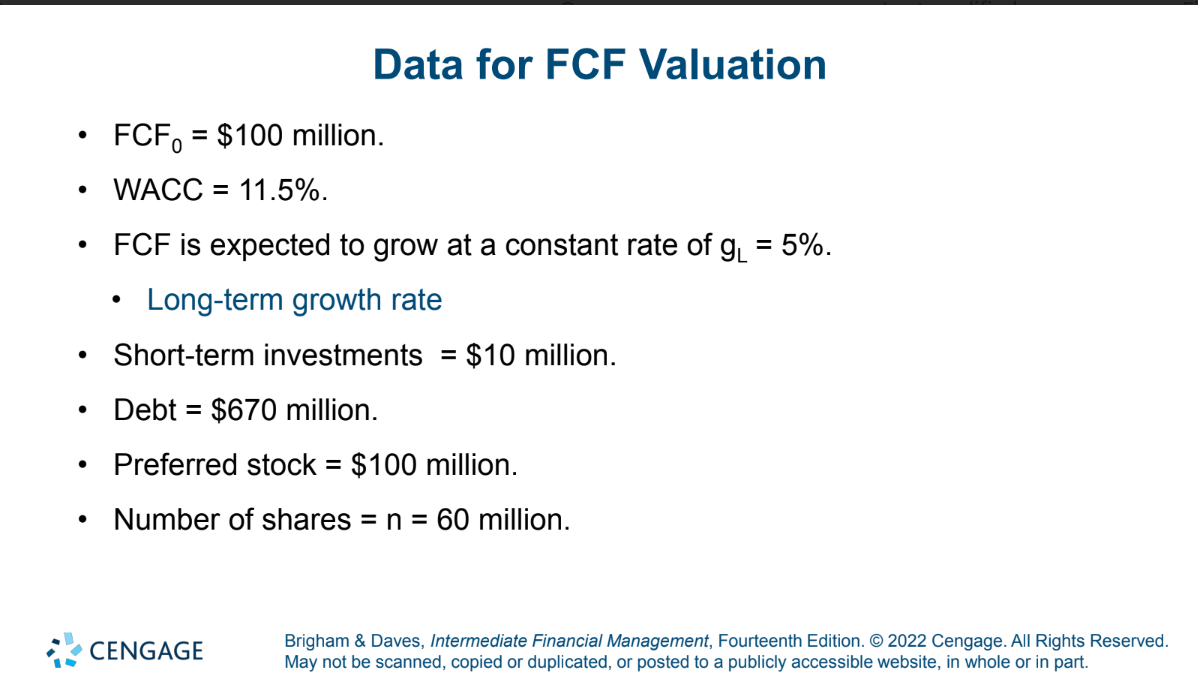
Find value of operations
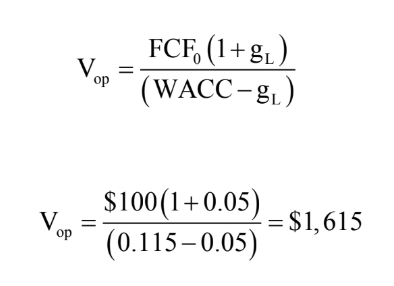
what is horizon value
value of alll fcf discounted back to horizon
horizon value is also called
terminal value
continuing value
Part 1
Find Horizon Value
FCF = $220
WACC = 11.5%
GL = 5%
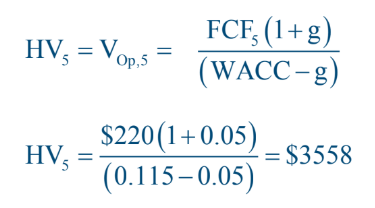
Part 2
FCF = $220
WACC = 11.5%
GL = 5%
The Horizon Value (HV5) is FCF from Year 6 and beyond, discounted back to Year 5.
The PV of HV5 is then discounted back to the beginning period.
The Value of Operations is the Present Value of all cash flows year 1 – 5
($460) plus the PV of HV5 ($2,064).

Part 3
Percent of Value Due to Long-term Cash Flows
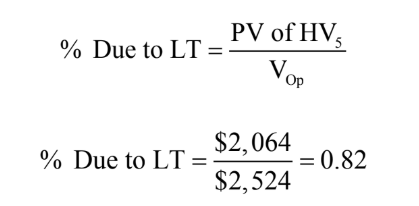
why do public companies focus on quarterly earnings?
change in quarterly earnings can signal changes in future cash flow
managers bonuses
what does ROIC mean
return on invested capital

PV of dividend
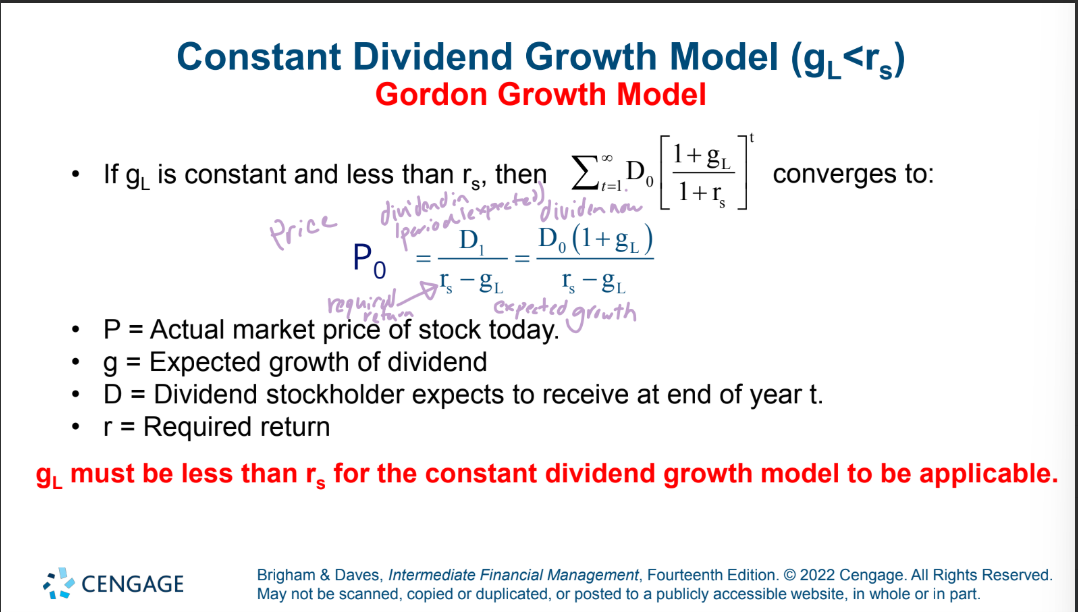
find estimated stock value
D0 = $2.00
rs = 13%,
gL = 6%
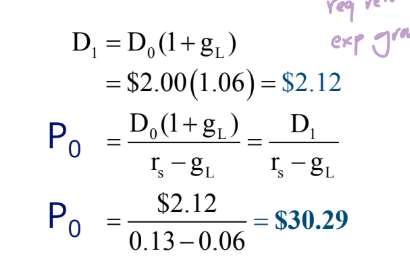
find Expected Stock Price 1 Year Later
D0 = $2.00
rs = 13%,
gL = 6%
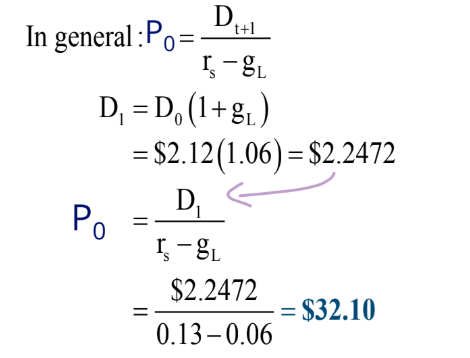
dividend yield formula Total return = dividend yield + capital gains yield.
dividend yield = dividend/price
capital gain yield formula
capital gain yield = new price - old price / old price
total return formula
Total return = dividend yield + capital gains yield.
rate of return formula
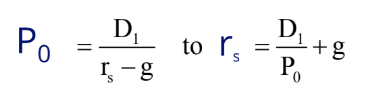
FCF model vs Dividend Growth Model
FCF
more situations
require forecasted f/s
Dividend Growth Model
constant growth rate
less than required return