Gene Expression and Regulation - I Need an 100
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Helicase
breaks hydrogen bonds (unzipping enzyme)
Primase
creates an RNA primer (makes anti-parallel landing pad)
DNA Polymerase III
adds complementary nucleotides to a DNA strand, only synthesizes DNA from 5’ to 3’
DNA Polymerase I
removes RNA primers (created by primase) and replaces them with DNA
Ligase
seals the DNA fragments (after DNA Pol. I), known as the “genetic glue”
Leading Strand
continuous, keeps on going, uninterrupted (DNA can only be continuous on one strand)
Lagging Strand
discontinuous, interrupted, contains the okazaki fragments
Bacteriophage
(used in hershey/chase) viruses that exclusively infect bacterial cells (not human cells)
Codon/Triplet
a sequence of 3 bases on mRNA that codes for an amino acid
Start codon
AUG
RNA Polymerase
synthesizes mRNA from a gene from 5’ to 3’
Promoter
sequence of bases in front of a gene recognized by RNA polymerase
Transcription Factors
proteins that help RNA polymerase attach to the promoter (some proteins attach to the RNA pol., others attach to the T and A bases in the promotor aka the TATA box), allows for control over RNA polymerase
Control Element
a sequence of bases on DNA that controls transcription of a gene
Promotor
TATA box
Enhancer
Spliceosome
enzyme that removes introns and joins exons together
RNA Processing
when you convert pre-mRNA to mature mRNA (occurs in nucleus)
Remove introns and splice exons together via enzyme
Addition of 5’ cap (consists of mostly G’s)
Add Poly - A tail (consists of mostly A’s)
Mutation
a change in the base sequence of DNA
Point Mutation
a change in the base in a nucleotide
Substitution– a base is replaced by another base
Deletion - a base is removed
Insertion - a base is added
tRNA
(folded RNA) transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome
Anticodon
sequence of 3 bases on tRNA that complement the codon on mRNA
Transcription
the process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence, happens in nucleus, (DNA → mRNA)
Translation
happens in the ribosomes, the process of making protein from mRNA (mRNA → protein)
LacZ gene
Gene codes for β-gal (beta-galactosidase)
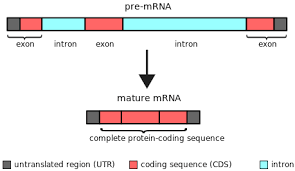
Introns
Non-coding regions of a gene, removed by RNA splicing (spliceosome) as RNA matures
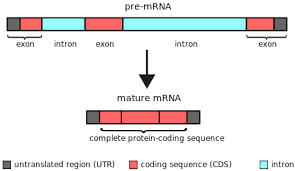
Exons
Coding sequences of a gene, covalently bond to one another to create mature mRNA
Operator
found in prokaryotes, it is a sequence of bases on DNA that bind the repressor + controls whether RNA polymerase can access the DNA to start transcribing genes (transcription)
Lac Operon
Catabolic Pathway, contains an active repressor that binds to the operator + a lactose inducer that deactivates the repressor
Repressor
active, binds to the operator
TRP Operon
Anabolic pathway, contains inactive repressor that doesn’t bind to the operator, contains the co-repressor “trp” that activates the repressor
Polycistronic
a single molecule of mRNA that codes for many different proteins (in prokaryotes)
Co-repressor
What trp (tryptophan) is considered to be in the trp operon. Means when trp levels are high, it binds to the trp repressor protein, allowing it to bind to the operator and preventing the transcription of operon genes, effectively inhibiting tryptophan synthesis.
Mutation Result
changes the function/activity of a protein
a) reduced activity
b) loss of function (no activity)
c) gain function (hyperactivity)
results in a new phenotype!
Stop Codons
UAA, UAG, and UGA are all
Operon
found in prokaryotes, it is a unit made up of linked genes which is thought to regulate other genes responsible for protein synthesis.
(also known by P.O.G. acronym meaning Promoter, Operator, and Gene)
Prokaryotes
no membrane-bound organelles
1 circular chromosome
no transcription factors + TATA box
no introns + no spliceosomes
no RNA processing
(so no 5’ cap or poly A tail)
contains operon (promoter, operator) and enhancer
Eukaryotes
contains membrane-bound organelles
many linear chromosomes
contains transcription factors + TATA box
has introns + spliceosomes
has RNA processing
does not contain operon (promoter, operator) and enhancer
Frederick Griffith’s 1928 transformation experiment
this experiment with bacterium helped lead to the discovery that DNA was the carrier of genetic information (involved mice and rough/smooth strains)
Hershey and Chase Experiment
this experiment proved that DNA was the genetic material; used bacteriophages to dock and kill e. coli by injecting their DNA + used radioactive elements to track